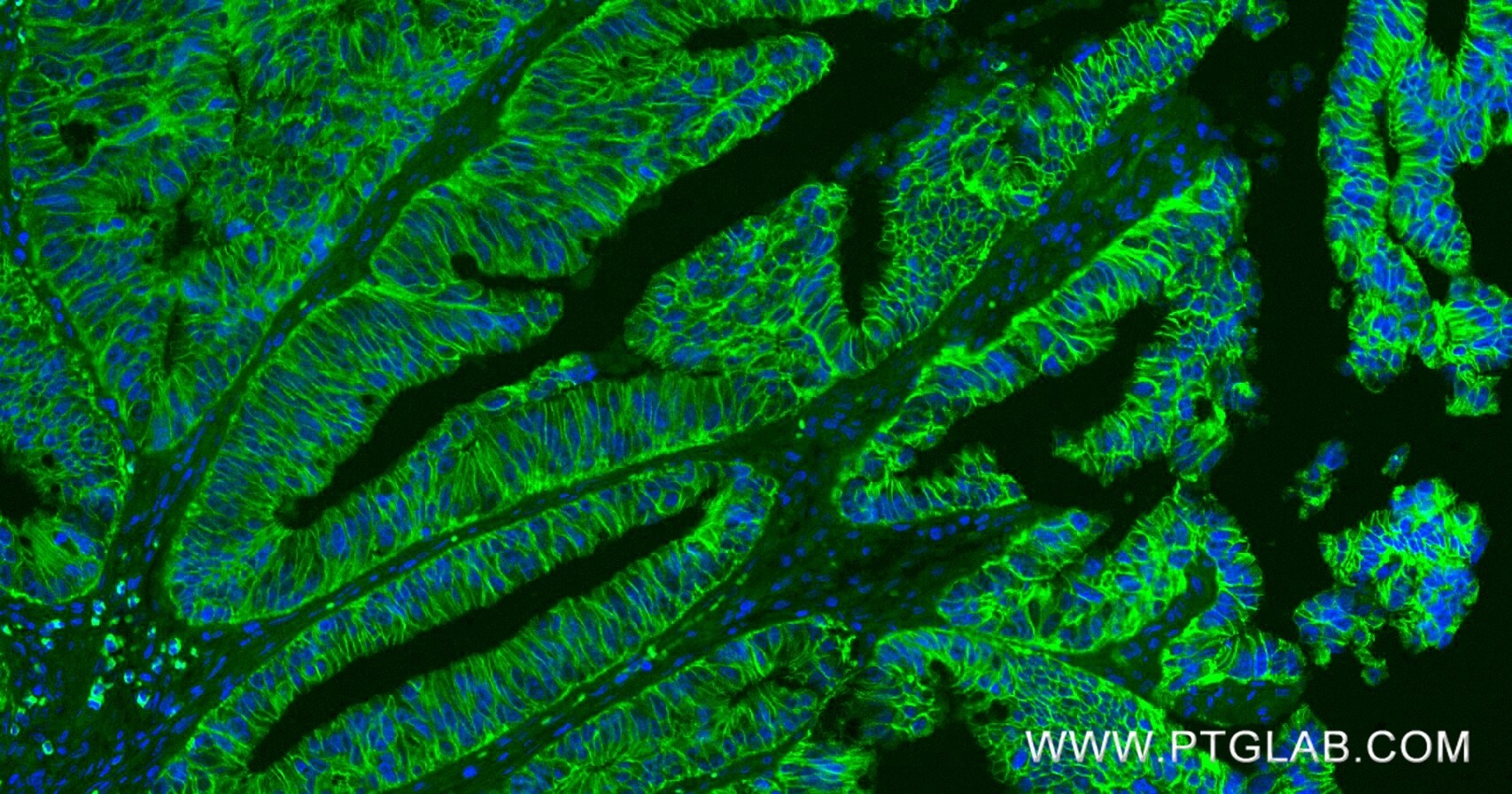
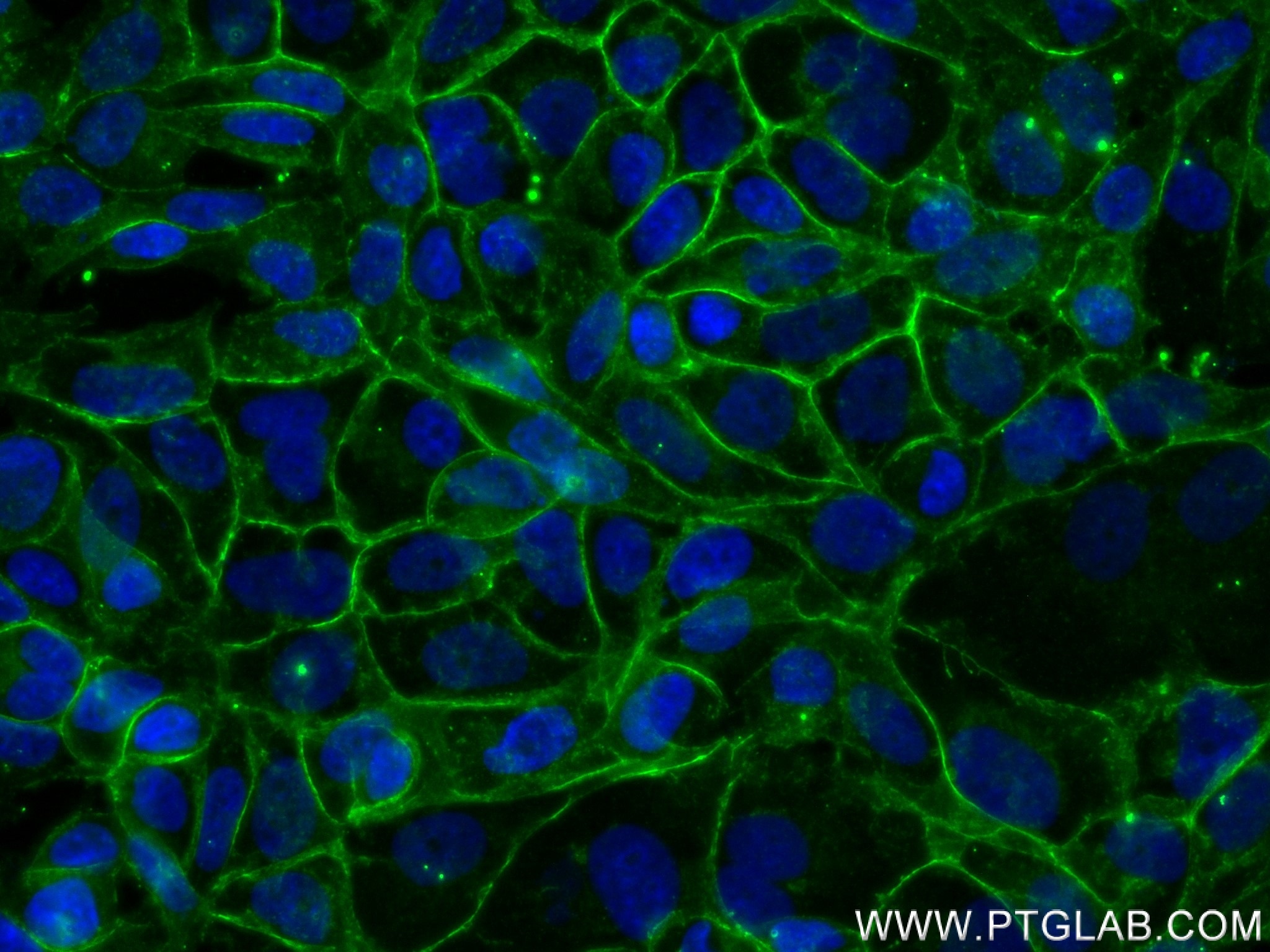
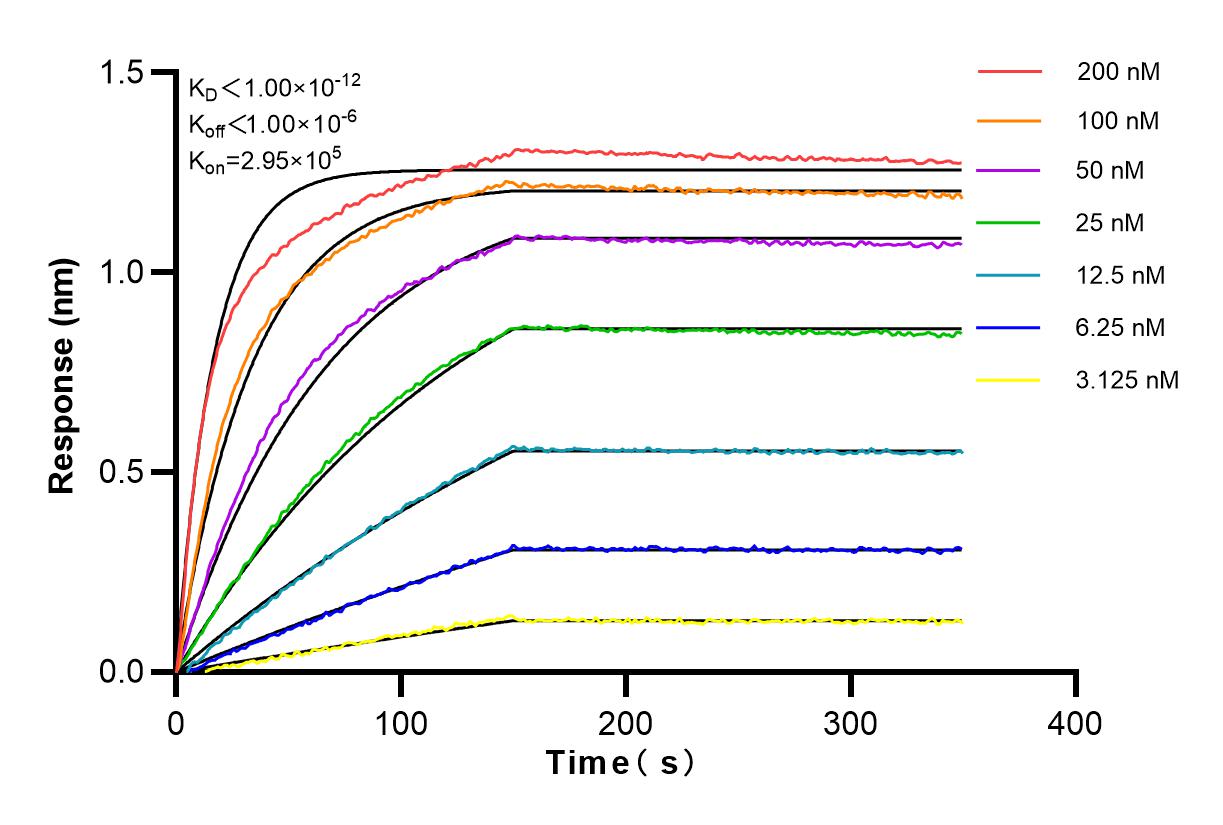
Product Information
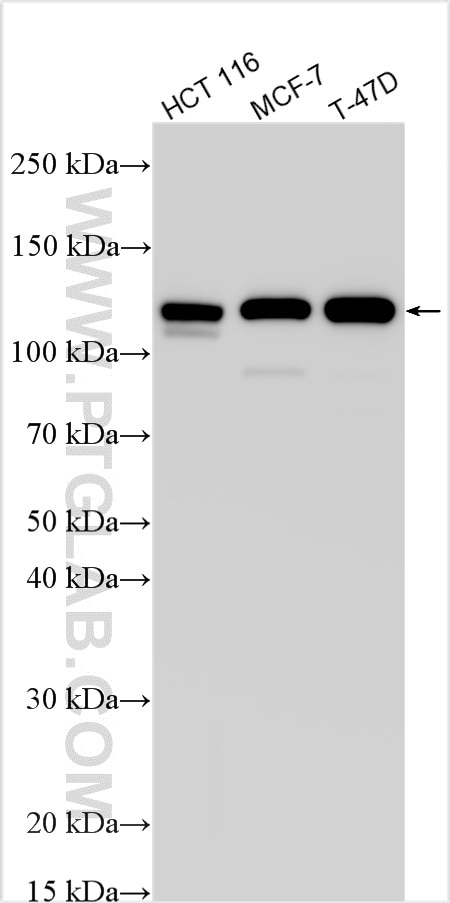
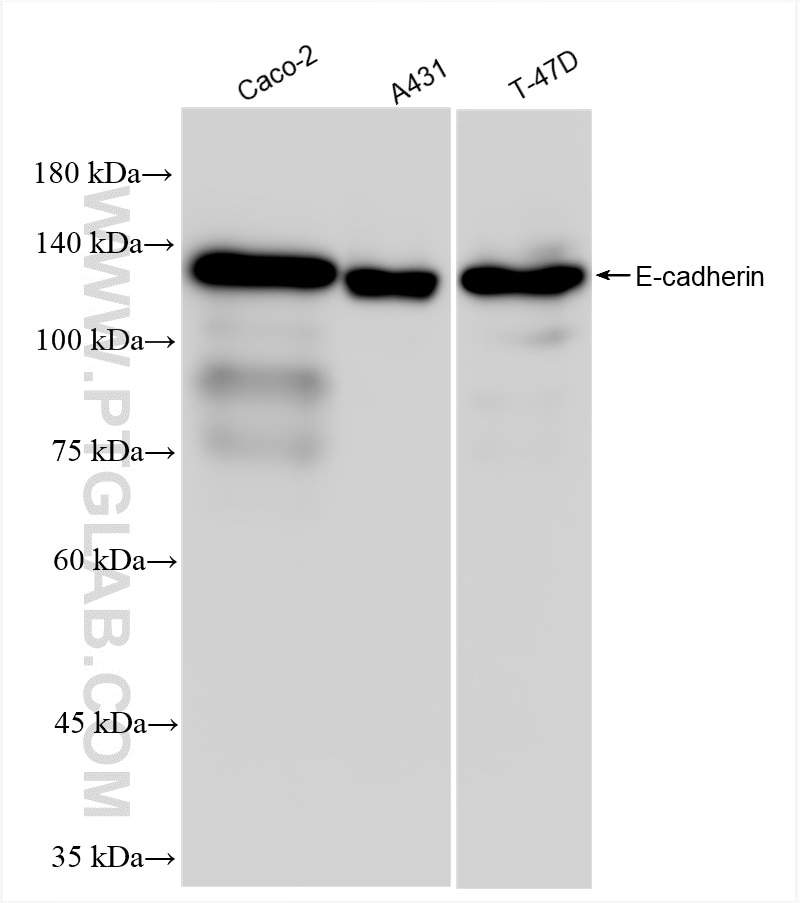
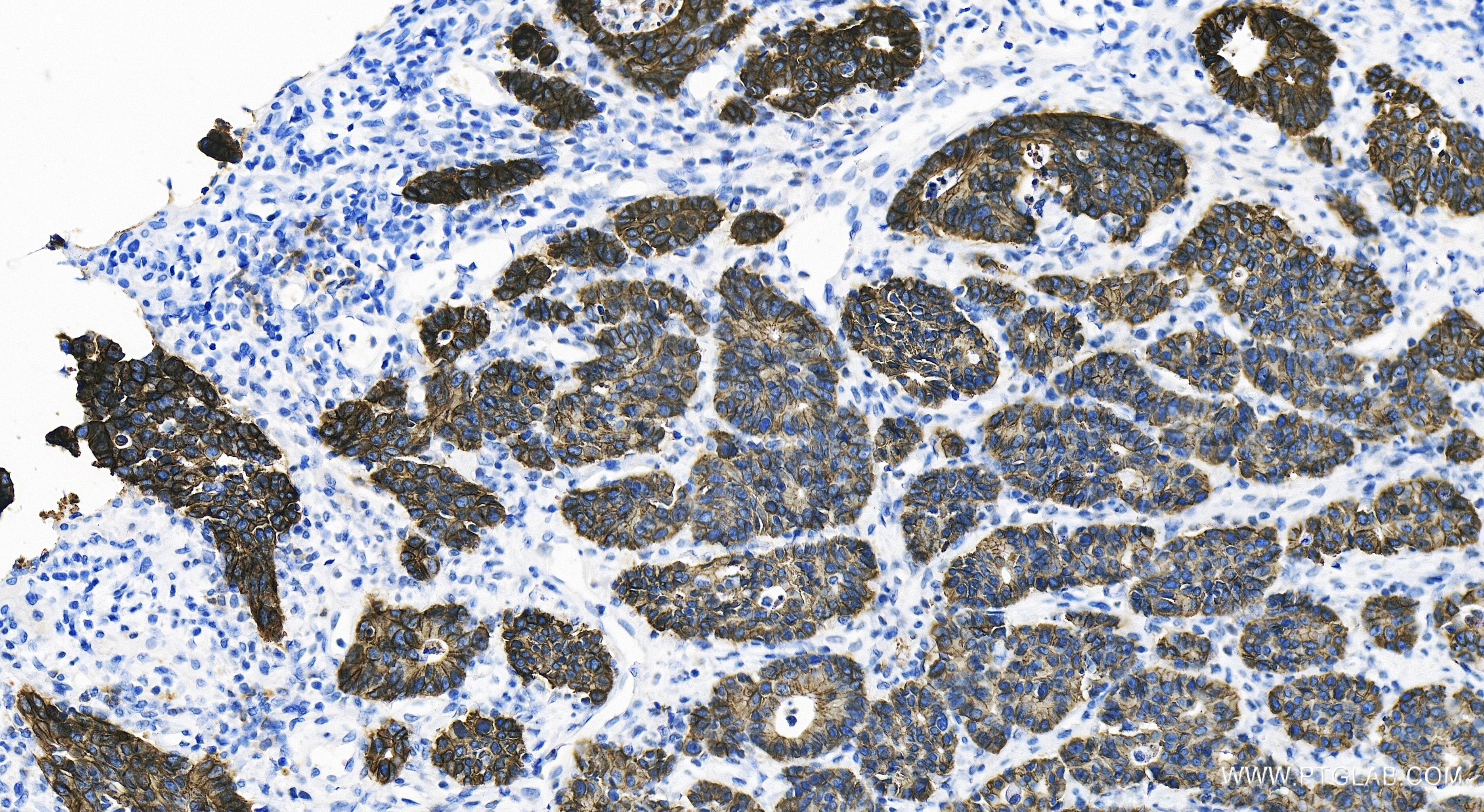
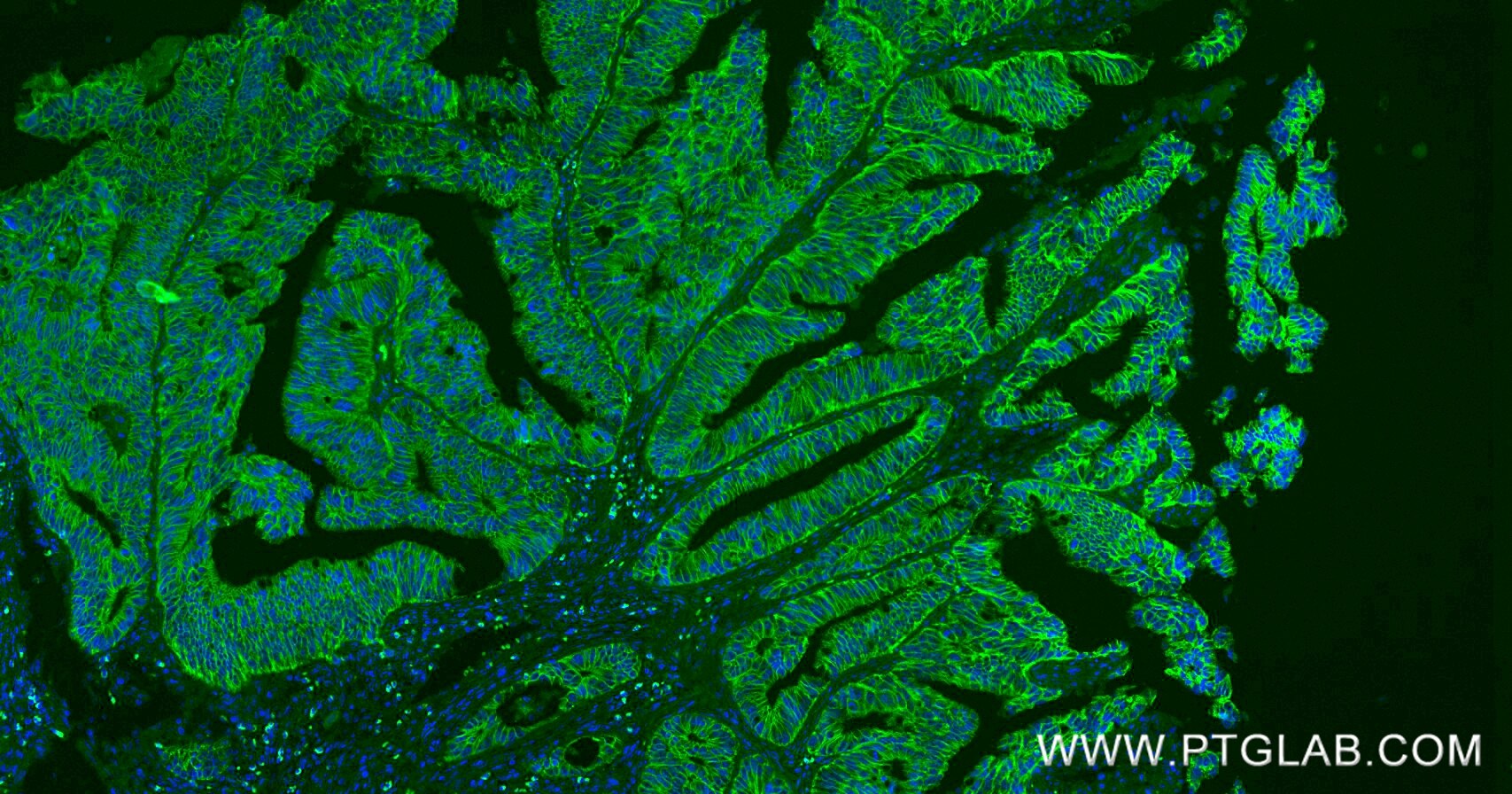
80541-7-PBS targets E-cadherin in WB, IHC, IF/ICC, IF-P, ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Recombinant |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen |
CatNo: Ag14973 Product name: Recombinant human E-cadherin protein Source: e coli.-derived, PGEX-4T Tag: GST Domain: 373-622 aa of BC141838 Sequence: PIFNPTTYKGQVPENEANVVITTLKVTDADAPNTPAWEAVYTILNDDGGQFVVTTNPVNNDGILKTAKGLDFEAKQQYILHVAVTNVVPFEVSLTTSTATVTVDVLDVNEAPIFVPPEKRVEVSEDFGVGQEITSYTAQEPDTFMEQKITYRIWRDTANWLEINPDTGAISTRAELDREDFEHVKNSTYTALIIATDNGSPVATGTGTLLLILSDVNDNAPIPEPRTIFFCERNPKPQVINIIDADLPPI Predict reactive species |
| Full Name | cadherin 1, type 1, E-cadherin (epithelial) |
| Calculated Molecular Weight | 882 aa, 97 kDa |
| Observed Molecular Weight | 135 kDa |
| GenBank Accession Number | BC141838 |
| Gene Symbol | E-cadherin |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 999 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Protein A purfication |
| UNIPROT ID | P12830 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS only, pH 7.3. |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -80°C. |
Background Information
Cadherins are a family of transmembrane glycoproteins that mediate calcium-dependent cell-cell adhesion and play an important role in the maintenance of normal tissue architecture. E-cadherin (epithelial cadherin), also known as CDH1 (cadherin 1) or CAM 120/80, is a classical member of the cadherin superfamily which also include N-, P-, R-, and B-cadherins. E-cadherin is expressed on the cell surface in most epithelial tissues. The extracellular region of E-cadherin establishes calcium-dependent homophilic trans binding, providing specific interaction with adjacent cells, while the cytoplasmic domain is connected to the actin cytoskeleton through the interaction with p120-, α-, β-, and γ-catenin (plakoglobin). E-cadherin is important in the maintenance of the epithelial integrity, and is involved in mechanisms regulating proliferation, differentiation, and survival of epithelial cell. E-cadherin may also play a role in tumorigenesis. It is considered to be an invasion suppressor protein and its loss is an indicator of high tumor aggressiveness.