Tested Applications
| Positive ELISA detected in | 4-Hydroxynonenal |
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Enzyme-linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) | ELISA : 1:5000-1:20000 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
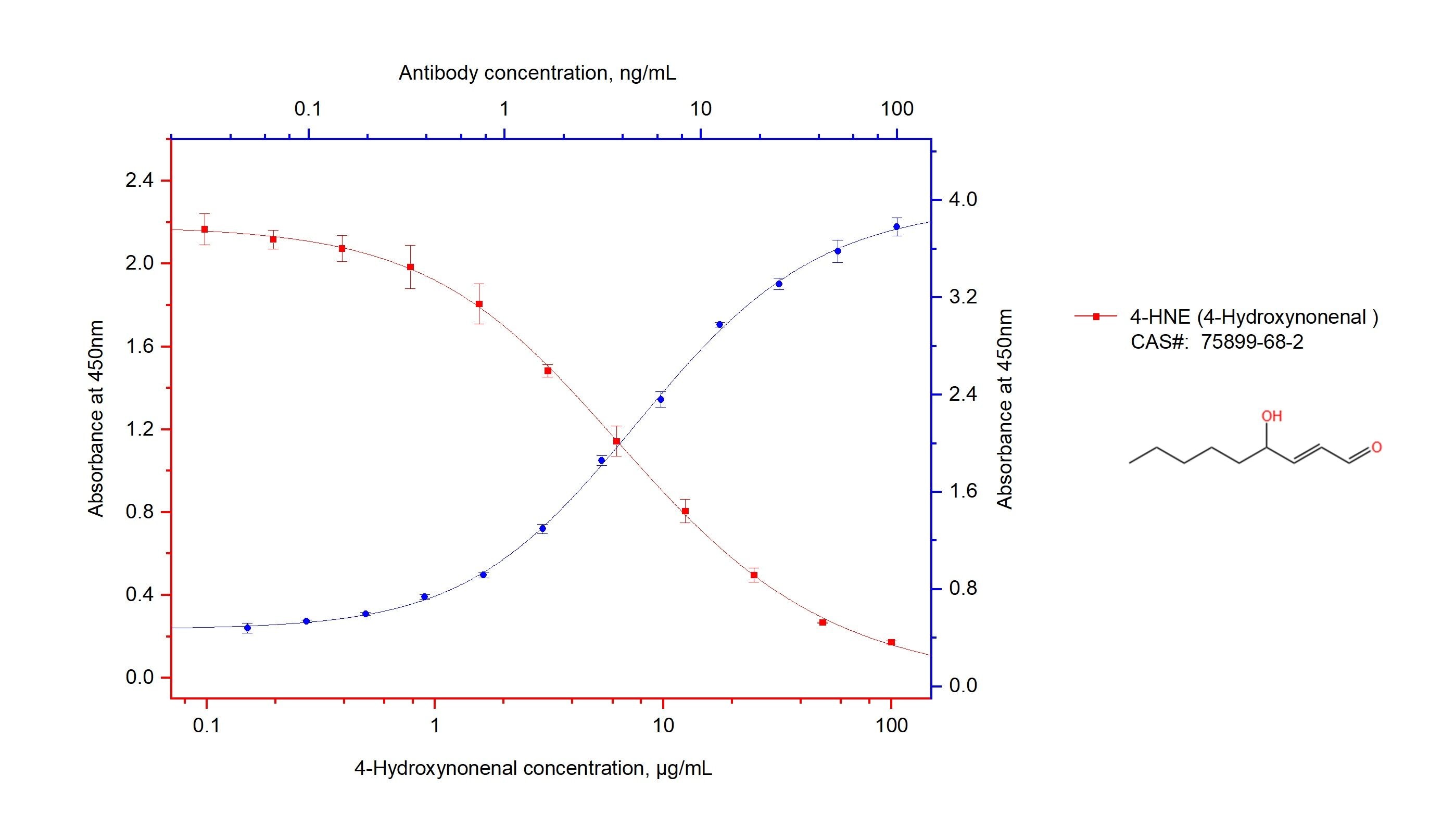
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
Published Applications
| WB | See 1 publications below |
| IHC | See 1 publications below |
| IF | See 1 publications below |
Product Information
68538-1-Ig targets 4-Hydroxynonenal in WB, IHC, IF, ELISA applications and shows reactivity with 4-hydroxynonenal, chemical compound samples.
| Tested Reactivity | 4-hydroxynonenal, chemical compound |
| Cited Reactivity | mouse, rat |
| Host / Isotype | Mouse / IgG2a |
| Class | Monoclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen |
Peptide Predict reactive species |
| Full Name | 4-Hydroxynonenal |
| Gene Symbol | |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | |
| RRID | AB_3085246 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Protein A purification |
| Storage Buffer | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol, pH 7.3. |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -20°C. Stable for one year after shipment. Aliquoting is unnecessary for -20oC storage. 20ul sizes contain 0.1% BSA. |
Background Information
4-Hydroxynonenal is a uremic toxin. Uremic toxins can be subdivided into three major groups based upon their chemical and physical characteristics: 1) small, water-soluble, non-protein-bound compounds, such as urea; 2) small, lipid-soluble and/or protein-bound compounds, such as the phenols and 3) larger so-called middle-molecules, such as beta2-microglobulin. 4-Hydroxynonenal (4-HNE) is a major aldehydic product of ω-6-unsaturated fatty acid peroxidation. It is considered a lipid peroxidation specific marker. 4-HNE has been found to induce differentiation and inhibit proliferation of HL-60 human leukemic cells. It has also been found to induce murine alveolar macrophage cell death. 4-HNE has been shown to inhibit State 3 respiration, causing a transient cytosolic Ca2+ increase. In addition, it irreversibly inhibits Na+-K+-ATPase activity.
Publications
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Free Radic Biol Med Mitochondrial ACSS1-K635 acetylation knock-in mice exhibit altered liver lipid metabolism on a ketogenic diet | ||
Adv Healthc Mater Extracellular Vesicles from Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Combined with PEG Hydrogel Alleviate Maternal Simulated Birth Injury in a Rat Model | ||
Biomaterials Molybdenum nanodots act as antioxidants for photothermal therapy osteoarthritis | ||
J Trace Elem Med Biol Metallothionein 2A alleviates ulcerative colitis by inhibiting ferroptosis in intestinal epithelial cells with Tfrc downregulation |