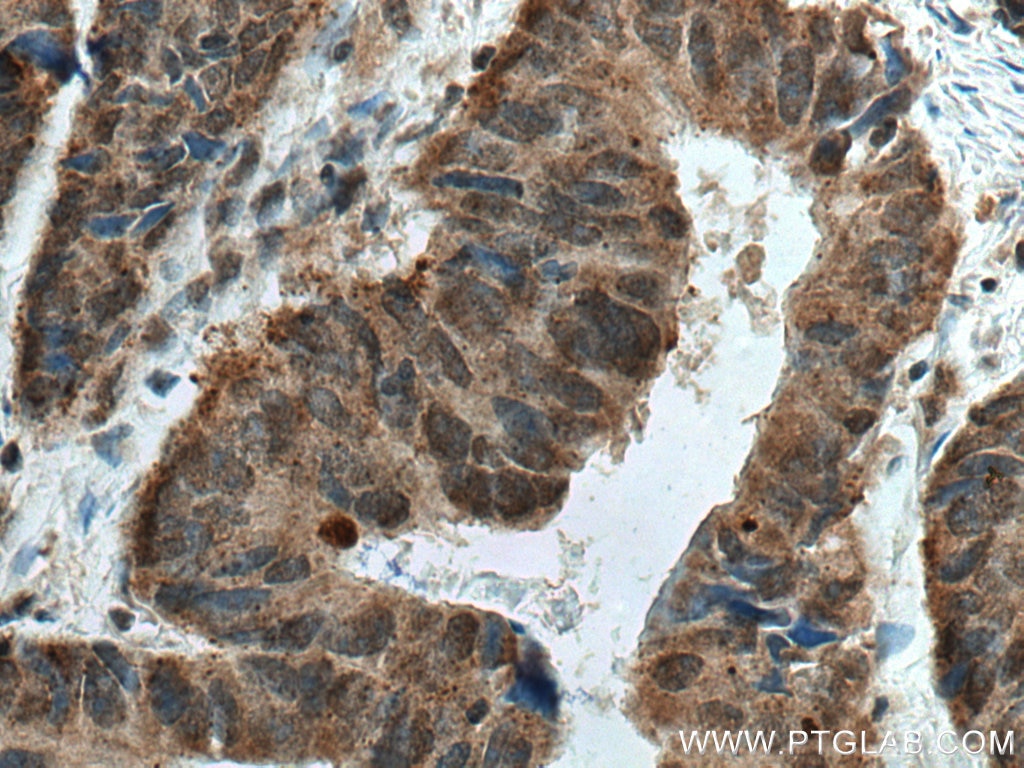
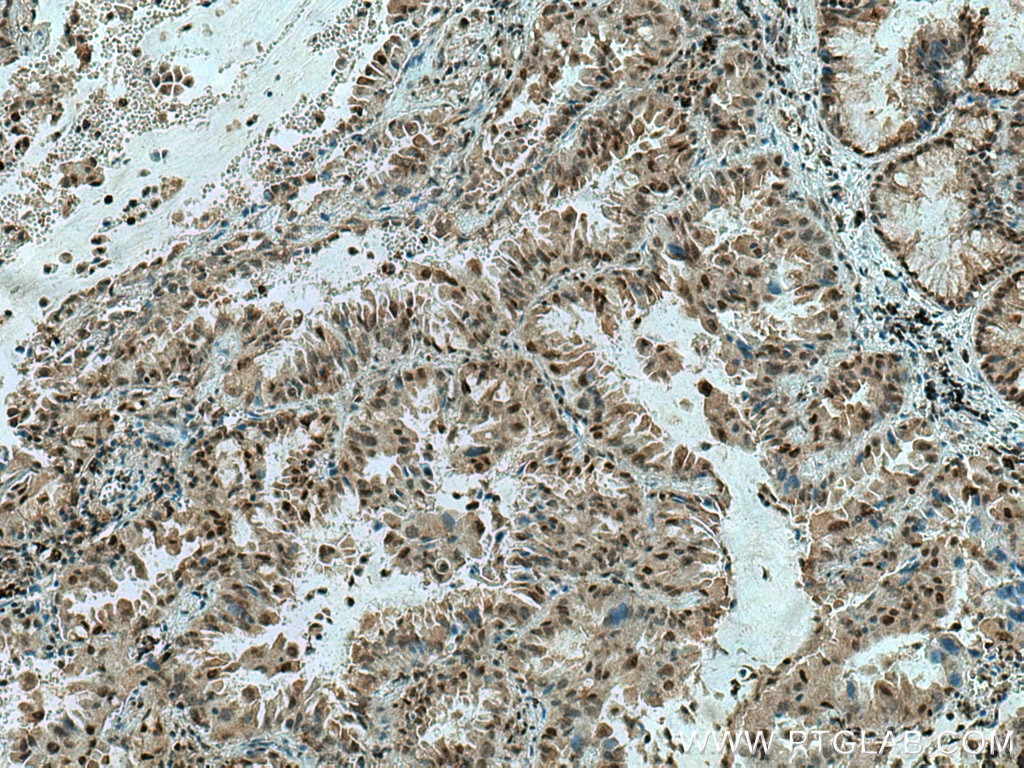
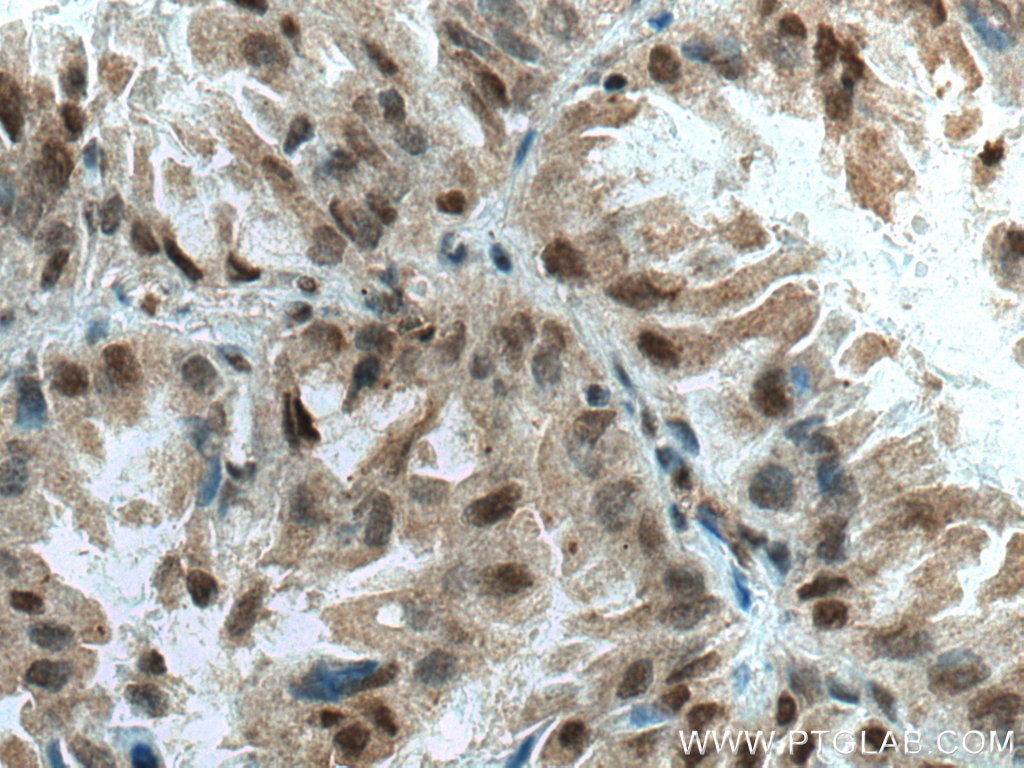
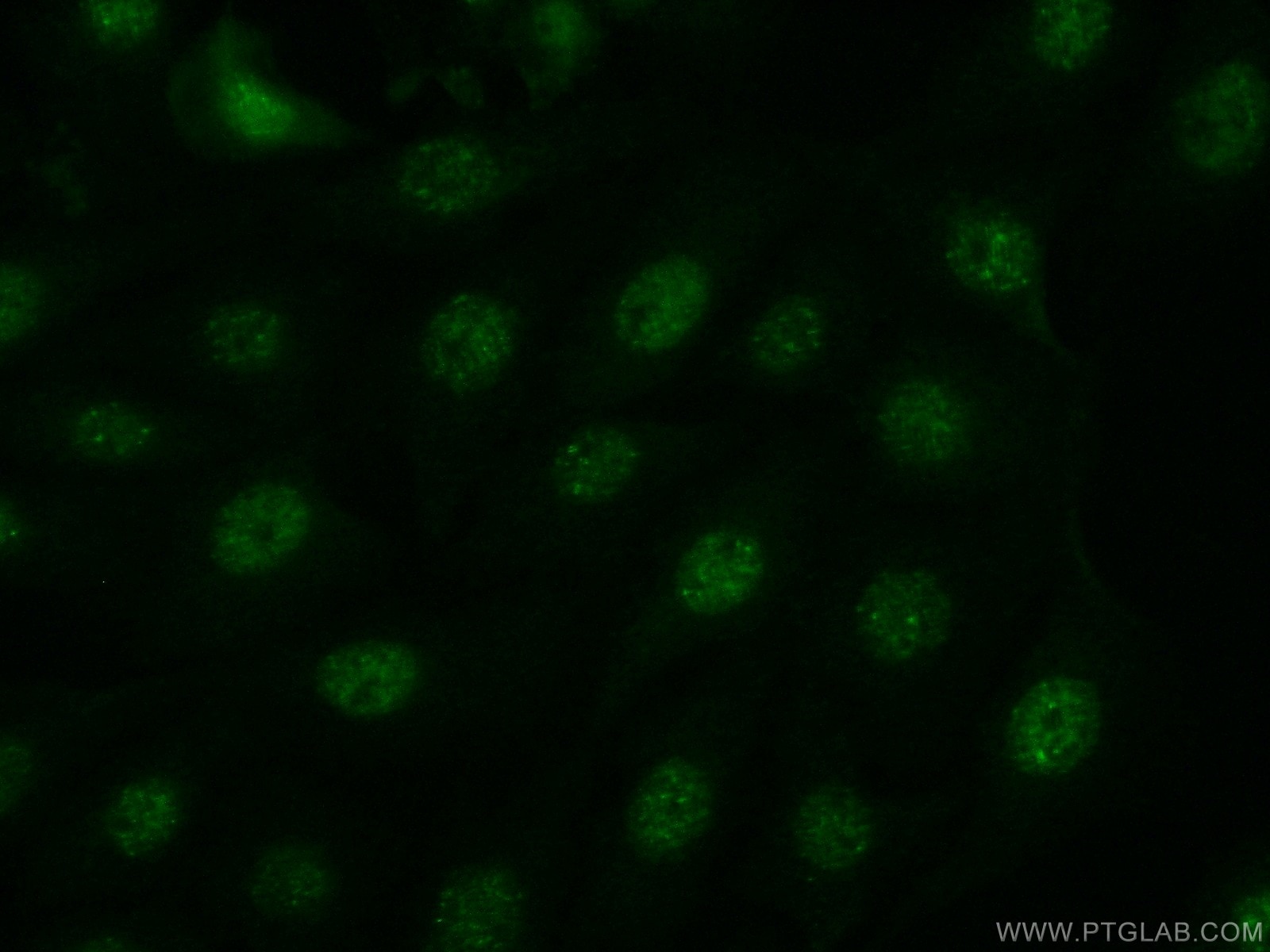
Product Information
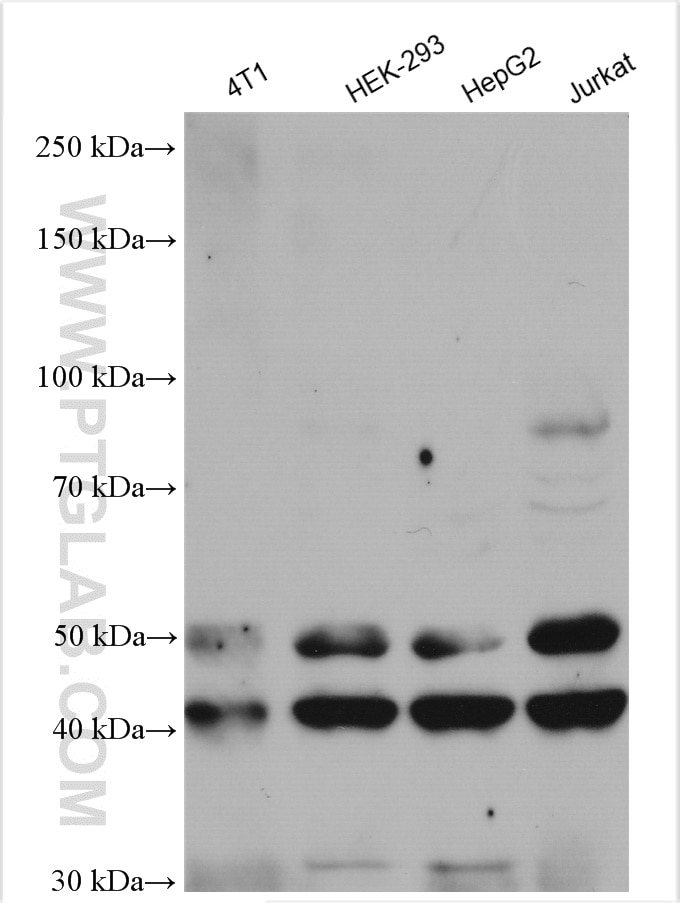
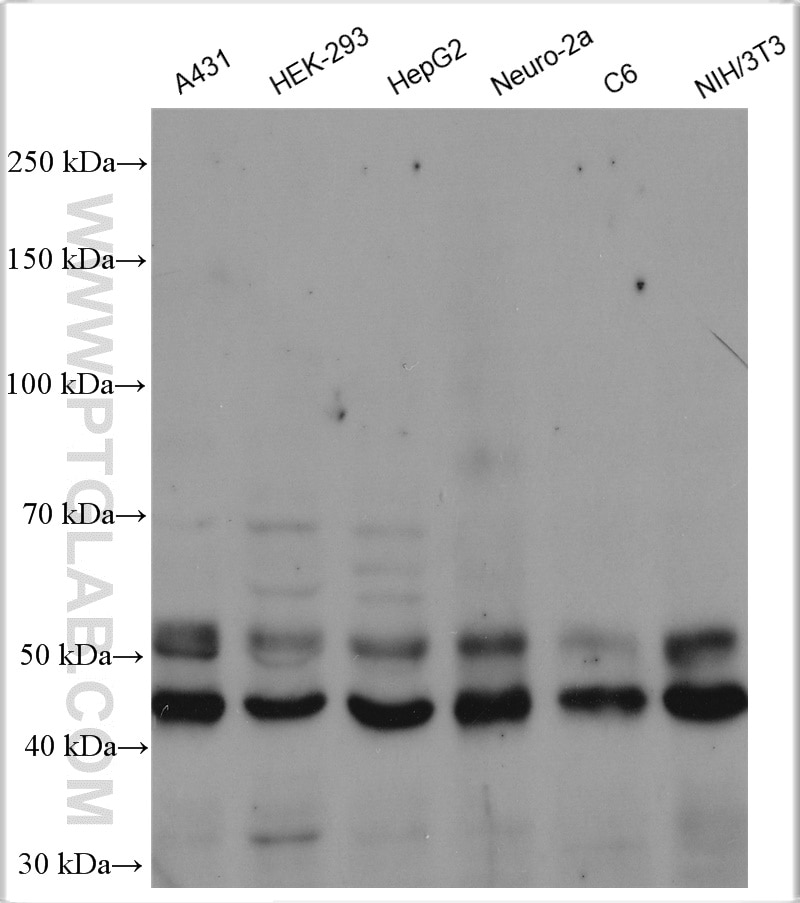
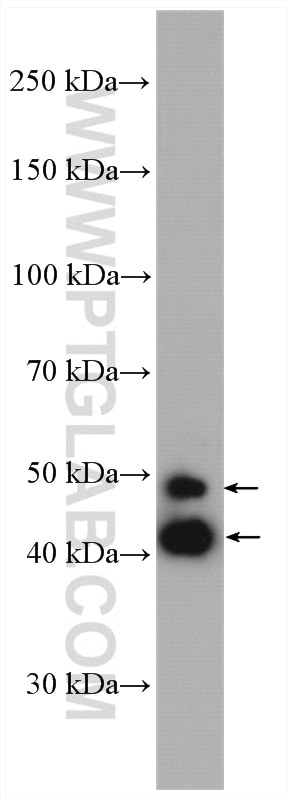
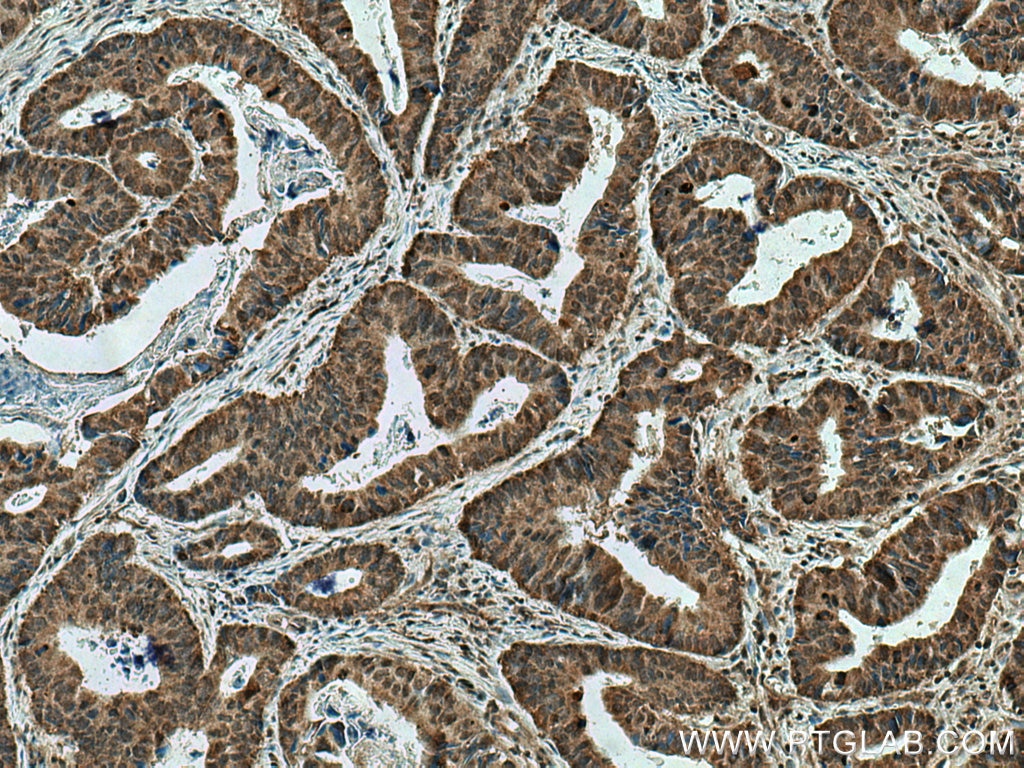
51151-1-PBS targets JNK in WB, IHC, IF/ICC, Indirect ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human, mouse samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human, mouse |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Polyclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen | Peptide Predict reactive species |
| Full Name | mitogen-activated protein kinase 8 |
| Calculated Molecular Weight | 48 kDa |
| Observed Molecular Weight | 44-48 kDa, 50-55 kDa |
| GenBank Accession Number | NM_138982 |
| Gene Symbol | JNK |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 5599 |
| RRID | AB_2140710 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Antigen affinity purification |
| UNIPROT ID | P45983 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS only, pH 7.3. |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -80°C. |
Background Information
Function
JNK1, also known as mitogen-activated protein kinase 8 - MAPK8, is a serine/threonine-protein kinase. It is an important player in signaling transduction pathways governing cellular response to external stimuli, including ultraviolet radiation (UV), inflammatory cytokines, and reactive oxygen species (ROS). JNK1 phosphorylates several transcription factors, such as c-Jun, Elk-1, and ATF2, affecting their transcription activity.
Tissue specificity
JNK1 is ubiquitously expressed.
Involvement in disease
JNK-mediated phosphorylation governs a variety of important cellular processes, and abnormalities of JNK1 activity have been implicated in obesity and cancer.
Isoforms
There are four isoforms of JNK1 (PMID: 8654373), giving rise to 46 kDa and 55 kDa isoforms. JNK1 isoforms differ in their substrate specificity and tissue expression profiles.
Post-translational modifications
JNK1 is phosphorylated by MAPK kinases (MAPKK).
Cellular localization
JNK1 is present both in the nucleus and in the cytoplasm. Stress conditions and other stimuli can cause a shift in JNK1 subcellular distribution.