Recombinant Human EpCAM/CD326 protein (His Tag)
Species
Human
Purity
>90 %, SDS-PAGE
Tag
His Tag
Activity
not tested
Cat no : Eg1370
Validation Data Gallery
Product Information
| Purity | >90 %, SDS-PAGE |
| Endotoxin | <0.1 EU/μg protein, LAL method |
| Activity |
Not tested |
| Expression | HEK293-derived Human EpCAM protein Gln24-Lys265 (Accession# P16422) with a His tag at the C-terminus. |
| GeneID | 4072 |
| Accession | P16422 |
| PredictedSize | 28.5 kDa |
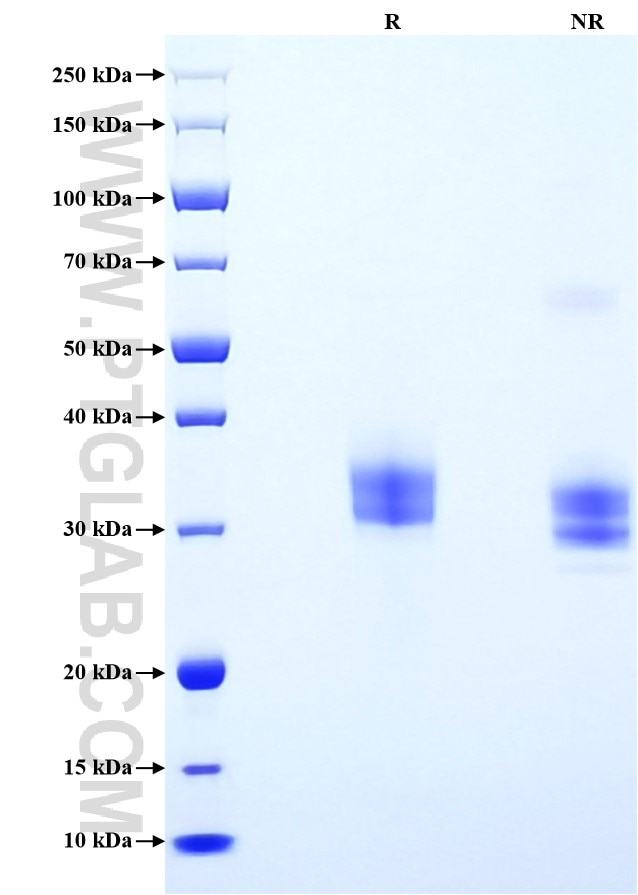
| SDS-PAGE | 30-37 kDa, reducing (R) conditions |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from 0.22 μm filtered solution in PBS, pH 7.4. Normally 5% trehalose and 5% mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. |
| Reconstitution | Briefly centrifuge the tube before opening. Reconstitute at 0.1-0.5 mg/mL in sterile water. |
| Storage Conditions |
It is recommended that the protein be aliquoted for optimal storage. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
| Shipping | The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the recommended temperature. |
Background
Epithelial cell adhesion molecule (EpCAM, CD326) is a type I transmembrane glycoprotein that functions as a homophilic, epithelial-specific intercellular cell-adhesion molecule. In addition to cell adhesion, EpCAM is also involved in cellular signaling, cell migration, proliferation, and differentiation. EpCAM is highly expressed on most carcinomas and therefore of potential use as a diagnostic and prognostic marker for a variety of carcinomas, and has become a therapeutic target. EpCAM may occur in distinct forms due to glycosylation.
References:
1. Christof Pauli, et al. (2003) Cancer Lett. 193(1):25-32. 2. Graham Carpenter, et al. (2009) Cancer Cell. 15(3):165-6. 3. Bernardina T F van der Gun, et al. (2010) Carcinogenesis. 31(11):1913-21. 4. Carlo Patriarca, et al. (2012) Cancer Treat Rev. 38(1):68-75. 5. Sannia Imrich, et al. (2012) Cell Adh Migr. 6(1):30-8.