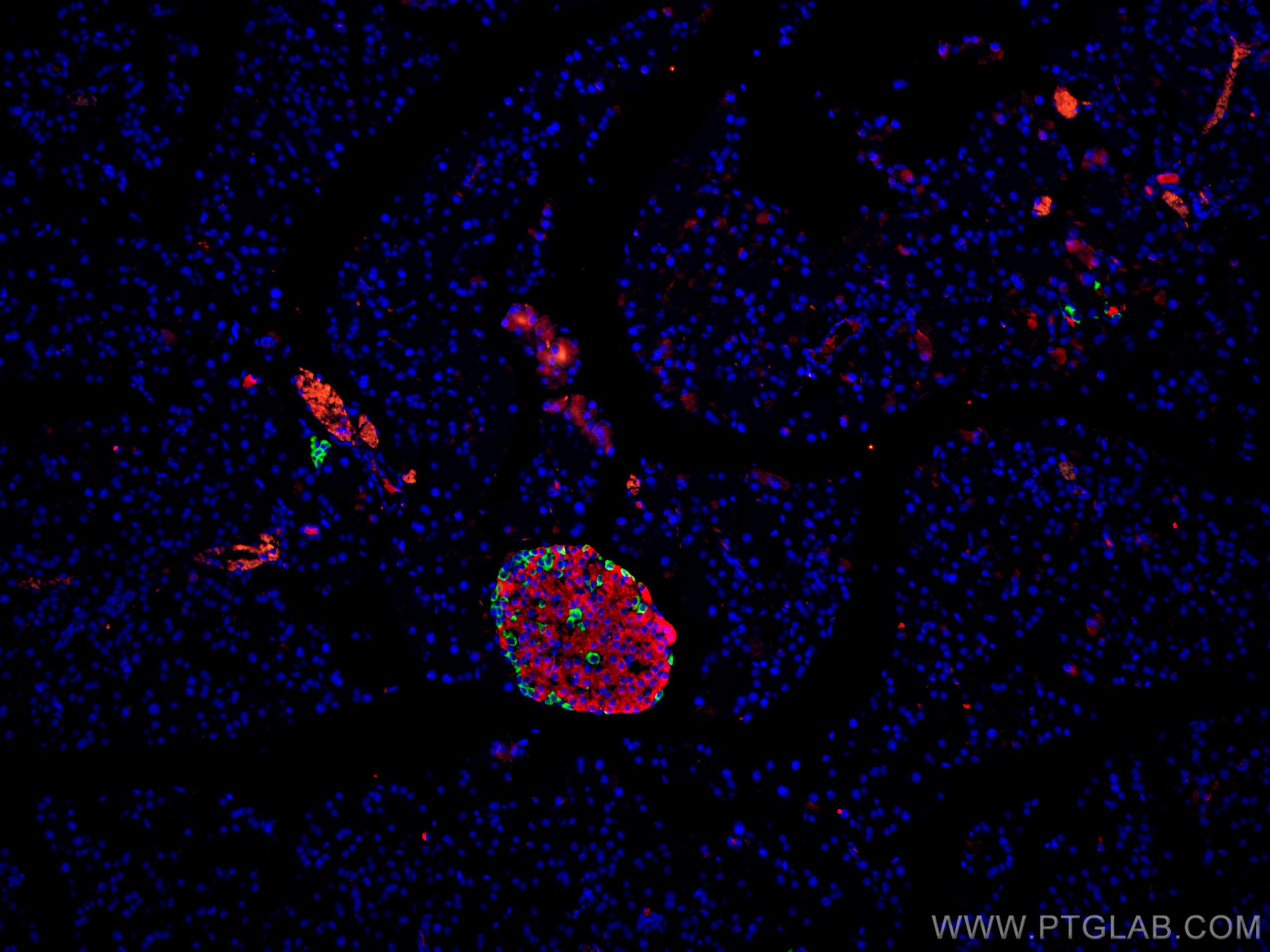
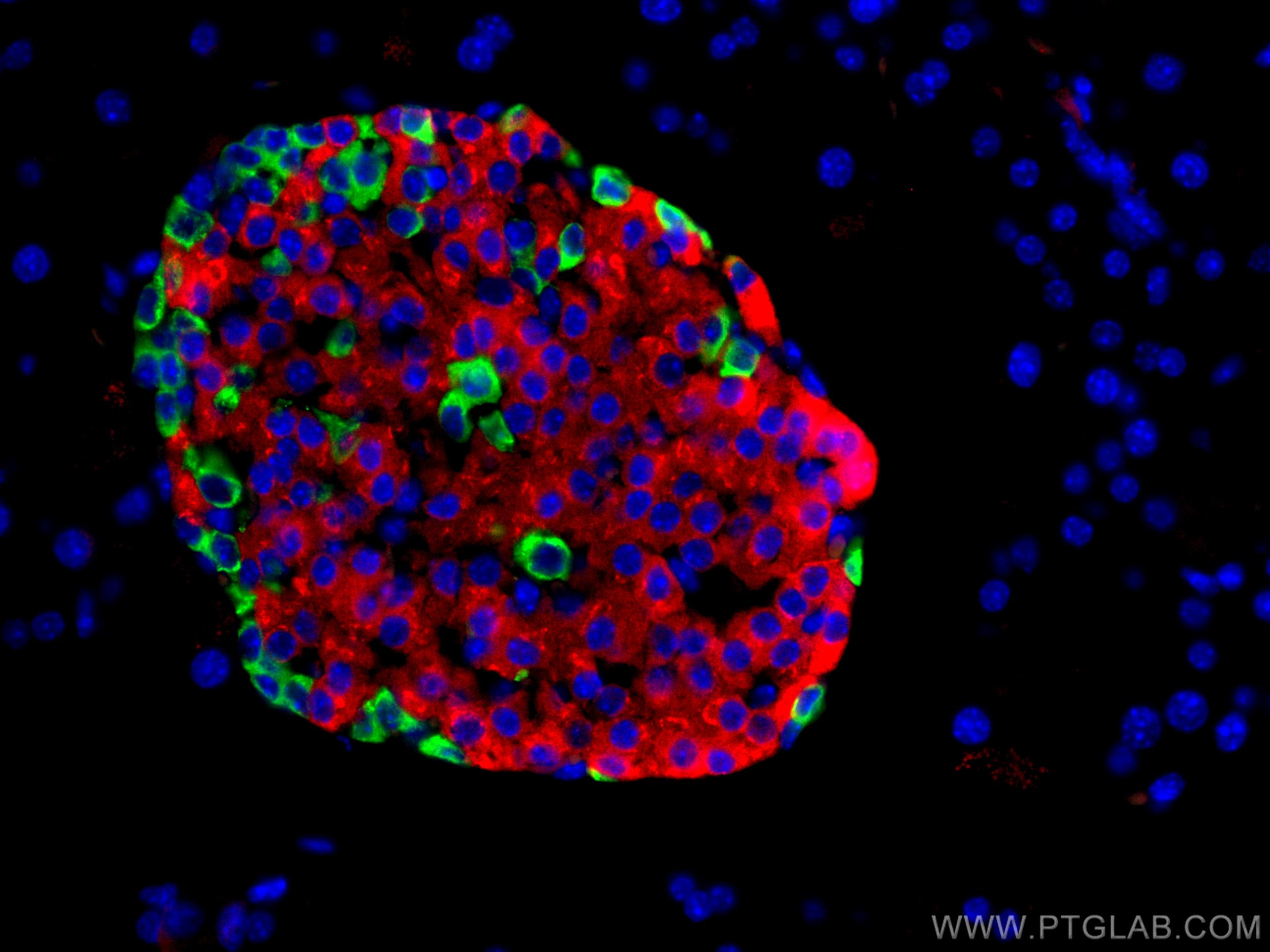
Tested Applications
| Positive IF-P detected in | mouse pancreas tissue |
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Immunofluorescence (IF)-P | IF-P : 1:50-1:500 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
Product Information
CL488-15954 targets Glucagon in IF-P applications and shows reactivity with human, mouse, rat samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human, mouse, rat |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Polyclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen |
CatNo: Ag8677 Product name: Recombinant human Glucagon protein Source: e coli.-derived, PGEX-4T Tag: GST Domain: 1-180 aa of BC005278 Sequence: MKSIYFVAGLFVMLVQGSWQRSLQDTEEKSRSFSASQADPLSDPDQMNEDKRHSQGTFTSDYSKYLDSRRAQDFVQWLMNTKRNRNNIAKRHDEFERHAEGTFTSDVSSYLEGQAAKEFIAWLVKGRGRRDFPEEVAIVEELGRRHADGSFSDEMNTILDNLAARDFINWLIQTKITDRK Predict reactive species |
| Full Name | glucagon |
| Calculated Molecular Weight | 180 aa, 21 kDa |
| GenBank Accession Number | BC005278 |
| Gene Symbol | Glucagon |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 2641 |
| RRID | AB_2919126 |
| Conjugate | CoraLite® Plus 488 Fluorescent Dye |
| Excitation/Emission Maxima Wavelengths | 493 nm / 522 nm |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Antigen affinity purification |
| UNIPROT ID | P01275 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS with 50% glycerol, 0.05% Proclin300, 0.5% BSA, pH 7.3. |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -20°C. Avoid exposure to light. Stable for one year after shipment. Aliquoting is unnecessary for -20oC storage. |
Background Information
Background
Glucagon is a protein cleaved from a precursor protein encoded by the GCG gene. The distinct peptides formed from this precursor include Glucagon, Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 (GLP-1), Glucagon-Like Peptide 2 (GLP-2), and oxyntomodulin. Glucagon is essential in maintaining blood glucose homeostasis and therefore has a key role in Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes.
What is the molecular weight of Glucagon?
21 kDa. Glucagon is composed of 180 amino acids and is a ligand for a specific G-protein coupled receptor (GPCR).
Where is it expressed?
Glucagon is a hormone secreted by the pancreas, in the α cells of the islets of Langerhans (PMID: 18880761). GLP-1, GLP-2, and oxyntomodulin are secreted by gut endocrine cells of the GI tract and also by selected neurons in the brain. These secreted proteins are transported to the target organ in plasma.
What is the function of glucagon?
The regulation of blood glucose levels is controlled by a balance of the hormones INS and glucagon in a negative feedback loop. A drop in blood glucose, or hypoglycemia, stimulates the release of glucagon. This initiates a cascade of signals, ultimately causing the conversion of stored glycogen into free glucose in a process called glycogenolysis, which takes place in liver and muscle cells. Glucagon can also stimulate gluconeogenesis in the liver, the process of forming glucose from non-carbohydrate sources such as amino acids (PMID: 13477815).
What diseases are associated with glucagon?
Glucagon is key in homeostasis of blood glucose and maintaining the balance between hyperglycaemia and hypoglycemia. It is therefore important in the study of Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes mellitus, where dysfunction of the pancreatic cells leads to a deregulation of blood glucose levels (PMID: 19326096). In both forms of the disease, glucagon secretion is impaired, from too much being secreted during hyperglycaemia, to too little being released to normalize hypoglycemia (PMID: 18197838).
Protocols
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| IF protocol for CL Plus 488 Glucagon antibody CL488-15954 | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |