Tested Applications
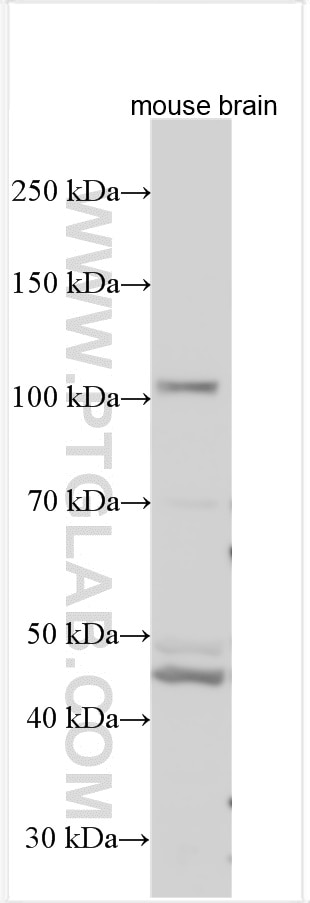
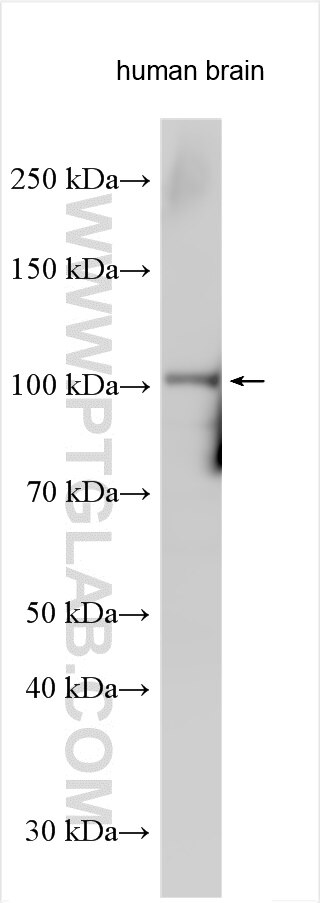
| Positive WB detected in | mouse brain tissue, human brain tissue |
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:1000-1:4000 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
Product Information
21932-1-AP targets SLC14A2 in WB, ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human, mouse samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human, mouse |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Polyclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen | SLC14A2 fusion protein Ag16561 Predict reactive species |
| Full Name | solute carrier family 14 (urea transporter), member 2 |
| Calculated Molecular Weight | 920 aa, 101 kDa |
| Observed Molecular Weight | 43 kDa, 101 kDa |
| GenBank Accession Number | BC110445 |
| Gene Symbol | SLC14A2 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 8170 |
| RRID | AB_3085679 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Antigen affinity purification |
| UNIPROT ID | Q15849 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol , pH 7.3 |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -20°C. Stable for one year after shipment. Aliquoting is unnecessary for -20oC storage. 20ul sizes contain 0.1% BSA. |
Background Information
SLC14A2, also known as human urea transporter -2 (HUT2), is the human homolog of UT-A2 and the only kidney-specific urea transporter cloned in humans. Urea transport in the kidney is mediated by a family of transporter proteins, including renal urea transporters (UT-A) and erythrocyte urea transporters (UT-B). UT-A proteins expressed in the kidney play a critical role in generating the hypertonic medulla, which is an integral component of the urinary concentrating mechanism (PMID: 11590132, 11880324). The 4.2-kb hUT-A1 cDNA encodes a 920-amino acid peptide, which is 89% identical to the rat UT-A1 protein (PMID: 11502588).
Protocols
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for SLC14A2 antibody 21932-1-AP | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |