- Phare
- Validé par KD/KO
Anticorps Polyclonal de lapin anti-FATP2
FATP2 Polyclonal Antibody for WB, IP, IF, IHC, ELISA
Hôte / Isotype
Lapin / IgG
Réactivité testée
Humain, rat, souris
Applications
WB, IHC, IF/ICC, IP, CoIP, ELISA
Conjugaison
Non conjugué
N° de cat : 14048-1-AP
Synonymes
Galerie de données de validation
Applications testées
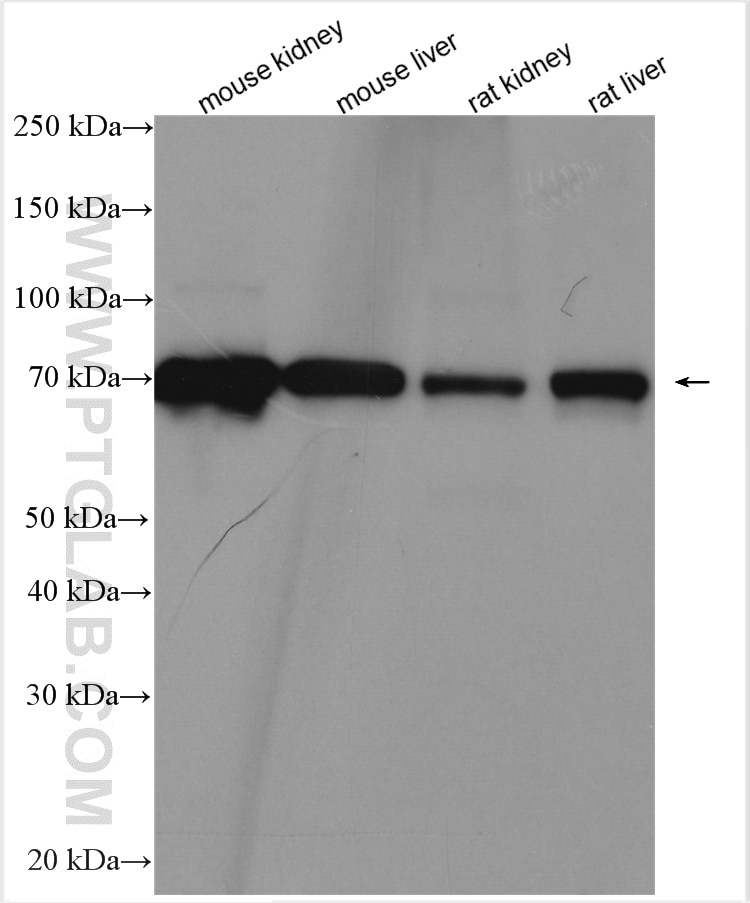
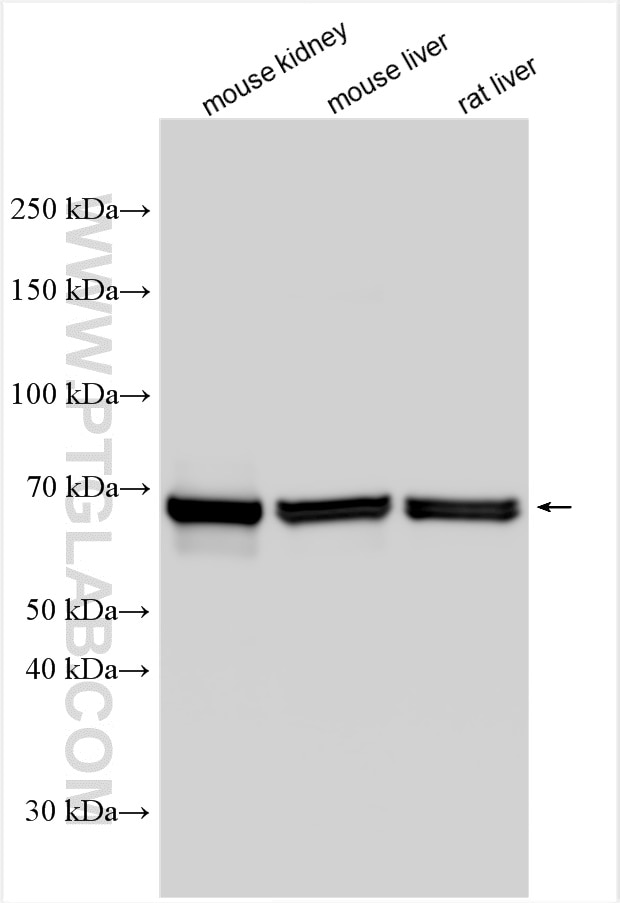
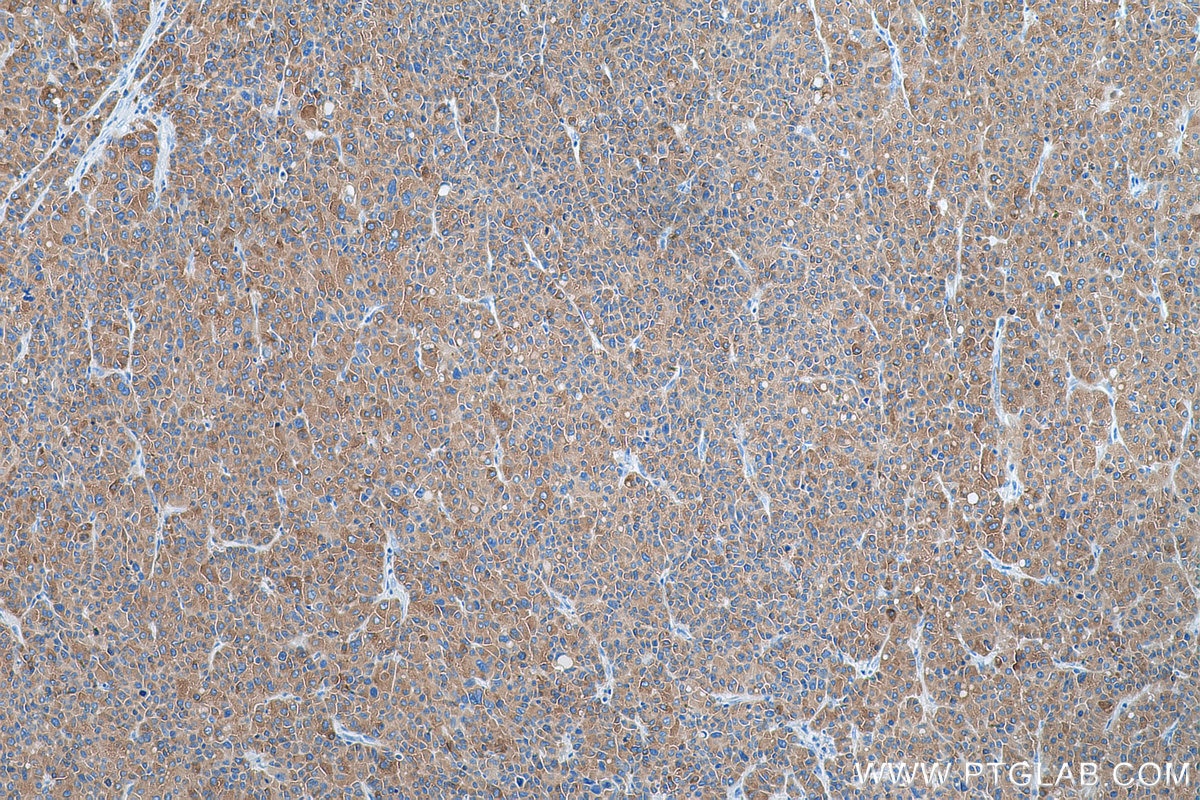
| Résultats positifs en WB | tissu rénal de souris, foie de rat, foie de souris, rein de rat, tissu hépatique de rat, tissu hépatique de souris |
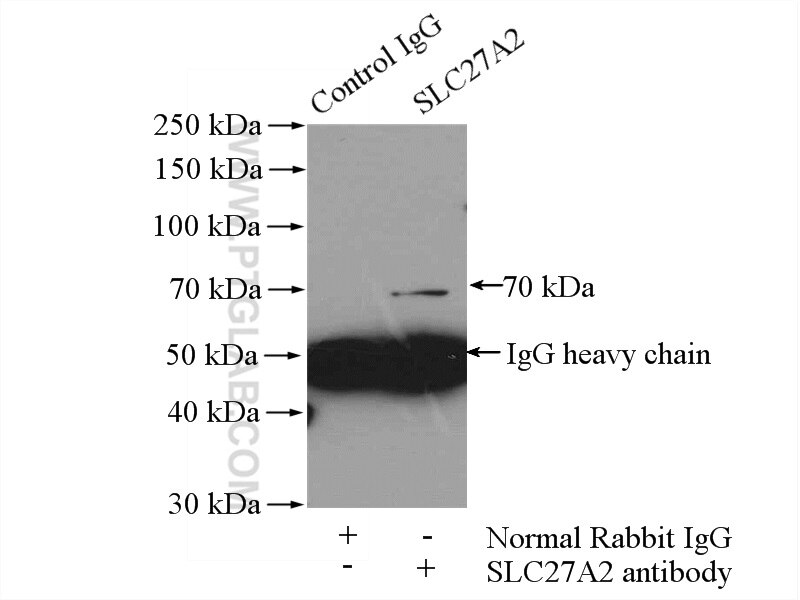
| Résultats positifs en IP | cellules HepG2 |
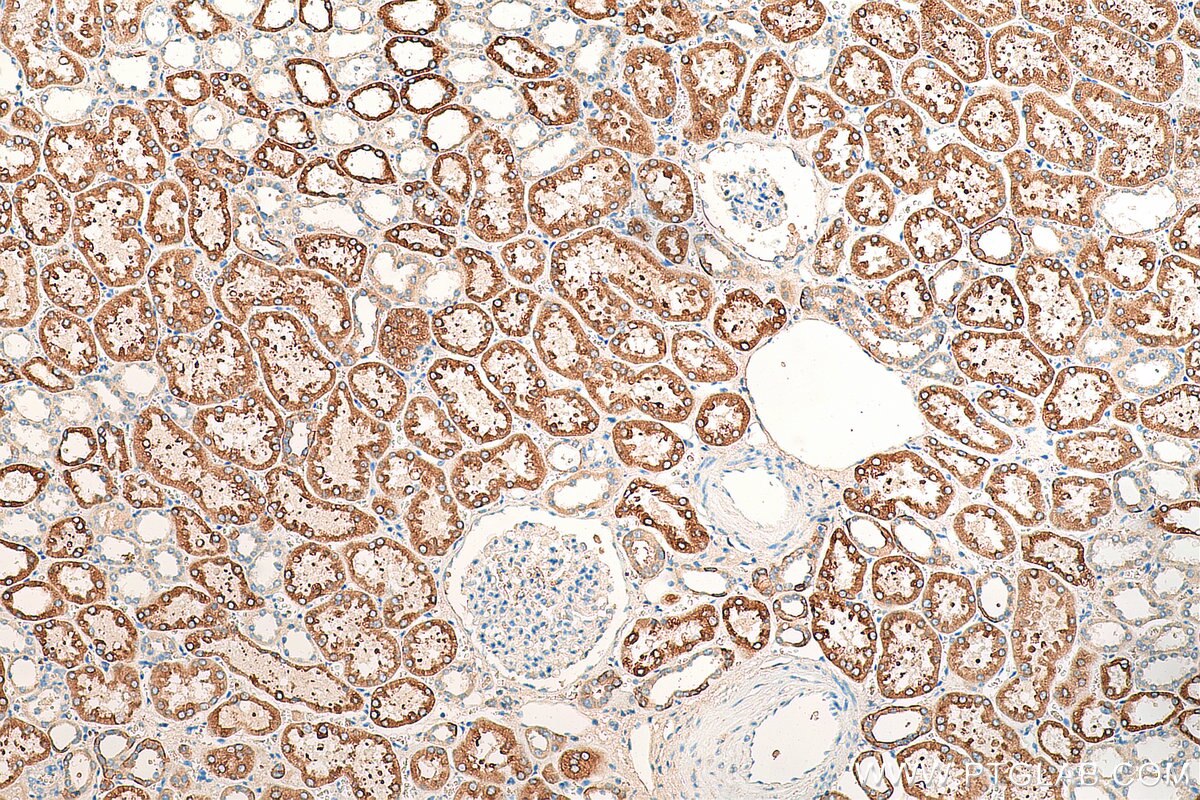
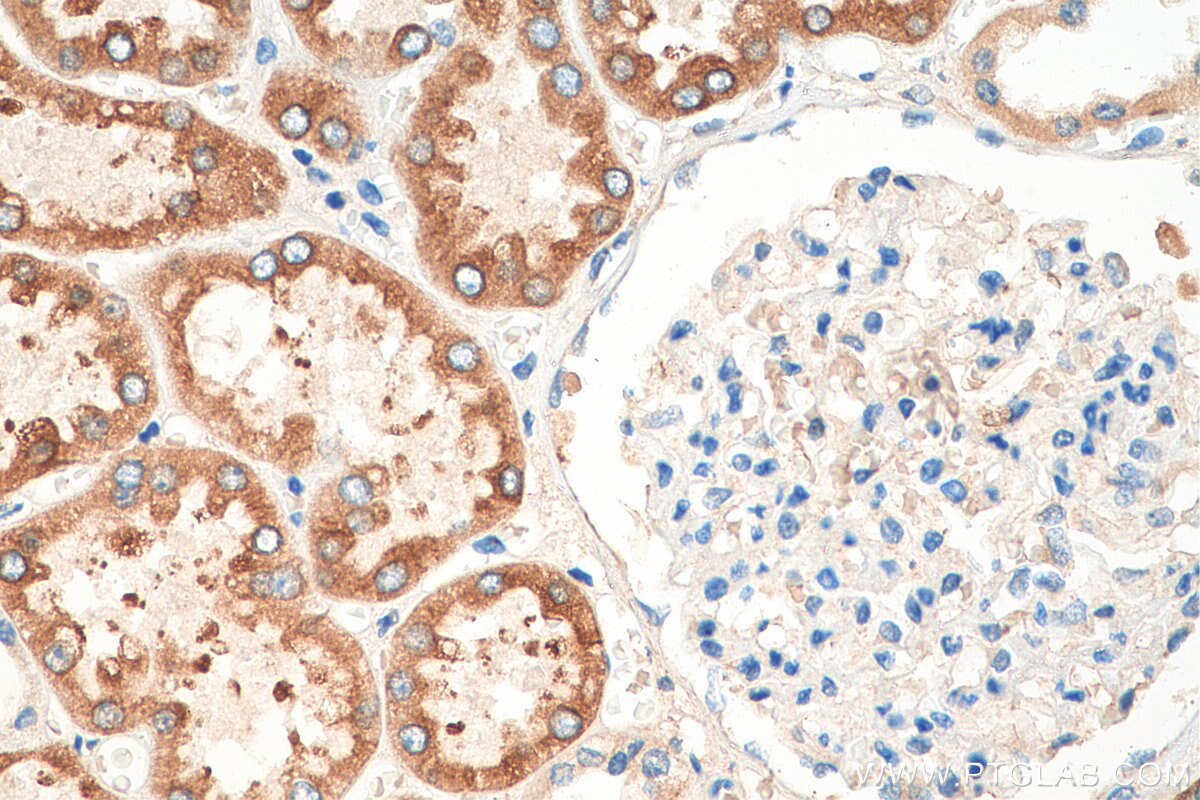
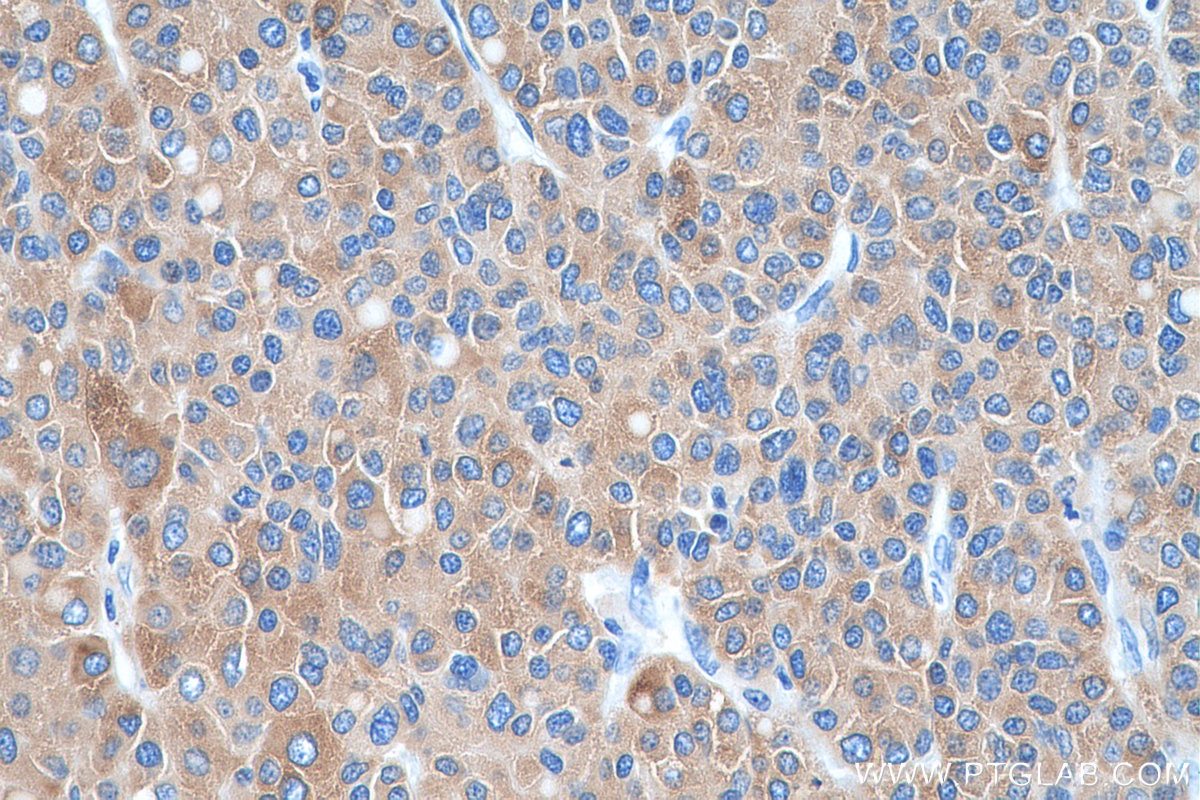
| Résultats positifs en IHC | tissu de cancer du foie humain, tissu rénal humain il est suggéré de démasquer l'antigène avec un tampon de TE buffer pH 9.0; (*) À défaut, 'le démasquage de l'antigène peut être 'effectué avec un tampon citrate pH 6,0. |
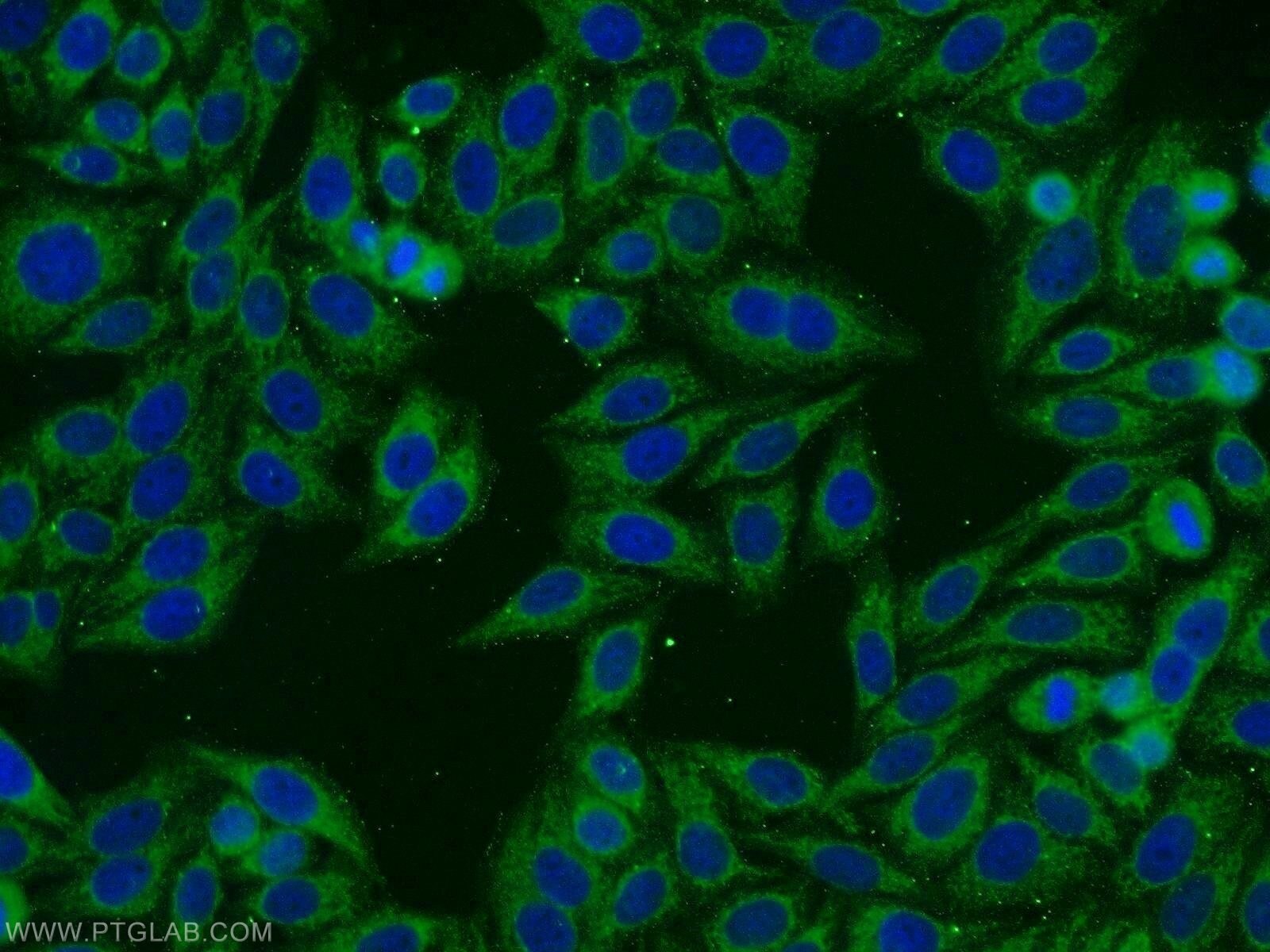
| Résultats positifs en IF/ICC | cellules HepG2 |
Dilution recommandée
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:2000-1:16000 |
| Immunoprécipitation (IP) | IP : 0.5-4.0 ug for 1.0-3.0 mg of total protein lysate |
| Immunohistochimie (IHC) | IHC : 1:250-1:1000 |
| Immunofluorescence (IF)/ICC | IF/ICC : 1:10-1:100 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, check data in validation data gallery | |
Applications publiées
| KD/KO | See 3 publications below |
| WB | See 31 publications below |
| IHC | See 2 publications below |
| IF | See 4 publications below |
| CoIP | See 1 publications below |
Informations sur le produit
14048-1-AP cible FATP2 dans les applications de WB, IHC, IF/ICC, IP, CoIP, ELISA et montre une réactivité avec des échantillons Humain, rat, souris
| Réactivité | Humain, rat, souris |
| Réactivité citée | rat, Humain, souris |
| Hôte / Isotype | Lapin / IgG |
| Clonalité | Polyclonal |
| Type | Anticorps |
| Immunogène | FATP2 Protéine recombinante Ag5217 |
| Nom complet | solute carrier family 27 (fatty acid transporter), member 2 |
| Masse moléculaire calculée | 567 aa, 65 kDa |
| Poids moléculaire observé | 70 kDa |
| Numéro d’acquisition GenBank | BC057770 |
| Symbole du gène | FATP2/SLC27A2 |
| Identification du gène (NCBI) | 11001 |
| Conjugaison | Non conjugué |
| Forme | Liquide |
| Méthode de purification | Purification par affinité contre l'antigène |
| Tampon de stockage | PBS avec azoture de sodium à 0,02 % et glycérol à 50 % pH 7,3 |
| Conditions de stockage | Stocker à -20°C. Stable pendant un an après l'expédition. L'aliquotage n'est pas nécessaire pour le stockage à -20oC Les 20ul contiennent 0,1% de BSA. |
Informations générales
FATP2 is a member of the FATP family which functions in lipid and bile metabolism. It is a 70-kDa protein predominantly expressed in liver and kidney. Kidney FATP2 is localized exclusively to proximal tubule epithelial cells along the apical but not the basolateral membrane, and regulates lipoapoptosis. FATP2 is involved in metabolism-related diseases including nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), and is a potential clinical biomarker and therapeutic target.
Protocole
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for FATP2 antibody 14048-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IHC protocol for FATP2 antibody 14048-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IF protocol for FATP2 antibody 14048-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IP protocol for FATP2 antibody 14048-1-AP | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |
Publications
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Hepatology Letter to the editor: Adipose lipolysis is important for ethanol to induce fatty liver in the NIAAA murine model of chronic and binge ethanol feeding | ||
Hepatology Adipose lipolysis is important for ethanol to induce fatty liver in the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism murine model of chronic and binge ethanol feeding. | ||
Environ Pollut Hepatotoxicity induced in rats by chronic exposure to F-53B, an emerging replacement of perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) | ||
EMBO Rep Lin28 enhances de novo fatty acid synthesis to promote cancer progression via SREBP-1. | ||
Anal Chem Ionic Liquid-Based Extraction System for In-Depth Analysis of Membrane Protein Complexes. | ||
Nephrol Dial Transplant Key enzyme in charge of ketone reabsorption of renal tubular SMCT1 may be a new target in diabetic kidney disease |