Published Applications
| WB | See 1 publications below |
Product Information
60350-1-PBS targets CD41 in WB, Indirect ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human |
| Cited Reactivity | rat |
| Host / Isotype | Mouse / IgG1 |
| Class | Monoclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen |
Peptide Predict reactive species |
| Full Name | integrin, alpha 2b (platelet glycoprotein IIb of IIb/IIIa complex, antigen CD41) |
| Calculated Molecular Weight | 113 kDa |
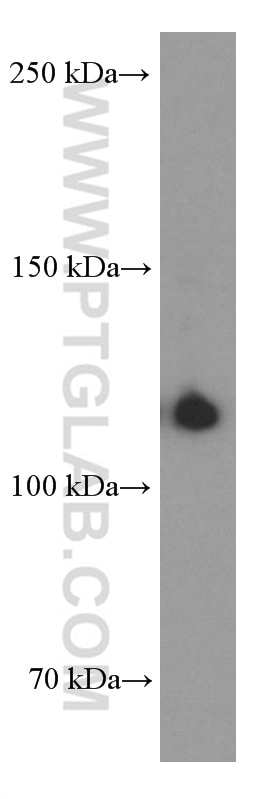
| Observed Molecular Weight | 125 kDa |
| GenBank Accession Number | BC126442 |
| Gene Symbol | CD41 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 3674 |
| RRID | AB_2881459 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Protein G purification |
| UNIPROT ID | P08514 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS only, pH 7.3. |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -80°C. |
Background Information
The integrins are a superfamily of cell adhesion receptors that bind to extracellular matrix ligands, cell-surface ligands, and soluble ligands (PMID: 17543136). They are transmembrane αβ heterodimers and at least 24 distinct integrin heterodimers are formed by the combination of 18 α and eight β known subunits (PMID: 17543136; 20029421). In addition to mediating cell adhesion, integrins also play important roles in modulating signal transduction pathways that control cellular responses including migration, proliferation, differentiation, and apoptosis (PMID: 19118207). Integrin alpha-IIb (ITGA2B, CD41) is expressed on platelets, megakaryocytes and some hematopoietic progenitor cells (PMID: 11934866). This protein undergoes post-translational cleavage to yield disulfide linked light beta (25 kDa) and heavy alpha (125 kDa) chains, which join with integrin beta3 (CD61) to form a receptor for fibronectin, fibrinogen, plasminogen, prothrombin, thrombospondin and vitronectin. CD41/CD61 is crucial for platelet aggregation through binding of soluble fibrinogen.