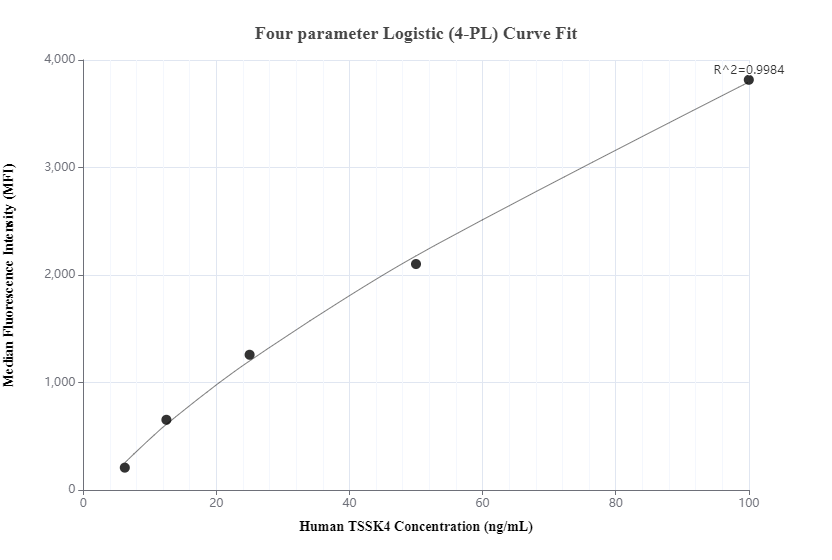
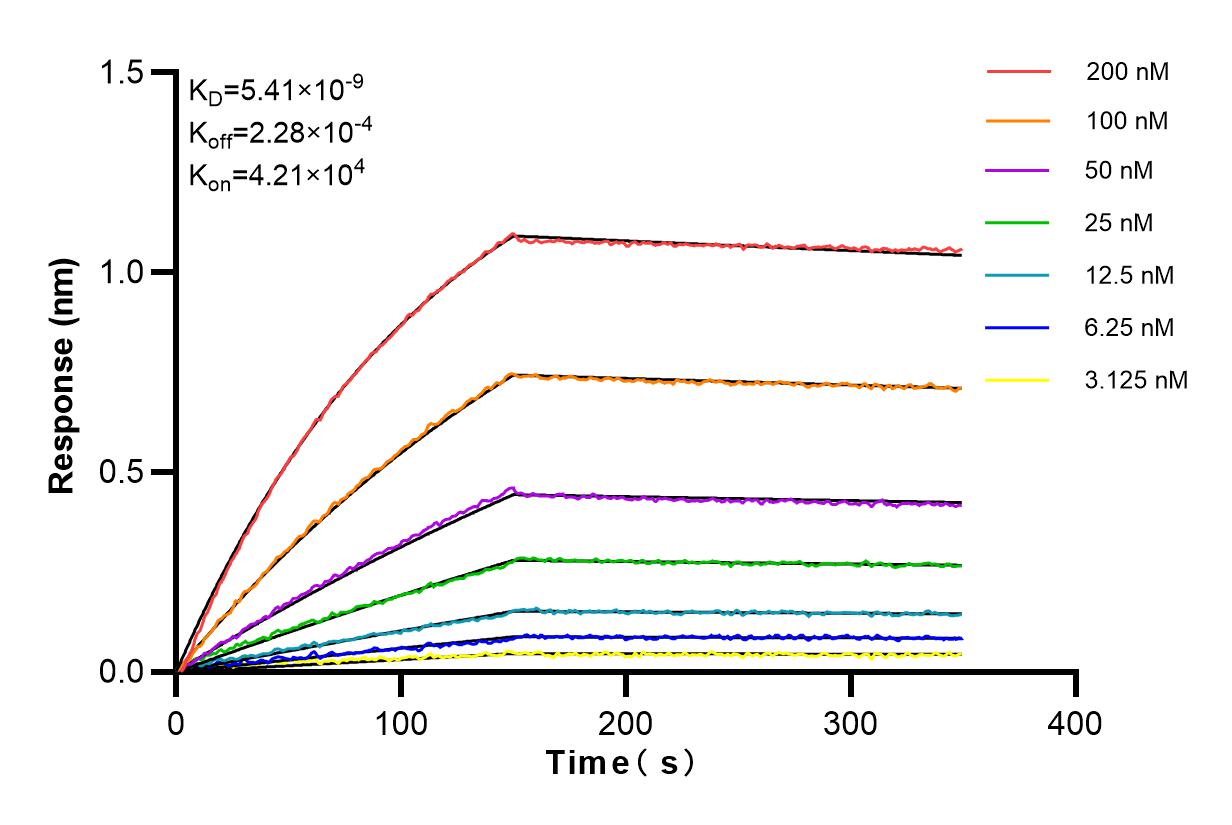
Product Information
83401-4-PBS targets TSSK4 as part of a matched antibody pair:
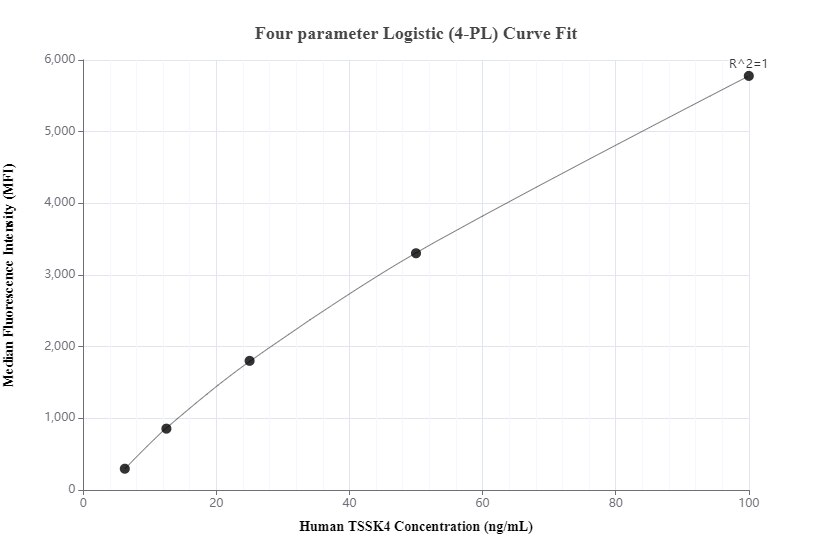
MP00436-2: 83401-1-PBS capture and 83401-4-PBS detection (validated in Cytometric bead array)
MP00436-3: 83401-2-PBS capture and 83401-4-PBS detection (validated in Cytometric bead array)
Unconjugated rabbit recombinant monoclonal antibody in PBS only (BSA and azide free) storage buffer at a concentration of 1 mg/mL, ready for conjugation. Created using Proteintech’s proprietary in-house recombinant technology. Recombinant production enables unrivalled batch-to-batch consistency, easy scale-up, and future security of supply.
This conjugation ready format makes antibodies ideal for use in many applications including: ELISAs, multiplex assays requiring matched pairs, mass cytometry, and multiplex imaging applications.Antibody use should be optimized by the end user for each application and assay.
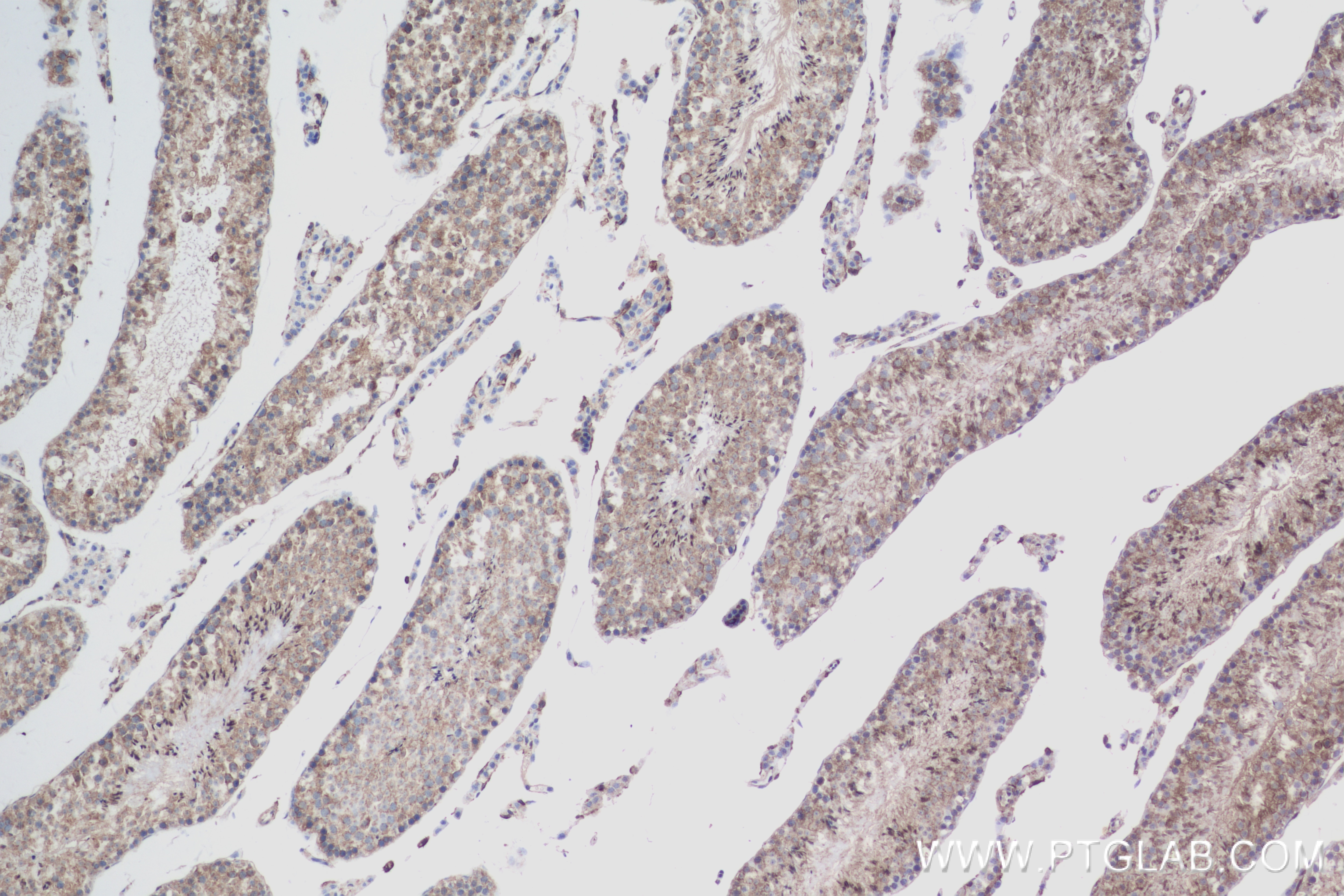
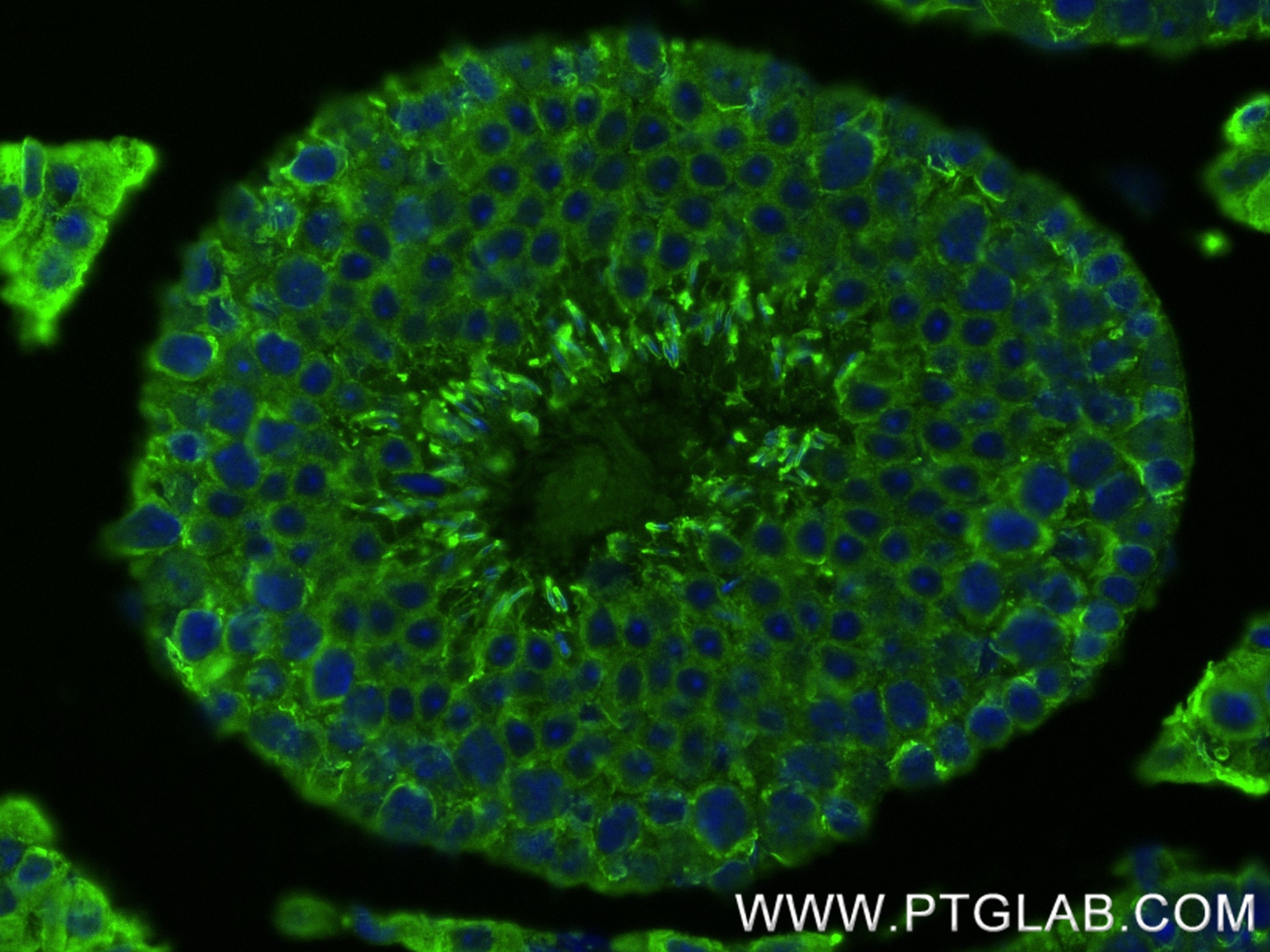
| Tested Reactivity | human, mouse, rat |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Recombinant |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen | TSSK4 fusion protein Ag16205 Predict reactive species |
| Full Name | testis-specific serine kinase 4 |
| Calculated Molecular Weight | 338 aa, 37 kDa |
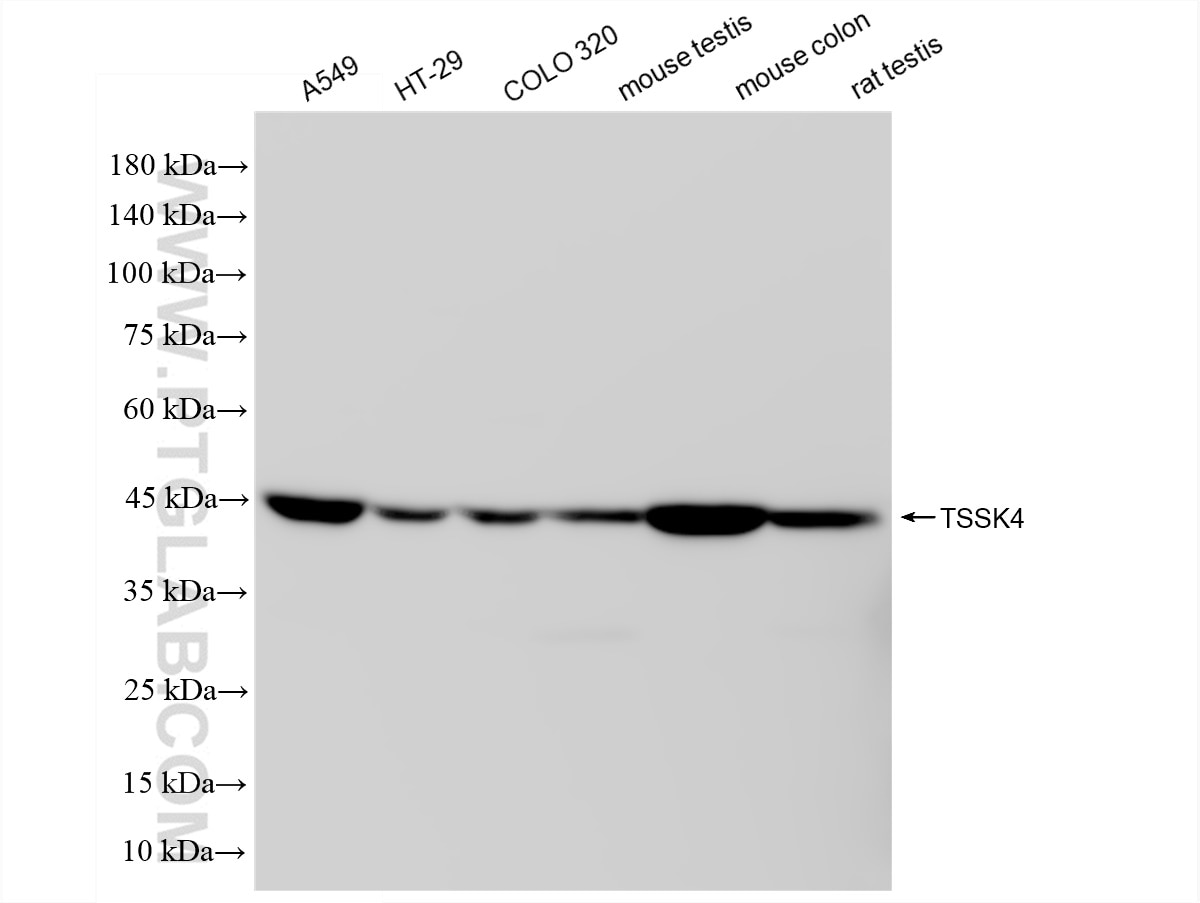
| Observed Molecular Weight | 38-45 kDa |
| GenBank Accession Number | BC111088 |
| Gene Symbol | TSSK4 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 283629 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Protein A purification |
| UNIPROT ID | Q6SA08 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS only , pH 7.3 |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -80°C. |
Background Information
TSSK4 (Testis-specific serine/threonine-protein kinase 4), testis-specific serine/threonine protein kinase 4, is a member of the testis-specific serine/threonine protein kinase family. It has autophosphorylation activity and self-binding properties; it can interact with and phosphorylate other proteins, e.g., it can bind to and phosphorylate Odf2. It's reported that TSSK4 plays an important role in spermatogenesis, TSSK4 knockout male mice develop reduced sperm motility and reduced fertility. In addition, TSSK4 regulates lung fibrosis by promoting the loss of alveolar epithelial type II cells through the HSP90-AKT signaling pathway.