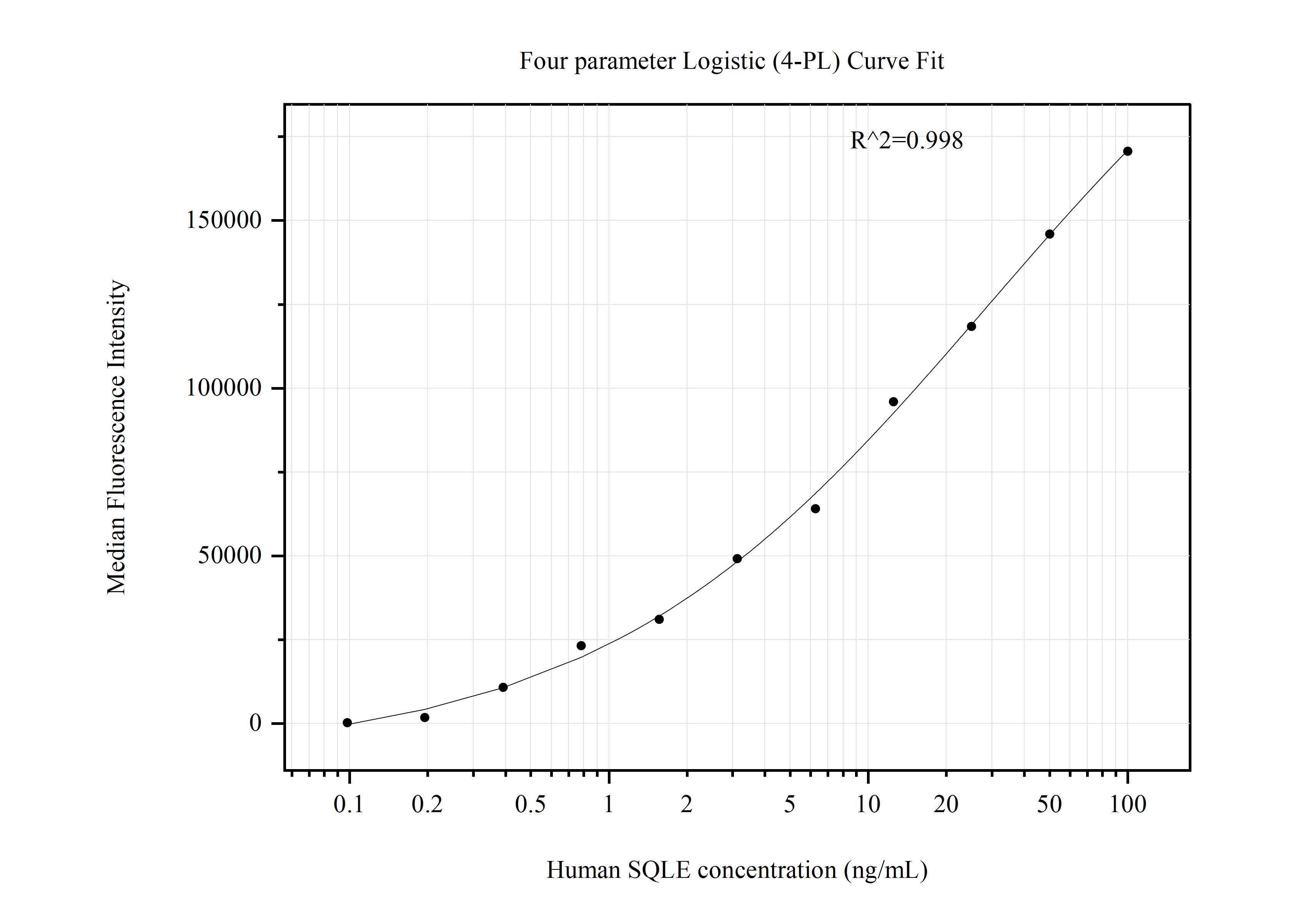
Product Information
67206-1-PBS targets SQLE as part of a matched antibody pair:
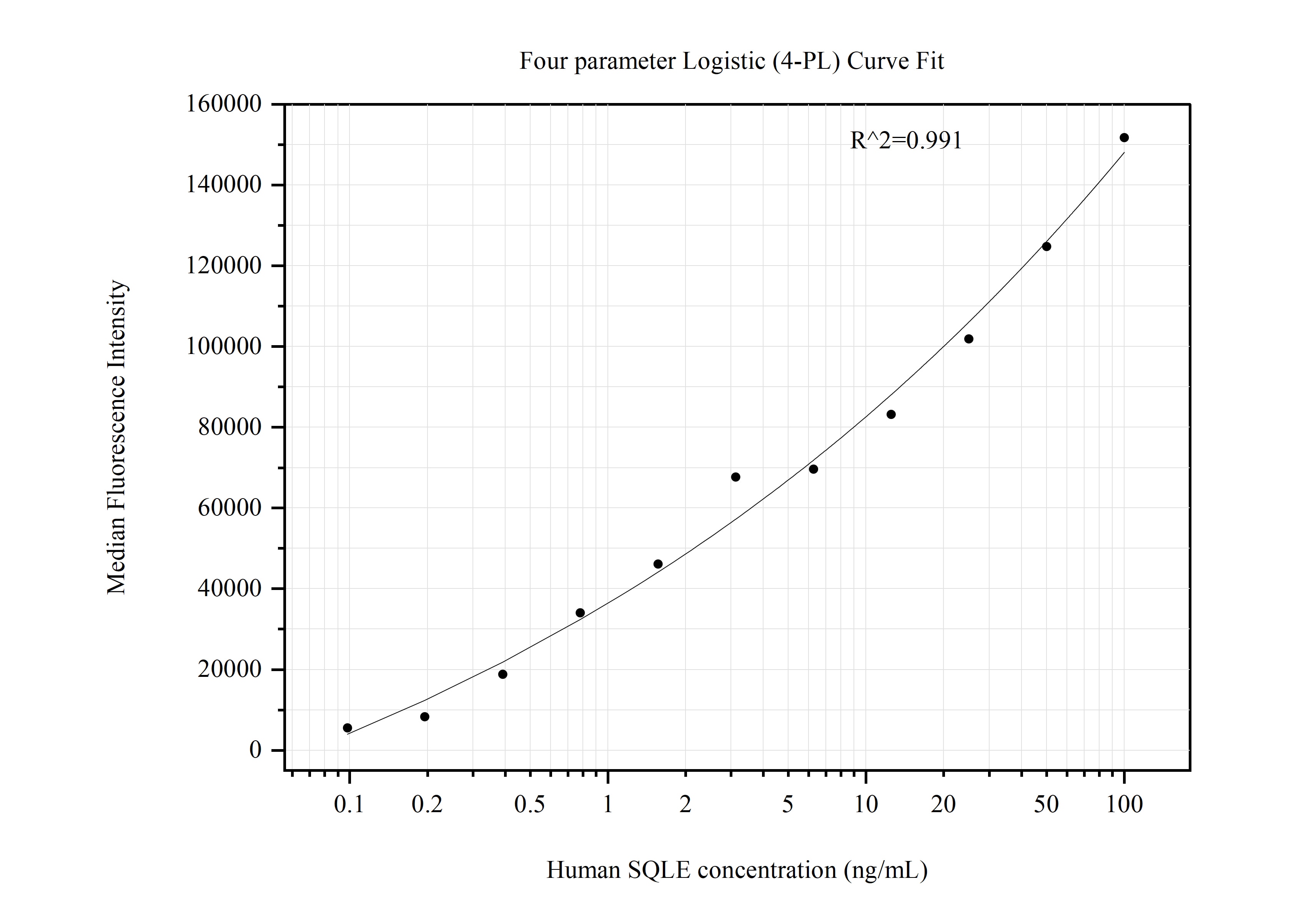
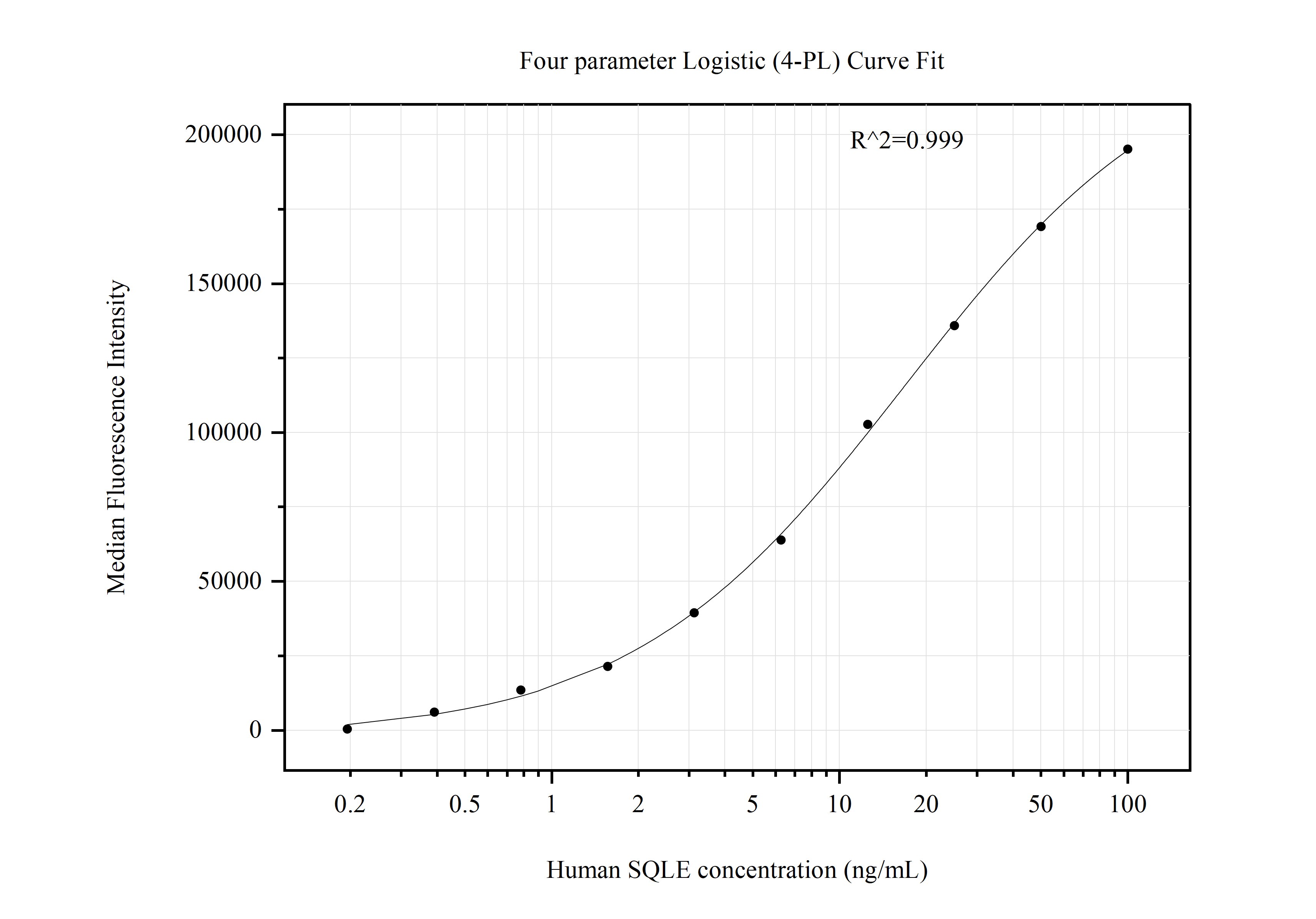
MP50872-2: 67206-1-PBS capture and 67206-3-PBS detection (validated in Cytometric bead array)
MP50872-3: 67206-1-PBS capture and 67206-4-PBS detection (validated in Cytometric bead array)
MP50872-4: 67206-1-PBS capture and 67206-5-PBS detection (validated in Cytometric bead array)
Unconjugated mouse monoclonal antibody pair in PBS only (BSA and azide free) storage buffer at a concentration of 1 mg/mL, ready for conjugation.
This conjugation ready format makes antibodies ideal for use in many applications including: ELISAs, multiplex assays requiring matched pairs, mass cytometry, and multiplex imaging applications.Antibody use should be optimized by the end user for each application and assay.
| Tested Reactivity | human, rat, pig |
| Host / Isotype | Mouse / IgG2a |
| Class | Monoclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen | SQLE fusion protein Ag3266 Predict reactive species |
| Full Name | squalene epoxidase |
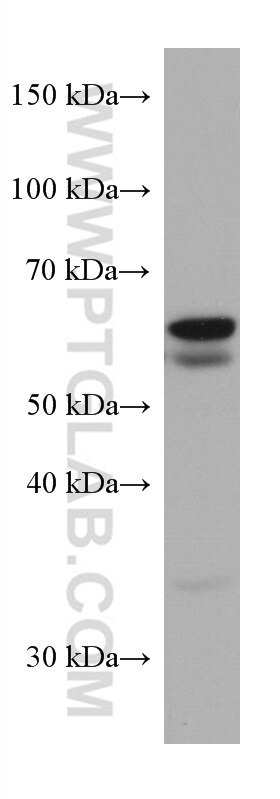
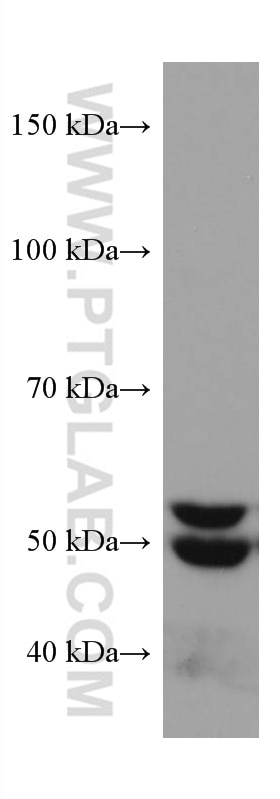
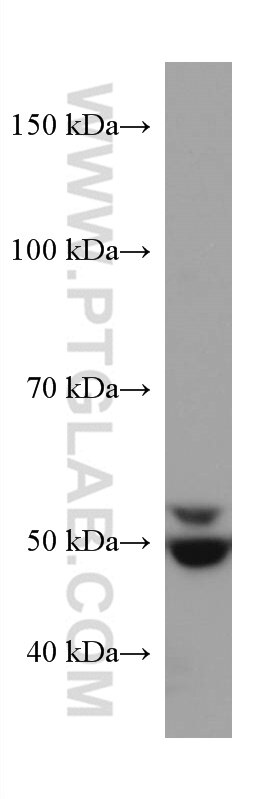
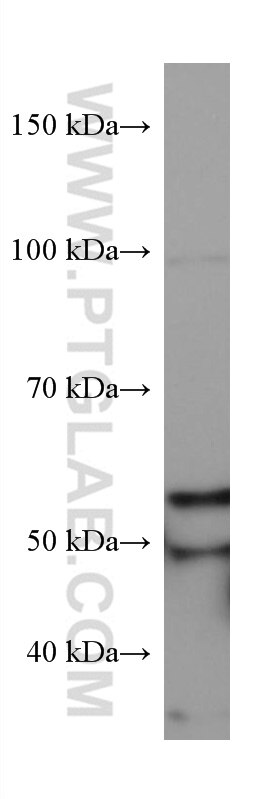
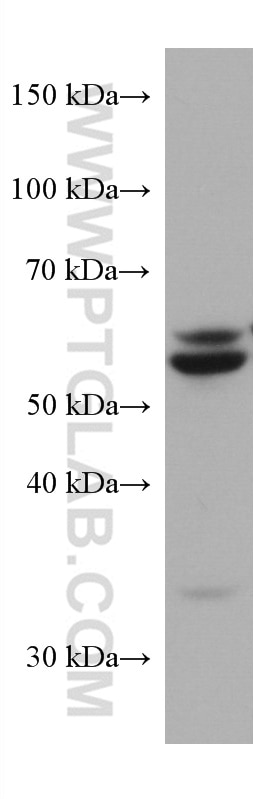
| Calculated Molecular Weight | 574 aa, 64 kDa |
| Observed Molecular Weight | 50-64 kDa |
| GenBank Accession Number | BC017033 |
| Gene Symbol | SQLE |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 6713 |
| RRID | AB_2882499 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Protein A purification |
| UNIPROT ID | Q14534 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS Only |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -80°C. |
Background Information
SQLE, also named as ERG1, SE and SM, belongs to the squalene monooxygenase family. It catalyzes the first oxygenation step in cholesterol synthesis, acting on squalene before cyclization into the basic steroid structure. SQLE may serve as a flux-controlling enzyme beyond 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase (HMGR, considered as rate limiting). It is also posttranslationally regulated by cholesterol-dependent proteasomal degradation. SQLE is subject to feedback regulation via cholesterol-induced degradation, which depends on its lipid-sensing N terminal regulatory domain. Truncation of SQLE occurs during its endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation and requires the proteasome, which partially degrades the SQLE N-terminus and eliminates cholesterol-sensing elements within this region. The MW of SQLE is about 50-64 kDa. (PMID:21356516, PMID: 28972164)