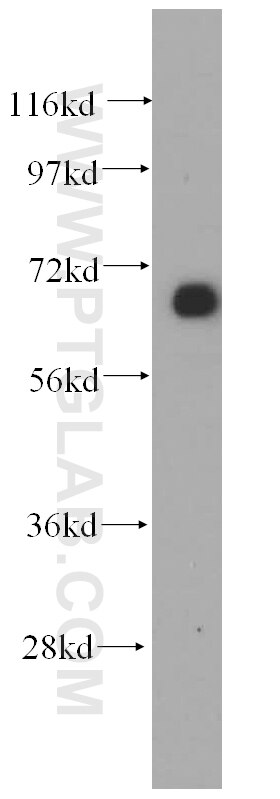
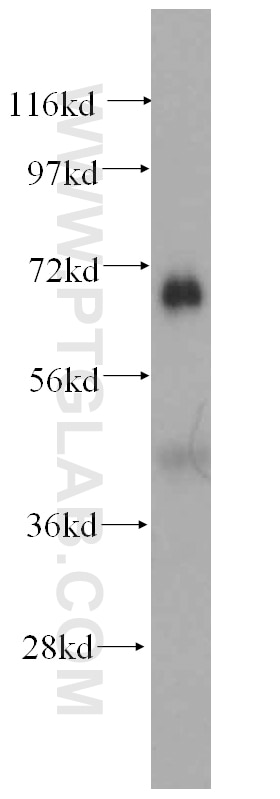
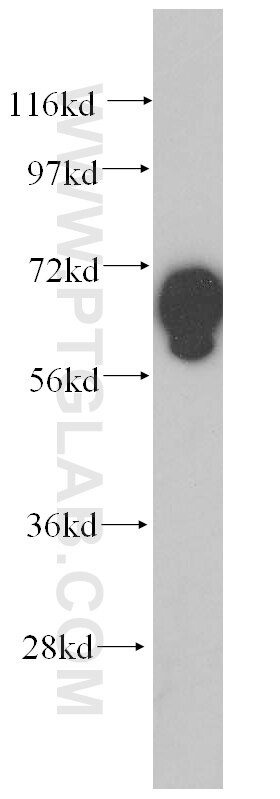
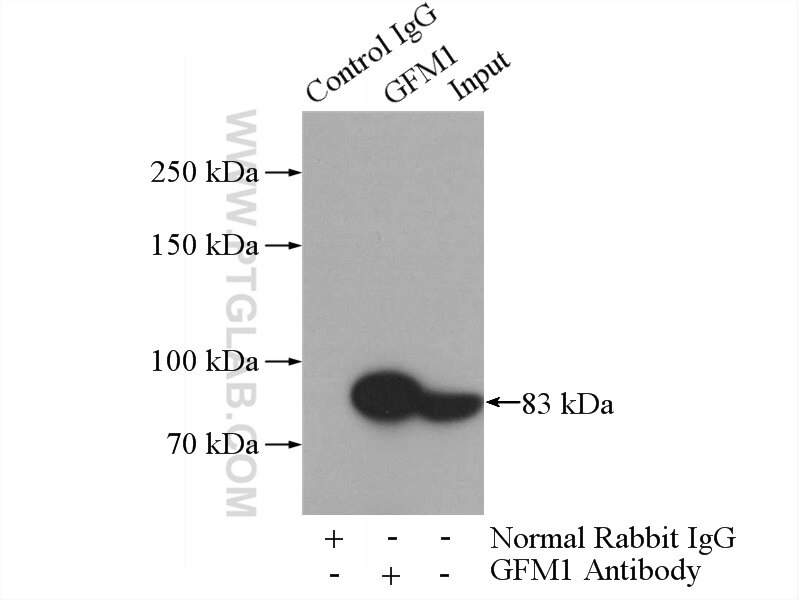
Tested Applications
| Positive WB detected in | mouse kidney tissue, HeLa cells, human heart tissue |
| Positive IP detected in | HeLa cells |
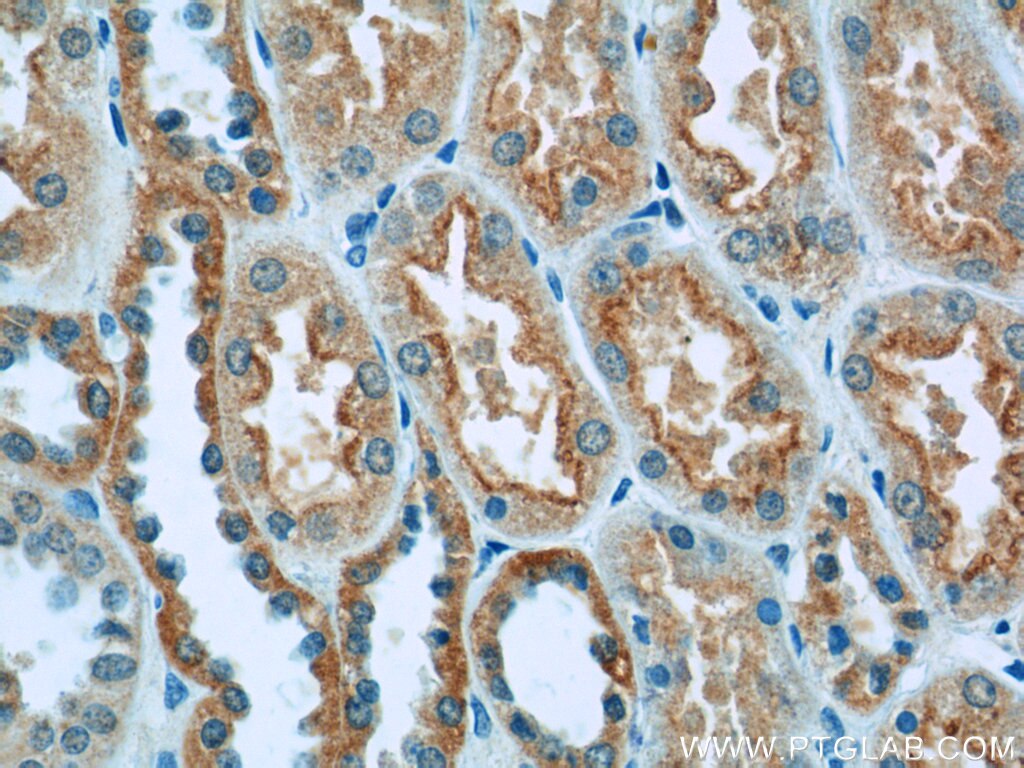
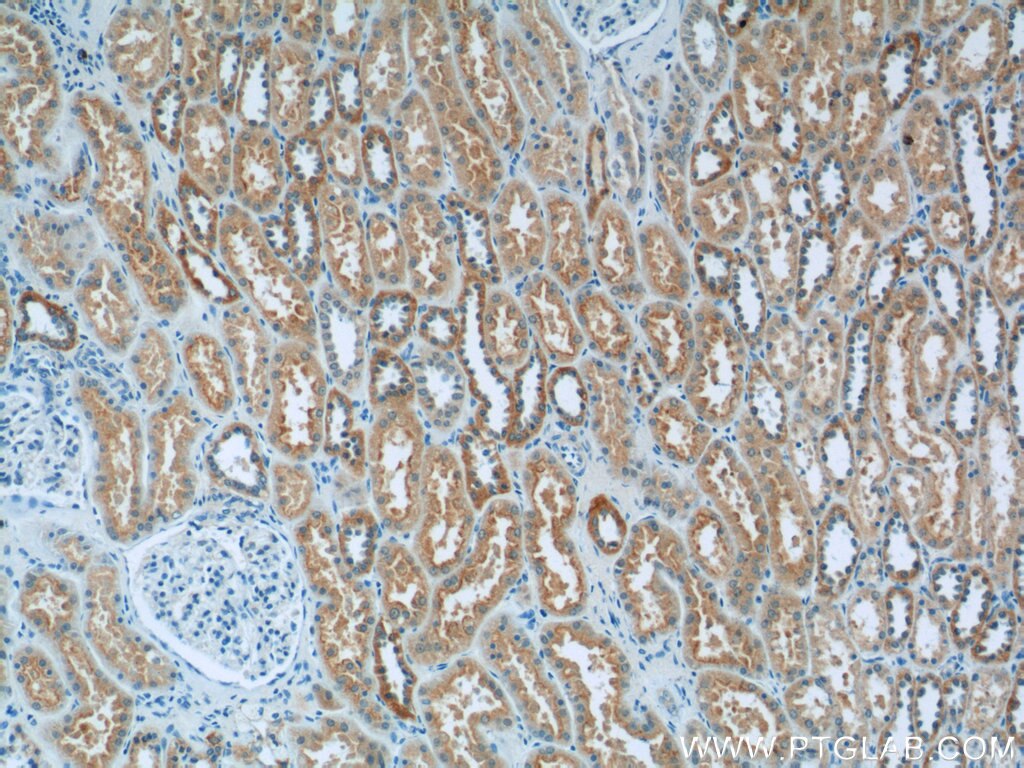
| Positive IHC detected in | human kidney tissue Note: suggested antigen retrieval with TE buffer pH 9.0; (*) Alternatively, antigen retrieval may be performed with citrate buffer pH 6.0 |
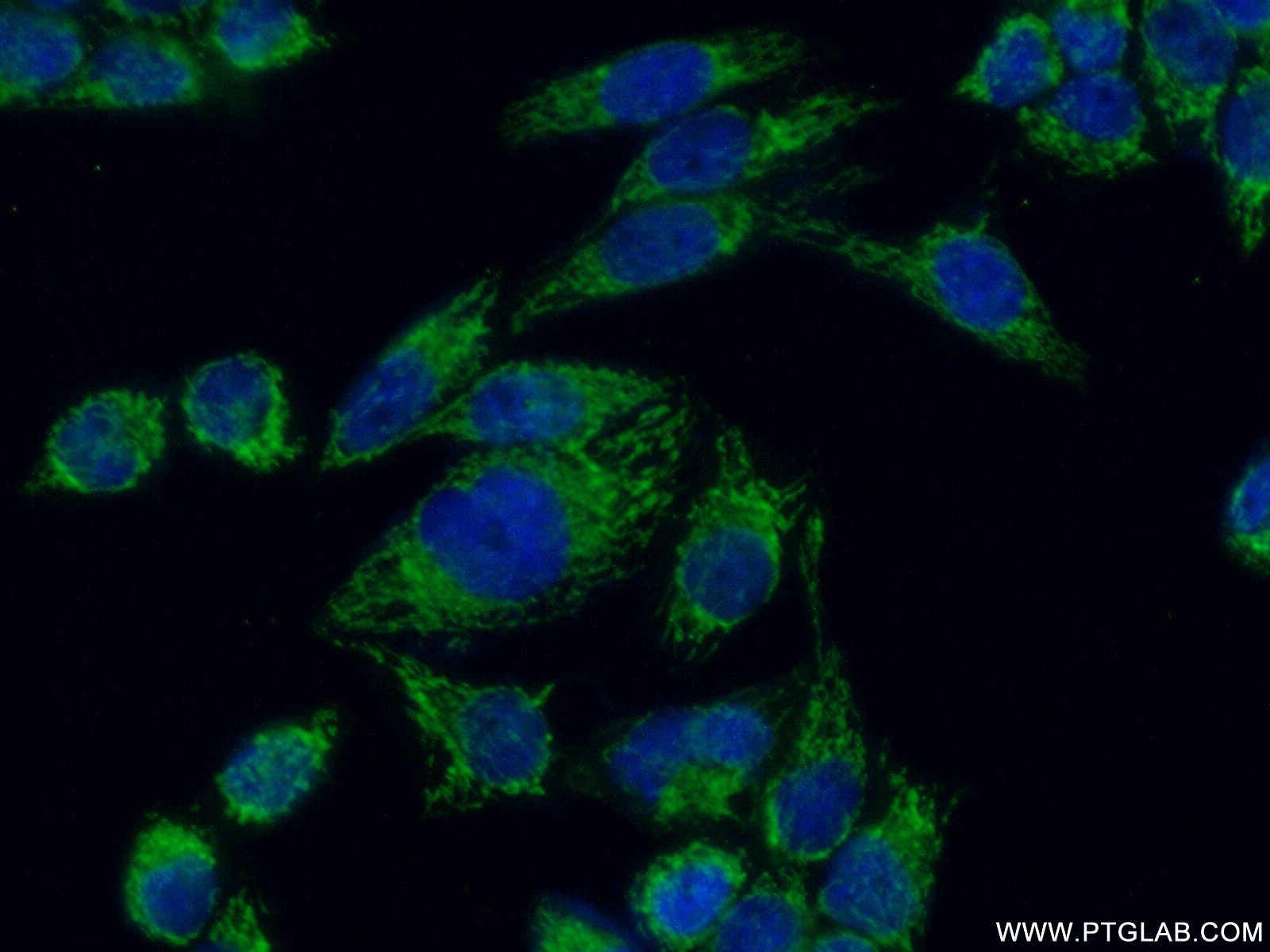
| Positive IF/ICC detected in | HeLa cells |
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:500-1:2000 |
| Immunoprecipitation (IP) | IP : 0.5-4.0 ug for 1.0-3.0 mg of total protein lysate |
| Immunohistochemistry (IHC) | IHC : 1:20-1:200 |
| Immunofluorescence (IF)/ICC | IF/ICC : 1:50-1:500 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
Published Applications
| WB | See 4 publications below |
| CoIP | See 1 publications below |
Product Information
14274-1-AP targets GFM1 in WB, IHC, IF/ICC, IP, CoIP, ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human, mouse, rat samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human, mouse, rat |
| Cited Reactivity | human, mouse |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Polyclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen | GFM1 fusion protein Ag5616 Predict reactive species |
| Full Name | G elongation factor, mitochondrial 1 |
| Calculated Molecular Weight | 86 kDa |
| Observed Molecular Weight | 70 kDa |
| GenBank Accession Number | BC049210 |
| Gene Symbol | GFM1 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 85476 |
| RRID | AB_2110140 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Antigen affinity purification |
| UNIPROT ID | Q96RP9 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol , pH 7.3 |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -20°C. Stable for one year after shipment. Aliquoting is unnecessary for -20oC storage. 20ul sizes contain 0.1% BSA. |
Background Information
Different factors catalyze the three stages of protein translation: initiation, elongation, and termination. There are two translational systems in eukaryotes, one in the cytoplasm and the other in the mitochondria. In mitochondria, the elongation phase requires three elongation factors (EF): Tu (TUFM), Ts (TSFM), and G (GFM1)[PMID:19716793]. GFM1 catalyzes translocation during peptide elongation and mediates ribosomal disassembly during ribosome recycling in concert with the ribosomal recycling factor (RRF). [PMID:16487710]
Protocols
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for GFM1 antibody 14274-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IHC protocol for GFM1 antibody 14274-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IF protocol for GFM1 antibody 14274-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IP protocol for GFM1 antibody 14274-1-AP | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |
Publications
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Sci Transl Med Molecular diagnosis of infantile mitochondrial disease with targeted next-generation sequencing. | ||
Int J Mol Sci Translation Fidelity and Respiration Deficits in CLPP-Deficient Tissues: Mechanistic Insights from Mitochondrial Complexome Profiling | ||
Cells Inactivity of Peptidase ClpP Causes Primary Accumulation of Mitochondrial Disaggregase ClpX with Its Interacting Nucleoid Proteins, and of mtDNA. | ||
Reviews
The reviews below have been submitted by verified Proteintech customers who received an incentive for providing their feedback.
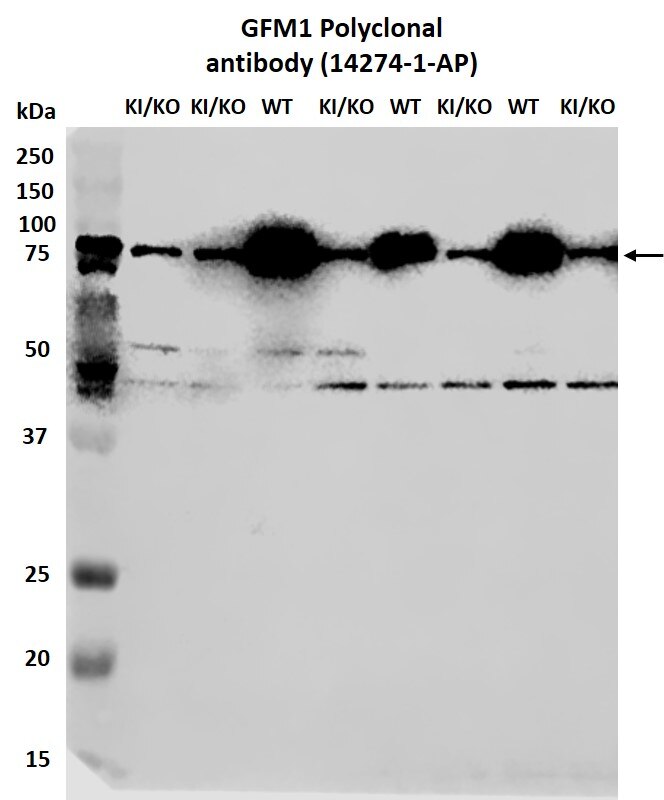
FH Miguel (Verified Customer) (03-21-2022) | WB analysis of mouse liver using 14274-1-AP. Mouse liver homogenates in Ripa buffer were subjected to SDS PAGE followed by western blot with 14274-1-AP (GFM1 antibody) at dilution of 1:1000 incubated at 4°C O/N. KI/KO: Compound heterozygous knock-in/knock-out (Gfm1R671C/-) mouse model (1). WT: Wild type control mice (Gfm1+/+). (1) ) Molina-Berenguer M, Vila-Julià F, Pérez-Ramos S, Salcedo-Allende MT, Cámara Y, Torres-Torronteras J, Martí R. Dysfunctional mitochondrial translation and combined oxidative phosphorylation deficiency in a mouse model of hepatoencephalopathy due to Gfm1 mutations. FASEB J. 2022 Jan;36(1):e22091. doi: 10.1096/fj.202100819RRR. PMID: 34919756.
 |