- Phare
- Validé par KD/KO
Anticorps Polyclonal de lapin anti-POLI
POLI Polyclonal Antibody for WB, IP, IHC, ELISA
Hôte / Isotype
Lapin / IgG
Réactivité testée
Humain, rat, souris et plus (1)
Applications
WB, IP, IF, IHC, ELISA
Conjugaison
Non conjugué
N° de cat : 13635-1-AP
Synonymes
Galerie de données de validation
Applications testées
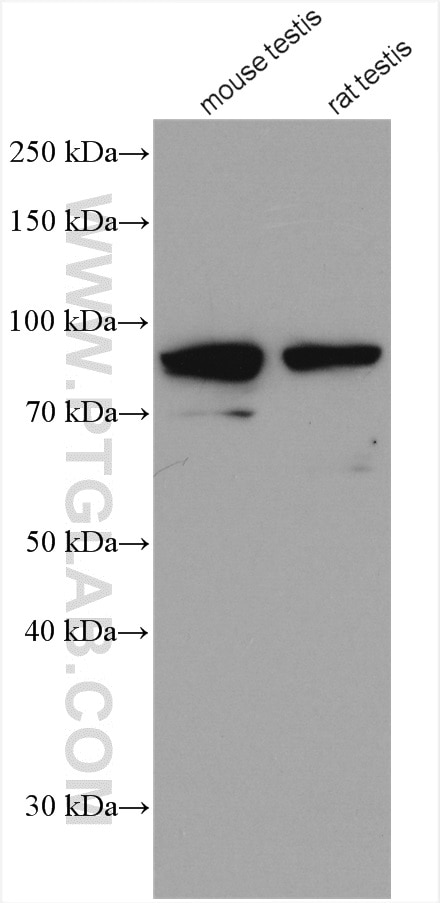
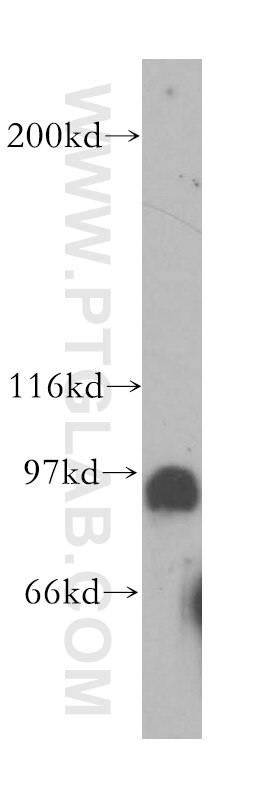
| Résultats positifs en WB | tissu testiculaire de souris, tissu cardiaque humain, tissu testiculaire de rat |
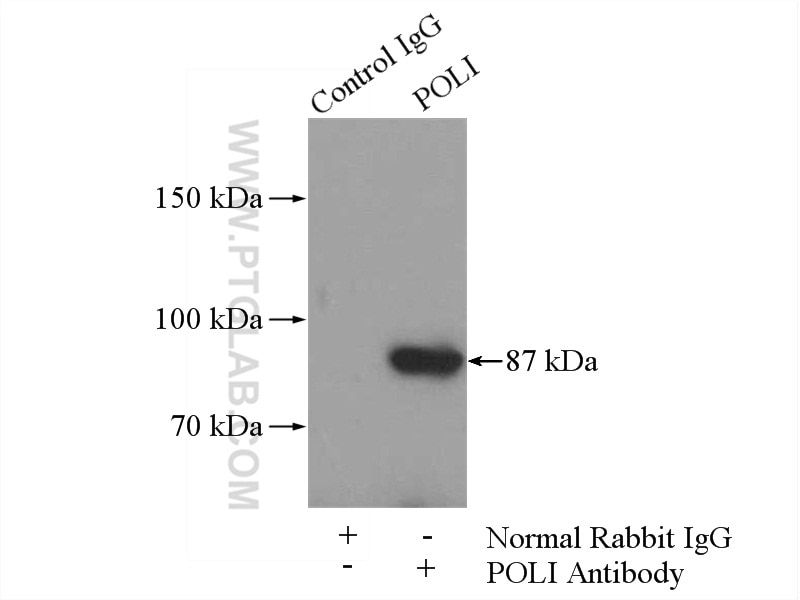
| Résultats positifs en IP | tissu testiculaire de souris |
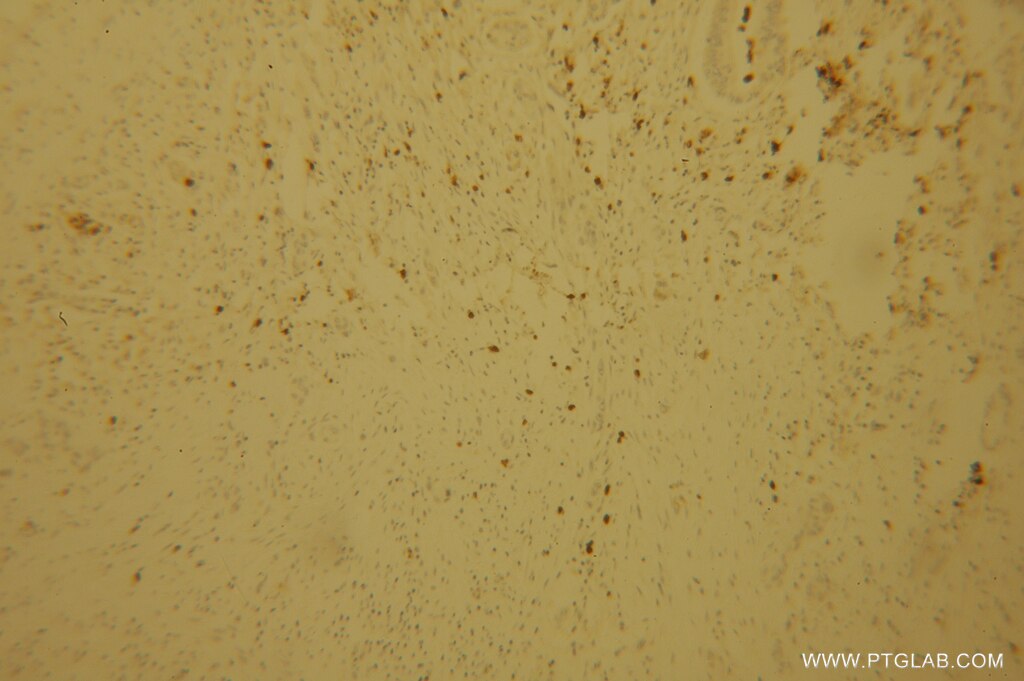
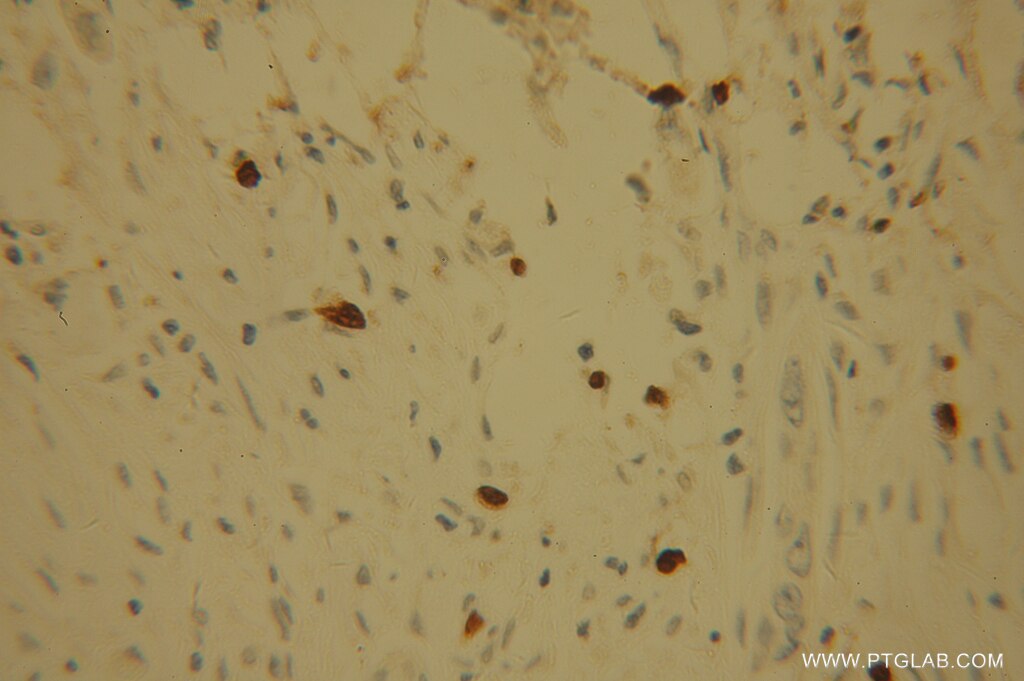
| Résultats positifs en IHC | tissu de cancer du pancréas humain il est suggéré de démasquer l'antigène avec un tampon de TE buffer pH 9.0; (*) À défaut, 'le démasquage de l'antigène peut être 'effectué avec un tampon citrate pH 6,0. |
Dilution recommandée
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:500-1:2000 |
| Immunoprécipitation (IP) | IP : 0.5-4.0 ug for 1.0-3.0 mg of total protein lysate |
| Immunohistochimie (IHC) | IHC : 1:20-1:200 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, check data in validation data gallery | |
Applications publiées
| KD/KO | See 2 publications below |
| WB | See 6 publications below |
| IHC | See 4 publications below |
| IF | See 4 publications below |
Informations sur le produit
13635-1-AP cible POLI dans les applications de WB, IP, IF, IHC, ELISA et montre une réactivité avec des échantillons Humain, rat, souris
| Réactivité | Humain, rat, souris |
| Réactivité citée | Humain, Moustique, souris |
| Hôte / Isotype | Lapin / IgG |
| Clonalité | Polyclonal |
| Type | Anticorps |
| Immunogène | POLI Protéine recombinante Ag4563 |
| Nom complet | polymerase (DNA directed) iota |
| Masse moléculaire calculée | 715 aa, 80 kDa |
| Poids moléculaire observé | 87 kDa |
| Numéro d’acquisition GenBank | BC032662 |
| Symbole du gène | POLI |
| Identification du gène (NCBI) | 11201 |
| Conjugaison | Non conjugué |
| Forme | Liquide |
| Méthode de purification | Purification par affinité contre l'antigène |
| Tampon de stockage | PBS avec azoture de sodium à 0,02 % et glycérol à 50 % pH 7,3 |
| Conditions de stockage | Stocker à -20°C. Stable pendant un an après l'expédition. L'aliquotage n'est pas nécessaire pour le stockage à -20oC Les 20ul contiennent 0,1% de BSA. |
Informations générales
Mammalian Pol ι owns an unusual combination of properties: it is stimulated by Mn2+ ions, can bypass some DNA lesions and misincorporates "G" opposite template "T" more frequently than incorporates the correct "A." [PMID:21304950] It also was shown to possess dRP lyase activity. In addition, Pol ι is much more efficient in the presence of Mn2+ in comparison to Mg2+. [PMID:17609217]. It has been proposed that POLI involves in immunoglobulin somatic hypermutation (SHM), bypass of deaminated cytosines, several adducts of the purine bases. DNA strand crosslinks and is involved in DNA repair under oxidative stress[PMID:15199127].
Protocole
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for POLI antibody 13635-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IHC protocol for POLI antibody 13635-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IP protocol for POLI antibody 13635-1-AP | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |
Publications
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Cell Death Dis DNA polymerase iota promotes EMT and metastasis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by interacting with USP7 to stabilize HIF-1α | ||
Oncogene The error-prone DNA polymerase ι provides quantitative resistance to lung tumorigenesis and mutagenesis in mice. | ||
Front Oncol DNA Polymerase Iota Promotes Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Proliferation Through Erk-OGT-Induced G6PD Overactivation.
| ||
Cancer Sci Phosphorylation of ETS-1 is a critical event in DNA polymerase iota-induced invasion and metastasis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. | ||
Insect Mol Biol Diverse cellular morphologies during lumen maturation in Anopheles gambiae larval salivary glands. | ||
Int J Clin Exp Pathol Elevated DNA polymerase iota (Poli) is involved in the acquisition of aggressive phenotypes of human esophageal squamous cell cancer. |