Tested Applications
| Positive FC detected in | Human peripheral blood lymphocytes |
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Flow Cytometry (FC) | FC : 0.2 ug per 10^6 cells in 100 μl suspension |
| This reagent has been pre-titrated and tested for flow cytometric analysis. The suggested use of this reagent is N/A per 10^6 cells in a 100 µl suspension or N/A per 100 µl of whole blood. | |
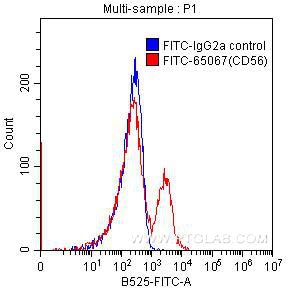
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
Product Information
FITC-65067 targets NCAM1/CD56 in FC applications and shows reactivity with human samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human |
| Host / Isotype | Mouse / IgG2a, kappa |
| Class | Monoclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen |
Acute myelogenous leukemia cell line KG-1 Predict reactive species |
| Full Name | neural cell adhesion molecule 1 |
| GenBank Accession Number | BC014205 |
| Gene Symbol | NCAM1 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 4684 |
| ENSEMBL Gene ID | ENSG00000149294 |
| RRID | AB_2883757 |
| Conjugate | FITC Fluorescent Dye |
| Excitation/Emission Maxima Wavelengths | 498 nm / 526 nm |
| Excitation Laser | Blue laser (488 nm) |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Affinity purification |
| UNIPROT ID | P13591 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS with 0.09% sodium azide, pH 7.3. |
| Storage Conditions | Store at 2-8°C. Avoid exposure to light. Stable for one year after shipment. |
Background Information
Neural cell adhesion molecule 1 (NCAM1, also known as CD56) is a cell adhesion glycoprotein of the immunoglobulin (Ig) superfamily. It is a multifunction protein involved in synaptic plasticity, neurodevelopment, and neurogenesis. NCAM1 is expressed on human neurones, glial cells, skeletal muscle cells, NK cells and a subset of T cells, and the expression is observed in a wide variety human tumors, including myeloma, myeloid leukemia, neuroendocrine tumors, Wilms' tumor, neuroblastoma, and NK/T cell lymphomas.