- Phare
- Validé par KD/KO
Anticorps Polyclonal de lapin anti-SDCCAG8
SDCCAG8 Polyclonal Antibody for IHC, IF/ICC, ELISA
Hôte / Isotype
Lapin / IgG
Réactivité testée
canin, Humain, poisson-zèbre, rat, souris
Applications
WB, IHC, IF/ICC, IP, ELISA
Conjugaison
Non conjugué
N° de cat : 13471-1-AP
Synonymes
Galerie de données de validation
Applications testées
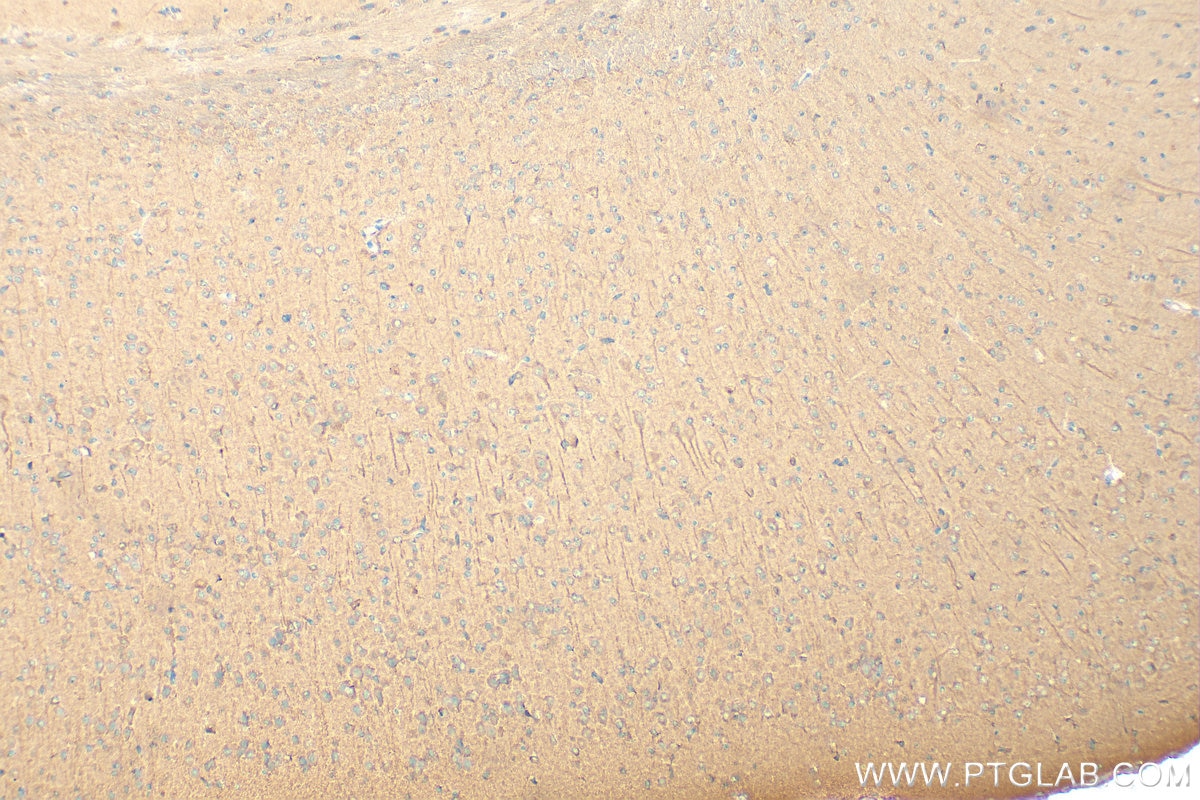
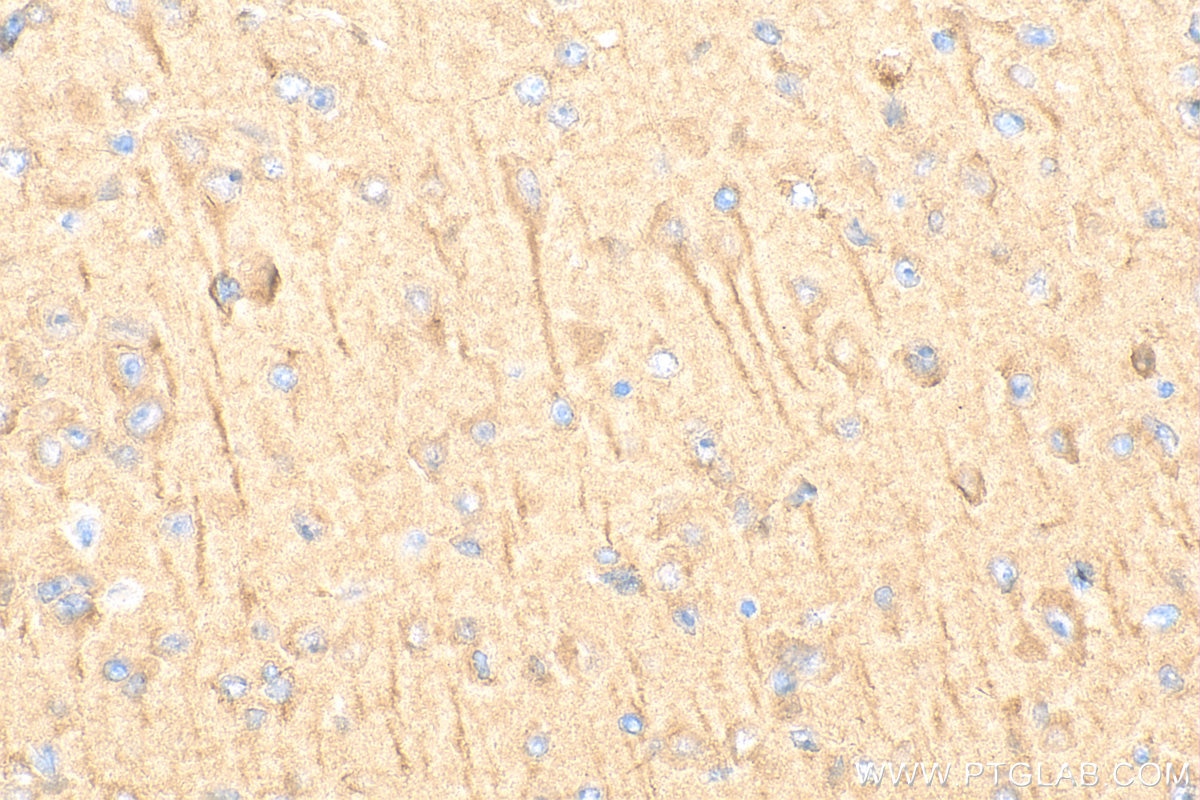
| Résultats positifs en IHC | tissu cérébral de souris, il est suggéré de démasquer l'antigène avec un tampon de TE buffer pH 9.0; (*) À défaut, 'le démasquage de l'antigène peut être 'effectué avec un tampon citrate pH 6,0. |
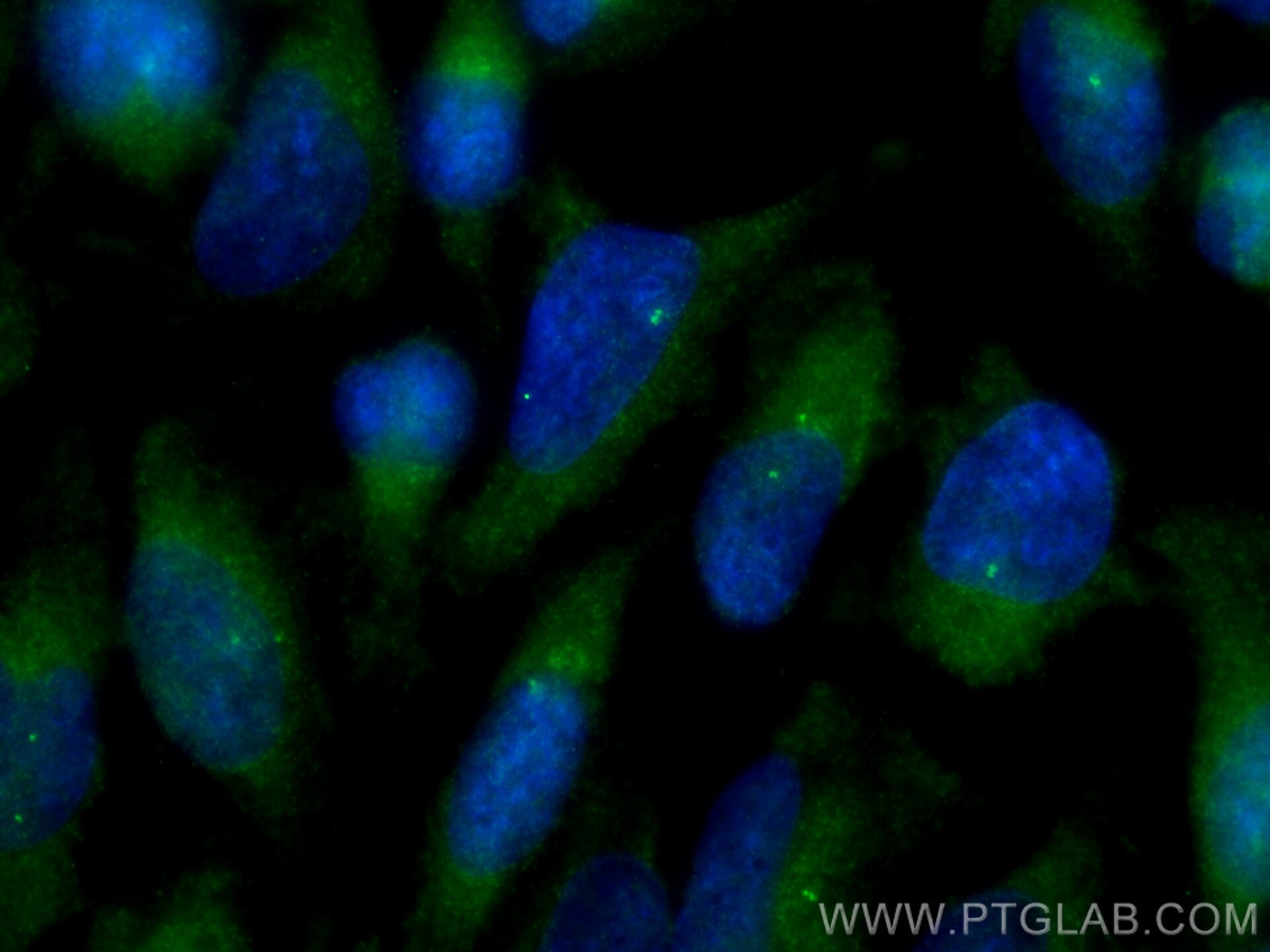
| Résultats positifs en IF/ICC | cellules HeLa, |
Dilution recommandée
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Immunohistochimie (IHC) | IHC : 1:50-1:500 |
| Immunofluorescence (IF)/ICC | IF/ICC : 1:400-1:1600 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, check data in validation data gallery | |
Applications publiées
| KD/KO | See 3 publications below |
| WB | See 9 publications below |
| IHC | See 2 publications below |
| IF | See 9 publications below |
| IP | See 1 publications below |
Informations sur le produit
13471-1-AP cible SDCCAG8 dans les applications de WB, IHC, IF/ICC, IP, ELISA et montre une réactivité avec des échantillons canin, Humain, poisson-zèbre, rat, souris
| Réactivité | canin, Humain, poisson-zèbre, rat, souris |
| Réactivité citée | rat, Humain, poisson-zèbre, souris |
| Hôte / Isotype | Lapin / IgG |
| Clonalité | Polyclonal |
| Type | Anticorps |
| Immunogène | SDCCAG8 Protéine recombinante Ag4264 |
| Nom complet | serologically defined colon cancer antigen 8 |
| Masse moléculaire calculée | 713 aa, 83 kDa |
| Poids moléculaire observé | 83 kDa |
| Numéro d’acquisition GenBank | BC032454 |
| Symbole du gène | SDCCAG8 |
| Identification du gène (NCBI) | 10806 |
| Conjugaison | Non conjugué |
| Forme | Liquide |
| Méthode de purification | Purification par affinité contre l'antigène |
| Tampon de stockage | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol |
| Conditions de stockage | Stocker à -20°C. Stable pendant un an après l'expédition. L'aliquotage n'est pas nécessaire pour le stockage à -20oC Les 20ul contiennent 0,1% de BSA. |
Informations générales
SDCCAG8, also named as CCCAP and NY-CO-8, plays a role in the establishment of cell polarity and epithelial lumen formation. It may play a role in ciliogenesis. Loss of SDCCAG8 function as a cause of a retinal-renal ciliopathy and validates exome capture analysis for broadly heterogeneous single-gene disorders. SDCCAG8 is localized at both centrioles and interacts directly with OFD1 (oral-facial-digital syndrome 1), which is associated with NPHP-RC. SDCCAG8 has 4 isoforms with MW 83,78,73 and 41 kDa (refer to UniProt). Catalog#13471-1-AP can recognize all the four isoforms.
Protocole
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| IHC protocol for SDCCAG8 antibody 13471-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IF protocol for SDCCAG8 antibody 13471-1-AP | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |
Publications
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Nat Genet Candidate exome capture identifies mutation of SDCCAG8 as the cause of a retinal-renal ciliopathy. | ||
Neuron SDCCAG8 Regulates Pericentriolar Material Recruitment and Neuronal Migration in the Developing Cortex. | ||
J Am Soc Nephrol Renal-retinal ciliopathy gene sdccag8 regulates DNA damage response signaling.
| ||
Cell Death Dis Selective loss of RPGRIP1-dependent ciliary targeting of NPHP4, RPGR and SDCCAG8 underlies the degeneration of photoreceptor neurons. |