Tested Applications
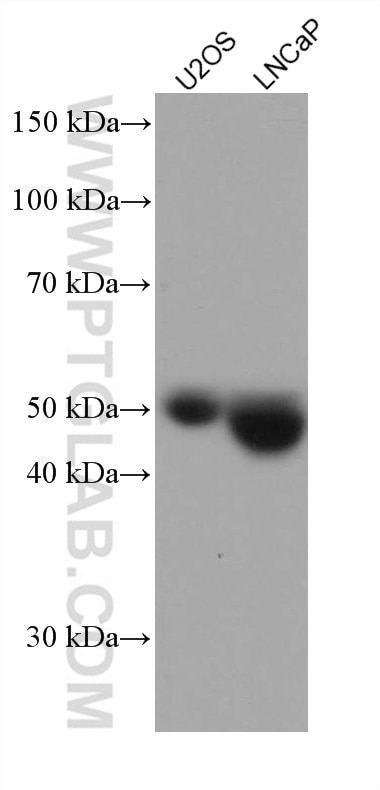
| Positive WB detected in | U2OS cells, LNCaP cells |
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:2000-1:10000 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
Product Information
67684-1-Ig targets NAGA in WB, ELISA applications and shows reactivity with Human samples.
| Tested Reactivity | Human |
| Host / Isotype | Mouse / IgG2b |
| Class | Monoclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen | NAGA fusion protein Ag7225 Predict reactive species |
| Full Name | N-acetylgalactosaminidase, alpha- |
| Calculated Molecular Weight | 47 kDa |
| Observed Molecular Weight | 50 kDa |
| GenBank Accession Number | BC000095 |
| Gene Symbol | NAGA |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 4668 |
| RRID | AB_2882877 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Protein A purification |
| UNIPROT ID | P17050 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol , pH 7.3 |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -20°C. Aliquoting is unnecessary for -20oC storage. 20ul sizes contain 0.1% BSA. |
Background Information
NAGA belongs to the glycosyl hydrolase 27 family. It removes terminal alpha-N-acetylgalactosamine residues from glycolipids and glycopeptides. It is required for the breakdown of glycolipids. Biosynthetic studies performed with cultured fibroblasts indicated that the human enzyme was synthesized as a 65 kDa glycosylated precursor which was processed to a mature 48-kDa lysosomal form; both the precursor and mature forms had high mannose type oligosaccharide chains, but only the precursor's mannose residues were phosphorylated. 90-117 kDa is a homodimer of NAGA.
Protocols
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for NAGA antibody 67684-1-Ig | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |