Tested Applications
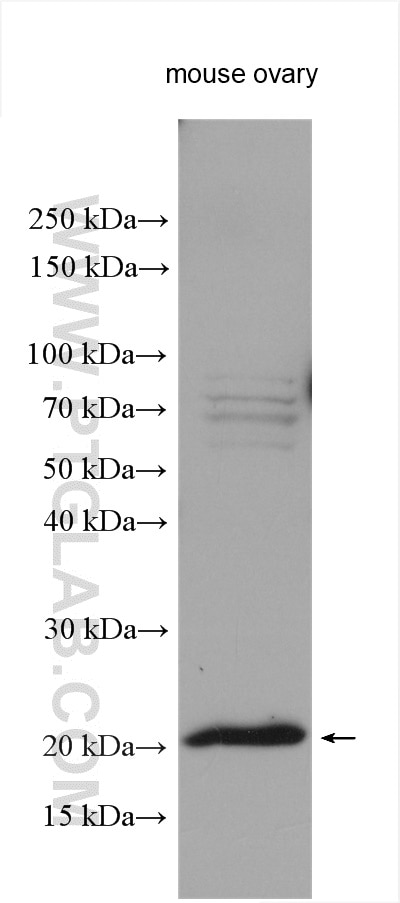
| Positive WB detected in | mouse ovary tissue |
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:500-1:2000 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
Published Applications
| WB | See 1 publications below |
| IHC | See 1 publications below |
Product Information
12094-1-AP targets DDIT4L in WB, IHC, ELISA applications and shows reactivity with mouse samples.
| Tested Reactivity | mouse |
| Cited Reactivity | mouse |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Polyclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen | DDIT4L fusion protein Ag2735 Predict reactive species |
| Full Name | DNA-damage-inducible transcript 4-like |
| Calculated Molecular Weight | 193 aa, 22 kDa |
| Observed Molecular Weight | 22 kDa |
| GenBank Accession Number | BC013592 |
| Gene Symbol | DDIT4L |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 115265 |
| RRID | AB_2918027 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Antigen affinity purification |
| UNIPROT ID | Q96D03 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol , pH 7.3 |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -20°C. Stable for one year after shipment. Aliquoting is unnecessary for -20oC storage. 20ul sizes contain 0.1% BSA. |
Background Information
DNA-damage-inducible transcript 4-like protein(DDIT4L), encoded by the stress responsive gene REDD2, is a negative regulator of mTOR signaling, and expressed predominantly in skeletal muscle. It regulates the TOR signaling pathway upstream of the TSC1-TSC2 complex and downstream of AKT1. Also, DDIT4L involves in oxidized low-density lipoprotein-induced macrophage death sensitivity.
Protocols
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for DDIT4L antibody 12094-1-AP | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |
Publications
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
J Cell Sci Oocyte-dependent activation of MTOR in cumulus cells controls the development and survival of cumulus-oocyte complexes. | ||
Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab Disruption of REDD1 gene ameliorates sepsis-induced decrease in mTORC1 signaling but has divergent effects on proteolytic signaling in skeletal muscle. |