Tested Applications
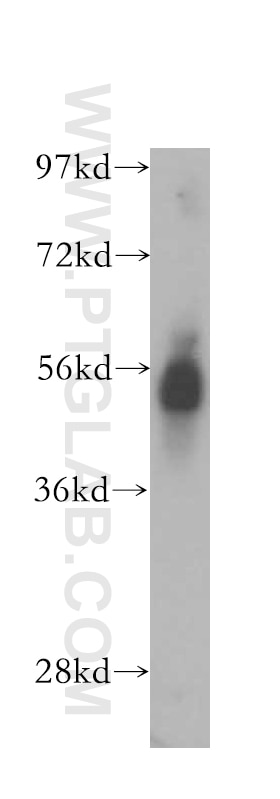
| Positive WB detected in | PC-3 cells |
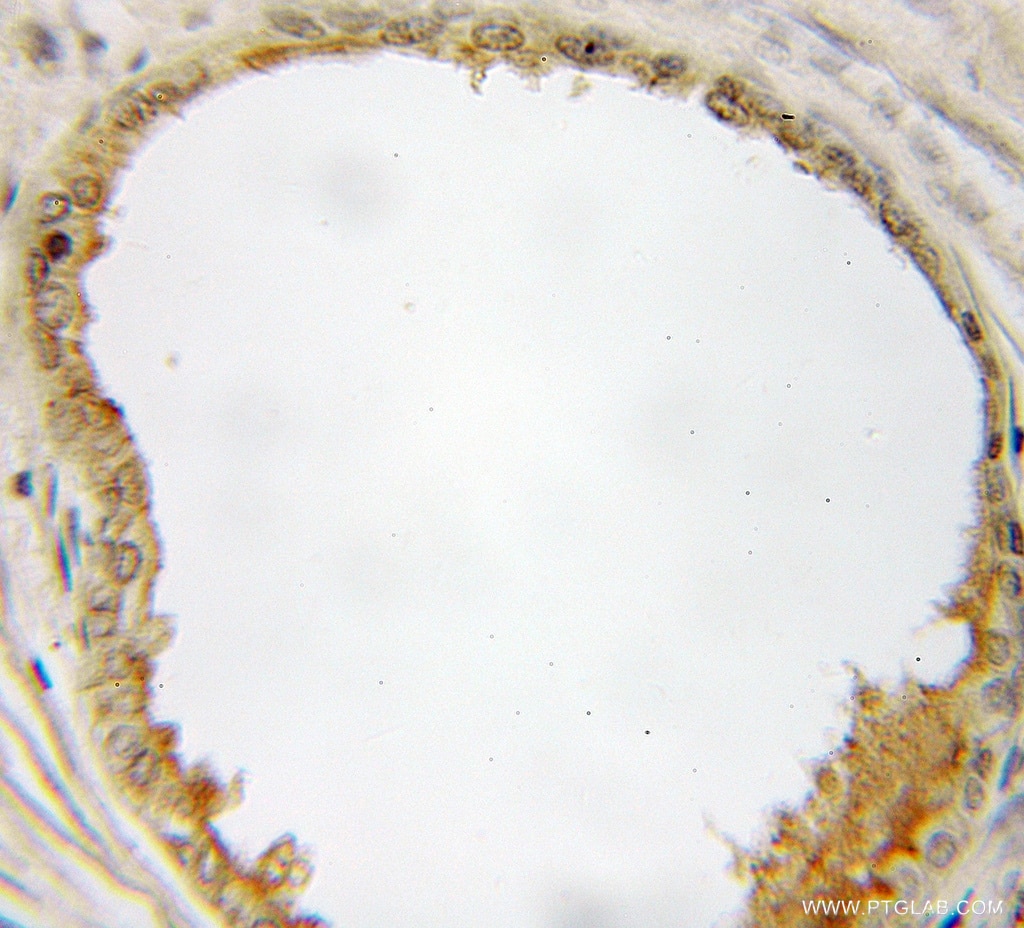
| Positive IHC detected in | human prostate cancer tissue Note: suggested antigen retrieval with TE buffer pH 9.0; (*) Alternatively, antigen retrieval may be performed with citrate buffer pH 6.0 |
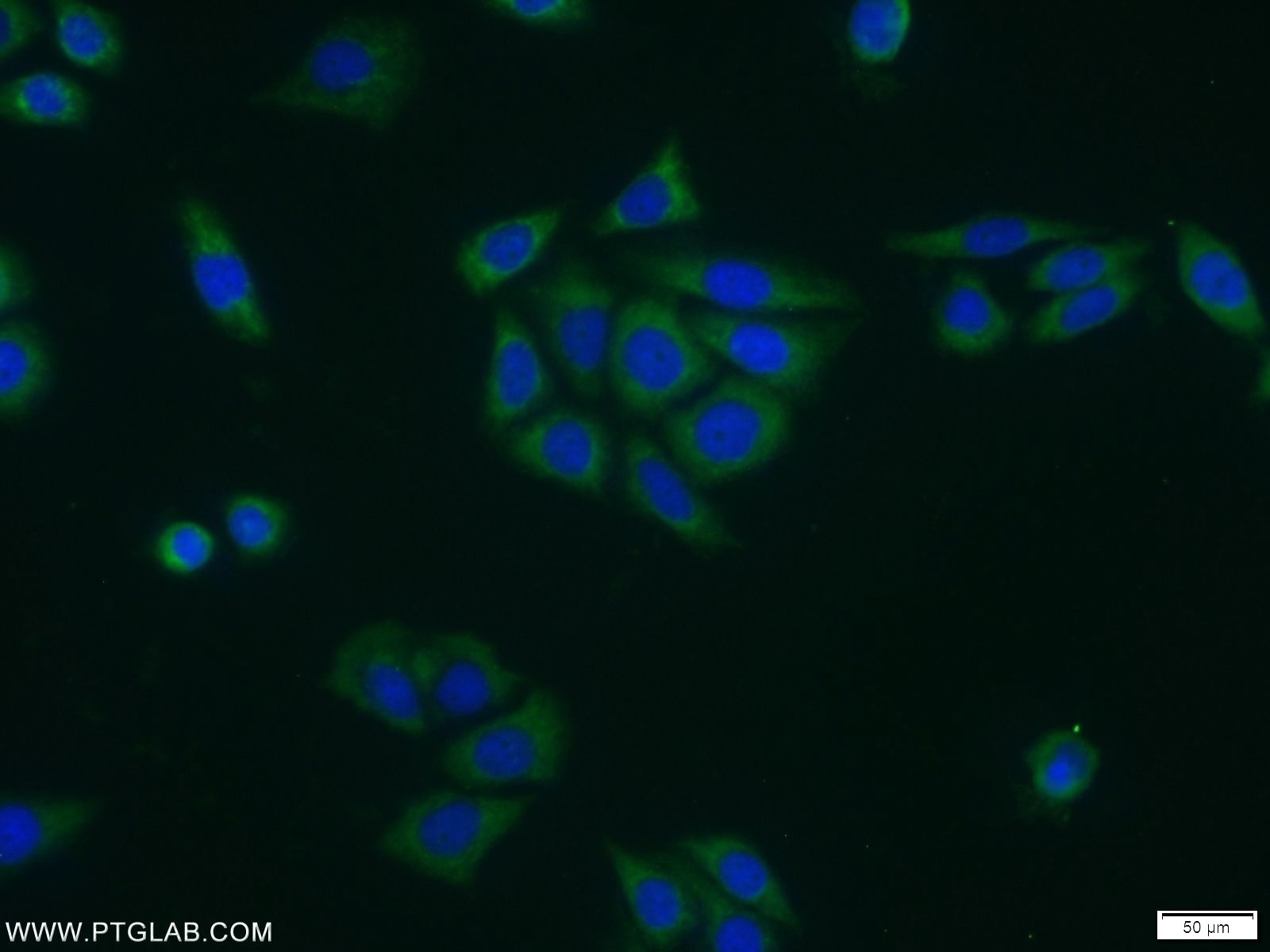
| Positive IF/ICC detected in | PC-3 cells |
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:500-1:1000 |
| Immunohistochemistry (IHC) | IHC : 1:20-1:200 |
| Immunofluorescence (IF)/ICC | IF/ICC : 1:10-1:100 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
Published Applications
| KD/KO | See 1 publications below |
| WB | See 7 publications below |
| IHC | See 2 publications below |
| IF | See 4 publications below |
Product Information
10940-1-AP targets DPP4/CD26 in WB, IF, IHC, ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human, hamster samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human, hamster |
| Cited Reactivity | human, rat |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Polyclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen | DPP4/CD26 fusion protein Ag1380 Predict reactive species |
| Full Name | dipeptidyl-peptidase 4 |
| Calculated Molecular Weight | 88 kDa |
| Observed Molecular Weight | 55-60 kDa |
| GenBank Accession Number | BC013329 |
| Gene Symbol | DPP4 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 1803 |
| RRID | AB_2093567 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Antigen affinity purification |
| UNIPROT ID | P27487 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol, pH 7.3. |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -20°C. Stable for one year after shipment. Aliquoting is unnecessary for -20oC storage. 20ul sizes contain 0.1% BSA. |
Background Information
DPP4 (also known as CD26) is a serine exopeptidase that cleaves X-proline dipeptides from the N terminus of polypeptides. It is an intrinsic membrane glycoprotein anchored into the cell membrane by its N-terminal end. High levels of the enzyme are found in the brush-border membranes of the kidney proximal tubule and of the small intestine, but several other tissues also express the enzyme. The enzyme is present in the fetal colon but disappears at birth. It is ectopically expressed in some human colon adenocarcinomas and human colon cancer cell lines(PMID:1977364).The dimeric 150- 220 kDa DPPIV has been reported to be active and accessible to DFP labeling, but the 110 kDa monomeric DPPIV is not(PMID:9065413). Sometimes traces of the 290 kDa active dimeric form of DPP IV as well as a 55-60 kDa protein appeared in the immunopurified DPP IV preparation. N-terminal amino acid sequence analysis revealed that the 55-60 kDa protein represents a fragment of DPP IV starting at amino acid 28.(PMID:9654125).
Protocols
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for DPP4/CD26 antibody 10940-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IHC protocol for DPP4/CD26 antibody 10940-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IF protocol for DPP4/CD26 antibody 10940-1-AP | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |
Publications
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Oncogene ApoC1 promotes the metastasis of clear cell renal cell carcinoma via activation of STAT3. | ||
Hypertension Dipeptidyl peptidase IV regulates proliferation of preglomerular vascular smooth muscle and mesangial cells. | ||
Int J Mol Sci Preclinical Repurposing of Sitagliptin as a Drug Candidate for Colorectal Cancer by Targeting CD24/CTNNB1/SOX4-Centered Signaling Hub | ||
Biochem Pharmacol Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibition improves endothelial senescence by activating AMPK/SIRT1/Nrf2 signaling pathway.
| ||
Endocrinology Dipeptidylpeptidase inhibition is associated with improvement in blood pressure and diastolic function in insulin-resistant male Zucker obese rats. | ||
J Agric Food Chem A Low ω-6/ω-3 Ratio High-Fat Diet Improves Rat Metabolism via Purine and Tryptophan Metabolism in the Intestinal Tract, While Reversed by Inulin. |