Recombinant Human ACE2 protein (His Tag)
Species
Human
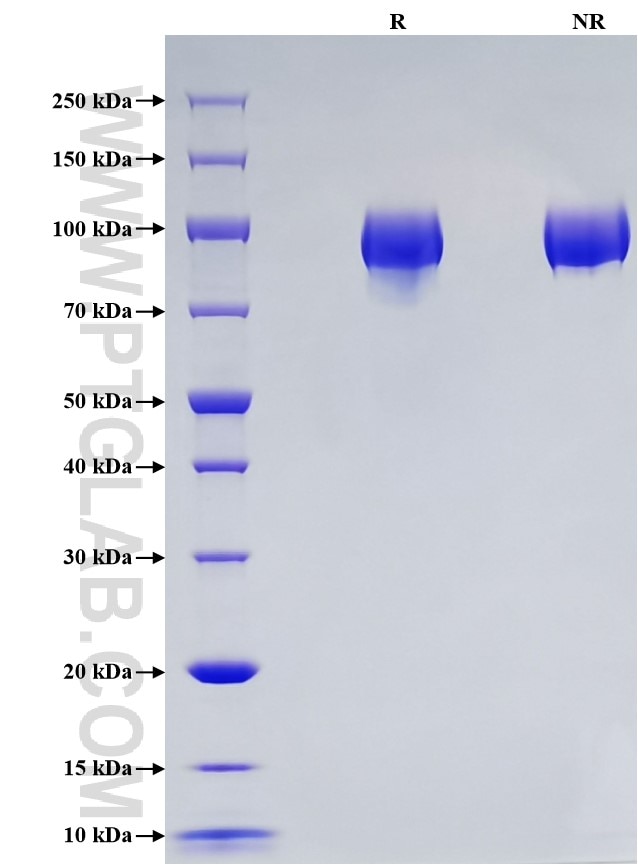
Purity
>95 %, SDS-PAGE
Tag
His Tag
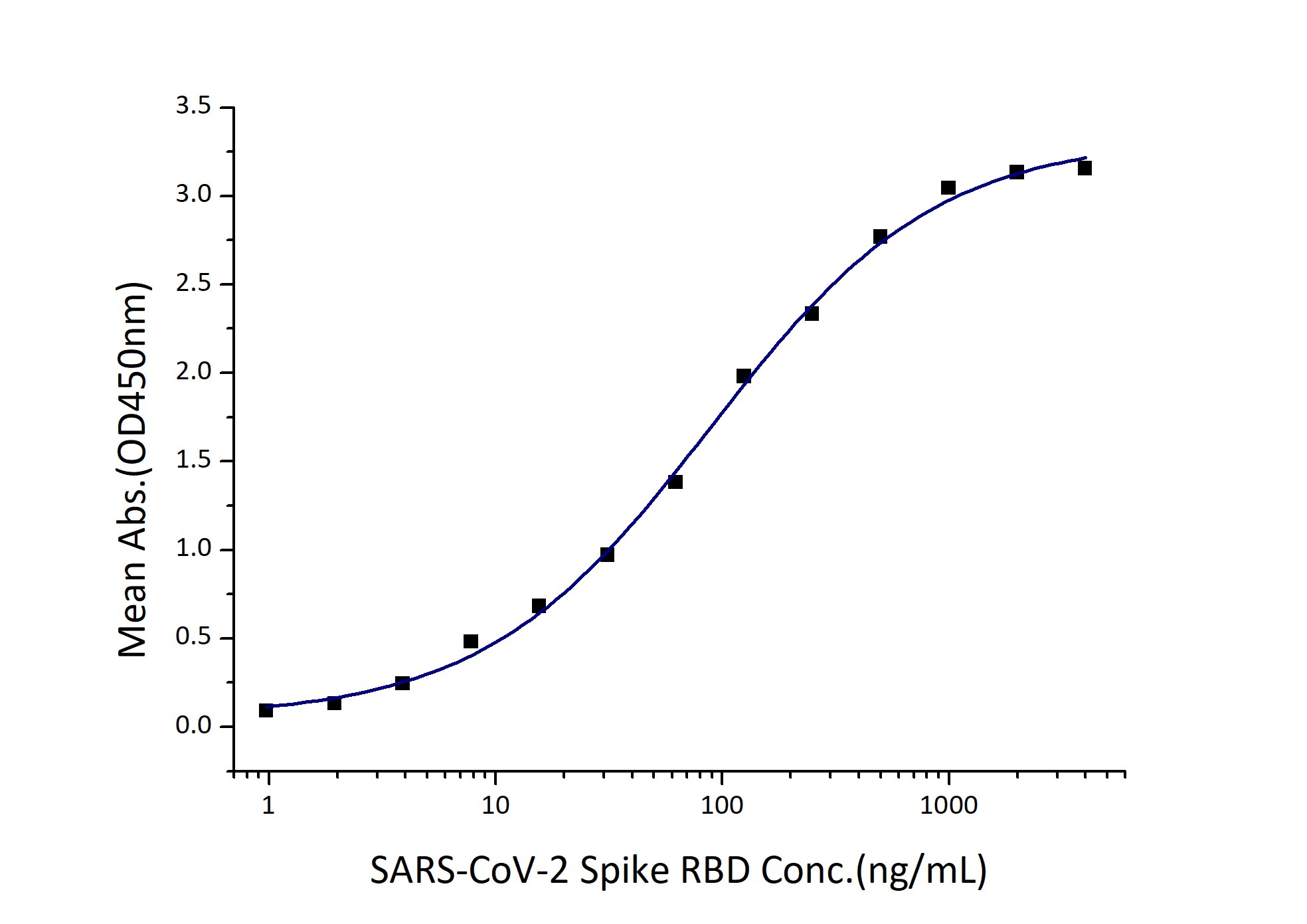
Activity
EC50: 44-176 ng/mL
Cat no : Eg0074
Validation Data Gallery
Product Information
| Purity | >95 %, SDS-PAGE |
| Endotoxin | <0.1 EU/μg protein, LAL method |
| Activity |
Immobilized Human ACE2 (His tag) at 2 μg/mL (100 μL/well) can bind SARS-CoV-2 Spike RBD (hFc tag, Myc tag, His tag) with a linear range of 44-176 ng/mL. |
| Expression | HEK293-derived Human ACE2 protein Gln18-Ser740 (Accession# Q9BYF1) with a His tag at the N-terminus. |
| GeneID | 59272 |
| Accession | Q9BYF1 |
| PredictedSize | 84.4 kDa |
| SDS-PAGE | 85-105 kDa, reducing (R) conditions |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from 0.22 μm filtered solution in PBS, pH 7.4. Normally 5% trehalose and 5% mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. |
| Reconstitution | Briefly centrifuge the tube before opening. Reconstitute at 0.1-0.5 mg/mL in sterile water. |
| Storage Conditions |
It is recommended that the protein be aliquoted for optimal storage. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
| Shipping | The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the recommended temperature. |
Background
Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2), a critical regulator of the renin-angiotensin system (RAS), belongs to the peptidase M2 family. It plays an important role in cardiovascular homeostasis by regulating vascular tone, fluid, and electrolyte balance. ACE2 functions as a carboxymonopeptidase hydrolyzing the cleavage of a single C-terminal residue from Angiotensin-II (Ang-II), the key peptide hormone of RAS, to form Angiotensin-(1-7) (Ang-(1-7)), which binds to the G-protein-coupled Mas receptor and activates signaling pathways that counteract the pathways activated by Ang-II. ACE2 is expressed in a variety of tissues, including the kidneys, testes, heart, and intestines, and is particularly enriched in lung epithelium. Recent studies have shown that increased ACE2 expression is likely to help prevent secondary fibrosis changes following COVID-19 pneumonia.
References:
1. Li Q, et al. (2020). Clin Sci (Lond). 134:2581-2595. 2. Li Y, et al. (2020). Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 526:947-952. 3. Hikmet F, et al. (2020). Mol Syst Biol. 16:e9610. 4. Chaudhry F, et al. (2020). Open Heart. 7:e001424.