Anticorps Polyclonal de lapin anti-RPL5
RPL5 Polyclonal Antibody for ELISA
Hôte / Isotype
Lapin / IgG
Réactivité testée
Humain, singe, souris et plus (1)
Applications
WB, IF, PLA, ELISA
Conjugaison
Non conjugué
N° de cat : 15430-1-AP
Synonymes
Galerie de données de validation
Applications testées
Applications publiées
| WB | See 2 publications below |
| IF | See 1 publications below |
Informations sur le produit
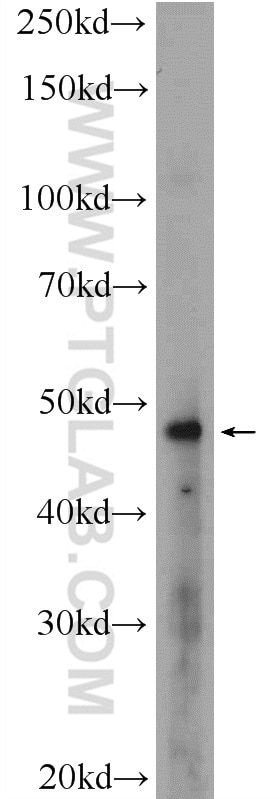
15430-1-AP cible RPL5 dans les applications de WB, IF, PLA, ELISA et montre une réactivité avec des échantillons Humain, singe, souris
| Réactivité | Humain, singe, souris |
| Réactivité citée | Humain, xénope |
| Hôte / Isotype | Lapin / IgG |
| Clonalité | Polyclonal |
| Type | Anticorps |
| Immunogène | RPL5 Protéine recombinante Ag7673 |
| Nom complet | ribosomal protein L5 |
| Masse moléculaire calculée | 34 kDa |
| Numéro d’acquisition GenBank | BC001882 |
| Symbole du gène | RPL5 |
| Identification du gène (NCBI) | 6125 |
| Conjugaison | Non conjugué |
| Forme | Liquide |
| Méthode de purification | Purification par affinité contre l'antigène |
| Tampon de stockage | PBS avec azoture de sodium à 0,02 % et glycérol à 50 % pH 7,3 |
| Conditions de stockage | Stocker à -20°C. Stable pendant un an après l'expédition. L'aliquotage n'est pas nécessaire pour le stockage à -20oC Les 20ul contiennent 0,1% de BSA. |
Informations générales
The mammalian ribosome is a macromolecular assembly of 4 RNA species (rRNAs) and approximately 80 different proteins, including RPL5. RPL5 (ribosome protein L15) is rquired for rRNA maturation and formation of the 60S ribosomal subunits, and defects or mutation in RPL5 is the cause of DBA6.
Publications
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Sci Adv Genomic gain of RRS1 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma through reducing the RPL11-MDM2-p53 signaling. | ||
J Cell Biol Phase separation and toxicity of C9orf72 poly(PR) depends on alternate distribution of arginine. | ||
Elife Receptor-specific interactome as a hub for rapid cue-induced selective translation in axons. | ||
Cell Signal Interleukin-6 influences stress-signalling by reducing the expression of the mTOR-inhibitor REDD1 in a STAT3-dependent manner. | ||
Open Biol ESCRT-II controls retinal axon growth by regulating DCC receptor levels and local protein synthesis. |