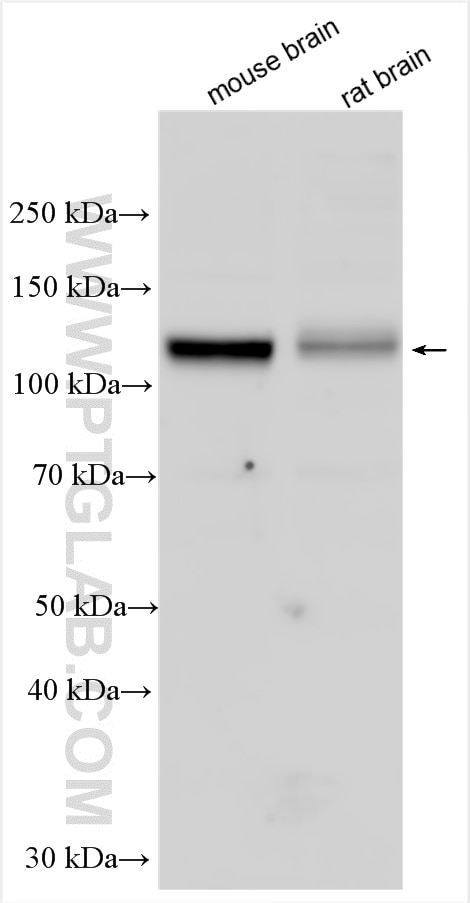
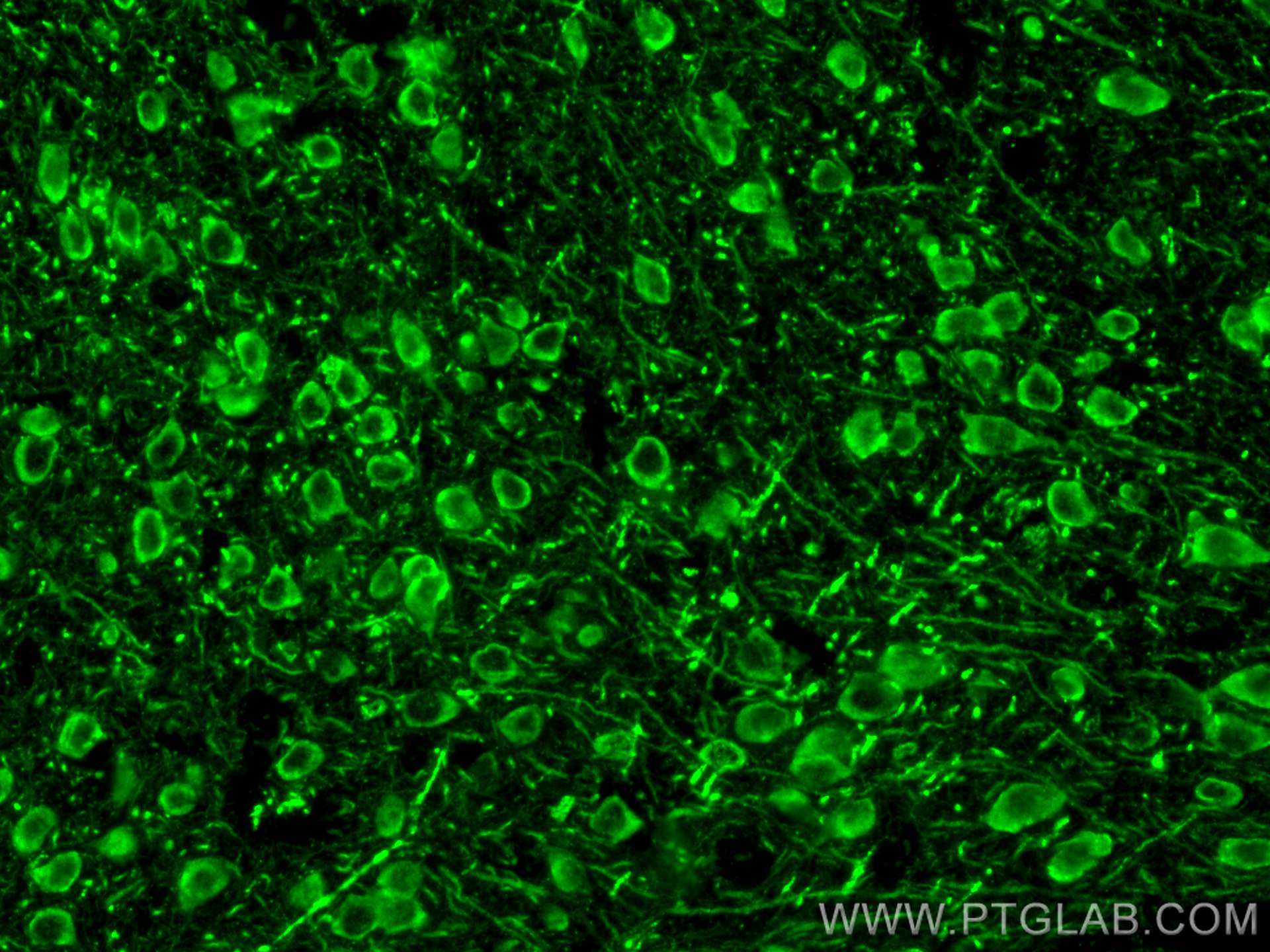
Tested Applications
| Positive WB detected in | mouse brain tissue, rat brain tissue |
| Positive IF-P detected in | mouse brain tissue |
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:500-1:2000 |
| Immunofluorescence (IF)-P | IF-P : 1:50-1:500 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
Product Information
29817-1-AP targets CCDC39 in WB, IF-P, ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human, mouse, rat samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human, mouse, rat |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Polyclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen | CCDC39 fusion protein Ag31067 Predict reactive species |
| Full Name | coiled-coil domain containing 39 |
| Calculated Molecular Weight | 110 kDa |
| Observed Molecular Weight | 110 kDa |
| GenBank Accession Number | NM_181426 |
| Gene Symbol | CCDC39 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 339829 |
| RRID | AB_3086172 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Antigen affinity purification |
| UNIPROT ID | Q9UFE4 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol , pH 7.3 |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -20°C. Stable for one year after shipment. Aliquoting is unnecessary for -20oC storage. 20ul sizes contain 0.1% BSA. |
Background Information
CCDC39 (Coiled-coil domain-containing protein 39) is an axonemal protein whose absence results in failure to correctly assemble DNALI1-containing inner dynein arm complexes, the DRC (dynein regulatory complex) and the radial spokes, thereby causing axonemal disorganization and dyskinetic beating. Alternatively, CCDC39 could participate in the transport of the inner dynein arms and DRC (PMID: 21131972). Its calculated molecular weight and observed molecular weight are both 110kDa.
Protocols
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for CCDC39 antibody 29817-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IF protocol for CCDC39 antibody 29817-1-AP | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |