Tested Applications
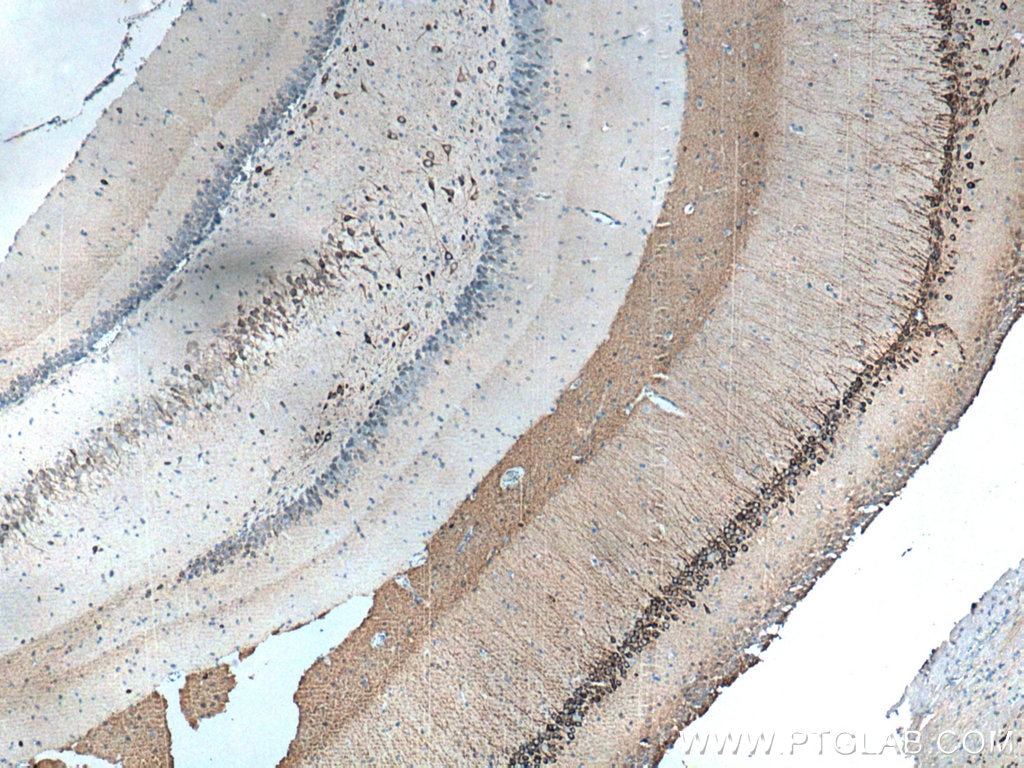
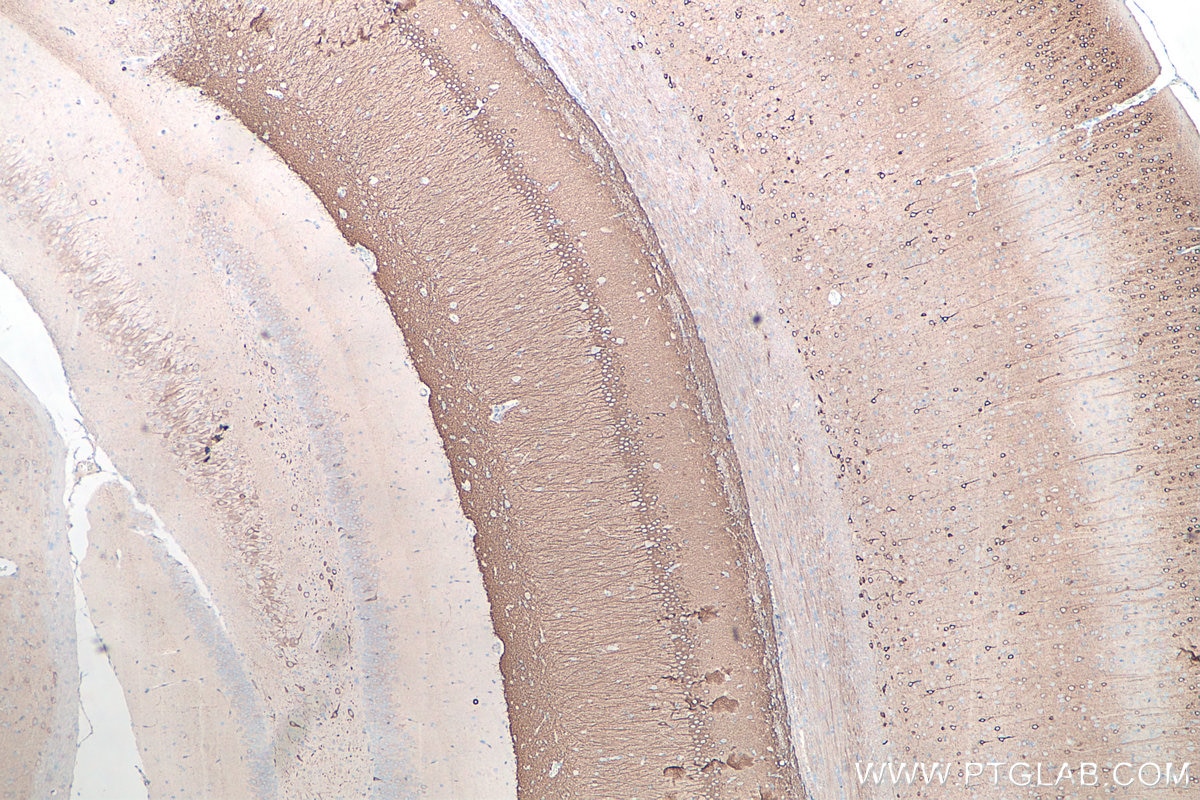
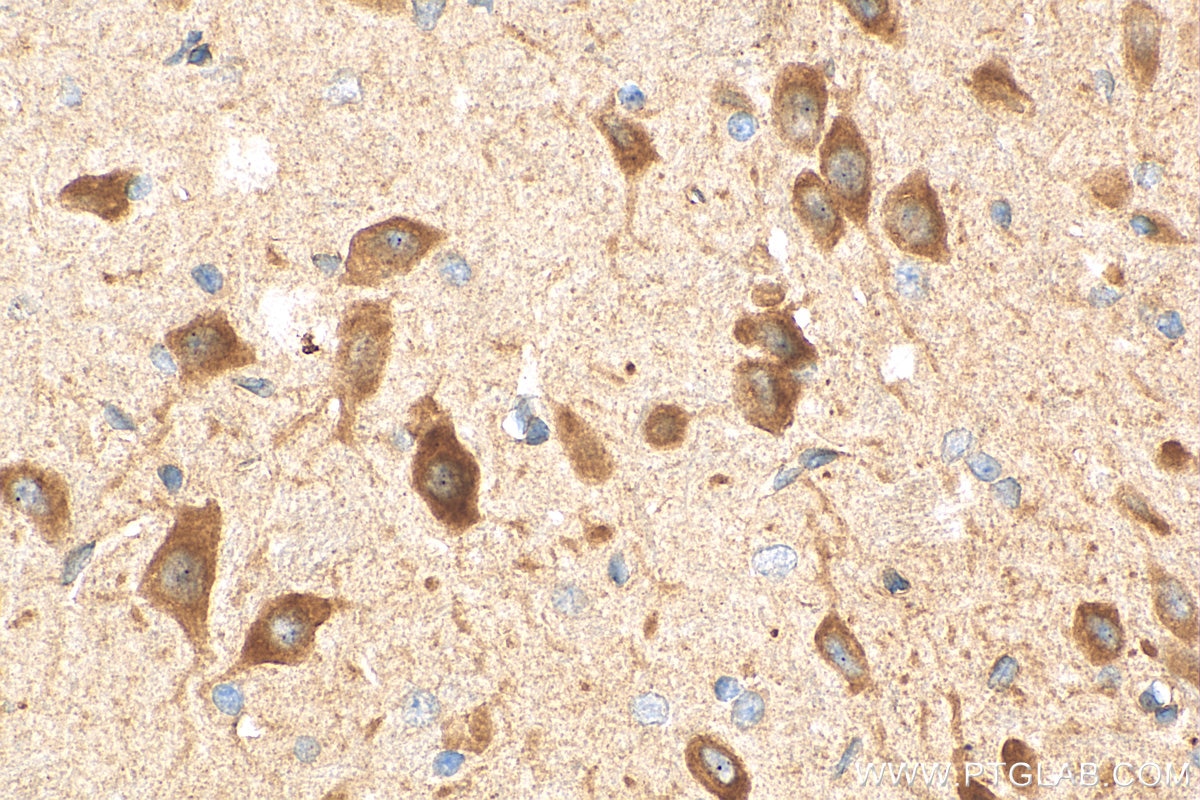
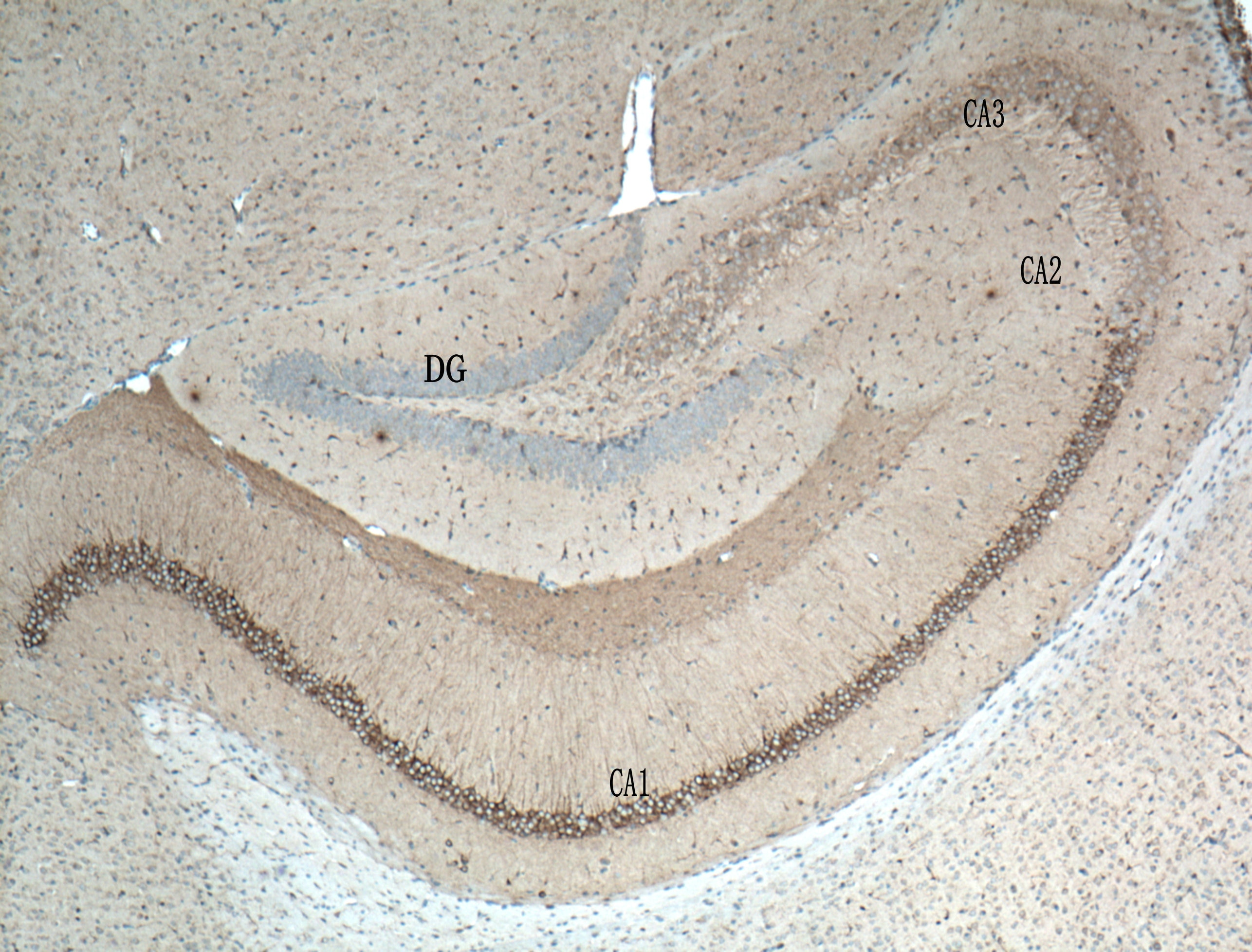
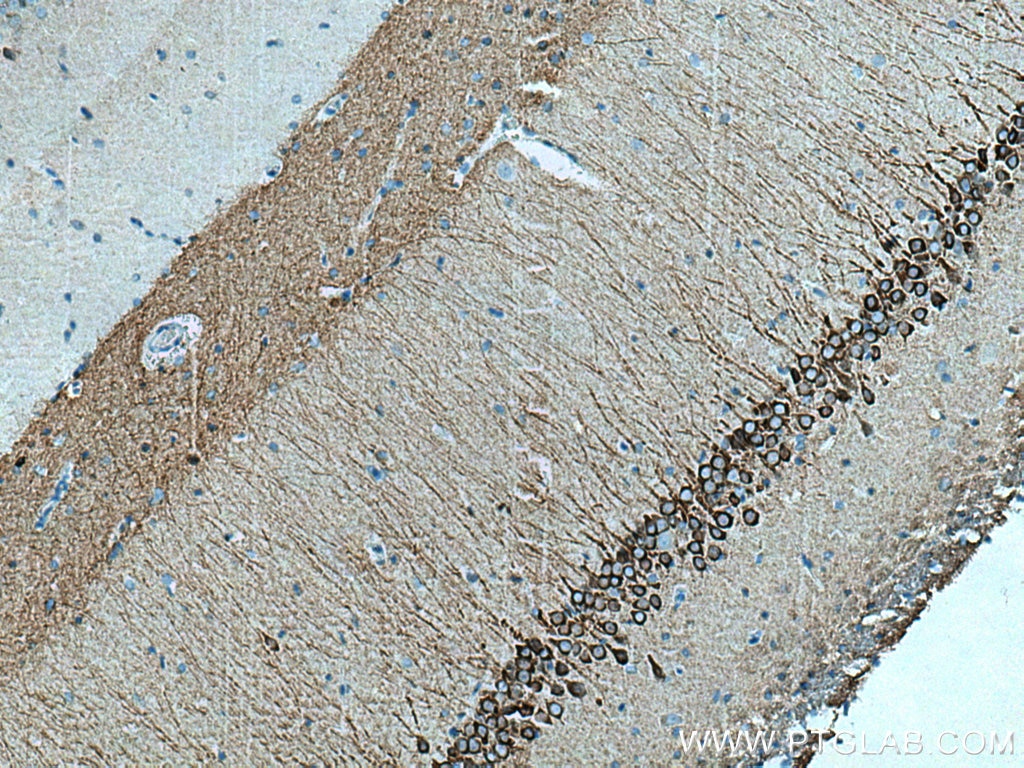
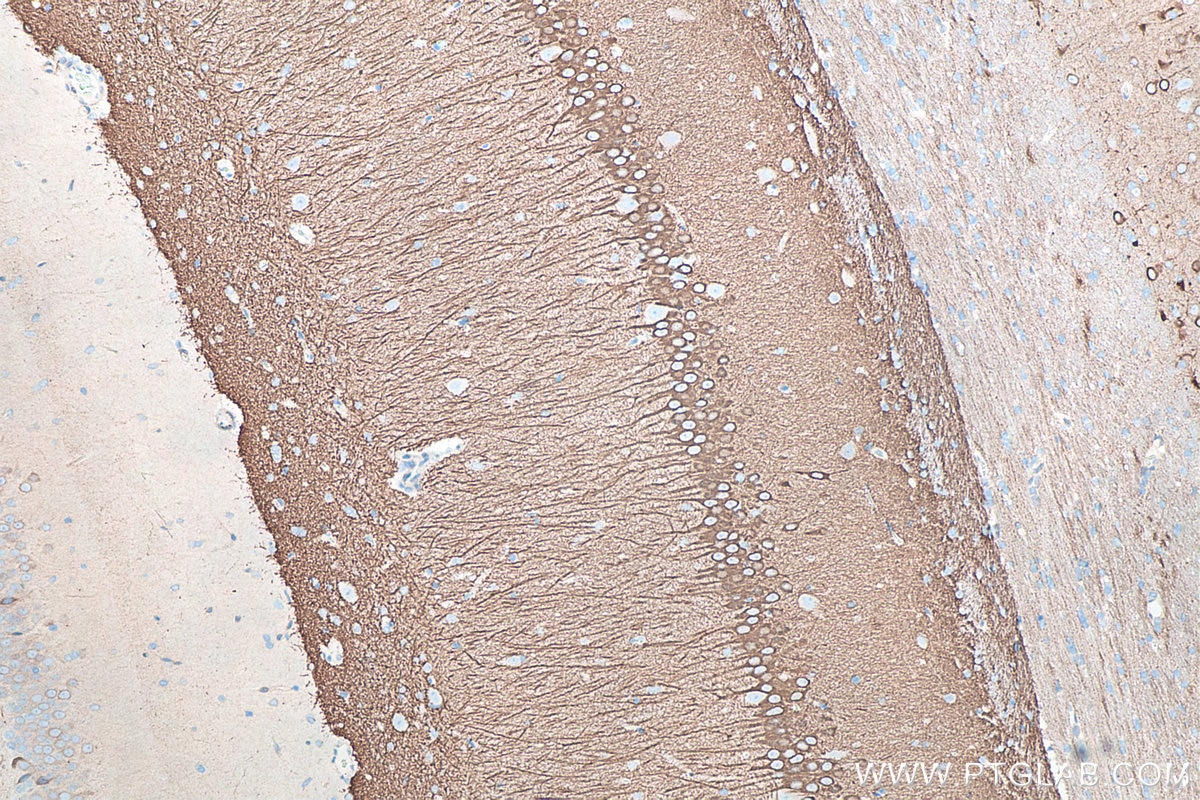
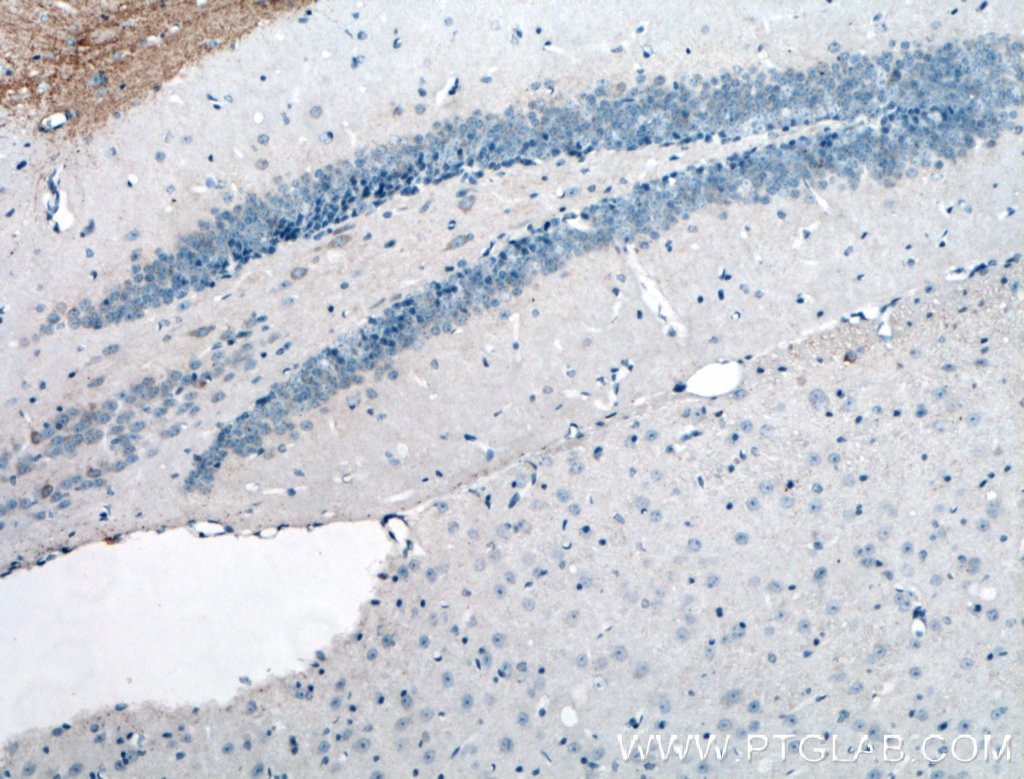
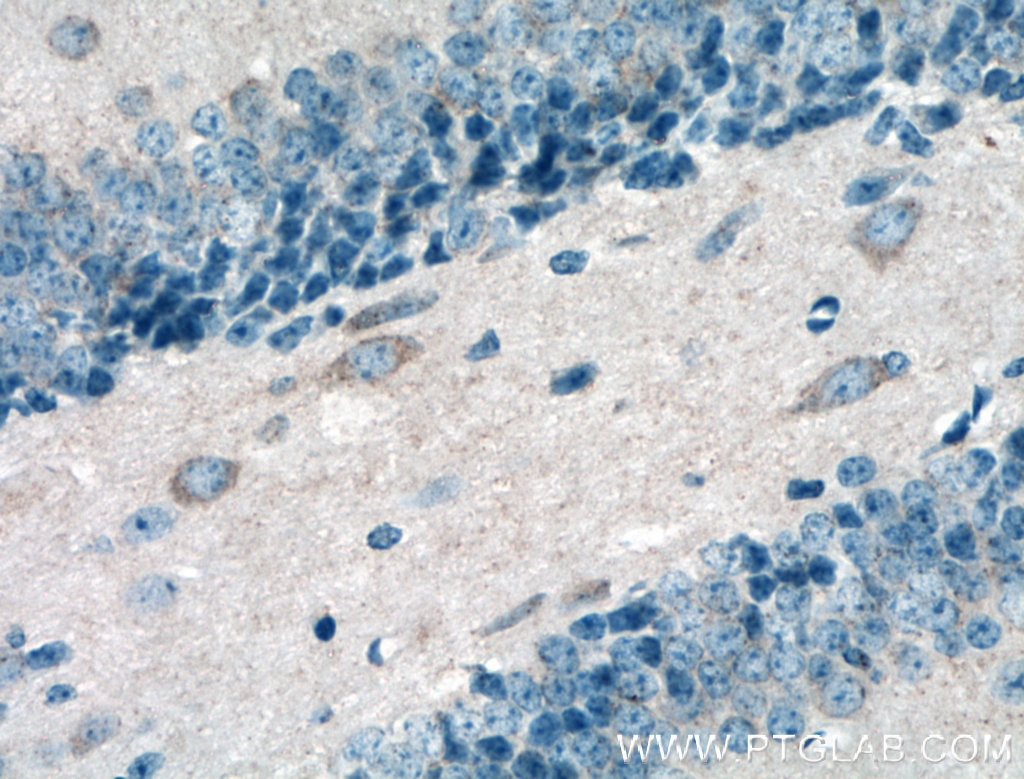
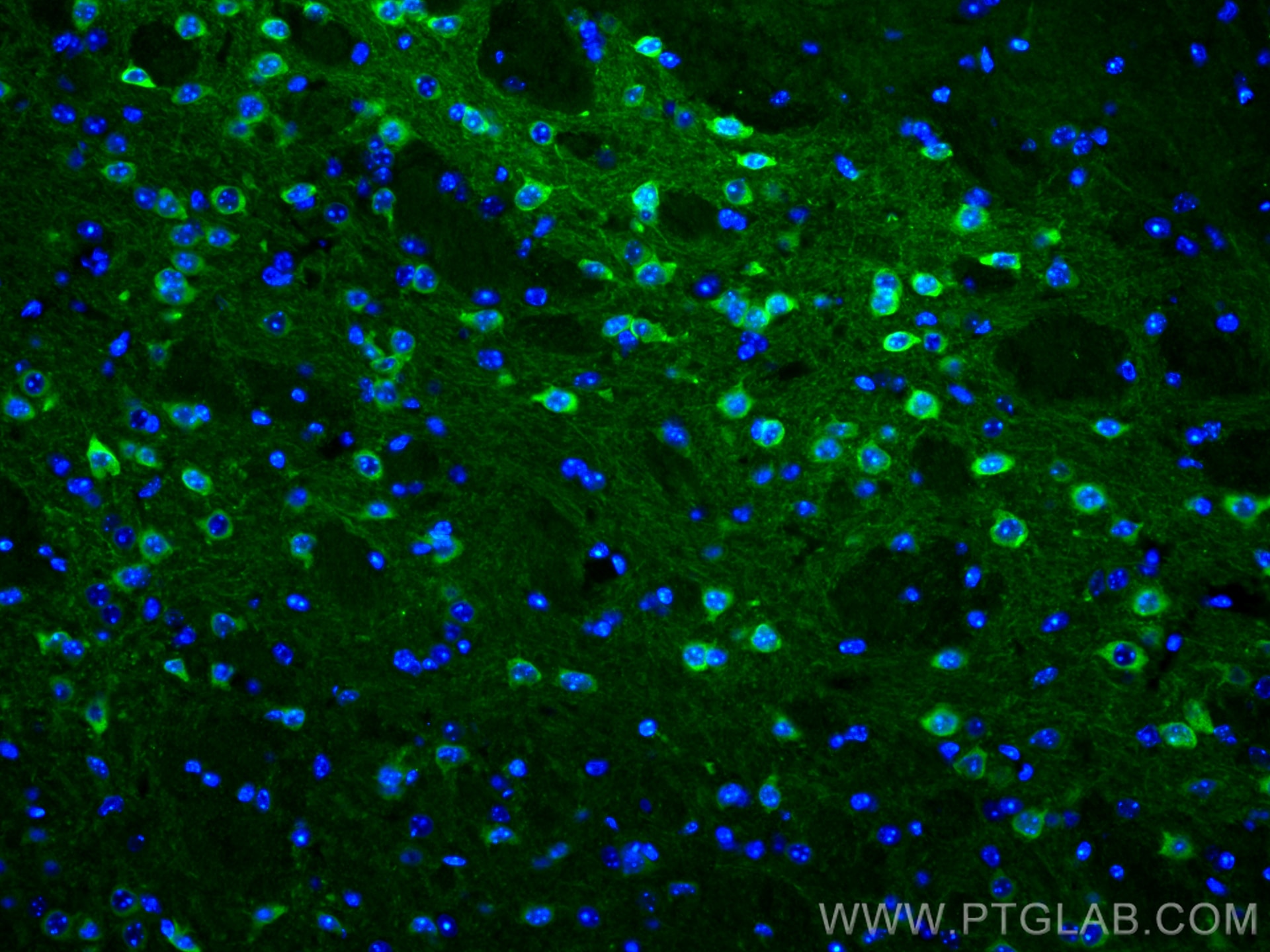
| Positive IHC detected in | rat brain tissue, mouse brain tissue Note: suggested antigen retrieval with TE buffer pH 9.0; (*) Alternatively, antigen retrieval may be performed with citrate buffer pH 6.0 |
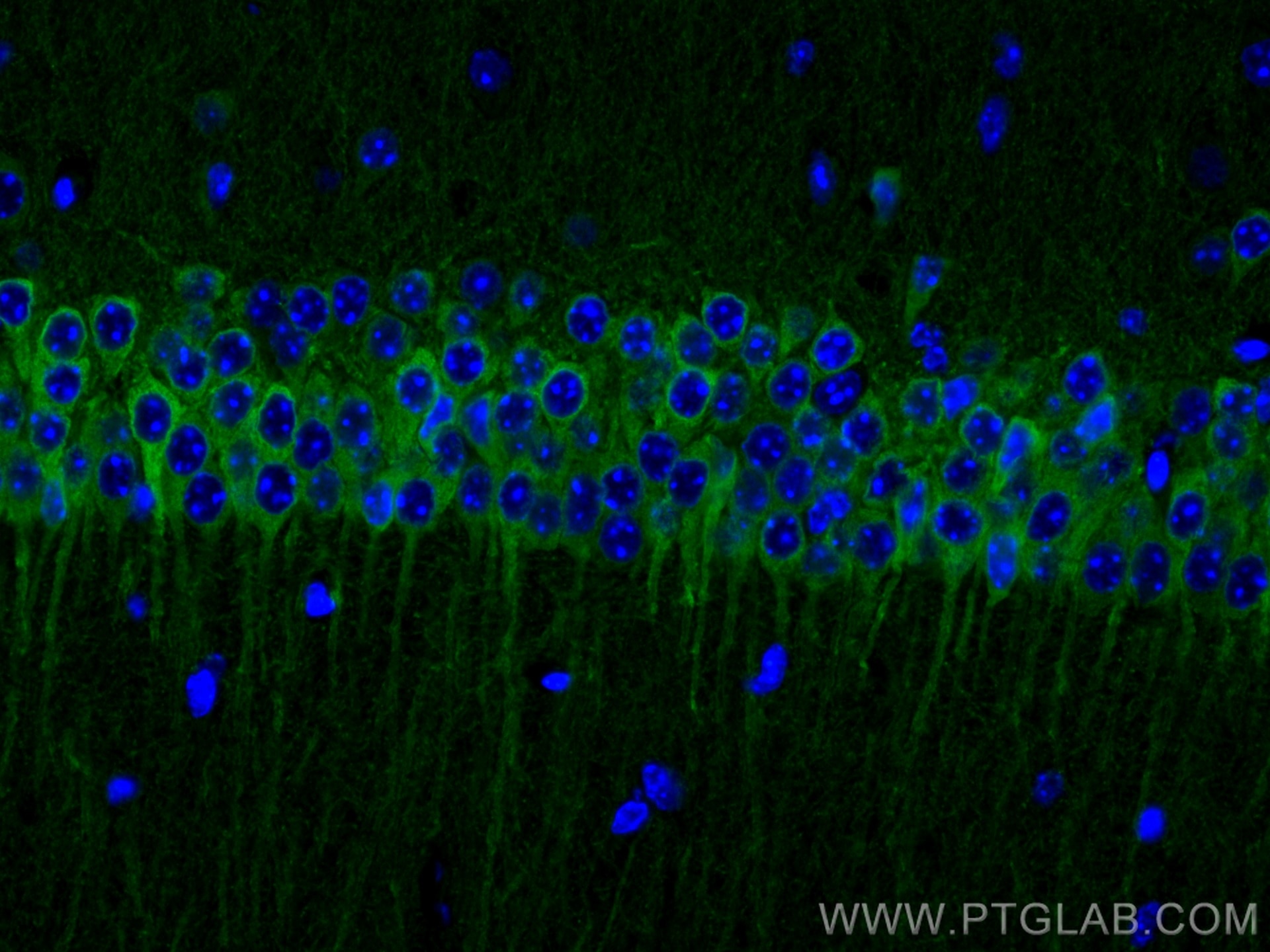
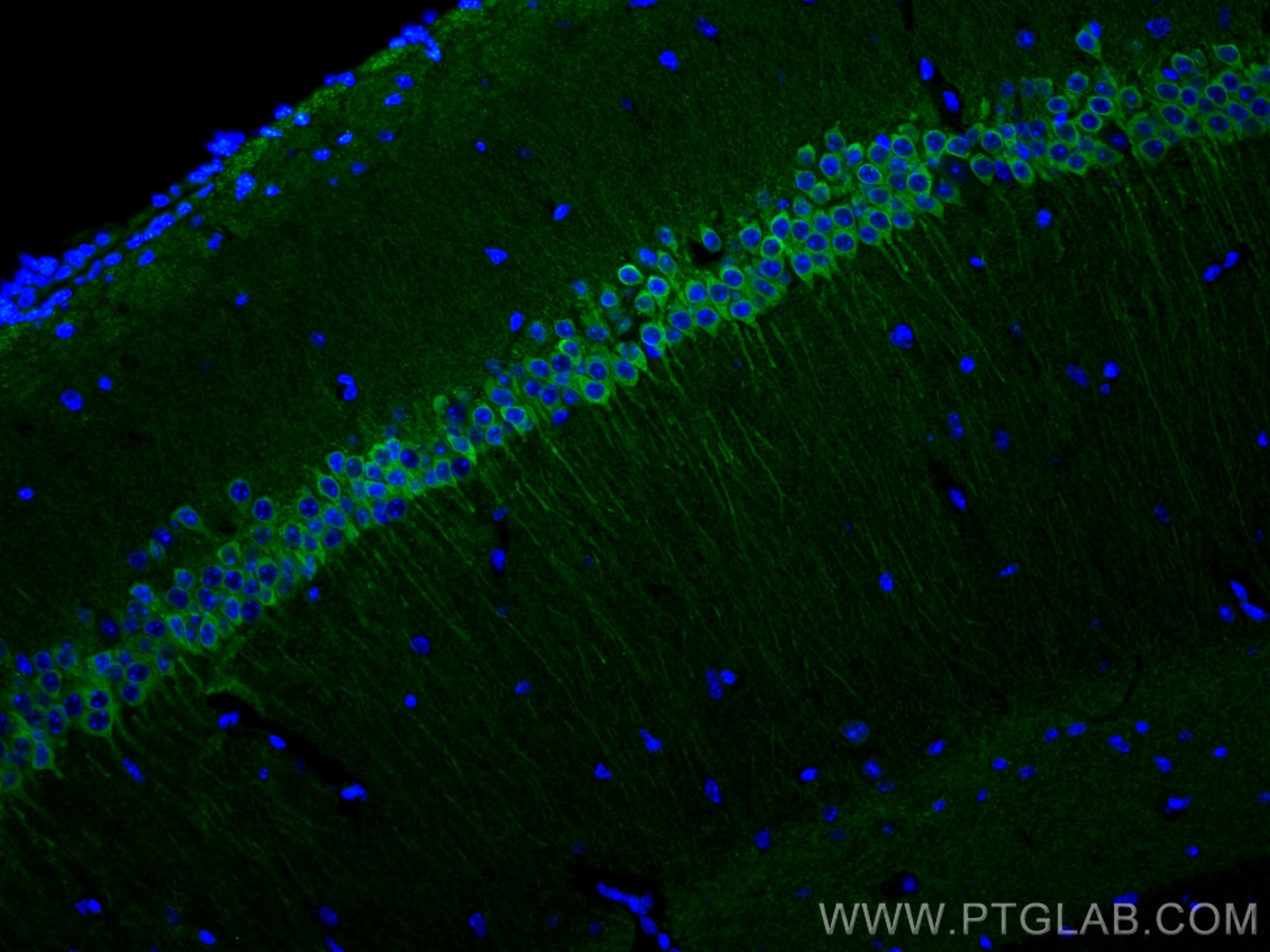
| Positive IF-P detected in | mouse brain tissue |
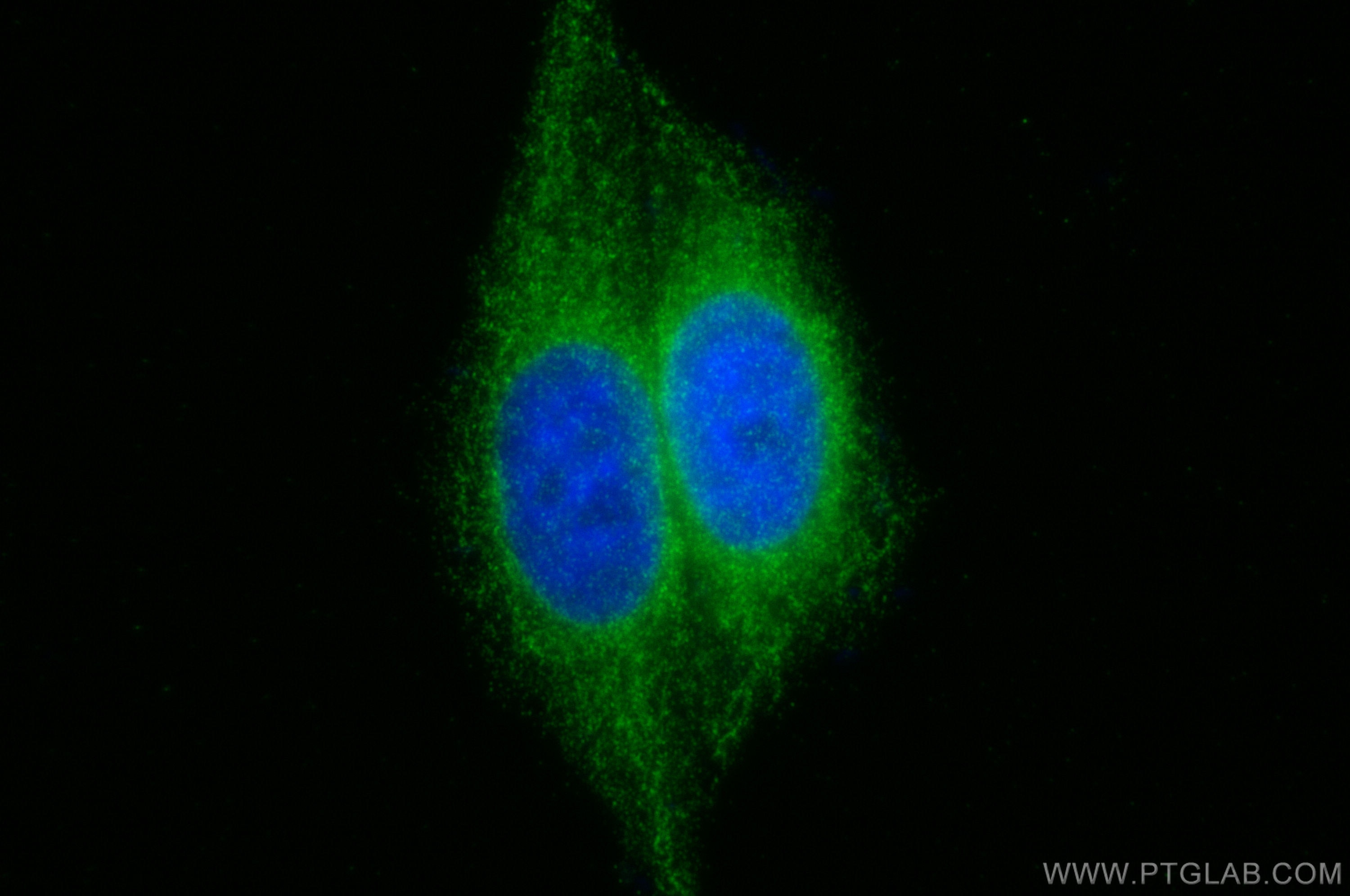
| Positive IF/ICC detected in | HepG2 cells |
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Immunohistochemistry (IHC) | IHC : 1:500-1:2000 |
| Immunofluorescence (IF)-P | IF-P : 1:50-1:500 |
| Immunofluorescence (IF)/ICC | IF/ICC : 1:50-1:500 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
Published Applications
| KD/KO | See 2 publications below |
| WB | See 8 publications below |
| IHC | See 5 publications below |
| IF | See 12 publications below |
| CoIP | See 2 publications below |
Product Information
26995-1-AP targets WFS1 in WB, IHC, IF/ICC, IF-P, CoIP, ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human, mouse, rat samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human, mouse, rat |
| Cited Reactivity | human, mouse, rat, zebrafish |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Polyclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen | WFS1 fusion protein Ag25724 Predict reactive species |
| Full Name | Wolfram syndrome 1 (wolframin) |
| Calculated Molecular Weight | 890 aa, 100 kDa |
| GenBank Accession Number | BC030130 |
| Gene Symbol | WFS1 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 7466 |
| RRID | AB_2880717 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Antigen affinity purification |
| UNIPROT ID | O76024 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol pH 7.3. |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -20°C. Stable for one year after shipment. Aliquoting is unnecessary for -20oC storage. 20ul sizes contain 0.1% BSA. |
Background Information
Wolfram syndrome protein (WFS1), also called wolframin, is a transmembrane protein, which is located primarily in the endoplasmic reticulum and its expression is induced in response to ER stress, partially through transcriptional activation. ER localization suggests that WFS1 protein has physiological functions in membrane trafficking, secretion, processing and/or regulation of ER calcium homeostasis. It is ubiquitously expressed with highest levels in brain, pancreas, heart, and insulinoma beta-cell lines. Mutations of the WFS1 gene are responsible for two hereditary diseases, autosomal recessive Wolfram syndrome and autosomal dominant low frequency sensorineural hearing loss.
Protocols
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| IHC protocol for WFS1 antibody 26995-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IF protocol for WFS1 antibody 26995-1-AP | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |
Publications
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Sci Transl Med Wolframin-1-expressing neurons in the entorhinal cortex propagate tau to CA1 neurons and impair hippocampal memory in mice. | ||
Neuron Astrocyte-mediated regulation of BLAWFS1 neurons alleviates risk-assessment deficits in DISC1-N mice | ||
Nat Commun WFS1 functions in ER export of vesicular cargo proteins in pancreatic β-cells.
| ||
Prog Neurobiol The fasciola cinereum subregion of the hippocampus is important for the acquisition of visual contextual memory. | ||
Cell Rep Acetylcholine synergizes with netrin-1 to drive persistent firing in the entorhinal cortex |
Reviews
The reviews below have been submitted by verified Proteintech customers who received an incentive for providing their feedback.
FH Jordan (Verified Customer) (01-25-2021) | Used free floating staining 16 hours in primary and 6 hours in secondary (Alexa 488+) at 4 degrees C. Antibody does a perfect job of labelling MEC layer 2 pyramidal neurons, alongside Parasubiculum neurons, some neurons in the subiculum and the majority of CA1 pyramidal neurons as widely reported in the literature
|