- Phare
- Validé par KD/KO
Anticorps Polyclonal de lapin anti-RBPJ
RBPJ Polyclonal Antibody for WB, IP, IHC, ELISA
Hôte / Isotype
Lapin / IgG
Réactivité testée
Humain, souris
Applications
WB, IP, IF, IHC, ELISA
Conjugaison
Non conjugué
N° de cat : 14613-1-AP
Synonymes
Galerie de données de validation
Applications testées
| Résultats positifs en WB | tissu rénal de souris, cellules HEK-293, cellules HeLa, cellules HepG2, cellules MCF-7, tissu cardiaque humain, tissu hépatique humain, tissu pancréatique de souris |
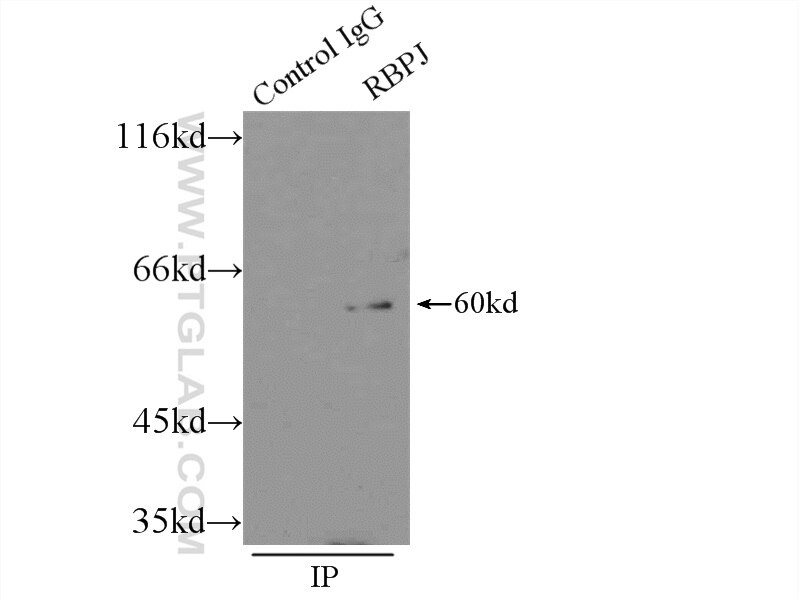
| Résultats positifs en IP | cellules HEK-293 |
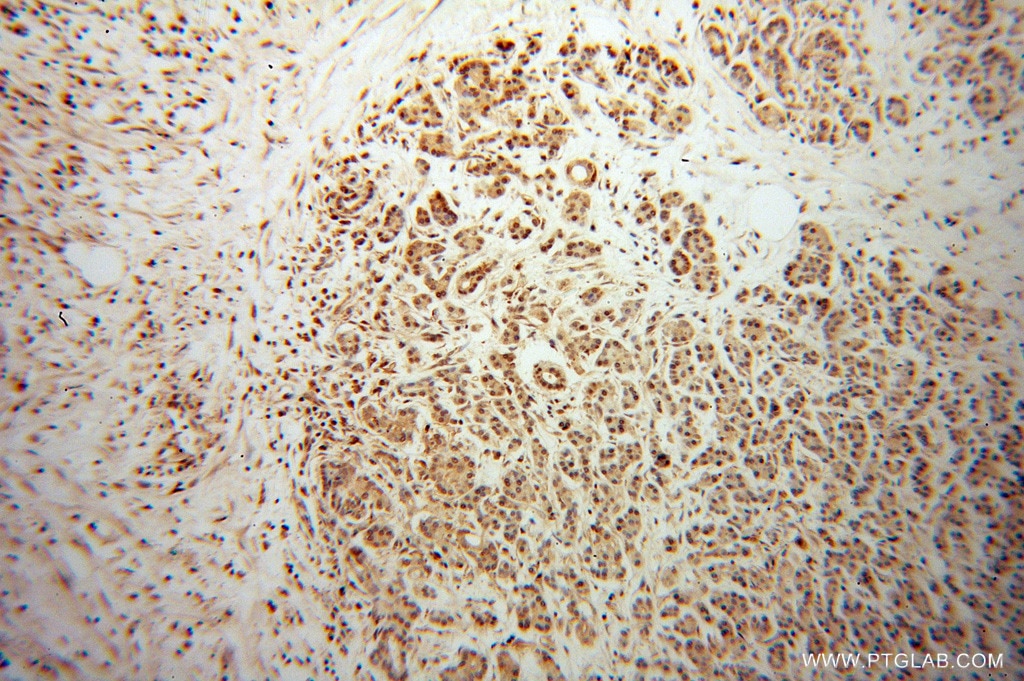
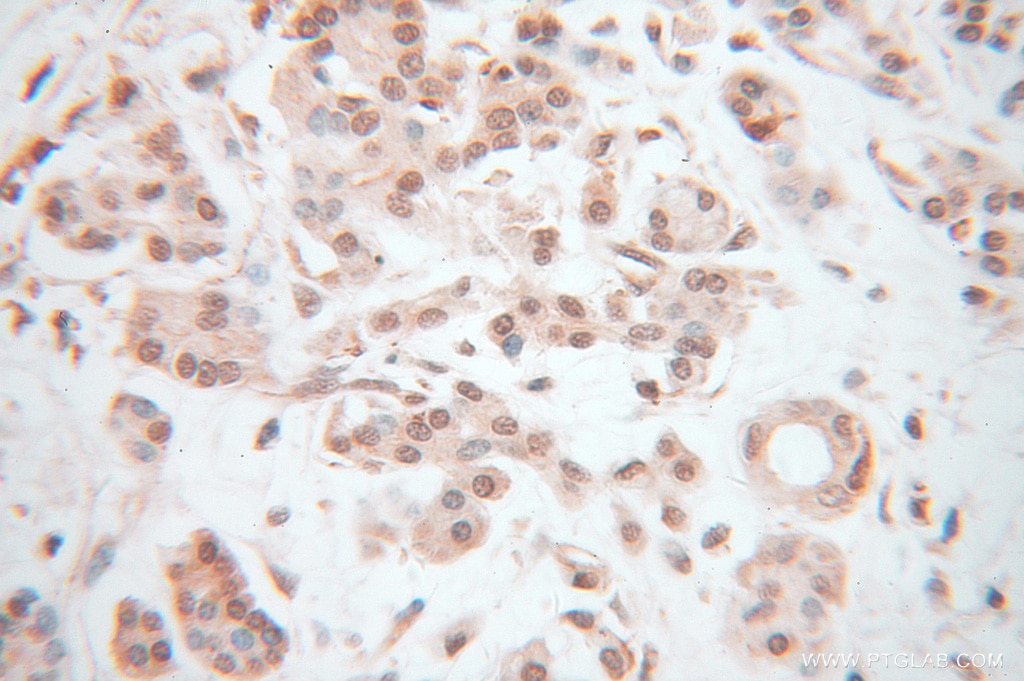
| Résultats positifs en IHC | tissu de cancer du pancréas humain il est suggéré de démasquer l'antigène avec un tampon de TE buffer pH 9.0; (*) À défaut, 'le démasquage de l'antigène peut être 'effectué avec un tampon citrate pH 6,0. |
Dilution recommandée
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:500-1:2000 |
| Immunoprécipitation (IP) | IP : 0.5-4.0 ug for 1.0-3.0 mg of total protein lysate |
| Immunohistochimie (IHC) | IHC : 1:20-1:200 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, check data in validation data gallery | |
Applications publiées
| KD/KO | See 2 publications below |
| WB | See 9 publications below |
| IHC | See 3 publications below |
| IF | See 1 publications below |
Informations sur le produit
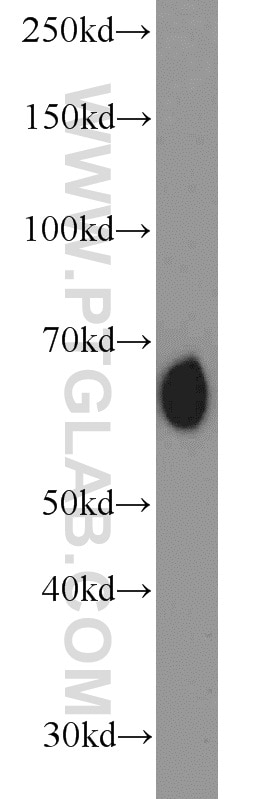
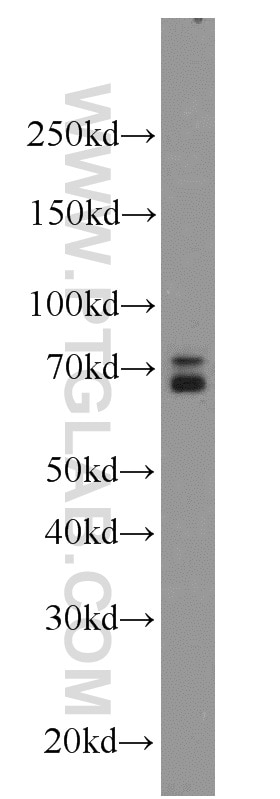
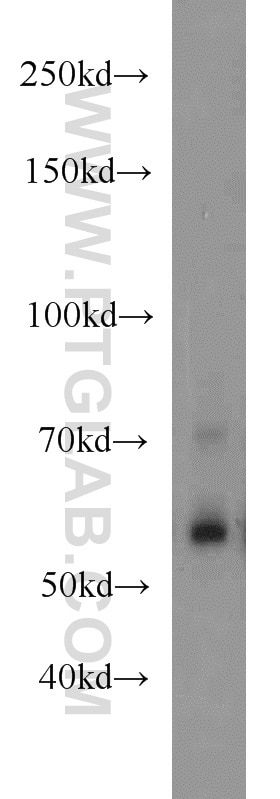
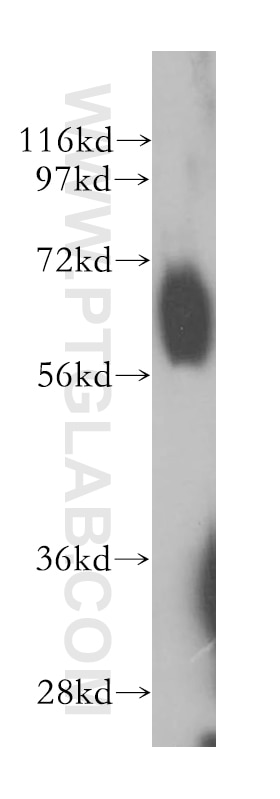
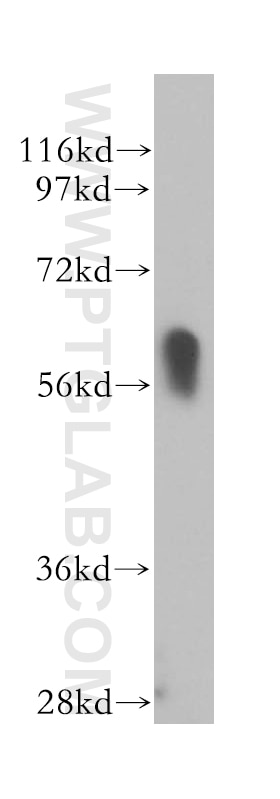
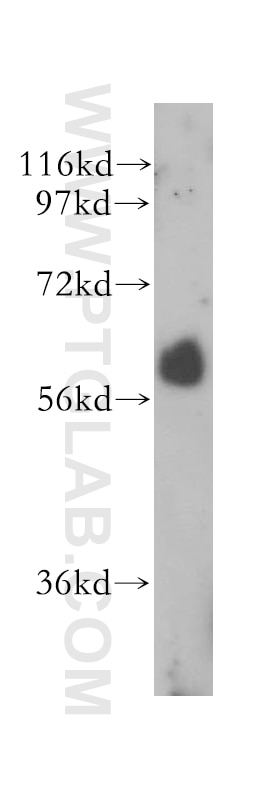
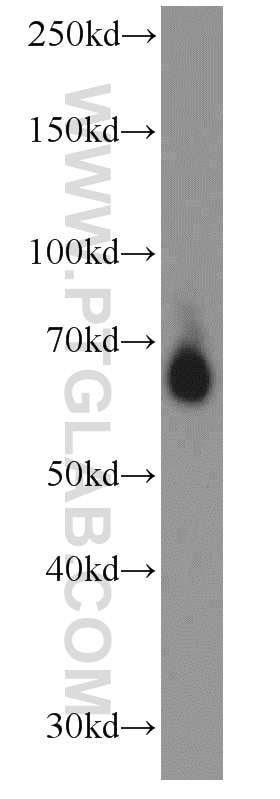
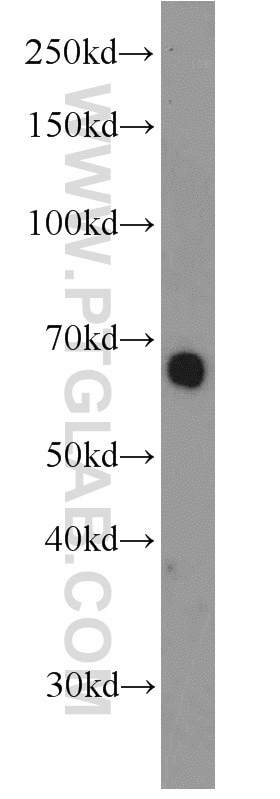
14613-1-AP cible RBPJ dans les applications de WB, IP, IF, IHC, ELISA et montre une réactivité avec des échantillons Humain, souris
| Réactivité | Humain, souris |
| Réactivité citée | Humain, souris |
| Hôte / Isotype | Lapin / IgG |
| Clonalité | Polyclonal |
| Type | Anticorps |
| Immunogène | RBPJ Protéine recombinante Ag6206 |
| Nom complet | recombination signal binding protein for immunoglobulin kappa J region |
| Masse moléculaire calculée | 56 kDa |
| Poids moléculaire observé | 60 kDa |
| Numéro d’acquisition GenBank | BC064976 |
| Symbole du gène | RBPJ |
| Identification du gène (NCBI) | 3516 |
| Conjugaison | Non conjugué |
| Forme | Liquide |
| Méthode de purification | Purification par affinité contre l'antigène |
| Tampon de stockage | PBS avec azoture de sodium à 0,02 % et glycérol à 50 % pH 7,3 |
| Conditions de stockage | Stocker à -20°C. Stable pendant un an après l'expédition. L'aliquotage n'est pas nécessaire pour le stockage à -20oC Les 20ul contiennent 0,1% de BSA. |
Informations générales
RBPJ, also named as IGKJRB, IGKJRB1, RBPJK, RBPSUH, NY-REN-30, CBF-1 and CSL, belongs to the Su(H) family. It is a transcriptional regulator that plays a central role in Notch signaling, a signaling pathway involved in cell-cell communication that regulates a broad spectrum of cell-fate determinations. RBPJ acts as a transcriptional repressor when it is not associated with Notch proteins. It is specifically binds to the immunoglobulin kappa-type J segment recombination signal sequence. RBPJ binds to the Runx3 promoter in the atrioventricular canal in vivo, and inhibition of Notch reduces RUNX3 expression in the cardiac cushion of embryonic hearts.
Protocole
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for RBPJ antibody 14613-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IHC protocol for RBPJ antibody 14613-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IP protocol for RBPJ antibody 14613-1-AP | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |
Publications
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Cell Biosci Blockade of the Arid5a/IL-6/STAT3 axis underlies the anti-inflammatory effect of Rbpjl in acute pancreatitis. | ||
J Biol Chem RUNX3 maintains the mesenchymal phenotype after termination of the Notch signal.
| ||
Front Pharmacol DAPT Attenuates Cadmium-Induced Toxicity in Mice by Inhibiting Inflammation and the Notch/HES-1 Signaling Axis. | ||
Inflamm Res Salidroside alleviates cadmium-induced toxicity in mice by restoring the notch/HES-1 and RIP1-driven inflammatory signaling axis. | ||
Inflamm Res Gisenoside Rg1 attenuates cadmium-induced neurotoxicity in vitro and in vivo by attenuating oxidative stress and inflammation | ||
Neurotoxicology Edaravone attenuates cadmium-induced toxicity by inhibiting oxidative stress and inflammation in ICR mice. |