- Phare
- Validé par KD/KO
Anticorps Polyclonal de lapin anti-PSPC1
PSPC1 Polyclonal Antibody for WB, IP, IF, ELISA
Hôte / Isotype
Lapin / IgG
Réactivité testée
Humain, rat, souris
Applications
WB, IF/ICC, IP, ELISA
Conjugaison
Non conjugué
N° de cat : 16714-1-AP
Synonymes
Galerie de données de validation
Applications testées
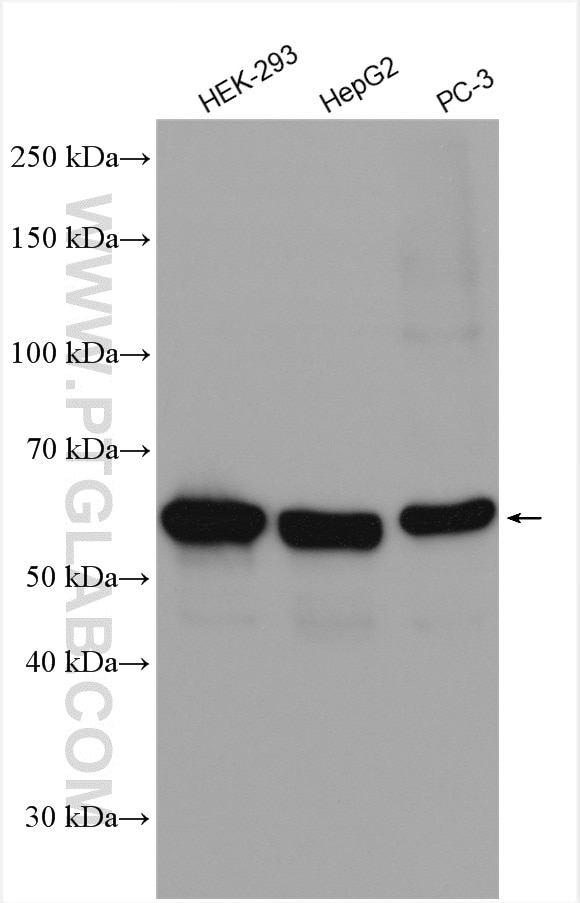
| Résultats positifs en WB | cellules HEK-293, cellules HepG2, cellules PC-3 |
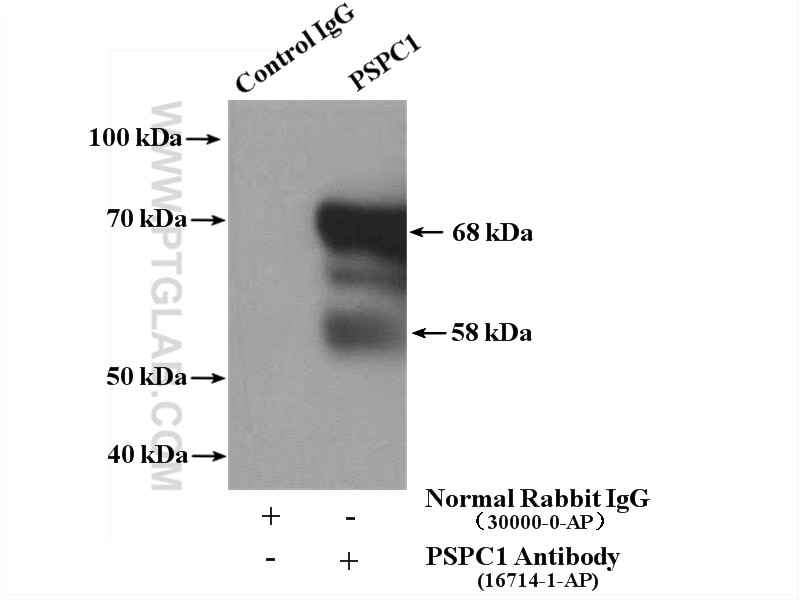
| Résultats positifs en IP | cellules HEK-293 |
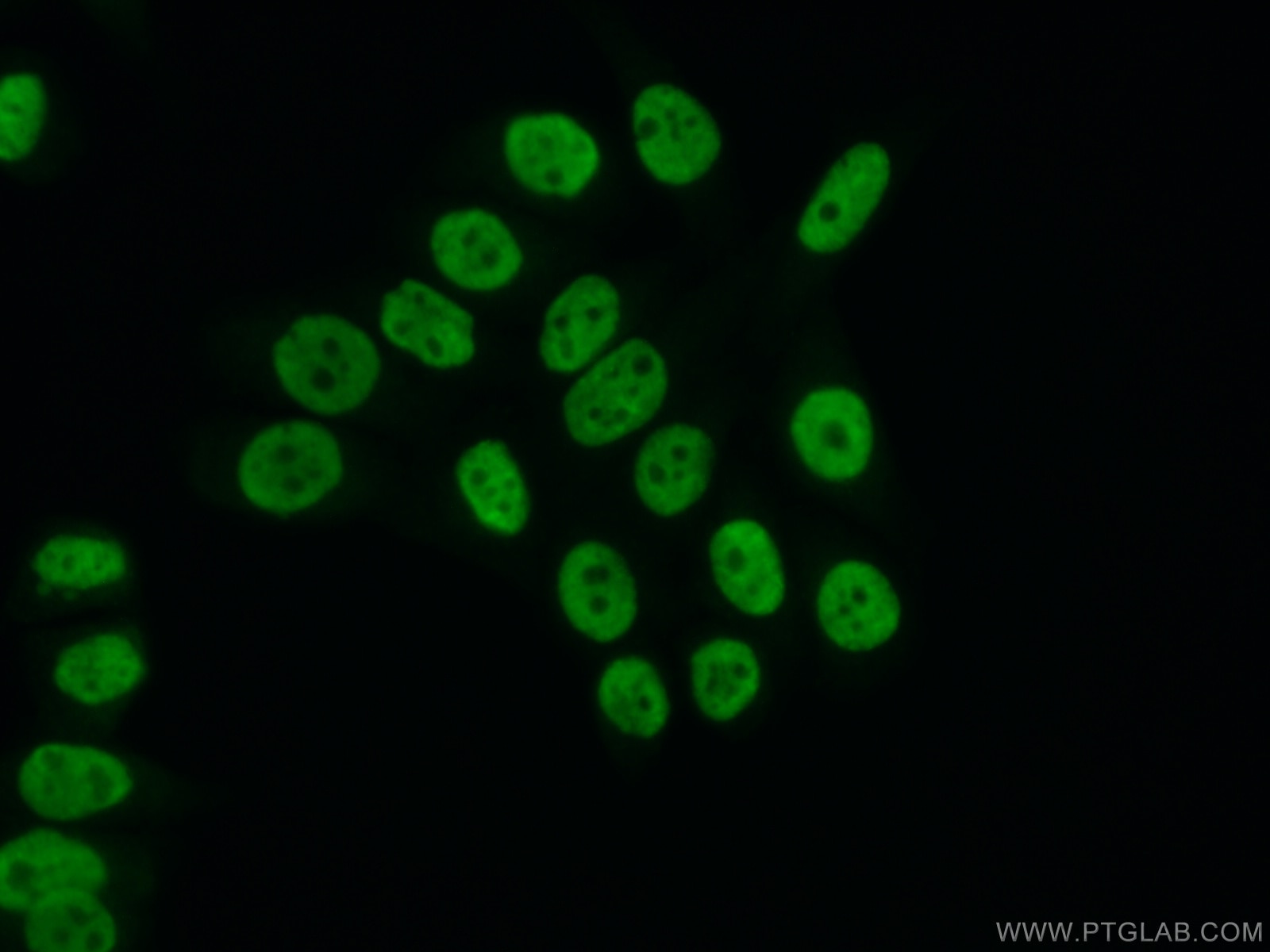
| Résultats positifs en IF/ICC | cellules PC-3 |
Dilution recommandée
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:5000-1:50000 |
| Immunoprécipitation (IP) | IP : 0.5-4.0 ug for 1.0-3.0 mg of total protein lysate |
| Immunofluorescence (IF)/ICC | IF/ICC : 1:50-1:500 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, check data in validation data gallery | |
Applications publiées
| KD/KO | See 1 publications below |
| WB | See 6 publications below |
| IF | See 2 publications below |
Informations sur le produit
16714-1-AP cible PSPC1 dans les applications de WB, IF/ICC, IP, ELISA et montre une réactivité avec des échantillons Humain, rat, souris
| Réactivité | Humain, rat, souris |
| Réactivité citée | Humain, souris |
| Hôte / Isotype | Lapin / IgG |
| Clonalité | Polyclonal |
| Type | Anticorps |
| Immunogène | PSPC1 Protéine recombinante Ag10136 |
| Nom complet | paraspeckle component 1 |
| Masse moléculaire calculée | 523 aa, 59 kDa |
| Poids moléculaire observé | 66 kDa |
| Numéro d’acquisition GenBank | BC014184 |
| Symbole du gène | PSPC1 |
| Identification du gène (NCBI) | 55269 |
| Conjugaison | Non conjugué |
| Forme | Liquide |
| Méthode de purification | Purification par affinité contre l'antigène |
| Tampon de stockage | PBS avec azoture de sodium à 0,02 % et glycérol à 50 % pH 7,3 |
| Conditions de stockage | Stocker à -20°C. Stable pendant un an après l'expédition. L'aliquotage n'est pas nécessaire pour le stockage à -20oC Les 20ul contiennent 0,1% de BSA. |
Informations générales
PSPC1 (paraspeckle component 1), a known paraspeckle biomarker, is a putative transcription factor that belongs to the Drosophila behavior/human splicing (DBHS) family. PSPC1 was recently identified as a contextual determinant of tumor progression in multiple cancer types involving oncogenic reprogramming to switch proapoptotic TGF-β to prometastatic TGF-β via hijacking of Smad2/3 targeting. Upregulated PSPC1 is correlated with advanced tumor stages and poor survival of patients with breast, lung, and liver cancers. Upregulated PSPC1 potentiates expression of mesenchymal markers, EMT transcription factors (EMT-TF), cancer stem-like cell transcription factors (CSC-TF), and c-Myc-related proliferation genes, thus promoting migration, invasion, spheroid formation, tumor formation, and metastasis.
Protocole
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for PSPC1 antibody 16714-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IF protocol for PSPC1 antibody 16714-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IP protocol for PSPC1 antibody 16714-1-AP | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |
Publications
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Drug Resist Updat Cell membrane-camouflaged bufalin targets NOD2 and overcomes multidrug resistance in pancreatic cancer | ||
Nat Commun K235 acetylation couples with PSPC1 to regulate the m6A demethylation activity of ALKBH5 and tumorigenesis | ||
Nucleic Acids Res mRNAs are sorted for export or degradation before passing through nuclear speckles. | ||
Cancer Lett SKP2 promotes the metastasis of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma by suppressing TRIM21-mediated PSPC1 degradation | ||
Int J Mol Sci The KDET Motif in the Intracellular Domain of the Cell Adhesion Molecule L1 Interacts with Several Nuclear, Cytoplasmic, and Mitochondrial Proteins Essential for Neuronal Functions
| ||
Int J Mol Sci The Interactions of the 70 kDa Fragment of Cell Adhesion Molecule L1 with Topoisomerase 1, Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor γ and NADH Dehydrogenase (Ubiquinone) Flavoprotein 2 Are Involved in Gene Expression and Neuronal L1-Dependent Functions |