Product Information
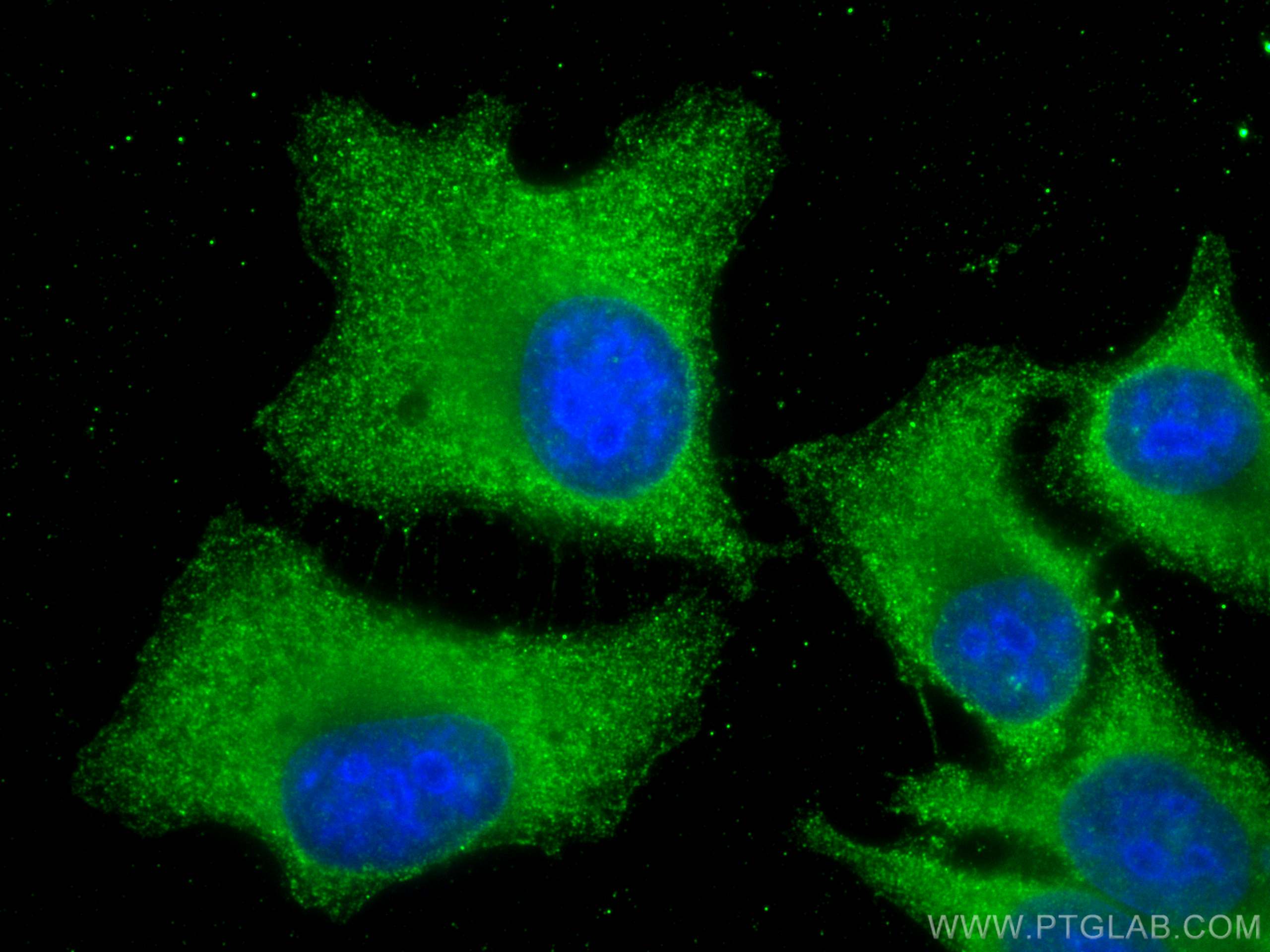
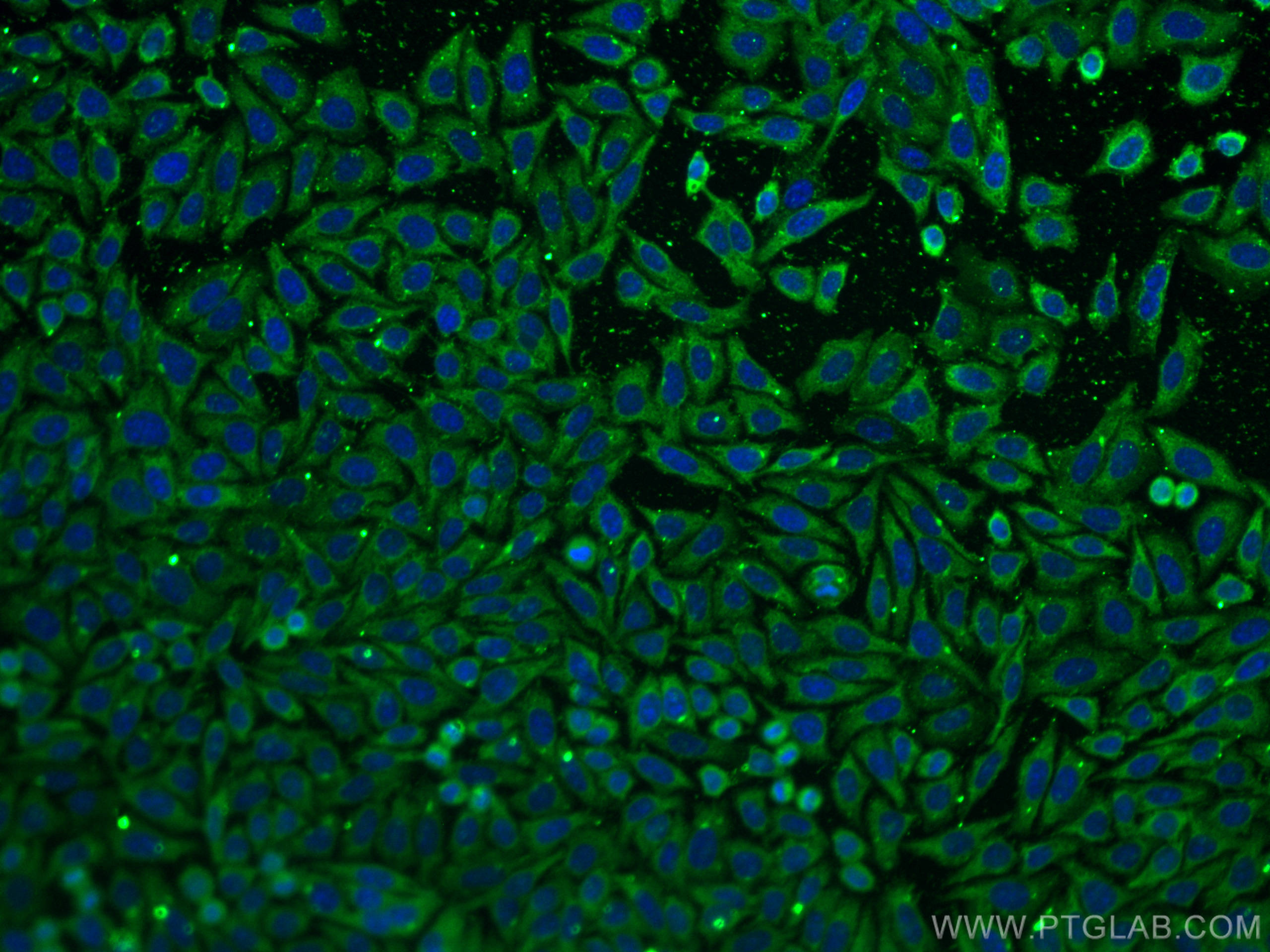
66954-1-PBS targets FGFR3 as part of a matched antibody pair:
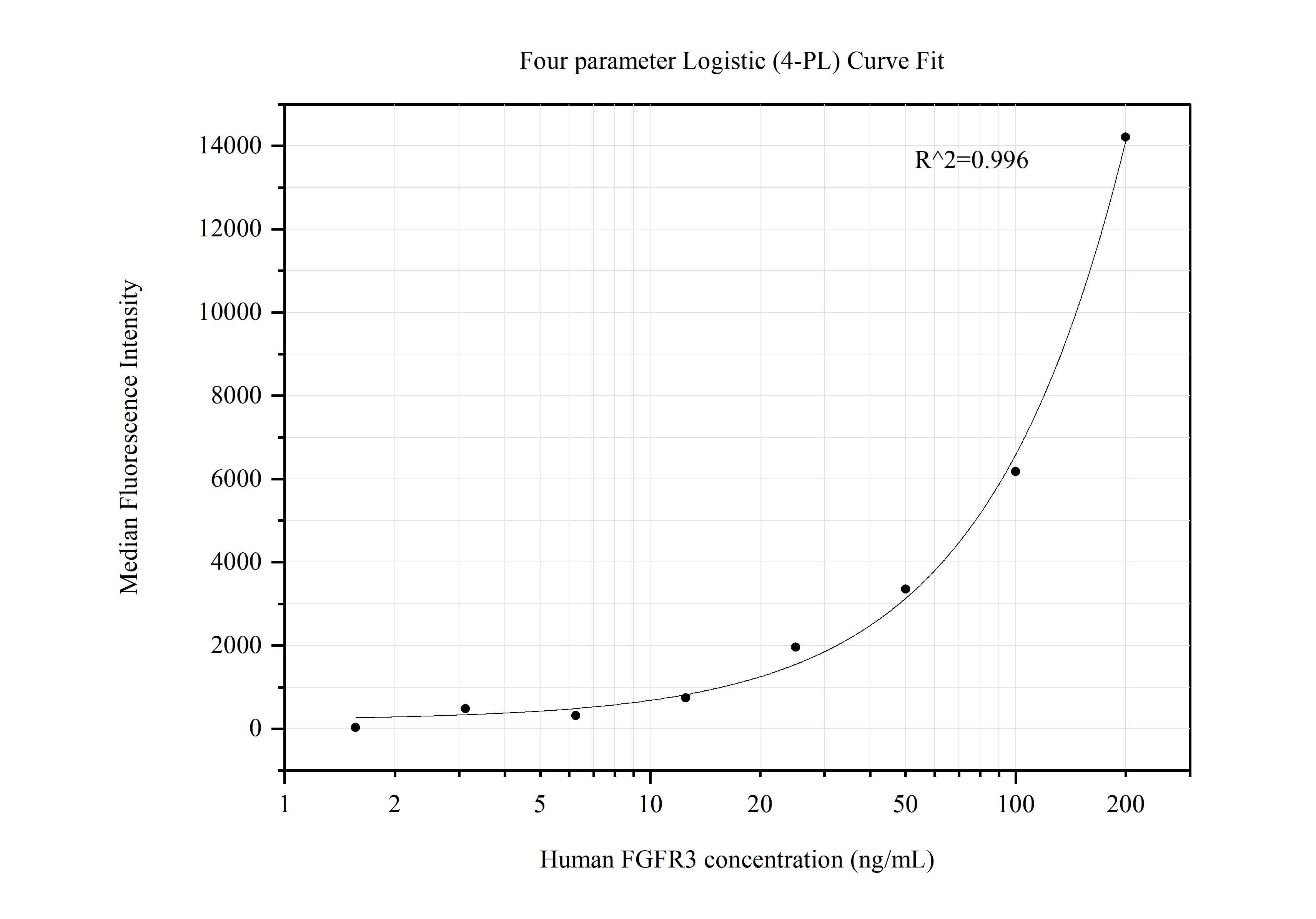
MP50578-1: 66954-1-PBS capture and 66954-2-PBS detection (validated in Cytometric bead array)
Unconjugated mouse monoclonal antibody pair in PBS only (BSA and azide free) storage buffer at a concentration of 1 mg/mL, ready for conjugation.
This conjugation ready format makes antibodies ideal for use in many applications including: ELISAs, multiplex assays requiring matched pairs, mass cytometry, and multiplex imaging applications.Antibody use should be optimized by the end user for each application and assay.
| Tested Reactivity | human |
| Host / Isotype | Mouse / IgG1 |
| Class | Monoclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen | FGFR3 fusion protein Ag26290 Predict reactive species |
| Full Name | fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 |
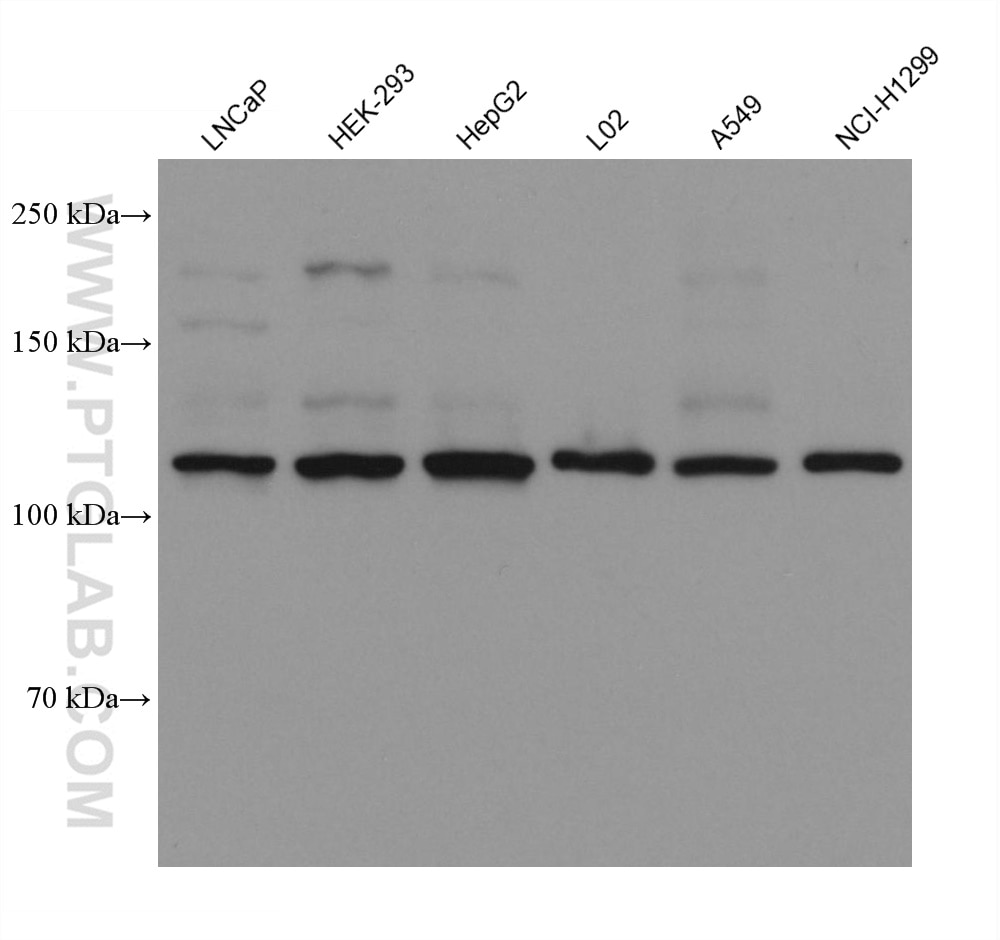
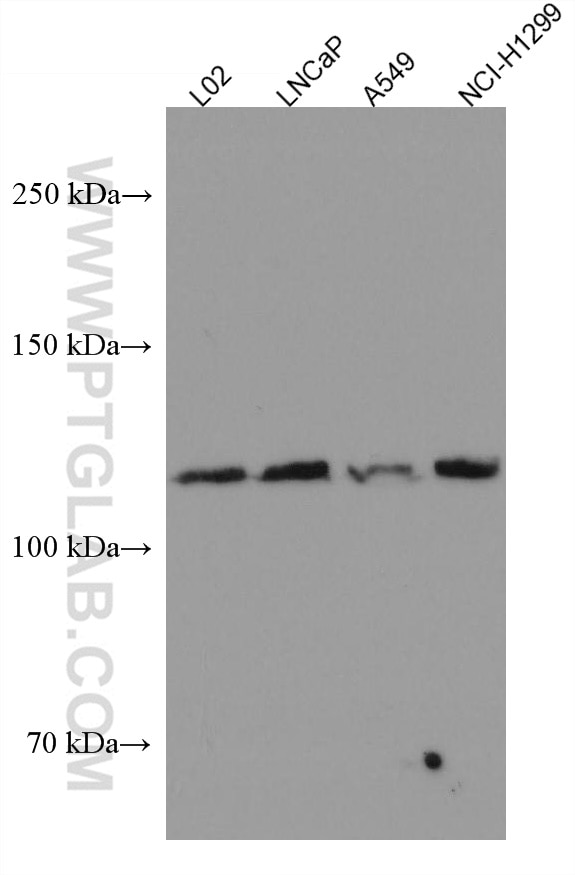
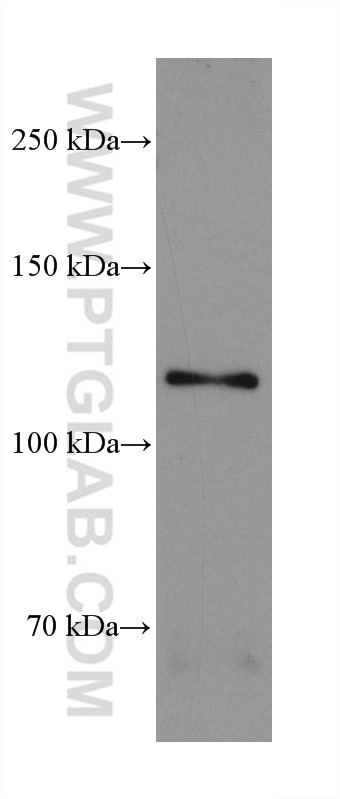
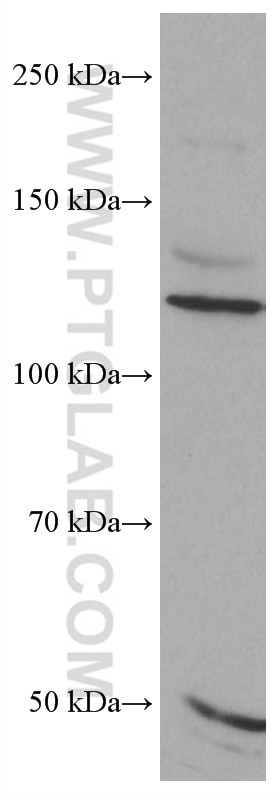
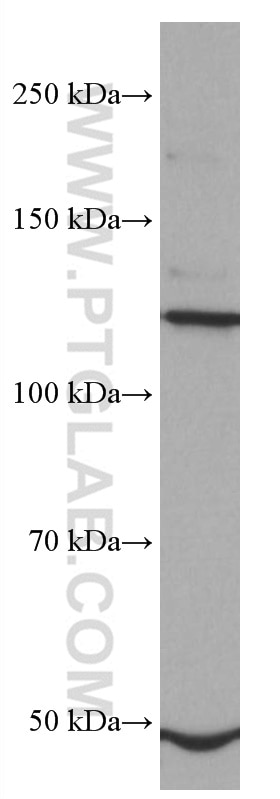
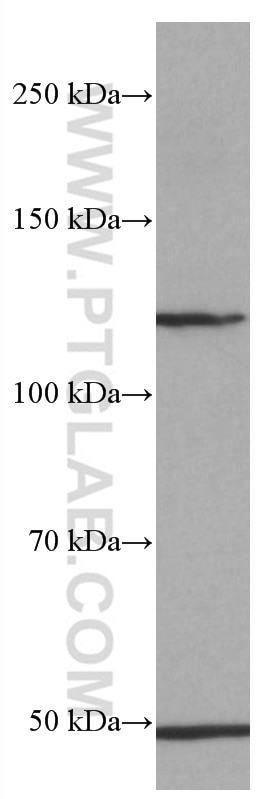
| Calculated Molecular Weight | 87 kDa |
| Observed Molecular Weight | 125-135 kDa |
| GenBank Accession Number | NM_000142 |
| Gene Symbol | FGFR3 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 2261 |
| RRID | AB_2882277 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Protein G purification |
| Storage Buffer | PBS only , pH 7.3 |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -80°C. |
Background Information
Fibroblast growth factors (FGFs) are polypeptide growth factors involved in a variety of activities including mitogenesis, angiogenesis, and wound healing (PMID: 1847508). The human FGF receptor family, a subfamily of receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs), comprises of four family members-FGFR1, FGFR2, FGFR3, and FGFR4 (PMID: 23900974). Each receptor contains an extracellular domain with either two or three immunoglobulin-like domains, a transmembrane domain, and a cytoplasmic tyrosine kinase domain. FGFR3 binds acidic and basic fibroblast GH and plays a role in bone development and maintenance. Mutations in the FGFR3 gene lead to craniosynostosis and multiple types of skeletal dysplasia. Due to frequent mutations in certain cancers, the FGFR3 gene has also been associated with tumor progression.