- Phare
- Validé par KD/KO
Anticorps Polyclonal de lapin anti-SATB1
SATB1 Polyclonal Antibody for WB, IP, ELISA
Hôte / Isotype
Lapin / IgG
Réactivité testée
Humain, rat, souris
Applications
WB, IP, ELISA
Conjugaison
Non conjugué
N° de cat : 15400-1-AP
Synonymes
Galerie de données de validation
Applications testées
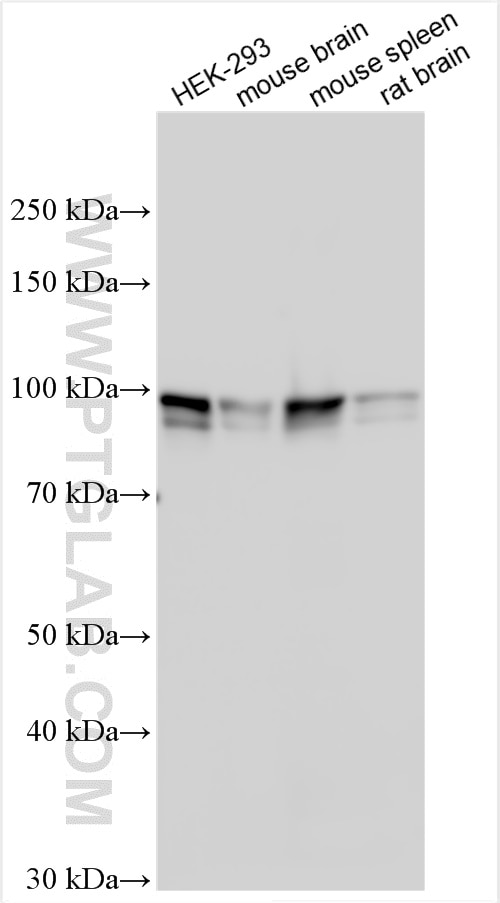
| Résultats positifs en WB | tissu cérébral humain, cellules HEK-293, tissu cérébral de rat, tissu cérébral de souris, tissu splénique de souris |
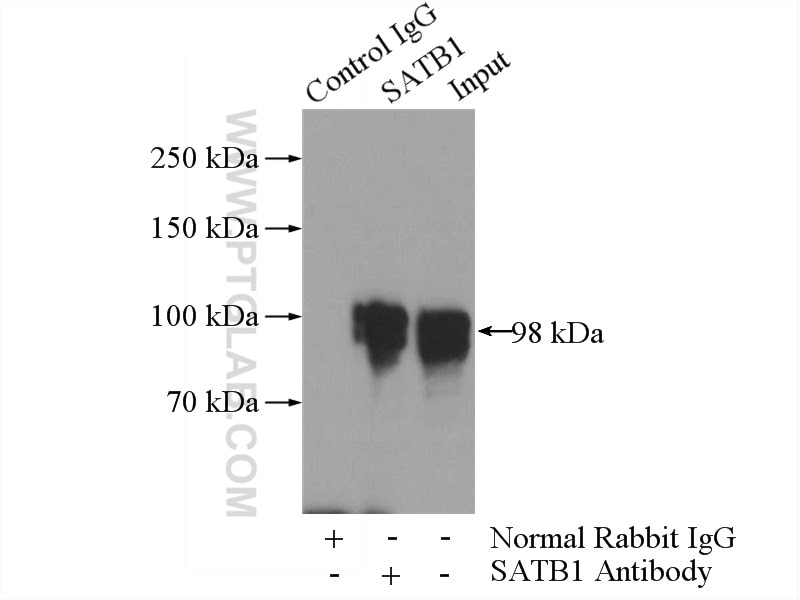
| Résultats positifs en IP | cellules HEK-293 |
Dilution recommandée
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:1000-1:8000 |
| Immunoprécipitation (IP) | IP : 0.5-4.0 ug for 1.0-3.0 mg of total protein lysate |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, check data in validation data gallery | |
Applications publiées
| KD/KO | See 3 publications below |
| WB | See 6 publications below |
| IP | See 1 publications below |
Informations sur le produit
15400-1-AP cible SATB1 dans les applications de WB, IP, ELISA et montre une réactivité avec des échantillons Humain, rat, souris
| Réactivité | Humain, rat, souris |
| Réactivité citée | rat, Humain, souris |
| Hôte / Isotype | Lapin / IgG |
| Clonalité | Polyclonal |
| Type | Anticorps |
| Immunogène | SATB1 Protéine recombinante Ag7615 |
| Nom complet | SATB homeobox 1 |
| Masse moléculaire calculée | 86 kDa |
| Poids moléculaire observé | 86-100 kDa |
| Numéro d’acquisition GenBank | BC001744 |
| Symbole du gène | SATB1 |
| Identification du gène (NCBI) | 6304 |
| Conjugaison | Non conjugué |
| Forme | Liquide |
| Méthode de purification | Purification par affinité contre l'antigène |
| Tampon de stockage | PBS avec azoture de sodium à 0,02 % et glycérol à 50 % pH 7,3 |
| Conditions de stockage | Stocker à -20°C. Stable pendant un an après l'expédition. L'aliquotage n'est pas nécessaire pour le stockage à -20oC Les 20ul contiennent 0,1% de BSA. |
Informations générales
Epigenetic modifications and dynamic changes in chromatin organization by organizer proteins have recently been shown to play an instrumental role in regulating cancer-promoting genes. Special AT-rich binding protein (SATB1) is a unique type of global regulator that integrates higher-order chromatin organization -withregulation of gene expression. [PMID:23076250,22998183,23121661] SATB1 is a T cell-enriched transcription factor and a chromatin organizer essential for controlling genes that participate in T-cell development and activation. It regulates gene expression by periodically anchoring matrix attachment regions to the nuclear matrix and directly recruiting chromatin-modifying factors. Depending on its posttranslational modifications, SATB1 activates or represses multiple genes.Its expression is regulated by interleukin-4 (IL4) during T helper-2(Th2) cell differentiation[PMID: 20522714]. The calculated molecular weight of SATB1 is 86 kDa, but modified SATB1 is about 100 kDa (PMID: 22879953).
Protocole
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for SATB1 antibody 15400-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IP protocol for SATB1 antibody 15400-1-AP | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |
Publications
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Cell Rep SATB1 regulates 3D genome architecture in T cells by constraining chromatin interactions surrounding CTCF-binding sites
| ||
Pharmacol Res Cyclo-(Phe-Tyr) as a novel cyclic dipeptide compound alleviates ischemic/reperfusion brain injury via JUNB/JNK/NF-κB and SOX5/PI3K/AKT pathways. | ||
Mol Neurobiol SATB1/SLC7A11/HO-1 Axis Ameliorates Ferroptosis in Neuron Cells After Ischemic Stroke by Danhong Injection | ||
Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci Effect of STAT3 mediated epigenetic regulation in pre-eclampsia: an analysis of trial data. | ||
Int J Med Sci SATB1 Knockdown Inhibits Proliferation and Invasion and Decreases Chemoradiation Resistance in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Cells by Reversing EMT and Suppressing MMP-9.
| ||
Int J Clin Exp Pathol Silencing SATB1 influences cell invasion, migration, proliferation, and drug resistance in nasopharyngeal carcinoma.
|