Tested Applications
| Positive WB detected in | mouse heart tissue, mouse brown adipose tissue, mouse kidney tissue, mouse liver tissue, mouse skeletal muscle tissue, rat heart tissue |
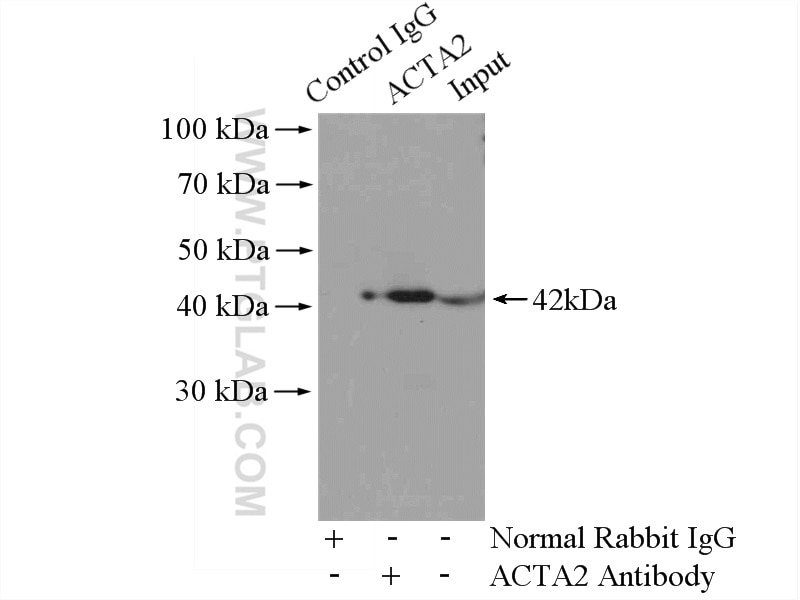
| Positive IP detected in | mouse heart tissue |
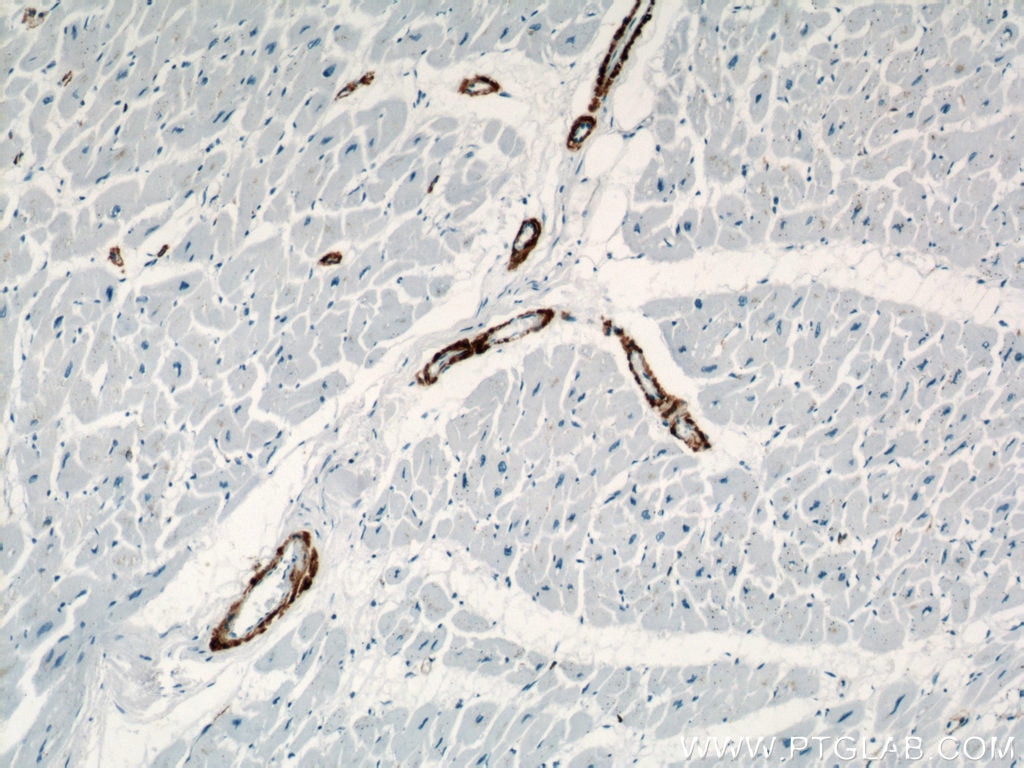
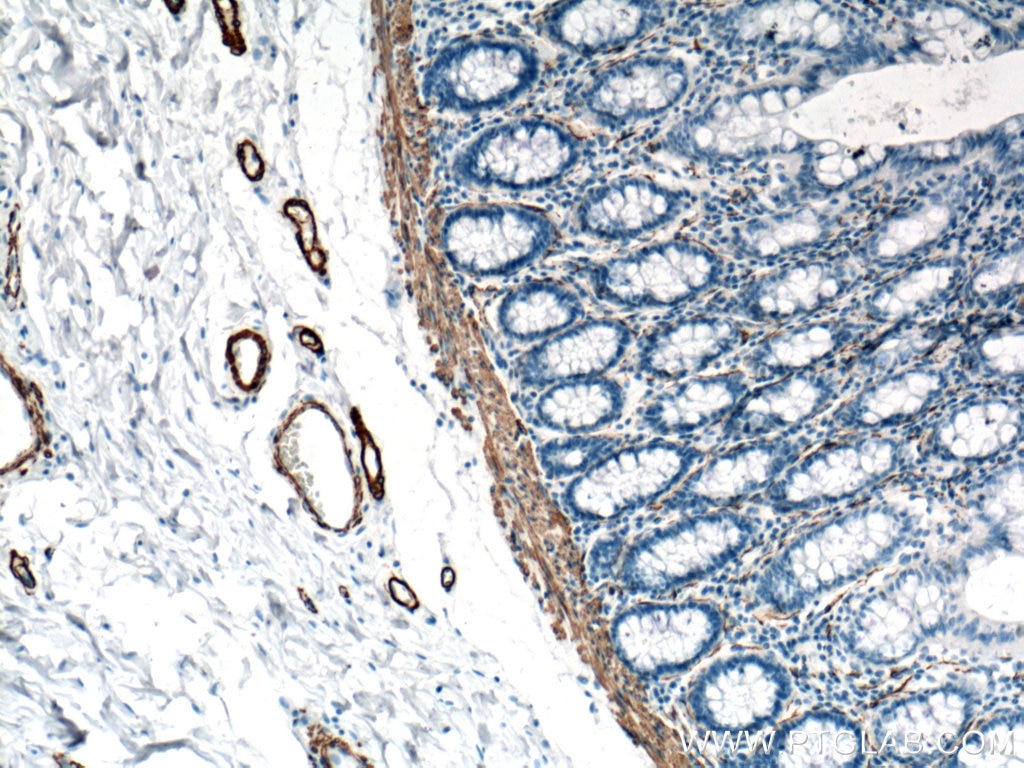
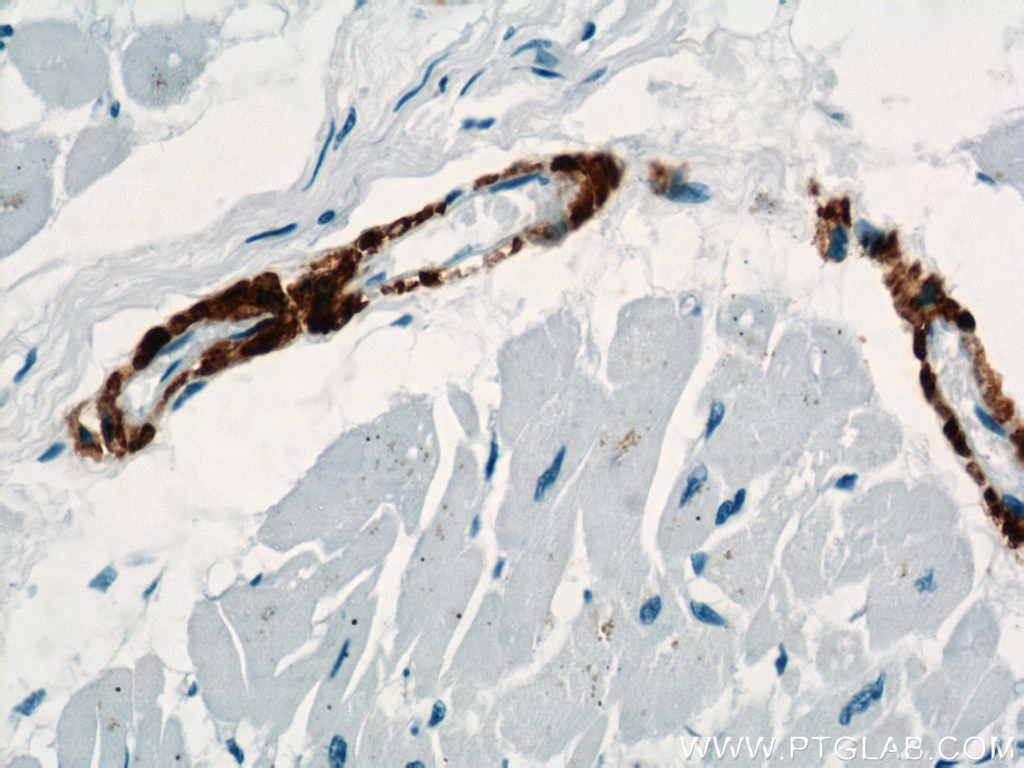
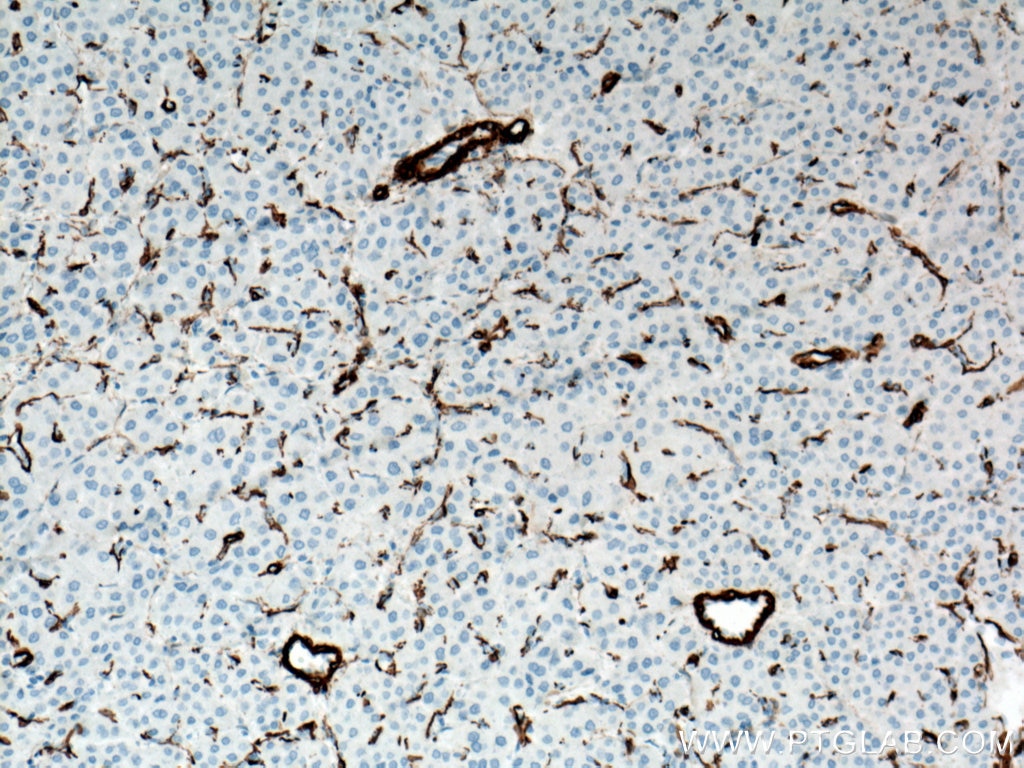
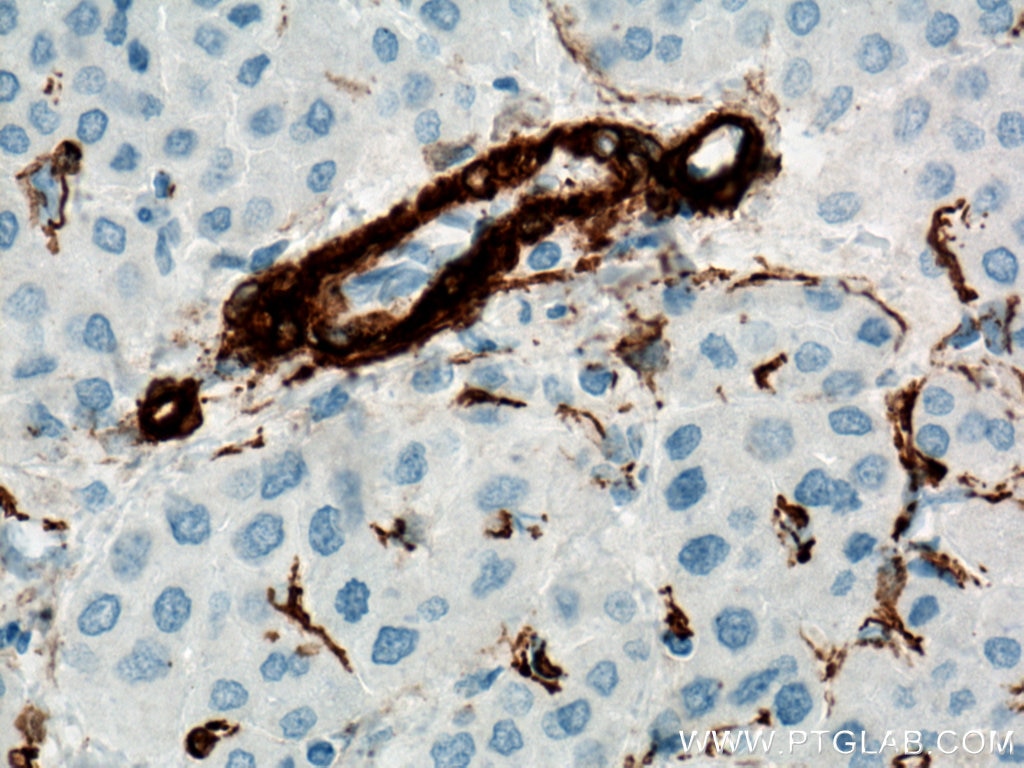
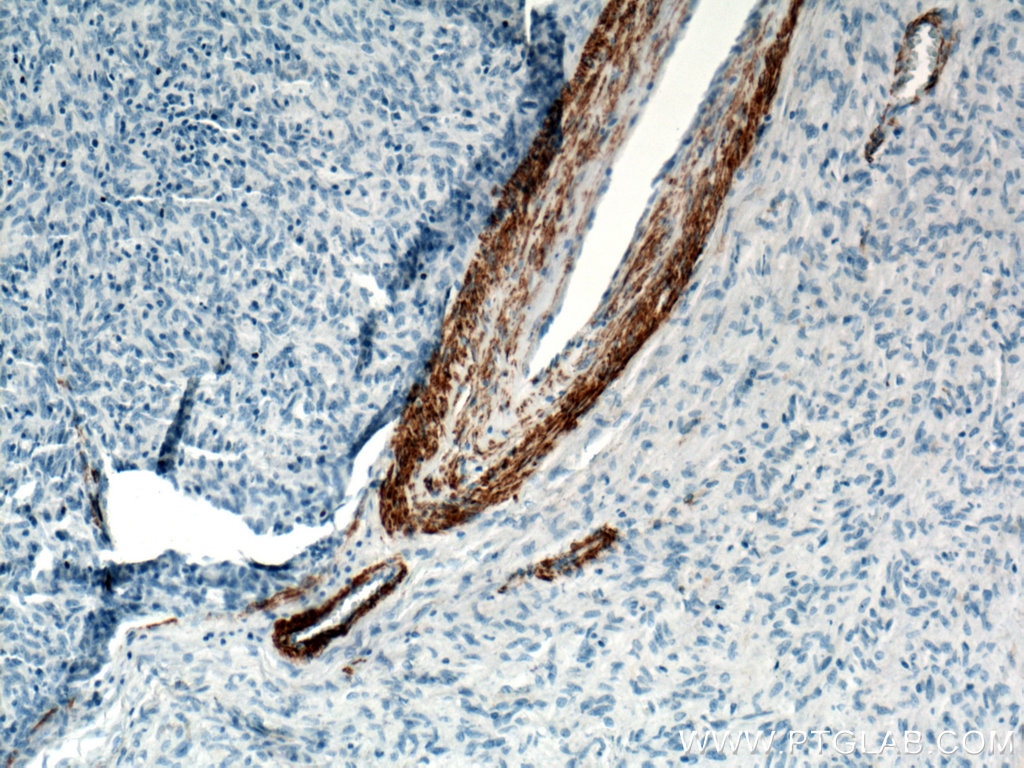
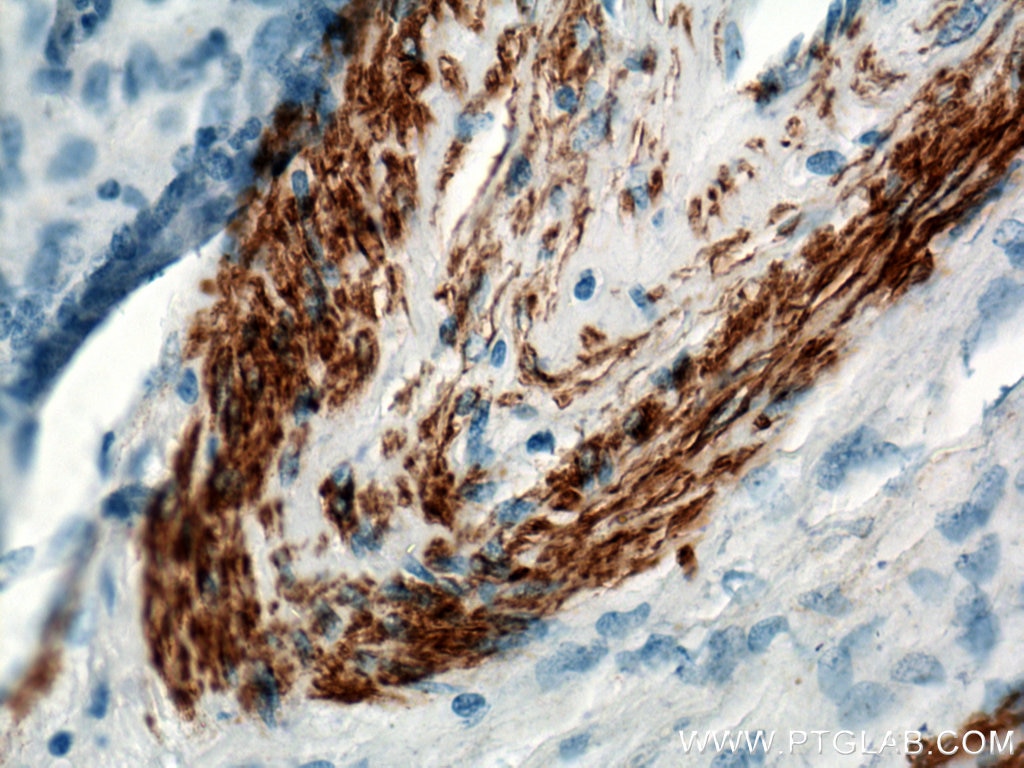
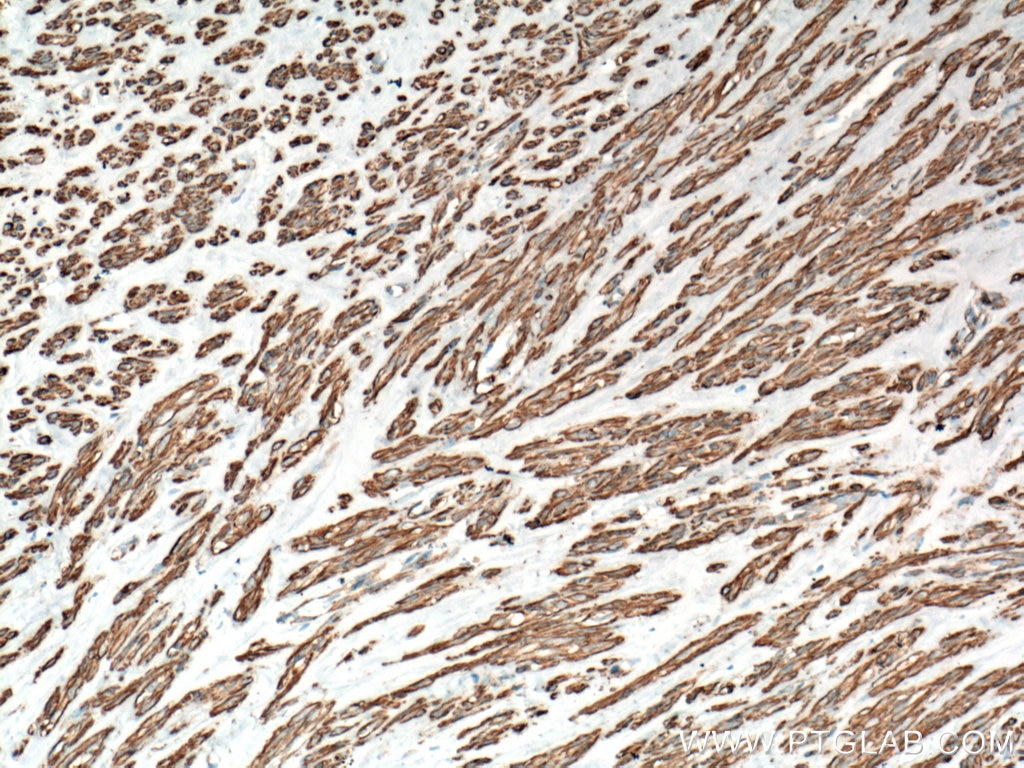
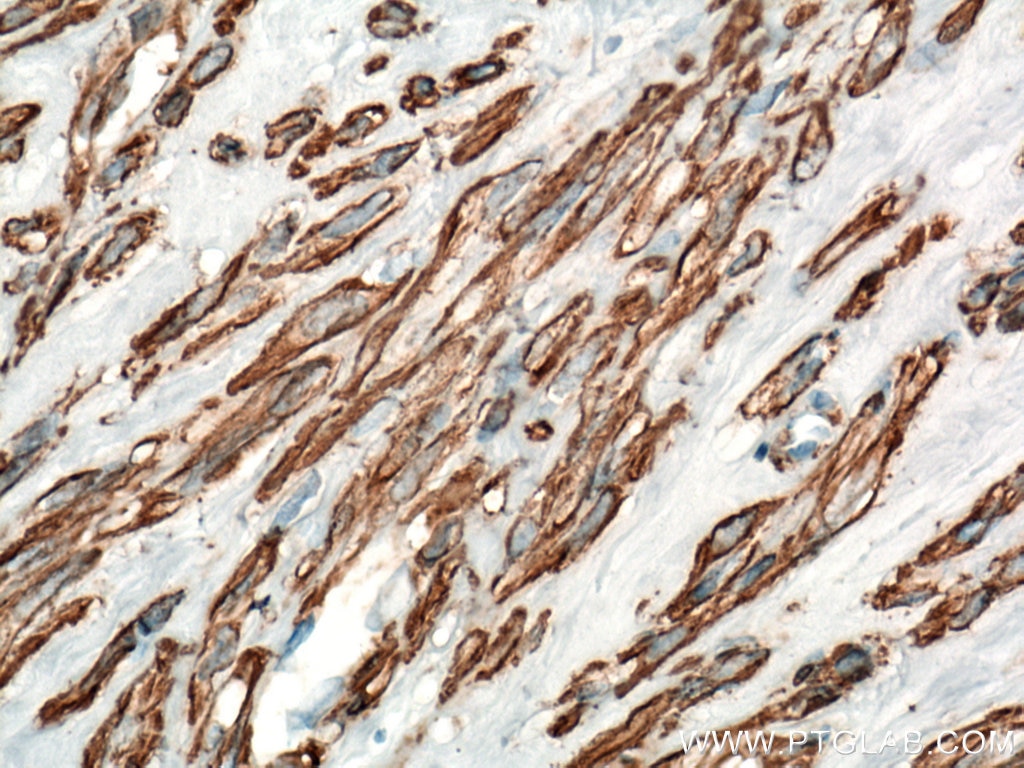
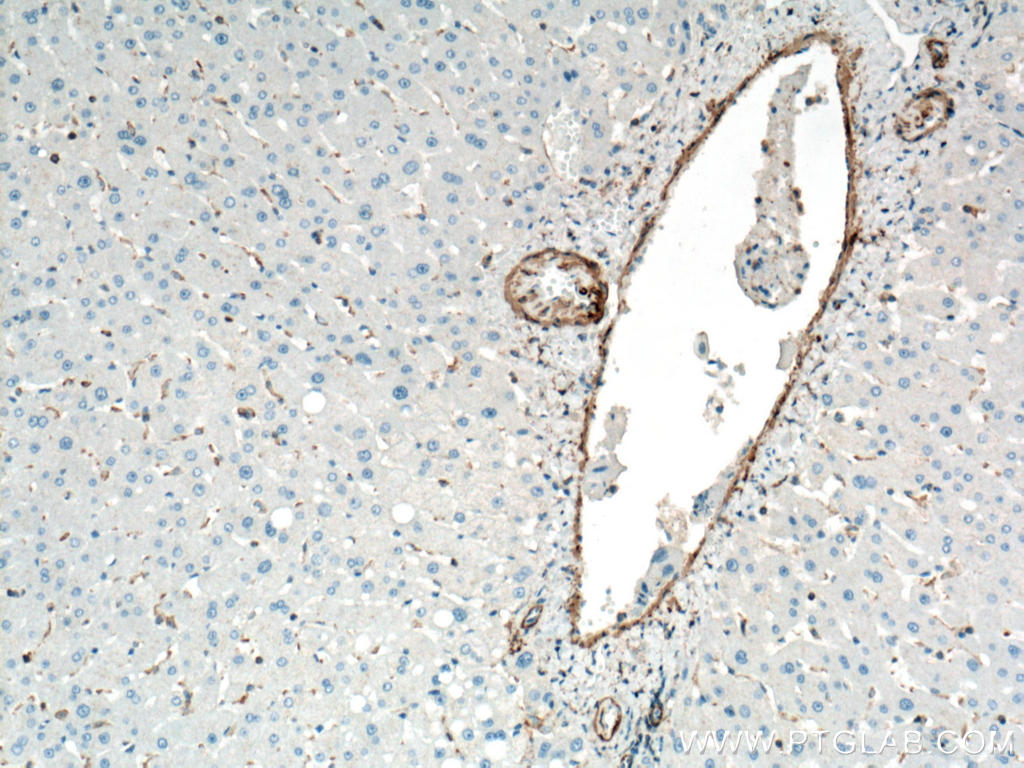
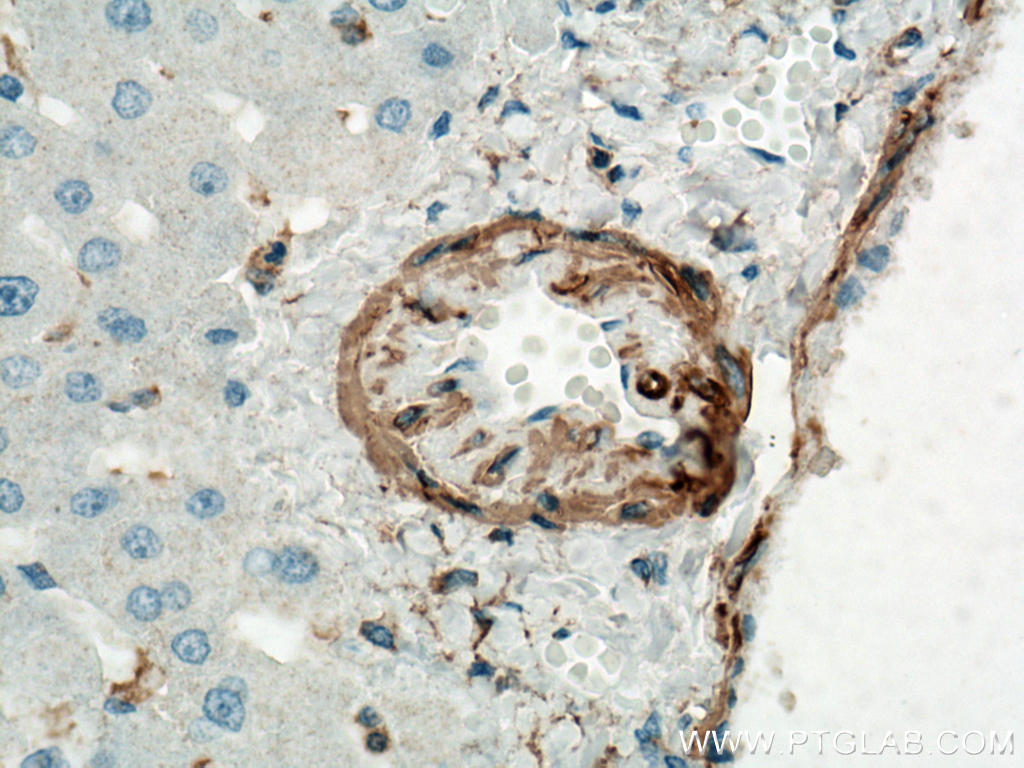
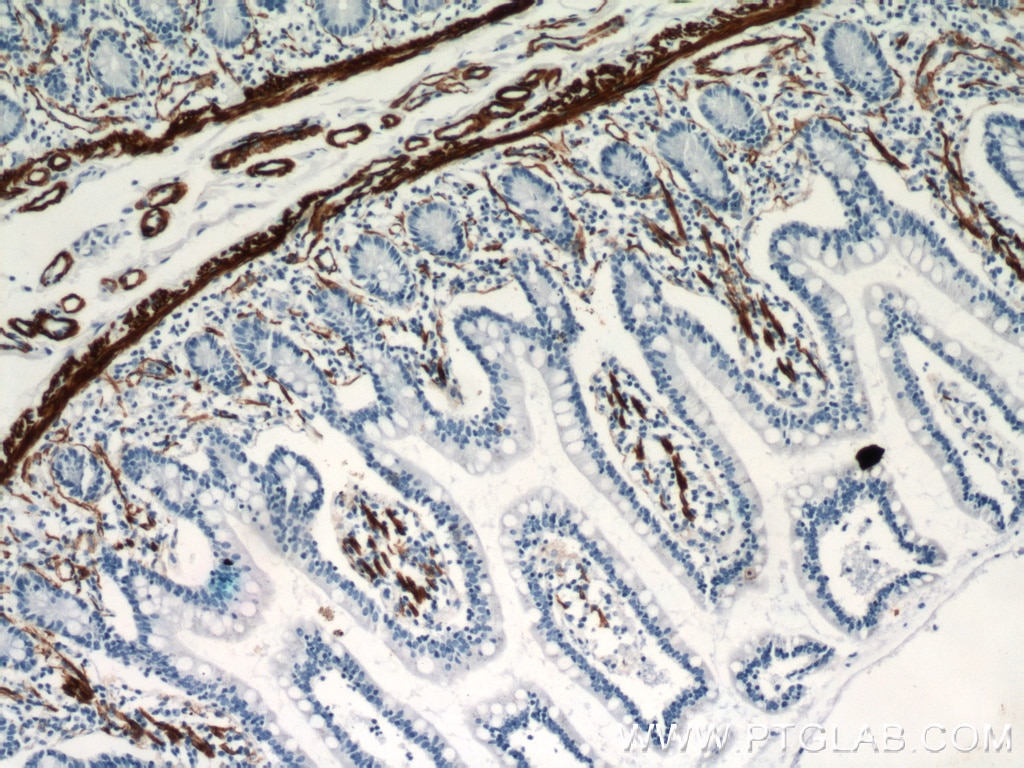
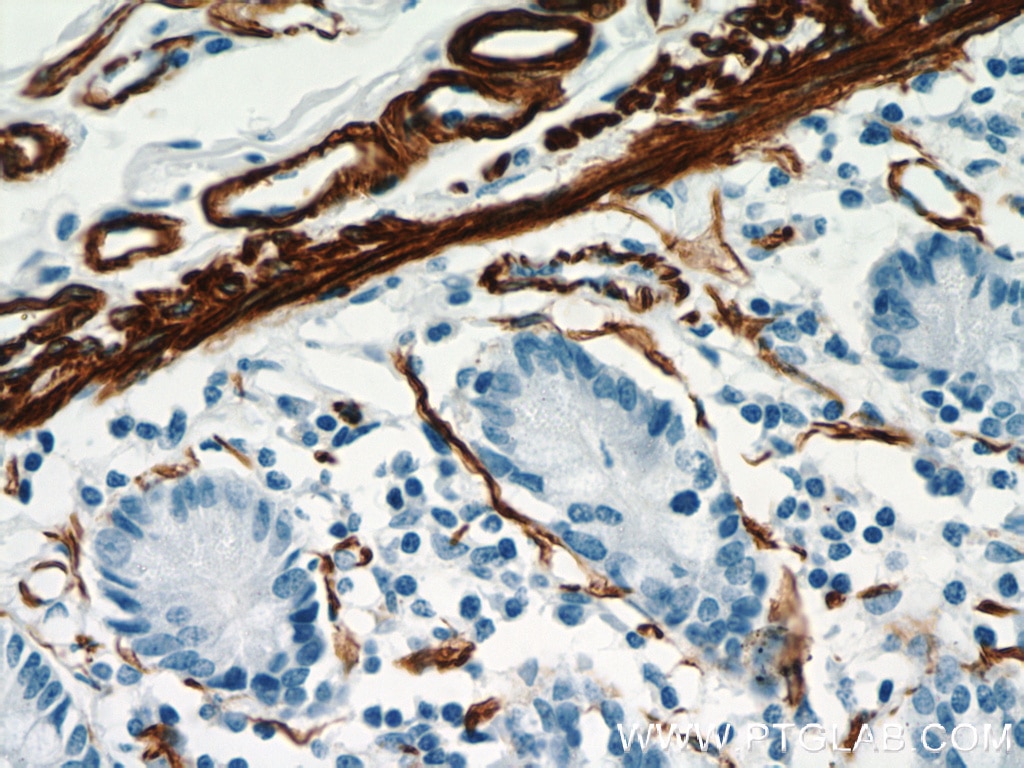
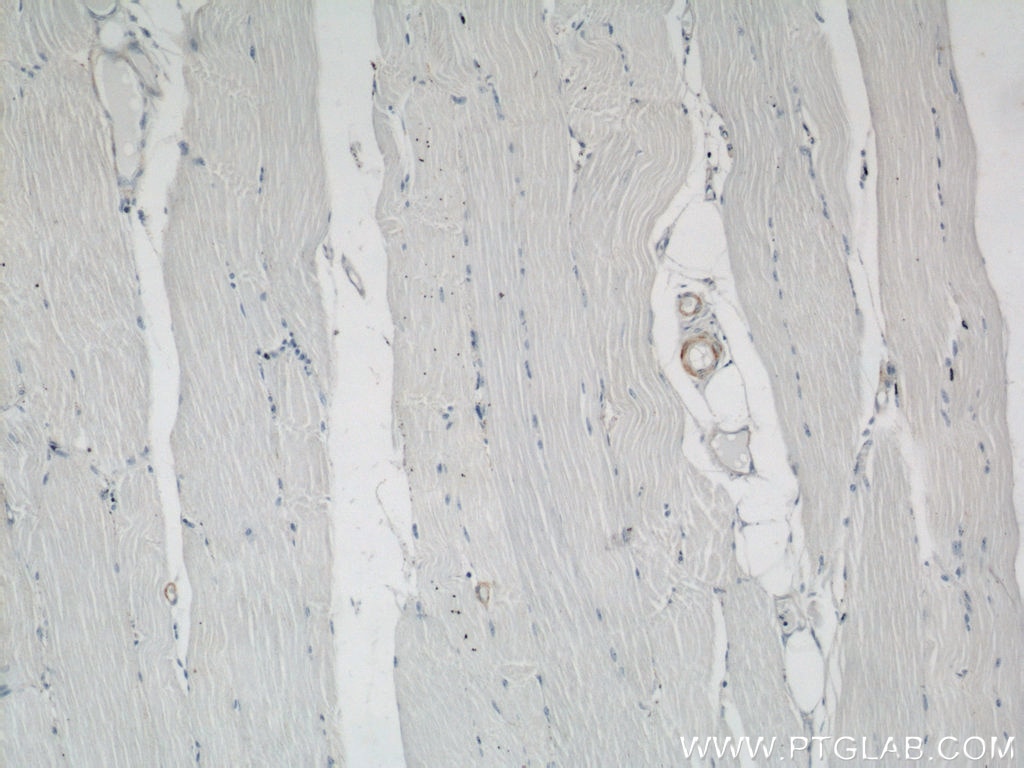
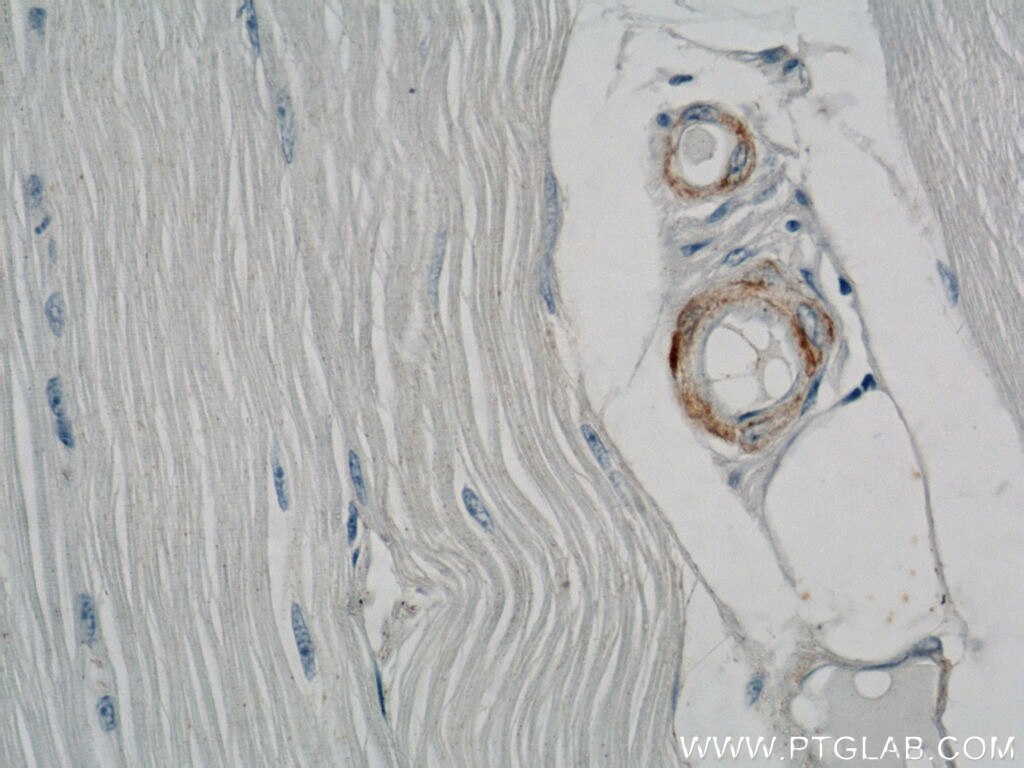
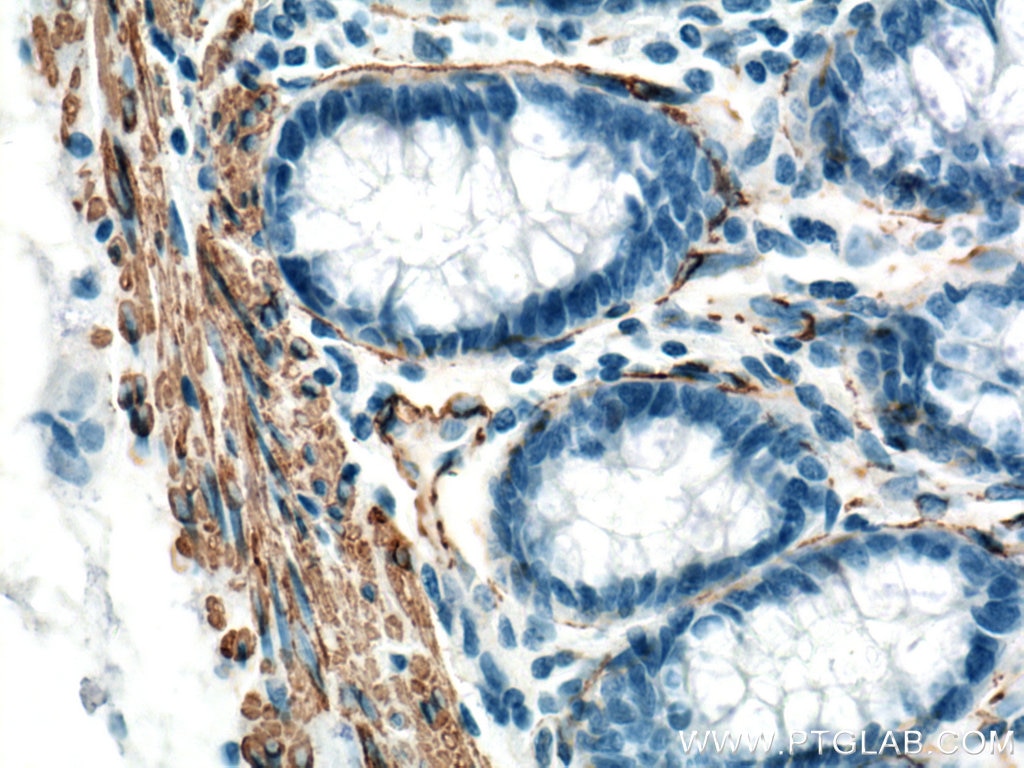
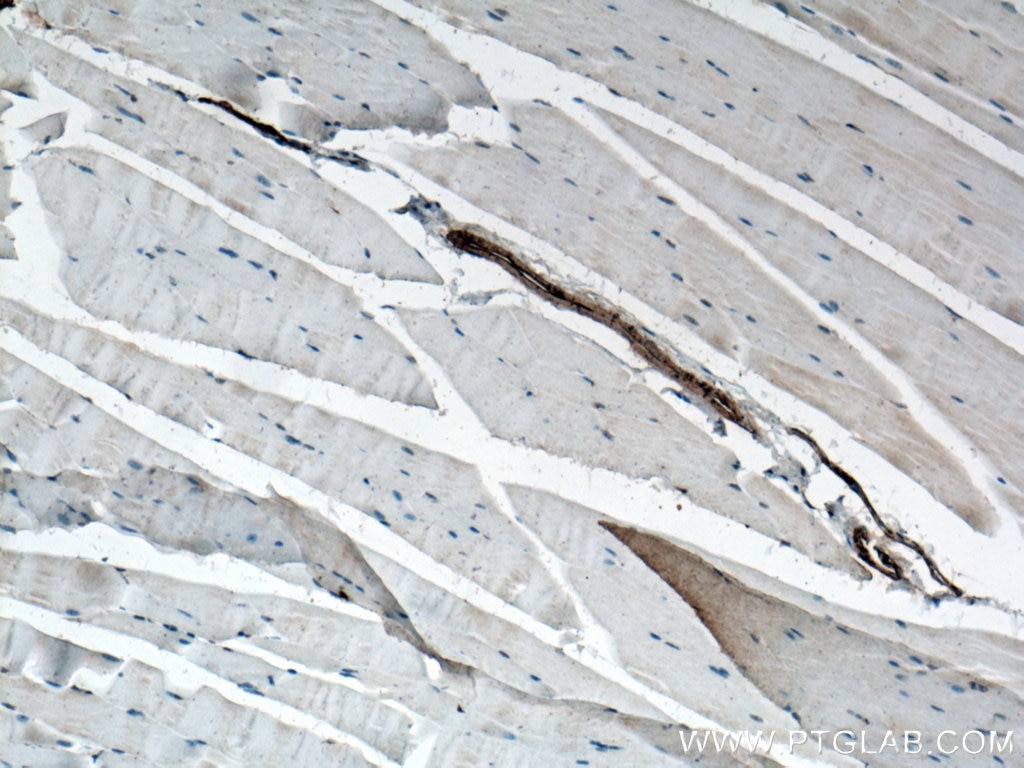
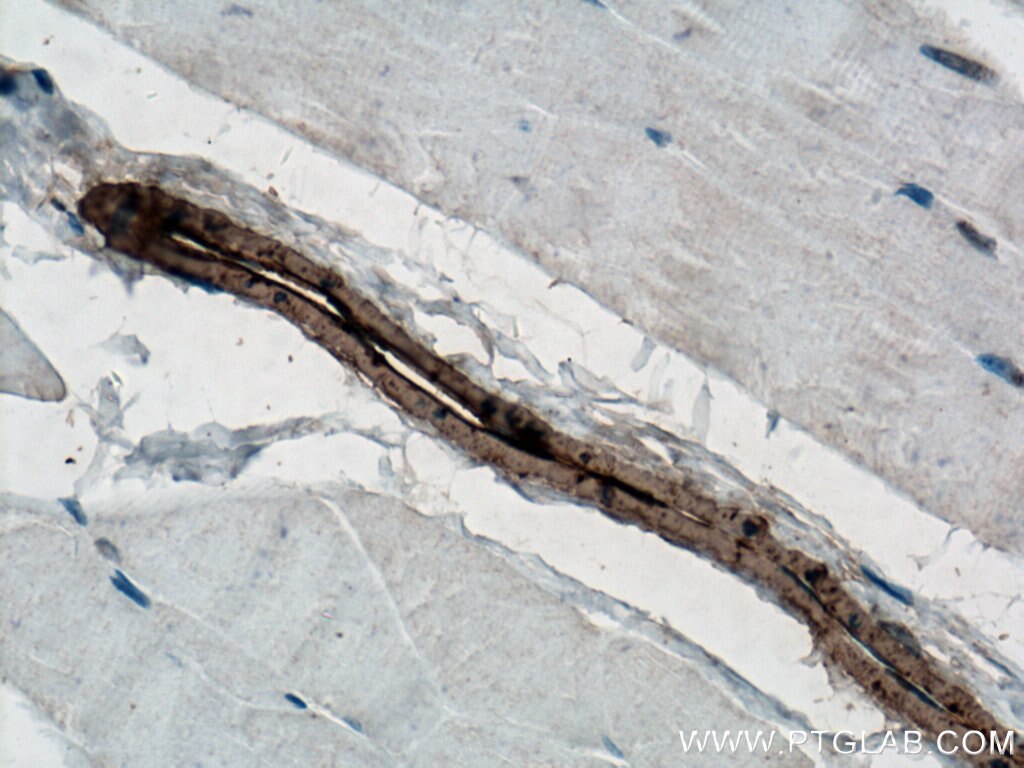
| Positive IHC detected in | human heart tissue, mouse skeletal muscle tissue, human colon tissue, human liver cancer tissue, stromal tumor tissue, human hysteromyoma tissue, human liver tissue, human small intestine tissue, human skeletal muscle tissue Note: suggested antigen retrieval with TE buffer pH 9.0; (*) Alternatively, antigen retrieval may be performed with citrate buffer pH 6.0 |
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:1000-1:4000 |
| Immunoprecipitation (IP) | IP : 0.5-4.0 ug for 1.0-3.0 mg of total protein lysate |
| Immunohistochemistry (IHC) | IHC : 1:200-1:1000 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
Published Applications
| WB | See 22 publications below |
| IHC | See 12 publications below |
| IF | See 8 publications below |
Product Information
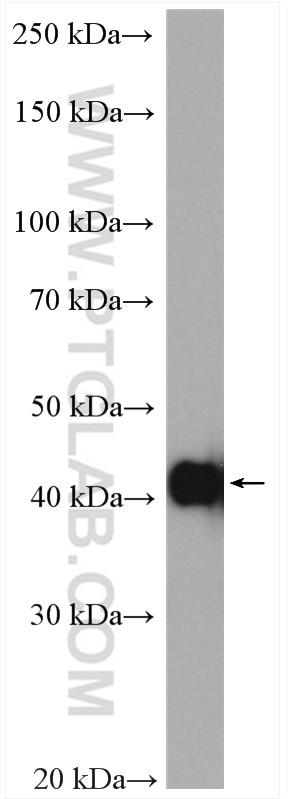
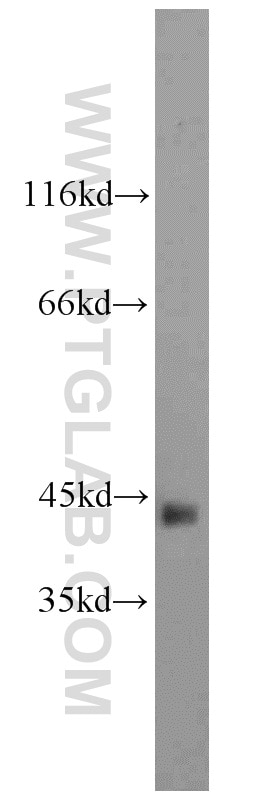
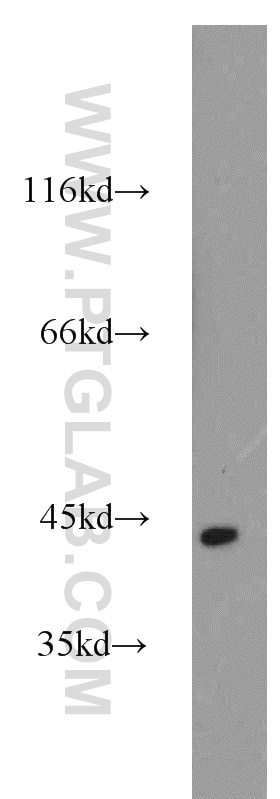
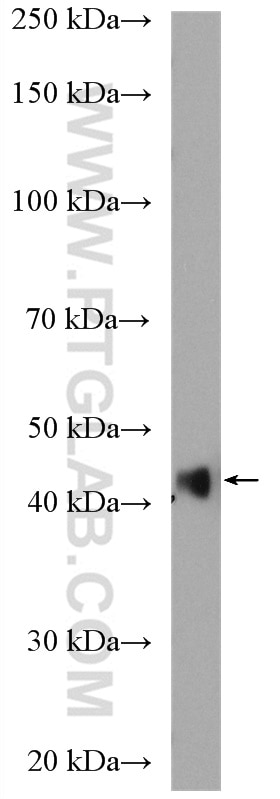
23081-1-AP targets Alpha smooth muscle actin in WB, IHC, IF, IP, ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human, mouse, rat samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human, mouse, rat |
| Cited Reactivity | human, mouse, rat |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Polyclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen | Alpha smooth muscle actin fusion protein Ag19481 Predict reactive species |
| Full Name | actin, alpha 2, smooth muscle, aorta |
| Calculated Molecular Weight | 377 aa, 42 kDa |
| Observed Molecular Weight | 42 kDa |
| GenBank Accession Number | BC017554 |
| Gene Symbol | Alpha smooth muscle actin |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 59 |
| RRID | AB_2815024 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Antigen affinity purification |
| UNIPROT ID | P62736 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol, pH 7.3. |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -20°C. Stable for one year after shipment. Aliquoting is unnecessary for -20oC storage. 20ul sizes contain 0.1% BSA. |
Background Information
ACTA2 (also known as α-smooth muscle actin or α-SMA) belongs to the actin family. Actins are highly conserved proteins that are involved in various types of cell motility and are ubiquitously expressed in all eukaryotic cells. ACTA2 is primarily expressed in vascular smooth muscle and anti-ACTA2 is commonly used to marker smooth muscle cells. This antibody is specific to the ACTA2. It selectively stains the vascular smooth muscle but not cardiac or skeletal muscle.
Protocols
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for Alpha smooth muscle actin antibody 23081-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IHC protocol for Alpha smooth muscle actin antibody 23081-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IP protocol for Alpha smooth muscle actin antibody 23081-1-AP | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |
Publications
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Nat Commun Dental cell type atlas reveals stem and differentiated cell types in mouse and human teeth. | ||
Drug Des Devel Ther Keloid Patient Plasma-Derived Exosomal hsa_circ_0020792 Promotes Normal Skin Fibroblasts Proliferation, Migration, and Fibrogenesis via Modulating miR-193a-5p and Activating TGF-β1/Smad2/3 Signaling | ||
Biofabrication Antibacterial, ROS scavenging and angiogenesis promotingϵ-Polylysine/gelatin based hydrogel containing CTLP to regulate macrophages for pressure ulcer healing | ||
Cardiovasc Res Plasma levels of trimethylamine-N-oxide can be increased with 'healthy' and 'unhealthy' diets and do not correlate with the extent of atherosclerosis but with plaque instability. | ||
Environ Pollut Polystyrene microplastics cause cardiac fibrosis by activating Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway and promoting cardiomyocyte apoptosis in rats. | ||