Product Information
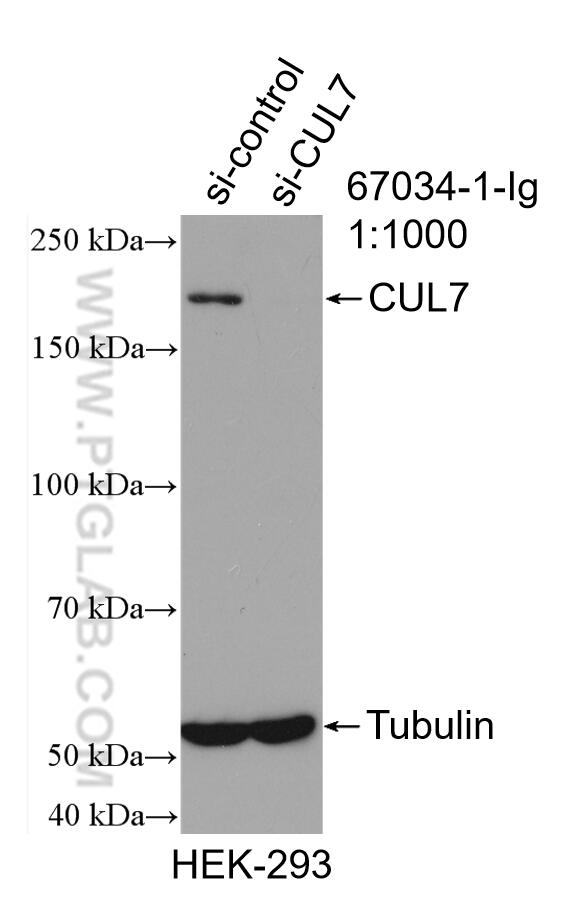
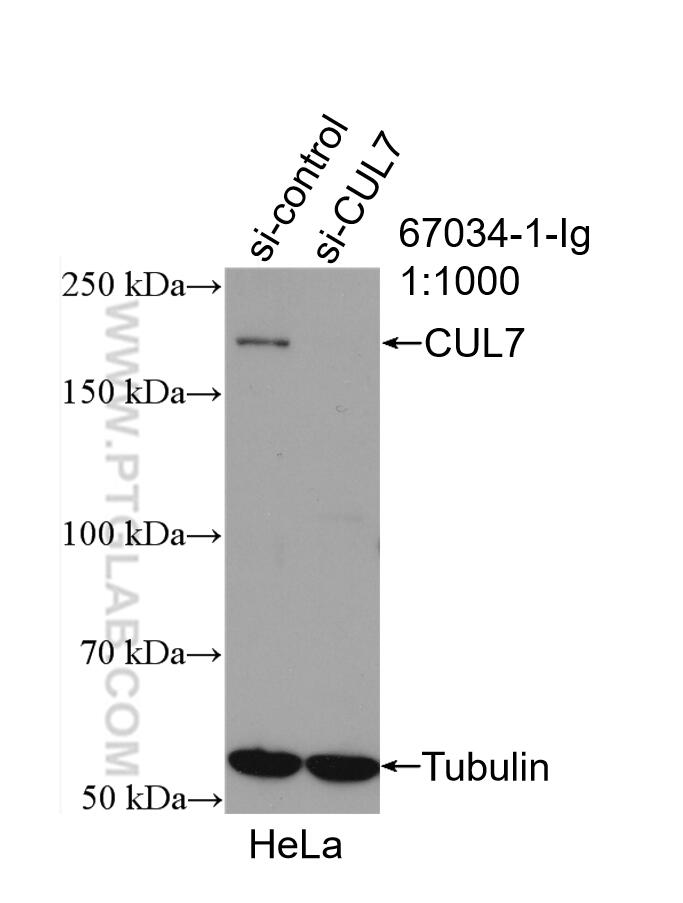
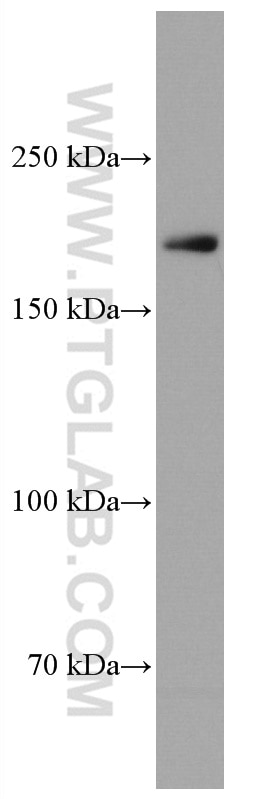
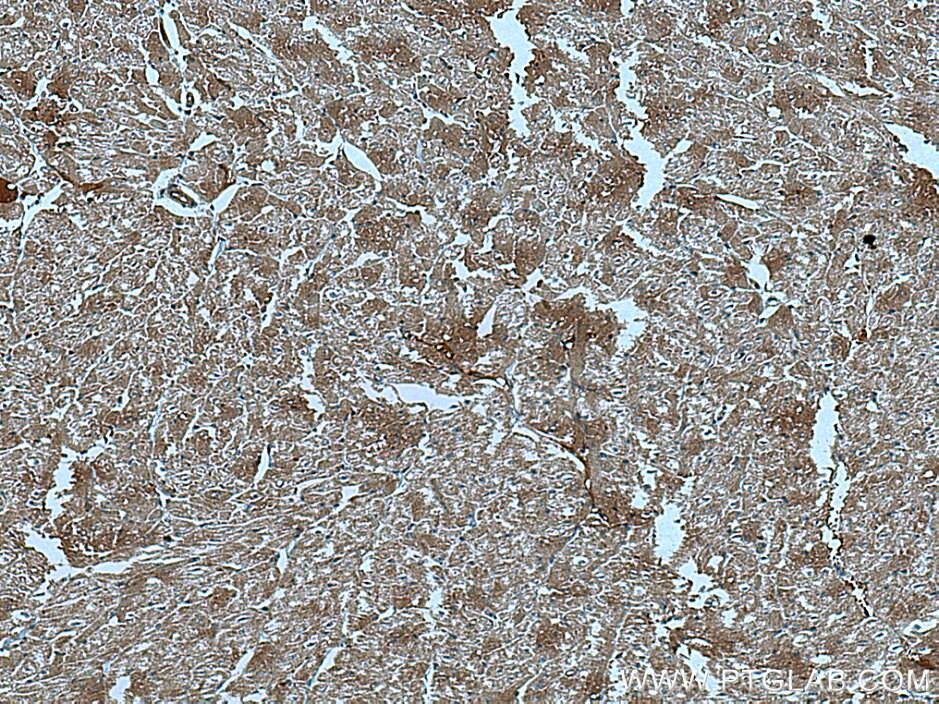
67034-1-PBS targets CUL7 in WB, IHC, Indirect ELISA applications and shows reactivity with Human, Mouse, Rat samples.
| Tested Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host / Isotype | Mouse / IgG2a |
| Class | Monoclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen | CUL7 fusion protein Ag6943 Predict reactive species |
| Full Name | cullin 7 |
| Calculated Molecular Weight | 1698 aa, 191 kDa |
| Observed Molecular Weight | 185 kDa |
| GenBank Accession Number | BC033647 |
| Gene Symbol | CUL7 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 9820 |
| RRID | AB_2882349 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Protein A purification |
| UNIPROT ID | Q14999 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS only , pH 7.3 |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -80°C. |
Background Information
he cullin family proteins are scaffold proteins for the Ring finger type E3 ligases, participating in the proteolysis through the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. Humans express seven cullin proeins: CUL1-3, CUL4A, CUL4B, CUL5, and CUL7. Each cullin protein can form an E3 ligase similar to the prototype Ring-type E3 ligase Skp1-CUL1-F-box complex. The Cullin-RING-finger type E3 ligases are important regulators in early embryonic development, as highlighted by genetic studies demonstrating that knock-out of CUL1, CUL3, or CUL4A in mice results in early embryonic lethality. CUL7 was originally discovered as 185-kDa protein associated with the large T antigen of simian virus 40 (SV40). CUL7-deficient mice exhibit neonatal lethality with reduced size and vascular defects. CUL7 presumably plays a role in the DNA damage response by limiting p53 activity. CUL7 mutations have also been identified in 3-Msyndrome and the Yakuts short stature syndrome, both of which are characterized by pre- and post-natal growth retardation but with relatively normal mental and endocrine functions, suggesting that CUL7 may also be crucial for human placental development.