- Phare
- Validé par KD/KO
Anticorps Polyclonal de lapin anti-RGS14
RGS14 Polyclonal Antibody for WB, IP, IHC, ELISA
Hôte / Isotype
Lapin / IgG
Réactivité testée
Humain, souris et plus (2)
Applications
WB, IHC, IP, CoIP, ELISA, IF
Conjugaison
Non conjugué
N° de cat : 16258-1-AP
Synonymes
Galerie de données de validation
Applications testées
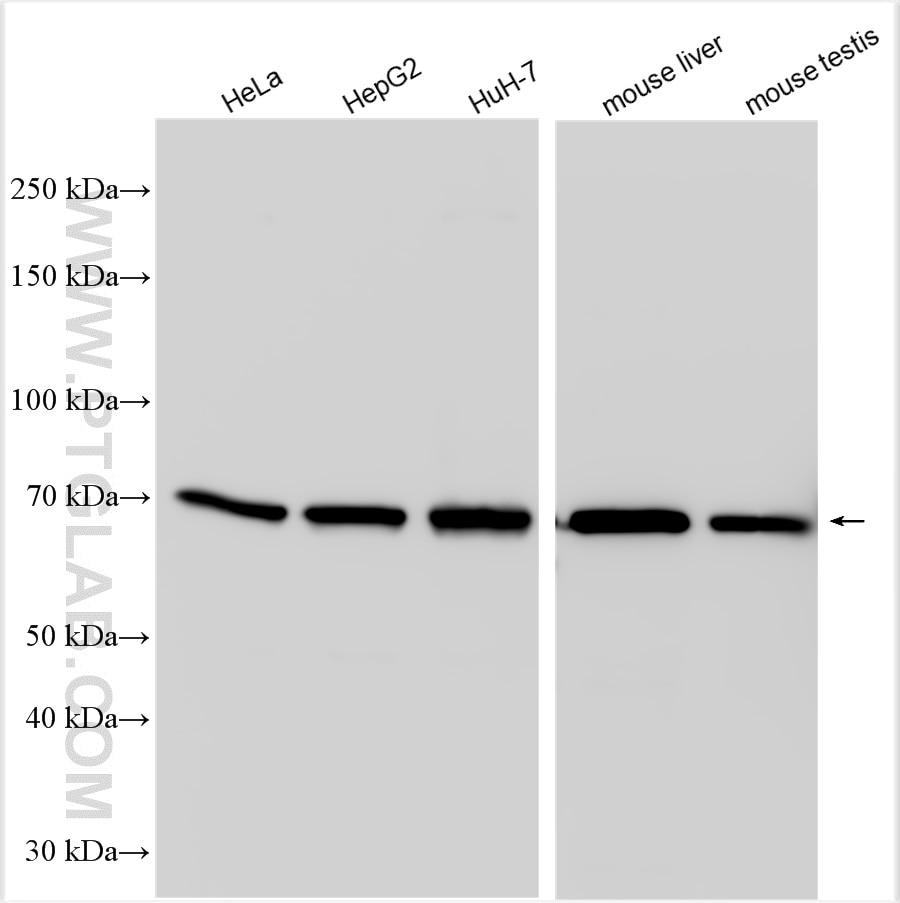
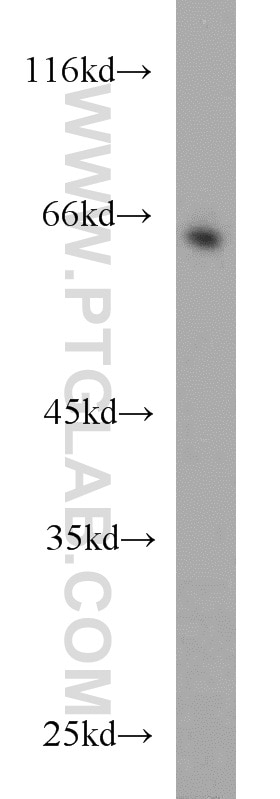
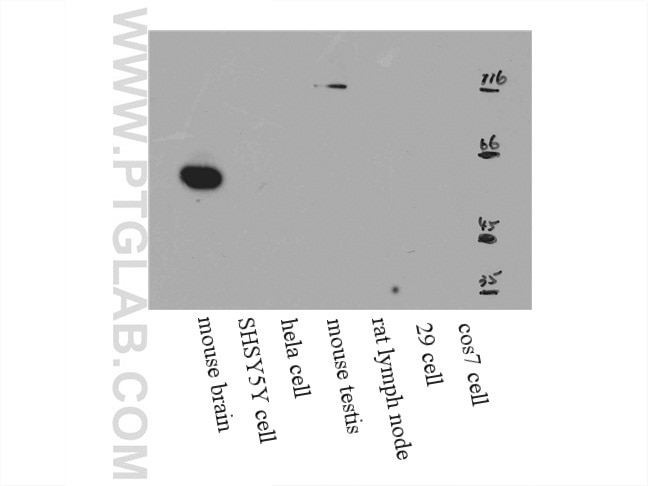
| Résultats positifs en WB | cellules HeLa, cellules HepG2, cellules HuH-7, tissu cérébral de souris, tissu hépatique de souris, tissu splénique de souris, tissu testiculaire de souris |
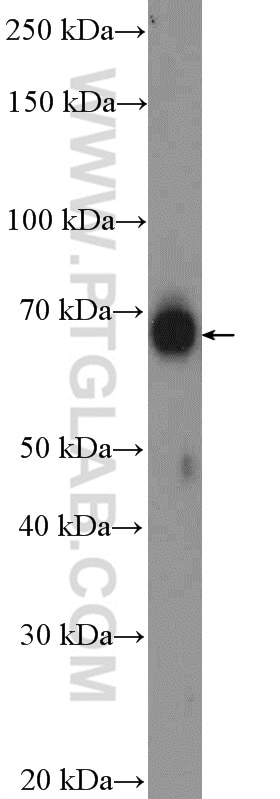
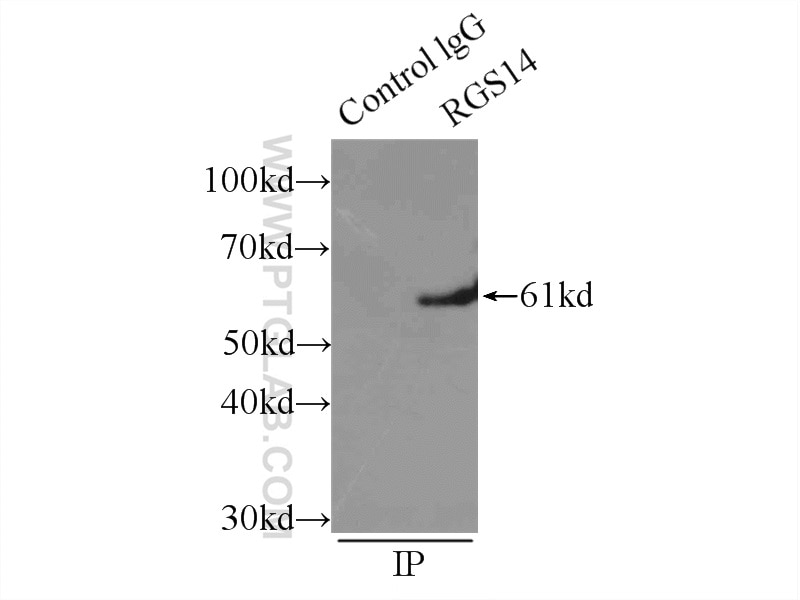
| Résultats positifs en IP | tissu cérébral de souris |
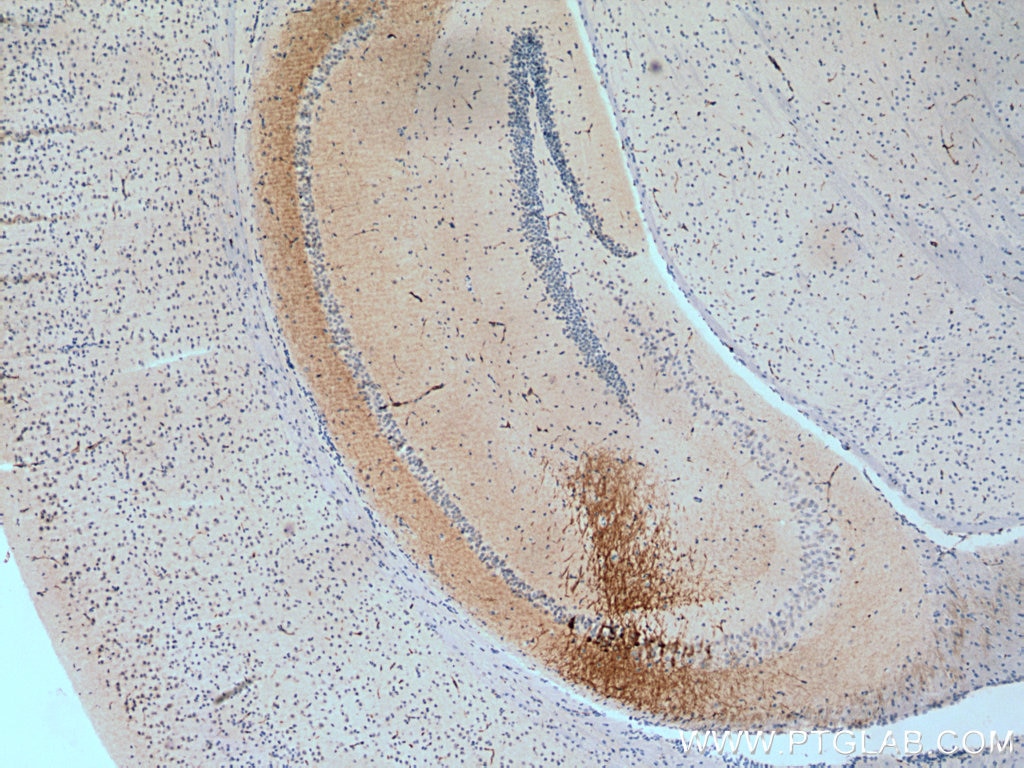
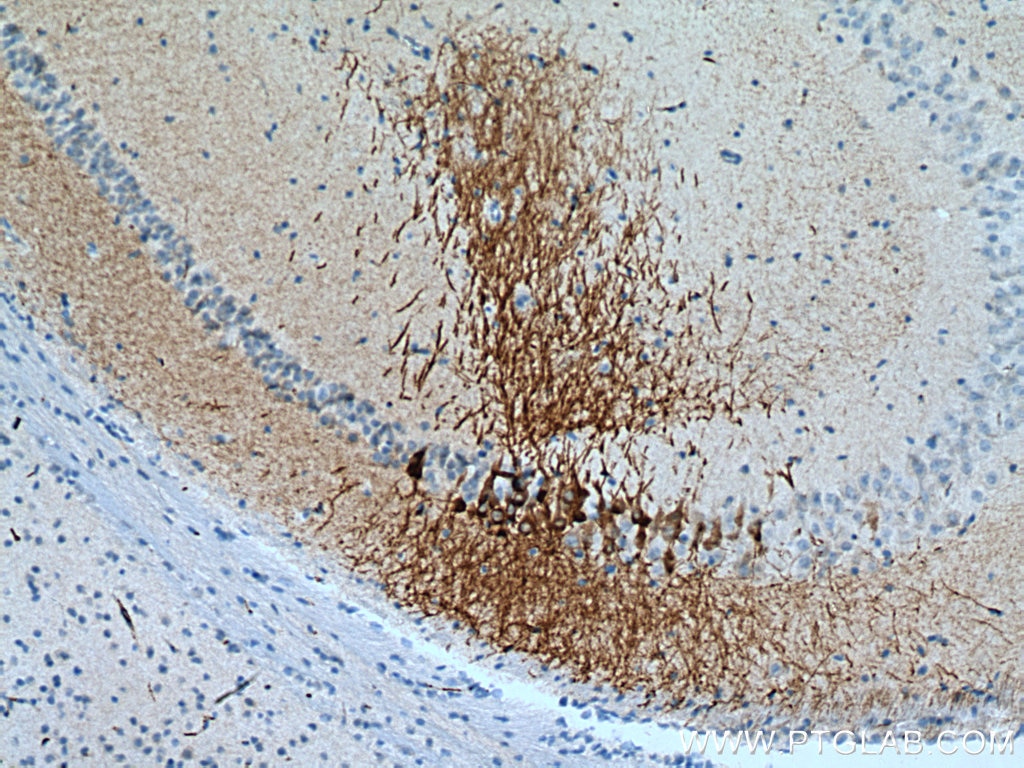
| Résultats positifs en IHC | tissu cérébral de souris, il est suggéré de démasquer l'antigène avec un tampon de TE buffer pH 9.0; (*) À défaut, 'le démasquage de l'antigène peut être 'effectué avec un tampon citrate pH 6,0. |
Dilution recommandée
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:1000-1:4000 |
| Immunoprécipitation (IP) | IP : 0.5-4.0 ug for 1.0-3.0 mg of total protein lysate |
| Immunohistochimie (IHC) | IHC : 1:2500-1:10000 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, check data in validation data gallery | |
Applications publiées
| KD/KO | See 2 publications below |
| WB | See 5 publications below |
| IHC | See 3 publications below |
| IF | See 4 publications below |
| IP | See 1 publications below |
| CoIP | See 1 publications below |
Informations sur le produit
16258-1-AP cible RGS14 dans les applications de WB, IHC, IP, CoIP, ELISA, IF et montre une réactivité avec des échantillons Humain, souris
| Réactivité | Humain, souris |
| Réactivité citée | rat, Humain, singe, souris |
| Hôte / Isotype | Lapin / IgG |
| Clonalité | Polyclonal |
| Type | Anticorps |
| Immunogène | RGS14 Protéine recombinante Ag9292 |
| Nom complet | regulator of G-protein signaling 14 |
| Masse moléculaire calculée | 566 aa, 61 kDa |
| Poids moléculaire observé | 60-65 kDa |
| Numéro d’acquisition GenBank | BC014094 |
| Symbole du gène | RGS14 |
| Identification du gène (NCBI) | 10636 |
| Conjugaison | Non conjugué |
| Forme | Liquide |
| Méthode de purification | Purification par affinité contre l'antigène |
| Tampon de stockage | PBS avec azoture de sodium à 0,02 % et glycérol à 50 % pH 7,3 |
| Conditions de stockage | Stocker à -20°C. Stable pendant un an après l'expédition. L'aliquotage n'est pas nécessaire pour le stockage à -20oC Les 20ul contiennent 0,1% de BSA. |
Informations générales
RGS14, a member of the R12 subfamily of RGS proteins, is highly expressed in the brain and is a natural suppressor of CA2 hippocampal synaptic plasticity and learning and memory. RGS14 was first identified as a complex scaffolding protein with an unconventional domain structure that allows it to interact with various protein binding partners. RGS14 contains one RGS domain, two Raf-like Ras-binding domains (RBDs), and one GoLoco domain. The protein attenuates the signaling activity of G-proteins by binding, through its GoLoco domain, to specific types of activated, GTP-bound G alpha subunits. Acting as a GTPase activating protein (GAP), the protein increases the rate of conversion of the GTP to GDP.
Protocole
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for RGS14 antibody 16258-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IHC protocol for RGS14 antibody 16258-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IP protocol for RGS14 antibody 16258-1-AP | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |
Publications
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Mol Metab Hepatic Regulator of G protein Signaling 14 Ameliorates NAFLD through Activating cAMP-AMPK Signaling by Targeting Giα1/3
| ||
Brain Struct Funct Regulator of G protein signaling 14 (RGS14) is expressed pre- and postsynaptically in neurons of hippocampus, basal ganglia, and amygdala of monkey and human brain. | ||
Exp Neurol Modelling cognitive deficits in Parkinson's disease: Is CA2 a gateway for hippocampal synucleinopathy? | ||
J Biol Chem Human genetic variants disrupt RGS14 nuclear shuttling and regulation of LTP in hippocampal neurons. | ||
J Biol Chem RGS14 regulates hormone-sensitive NPT2A-mediated renal phosphate uptake via binding to the NHERF1 scaffolding protein. | ||
J Biol Chem 14-3-3γ binds RGS14 at distinct sites to inhibit the RGS14:Gαi-AlF4- signaling complex and RGS14 nuclear localization. |