TurboGFP: Properties, Sequence, MW, origin
Everything you need to know about TurboGFP: properties and applications
TurboGFP is a bright green fluorescent protein used to study protein function, localization and dynamics in cells. Nanobody based research tools allow reproducible biochemical analysis including mass spectrometry and enzyme activity measurements of TurboGFP fusion proteins.
1. What are the differences between TurboGFP and GFP
Origin of turboGFP
TurboGFP is a bright dimeric green fluorescent protein derived from CopGFP of the copepod Pontellina plumata. CopGFP has been first published in 2004 (Shagin et al., 2004)
Origin of GFP
GFP has been originally isolated from jellyfish Aequorea Victoria. There are many GFP variants available such as EGFP, GFP S65T, YFP, CFP, mPhluorin, etc. These fluorescent protein derivatives differ in both functional and spectral properties, which have been subject to optimization. The first major improvement of GFP was a single substitution (S65T), which increased fluorescence intensity & stability and shifted the main excitation peak to 488 nm (Heim et al., 1995). EGFP is a further developed version of GFP, which allows the practical use of GFPs in a variety of different organisms and cells.
2. What are the physical-chemical properties of TurboGFP and EGFP?
|
TurboGFP vs. EGFP |
||
|
|
TurboGFP |
EGFP |
|
Spectrum, Wavelength |
|
|
|
- Excitation max |
482 nm |
488 nm |
|
- Emission max |
502 nm |
509 nm |
|
Structure |
dimer |
monomer |
|
Size, Molecular Weight |
2 x 26 kDa |
26.9 kDa |
|
Length |
232 aa |
239 aa |
3. What is the sequence similarity between TurboGFP and EGFP: Sequence comparison
Copepod TurboGFP is evolutionarily distant from jellyfish-derived fluorescent proteins such as EGFP: Turbo-GFP shares only ~20 % sequence identity with the commonly used GFP variants.
Please note: Most anti-GFP antibodies do not bind to TurboGFP, most anti-TurboGFP antibodies do not bind GFP and variants.

Fluorescent Jelly
4. What is the sequence of TurboGFP
For DNA-sequence, protein-sequence and vector plasmids containing TurboGFP, please contact Evrogen: http://evrogen.com/products/products-index-alph.shtml, customer-support@evrogen.com
5. TurboGFP variants
Other variants of TurboGFP are maxGFP and maxFP-Green.
6. What reliable tools for analyzing TurboGFP-tagged proteins are available?
Currently, there are only few tools for cell biological and biochemical analysis of TurboGFP-tagged proteins commercially available. For
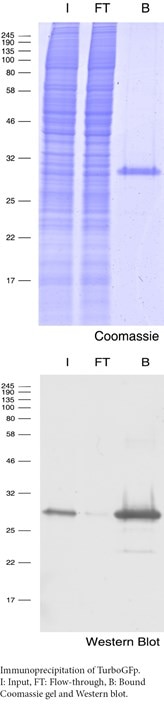
- Immunoprecipitation (IP) of Turbo-GFP fusion proteins
Anti-TurboGFP Nanobody coupled to beads for IP & Co-immunoprecipitation (Co-IP), i.e. for mass spec (MS) analysis: TurboGFP-Trap (ChromoTek)
The TurboGFP-Trap works also with copGFP, maxGFP and maxFP-Green.
- Western blot (WB), Immunoblotting and ICC
Rabbit polyclonal anti-TurboGFP(d) antibody (Evrogen)
- ELISA
Purified anti-TurboGFP Nanobody: TurboGFP- Binding Protein (ChromoTek)
7. What is best anti-TurboGFP antibody for immunoprecipitation?
TurboGFP-Trap, an anti-TurboGFP Nanobody coupled to agarose or magnetic agarose beads, is advantageous over conventional anti-turboGFP antibodies in IP:
- High binding affinity (KD = 0.5 nM)
- No contaminating antibody heavy and light chains
- Low background
- Stable under harsh washing conditions
Links:
http://evrogen.com/products/TurboGFP/TurboGFP_Detailed_description.shtml
Shagin DA, Barsova EV, Yanushevich YG, Fradkov AF, Lukyanov KA, Labas YA, Semenova TN, Ugalde JA, Meyers A, Nunez JM, Widder EA, Lukyanov SA, Matz MV. GFP-like proteins as ubiquitous metazoan superfamily: evolution of functional features and structural complexity, Mol Biol Evol. 2004 May;21(5):841-50. Epub 2004 Feb 12.
Heim R, Cubitt A, Tsien R. Improved green fluorescence, Nature.1995, Feb; 373 (6516): 663–4.
