Anticorps Polyclonal de lapin anti-TEX14
TEX14 Polyclonal Antibody for IHC, ELISA
Hôte / Isotype
Lapin / IgG
Réactivité testée
Humain, souris
Applications
WB, IF, IHC, ELISA
Conjugaison
Non conjugué
N° de cat : 18351-1-AP
Synonymes
Galerie de données de validation
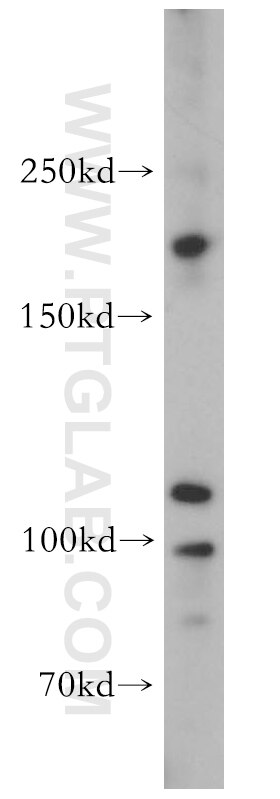
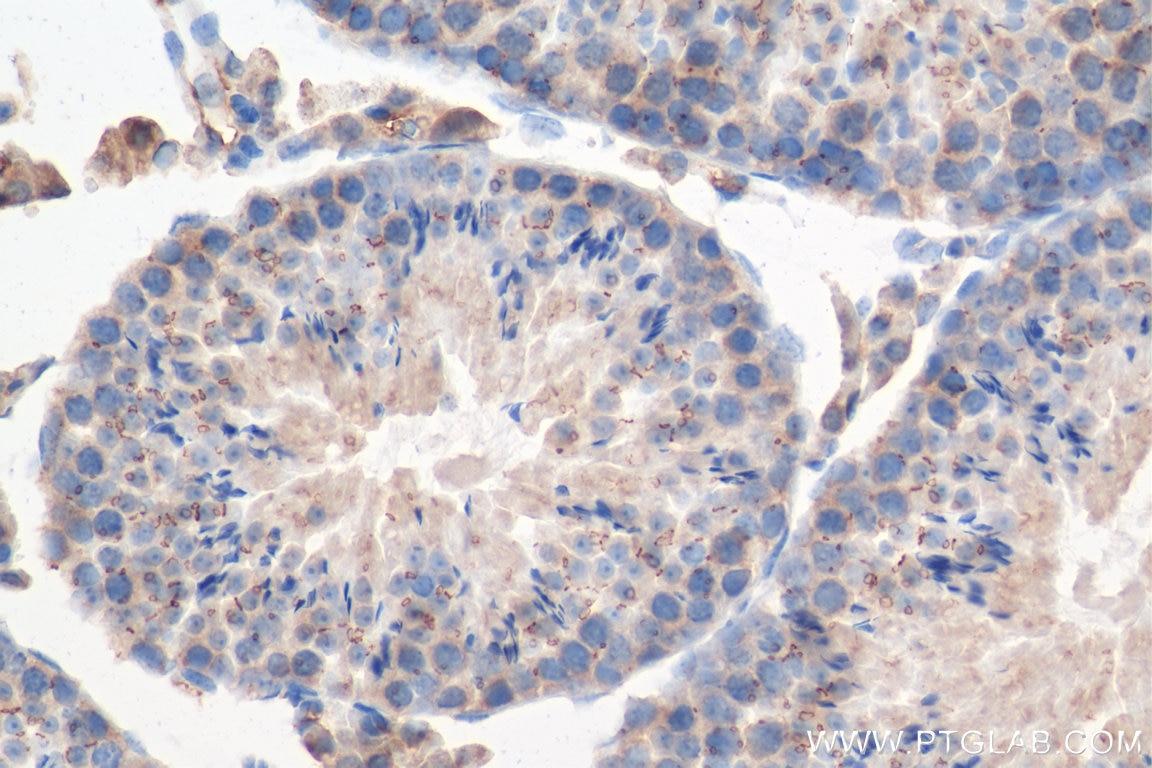
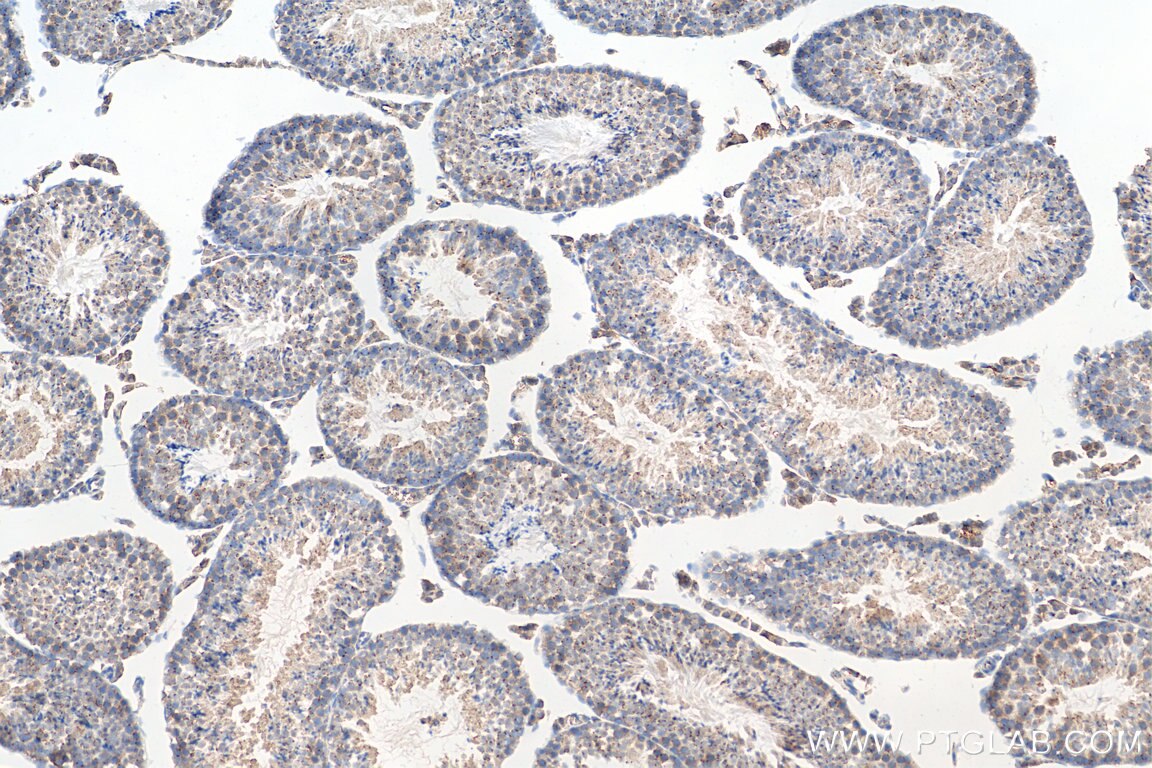
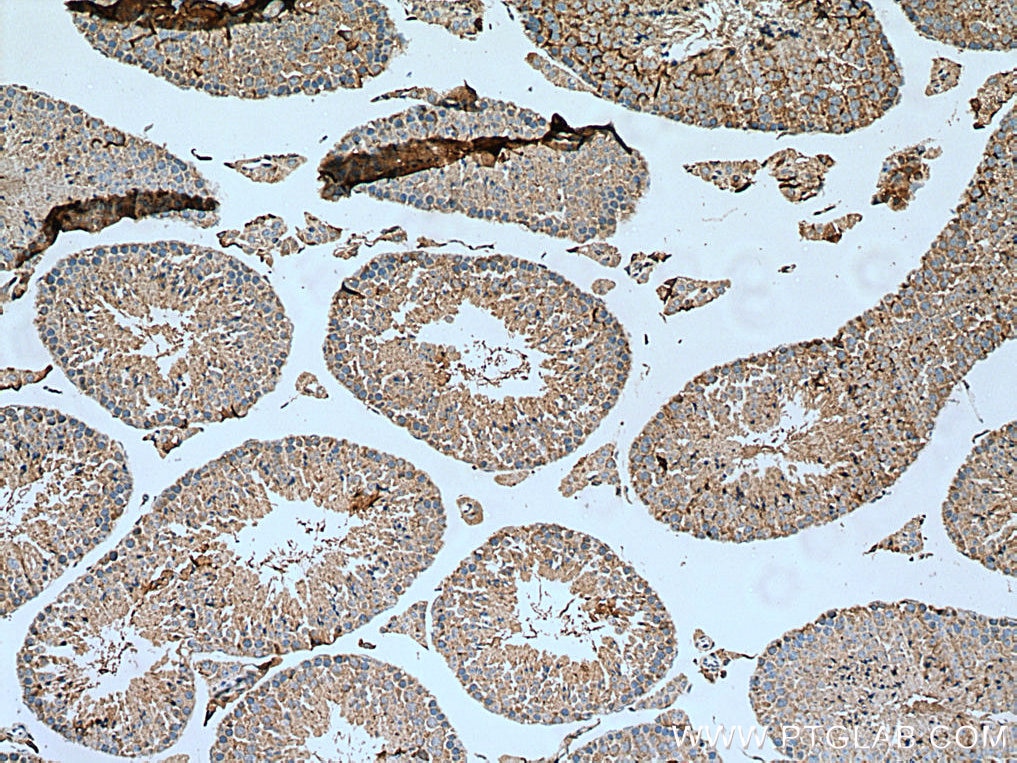
Applications testées
| Résultats positifs en IHC | tissu testiculaire de souris, il est suggéré de démasquer l'antigène avec un tampon de TE buffer pH 9.0; (*) À défaut, 'le démasquage de l'antigène peut être 'effectué avec un tampon citrate pH 6,0. |
Dilution recommandée
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Immunohistochimie (IHC) | IHC : 1:400-1:1600 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, check data in validation data gallery | |
Applications publiées
| WB | See 1 publications below |
| IHC | See 1 publications below |
| IF | See 4 publications below |
Informations sur le produit
18351-1-AP cible TEX14 dans les applications de WB, IF, IHC, ELISA et montre une réactivité avec des échantillons Humain, souris
| Réactivité | Humain, souris |
| Réactivité citée | Humain, souris |
| Hôte / Isotype | Lapin / IgG |
| Clonalité | Polyclonal |
| Type | Anticorps |
| Immunogène | TEX14 Protéine recombinante Ag13177 |
| Nom complet | testis expressed 14 |
| Masse moléculaire calculée | 957aa,107 kDa; 1497aa,168 kDa |
| Poids moléculaire observé | 180-200 kDa, 106 kDa |
| Numéro d’acquisition GenBank | BC040526 |
| Symbole du gène | TEX14 |
| Identification du gène (NCBI) | 56155 |
| Conjugaison | Non conjugué |
| Forme | Liquide |
| Méthode de purification | Purification par affinité contre l'antigène |
| Tampon de stockage | PBS avec azoture de sodium à 0,02 % et glycérol à 50 % pH 7,3 |
| Conditions de stockage | Stocker à -20°C. Stable pendant un an après l'expédition. L'aliquotage n'est pas nécessaire pour le stockage à -20oC Les 20ul contiennent 0,1% de BSA. |
Informations générales
Tex14 is required both for the formation of intercellular bridges during meiosis and for kinetochore-microtubule attachment during mitosis. Intercellular bridges are evolutionarily conserved structures that connect differentiating germ cells and are required for spermatogenesis and male fertility. Tex14 acts by promoting the conversion of midbodies into intercellular bridges via its interaction with CEP55: interaction with CEP55 inhibits the interaction between CEP55 and PDCD6IP/ALIX and TSG101, blocking cell abscission and leading to transform midbodies into intercellular bridges.Tex14 also plays a role during mitosis: recruited to kinetochores by PLK1 during early mitosis and regulates the maturation of the outer kinetochores and microtubule attachment. Tex14 has several variant isoforms with the MW from about 100 kDa to 168 kDa.
Protocole
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for TEX14 antibody 18351-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IHC protocol for TEX14 antibody 18351-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IP protocol for TEX14 antibody 18351-1-AP | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |
Publications
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Int J Mol Sci MCF7 Spheroid Development: New Insight about Spatio/Temporal Arrangements of TNTs, Amyloid Fibrils, Cell Connections, and Cellular Bridges. | ||
FASEB J Dazl determines primordial follicle formation through the translational regulation of Tex14. | ||
Methods Mol Biol Whole-mount immunohistochemistry to study spermatogonial stem cells and spermatogenic lineage development in mice, monkeys, and humans. | ||
Cell Death Dis Specific deletion of protein phosphatase 6 catalytic subunit in Sertoli cells leads to disruption of spermatogenesis. | ||
Cells The Male Mouse Meiotic Cilium Emanates from the Mother Centriole at Zygotene Prior to Centrosome Duplication |