- Featured Product
- KD/KO Validated
Alpha Tubulin Monoklonaler Antikörper
Alpha Tubulin Monoklonal Antikörper für WB
Wirt / Isotyp
Maus / IgG2b
Getestete Reaktivität
human, Maus, Ratte
Anwendung
WB, CoIP
Konjugation
HRP
CloneNo.
1E4C11
Kat-Nr. : HRP-66031
Synonyme
Geprüfte Anwendungen
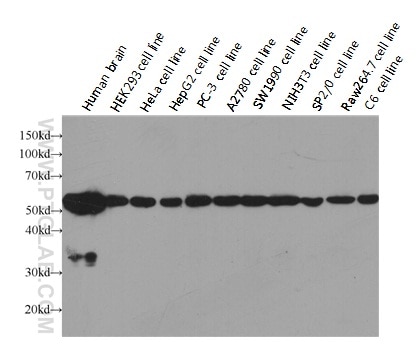
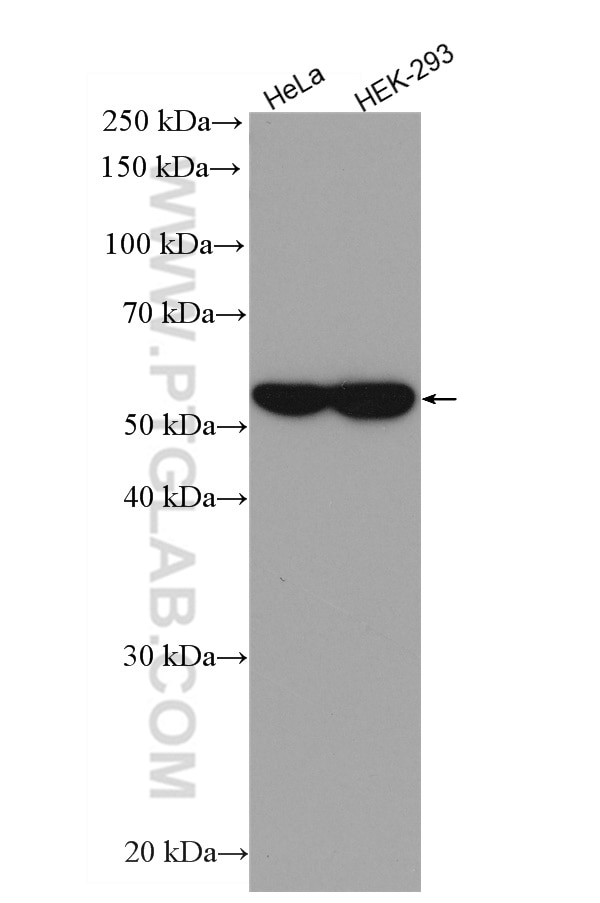
| Erfolgreiche Detektion in WB | HeLa-Zellen, HEK-293-Zellen |
Empfohlene Verdünnung
| Anwendung | Verdünnung |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:5000-1:50000 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, check data in validation data gallery | |
Veröffentlichte Anwendungen
| WB | See 143 publications below |
| CoIP | See 1 publications below |
Produktinformation
HRP-66031 bindet in WB, CoIP Alpha Tubulin und zeigt Reaktivität mit human, Maus, Ratten
| Getestete Reaktivität | human, Maus, Ratte |
| In Publikationen genannte Reaktivität | human, Maus, Ratte |
| Wirt / Isotyp | Maus / IgG2b |
| Klonalität | Monoklonal |
| Typ | Antikörper |
| Immunogen | Rekombinantes Protein |
| Vollständiger Name | tubulin, alpha 1b |
| Berechnetes Molekulargewicht | 50 kDa |
| Beobachtetes Molekulargewicht | 52 kDa |
| GenBank-Zugangsnummer | BC009314 |
| Gene symbol | Alpha Tubulin |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 10376 |
| Konjugation | HRP |
| Form | Liquid |
| Reinigungsmethode | Antigen-Affinitätsreinigung |
| Lagerungspuffer | PBS with 50% glycerol, 0.05% Proclin300, 0.5% BSA |
| Lagerungsbedingungen | Bei -20°C lagern. Vor Licht schützen. Nach dem Versand ein Jahr stabil. Aliquotieren ist bei -20oC Lagerung nicht notwendig. 20ul Größen enthalten 0,1% BSA. |
Hintergrundinformationen
What is the function of alpha-tubulin?
Alpha-tubulin belongs to a large superfamily of tubulin proteins. There are a number of different subtypes that have a molecular weight of ~50kDa and are able to bind to beta-tubulin, forming a heterodimer that polymerizes to microtubules as part of the cytoskeleton. These maintain cell structure, provide platforms for intracellular transport, and are also involved in cell division.
Where is alpha-tubulin expressed?
Alpha-tubulin is highly conserved and is present in nearly all eukaryotic cells as one of the building blocks of microtubules. The ubiquitous nature of this protein has led to its common use as a control protein for many tissue types as well as highlighting the structure of the cytoskeleton.
What are the post-translational modifications of alpha-tubulin?
The function and properties of microtubules are drastically affected by the post-translational modifications undergone by tubulin, which may occur to the tubulin dimer directly or to the polymerized microtubule. For example, the first modification to be identified was detyrosination,1 as most alpha-tubulins have a tyrosine at their terminus. This process affects microtubules more than dimers and leads to patches of detyrosination along the structure, regulating protein interactions and allowing subcellular compartments to be defined.2,3 Polyglutamylation also occurs at several sites within the carboxy-terminal tails. However, to date, the most-studied alpha tubulin modification is related to acetylation of lysine 40 (K40).
Gundersen, G. G., Khawaja, S. & Bulinski, J. C. Postpolymerization detyrosination of alpha-tubulin: a mechanism for subcellular differentiation of microtubules. J. Cell Biol. 105, 251-64 (1987).
Galjart, N. Plus-End-Tracking Proteins and Their Interactions at Microtubule Ends. Curr. Biol. 20, R528-R537 (2010).
Jiang, K. & Akhmanova, A. Microtubule tip-interacting proteins: a view from both ends. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 23, 94-101 (2011).
Protokolle
| PRODUKTSPEZIFISCHE PROTOKOLLE | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for HRP Alpha Tubulin antibody HRP-66031 | Protokoll herunterladen |
| STANDARD-PROTOKOLLE | |
|---|---|
| Klicken Sie hier, um unsere Standardprotokolle anzuzeigen |
Publikationen
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Cell Human T-bet Governs Innate and Innate-like Adaptive IFN-γ Immunity against Mycobacteria. | ||
Mol Cancer Cell surface CD55 traffics to the nucleus leading to cisplatin resistance and stemness by inducing PRC2 and H3K27 trimethylation on chromatin in ovarian cancer | ||
Cell Immune Checkpoint Inhibition Overcomes ADCP-Induced Immunosuppression by Macrophages. | ||
Cell Stem Cell A small-molecule cocktail promotes mammalian cardiomyocyte proliferation and heart regeneration. | ||
Immunity Very-low-density lipoprotein receptor-enhanced lipid metabolism in pancreatic stellate cells promotes pancreatic fibrosis. |
Rezensionen
The reviews below have been submitted by verified Proteintech customers who received an incentive for providing their feedback.
FH Sara (Verified Customer) (10-05-2024) | I love Proteintech HRP-conjugated antibodies. These are def my favourites for WB controls (housekeeping proteins), I have got actin, tubulin and GAPDH. Very good bands, super reliable.
|