Anticorps Polyclonal de lapin anti-Phospho-TAU (Thr181)
Phospho-TAU (Thr181) Polyclonal Antibody for WB, IHC, ELISA
Hôte / Isotype
Lapin / IgG
Réactivité testée
Humain, souris
Applications
WB, IHC, IF, ELISA
Conjugaison
Non conjugué
N° de cat : 28866-1-AP
Synonymes
Galerie de données de validation
Applications testées
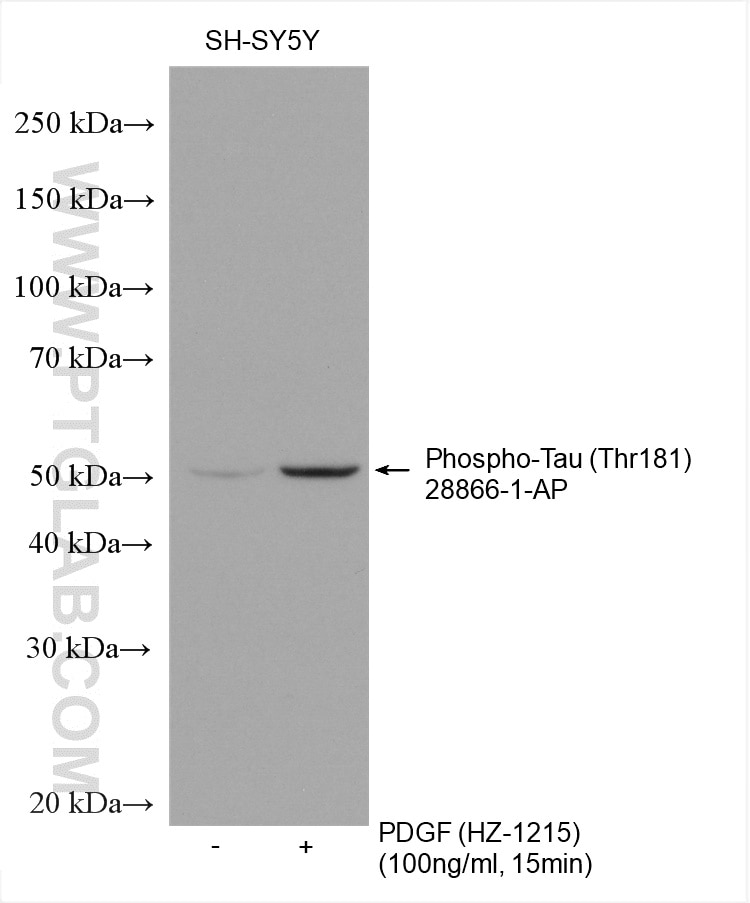
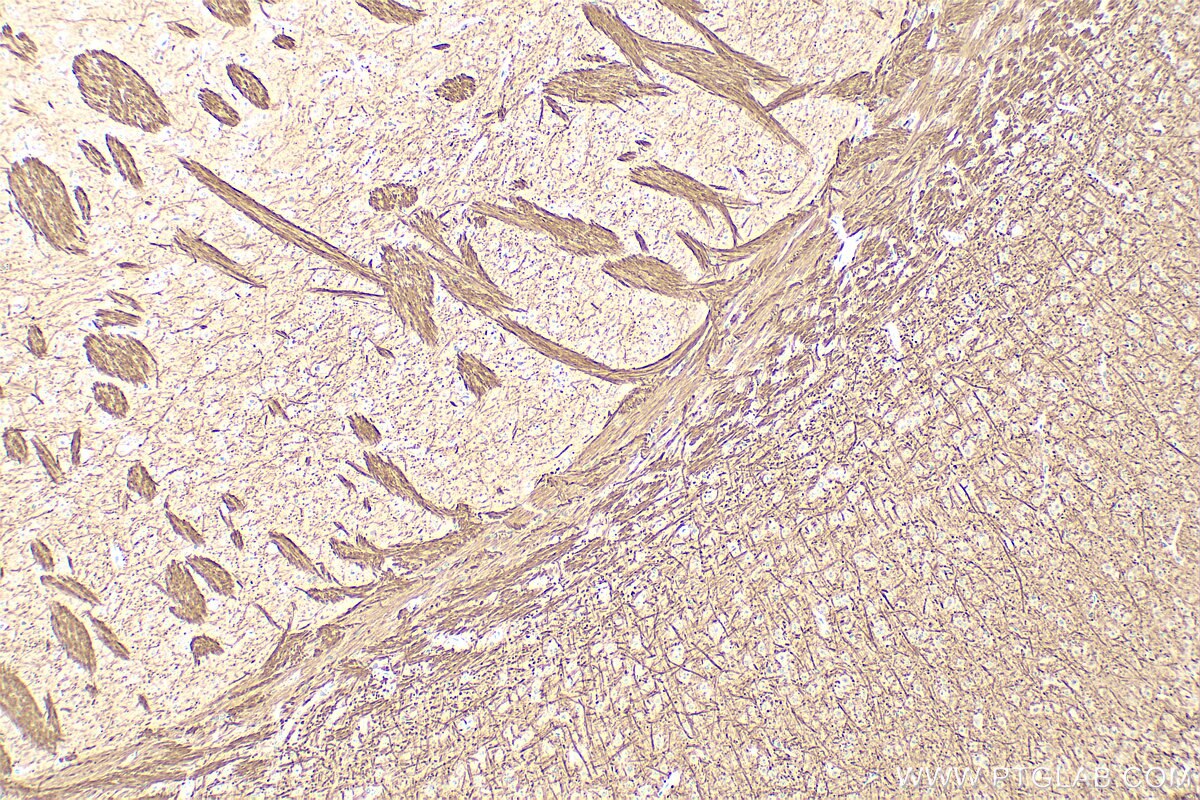
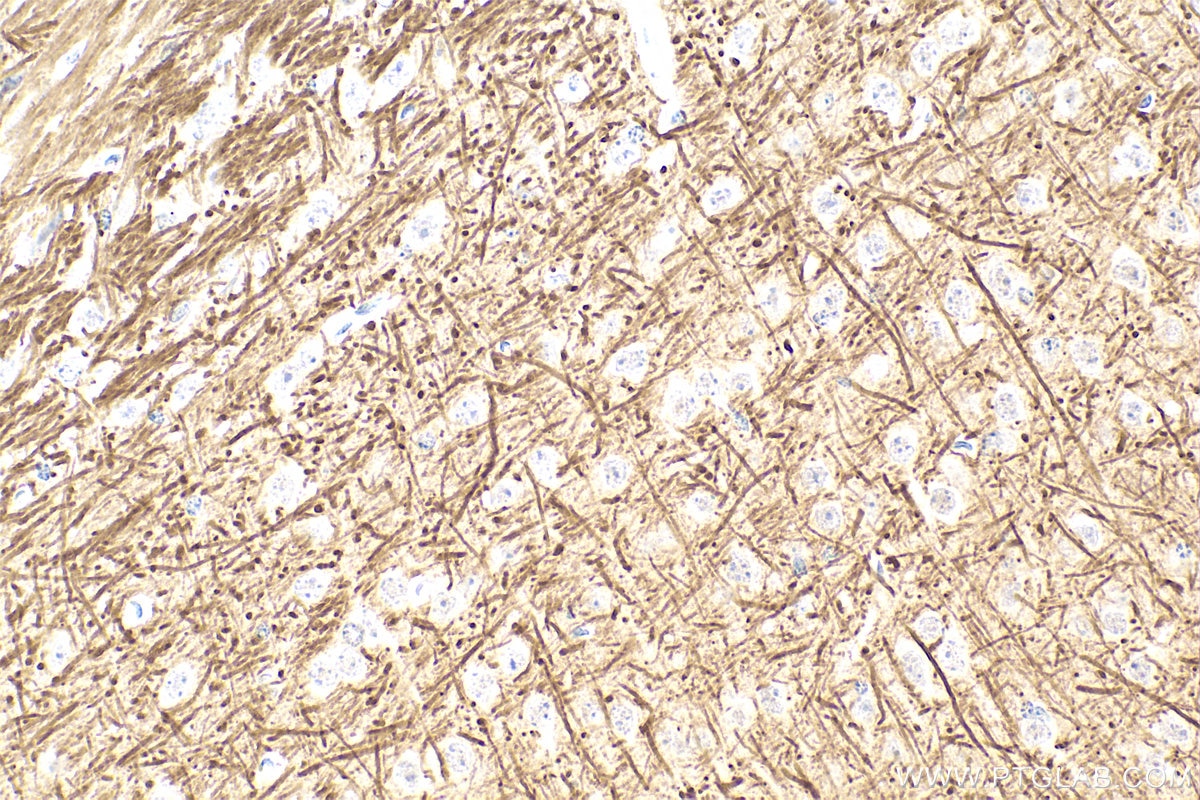
| Résultats positifs en WB | cellules SH-SY5Y traitées au PDGF, |
| Résultats positifs en IHC | tissu cérébral de souris, il est suggéré de démasquer l'antigène avec un tampon de TE buffer pH 9.0; (*) À défaut, 'le démasquage de l'antigène peut être 'effectué avec un tampon citrate pH 6,0. |
Dilution recommandée
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:500-1:1000 |
| Immunohistochimie (IHC) | IHC : 1:50-1:500 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, check data in validation data gallery | |
Applications publiées
| WB | See 10 publications below |
| IF | See 1 publications below |
Informations sur le produit
28866-1-AP cible Phospho-TAU (Thr181) dans les applications de WB, IHC, IF, ELISA et montre une réactivité avec des échantillons Humain, souris
| Réactivité | Humain, souris |
| Réactivité citée | Humain, souris |
| Hôte / Isotype | Lapin / IgG |
| Clonalité | Polyclonal |
| Type | Anticorps |
| Immunogène | Peptide |
| Nom complet | microtubule-associated protein tau |
| Masse moléculaire calculée | 37-46, 79-81 kDa |
| Poids moléculaire observé | 50-80 kDa |
| Numéro d’acquisition GenBank | BC000558 |
| Symbole du gène | TAU |
| Identification du gène (NCBI) | 4137 |
| Conjugaison | Non conjugué |
| Forme | Liquide |
| Méthode de purification | Purification par protéine A |
| Tampon de stockage | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol |
| Conditions de stockage | Stocker à -20°C. Stable pendant un an après l'expédition. L'aliquotage n'est pas nécessaire pour le stockage à -20oC Les 20ul contiennent 0,1% de BSA. |
Informations générales
Tau (tubulin-associated unit) is a microtubule-associated protein (also known as MAPT), expressed mainly in neurons of the central nervous system. Its primary function is to modulate microtubule dynamics for maintaining axonal cytoskeleton. The Tau protein has six isoforms produced from a single gene through alternative RNA splicing. Isoforms differ in number of inserts at the N-terminal half and the number of repeats at the C-terminal half (3 repeat-3R; 4 repeat-4R). Tau is hyperphosphorylated during aging and in age-related neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's disease (AD) and fronto-temporal dementia. Hyperphosphorylation of Tau leads to the formation of neurofibrillary tangles (NFT) in the neurons and glia cells, which is one of the hallmarks of AD.
Protocole
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for Phospho-TAU (Thr181) antibody 28866-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IHC protocol for Phospho-TAU (Thr181) antibody 28866-1-AP | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |
Publications
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis Apolipoprotein E ε4 triggers neurotoxicity via cholesterol accumulation, acetylcholine dyshomeostasis, and PKCε mislocalization in cholinergic neuronal cells | ||
Neural Plast Treatment Combining Focused Ultrasound with Gastrodin Alleviates Memory Deficit and Neuropathology in an Alzheimer's Disease-Like Experimental Mouse Model. | ||
Neurotoxicology Protective mechanism of gold nanoparticles on human neural stem cells injured by β-amyloid protein through miR-21-5p/SOCS6 pathway | ||
ACS Biomater Sci Eng RVG29 Peptide-Modified Exosomes Loaded with Mir-133b Mediate the RhoA-ROCK Pathway to Improve Motor and Neurological Symptoms in Parkinson's Disease | ||
ACS Chem Neurosci First in Class Dual Non-ATP-Competitive Glycogen Synthase Kinase 3β/Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors as a Potential Therapeutic to Treat Alzheimer's Disease | ||
Eur J Pharmacol Cerebroprotein hydrolysate-I ameliorates cognitive dysfunction in APP/PS1 mice by inhibiting ferroptosis via the p53/SAT1/ALOX15 signalling pathway |