Anticorps Polyclonal de lapin anti-MYLK
MYLK Polyclonal Antibody for WB, IF, IHC, ELISA
Hôte / Isotype
Lapin / IgG
Réactivité testée
Humain, rat, souris et plus (2)
Applications
WB, IHC, IF-P, CoIP, ELISA
Conjugaison
Non conjugué
N° de cat : 21642-1-AP
Synonymes
Galerie de données de validation
Applications testées
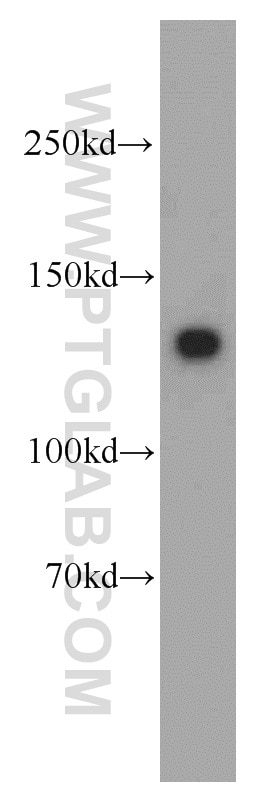
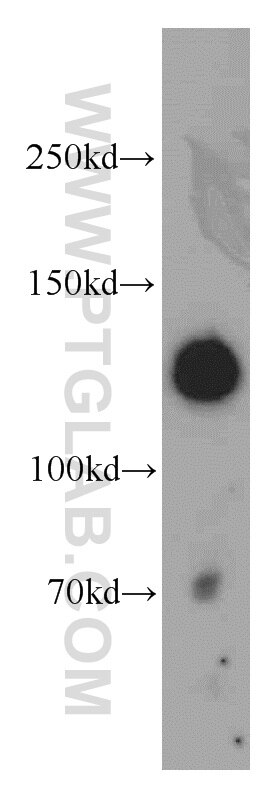
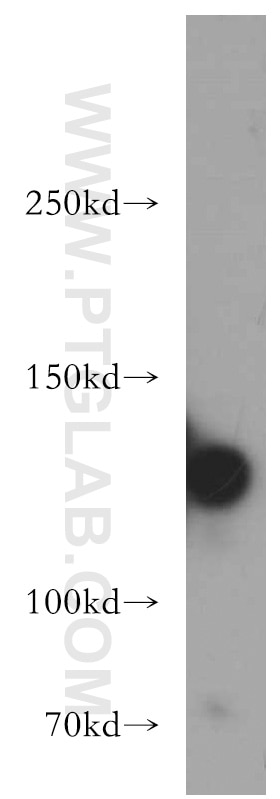
| Résultats positifs en WB | tissu utérin de souris, tissu de gros intestin de souris |
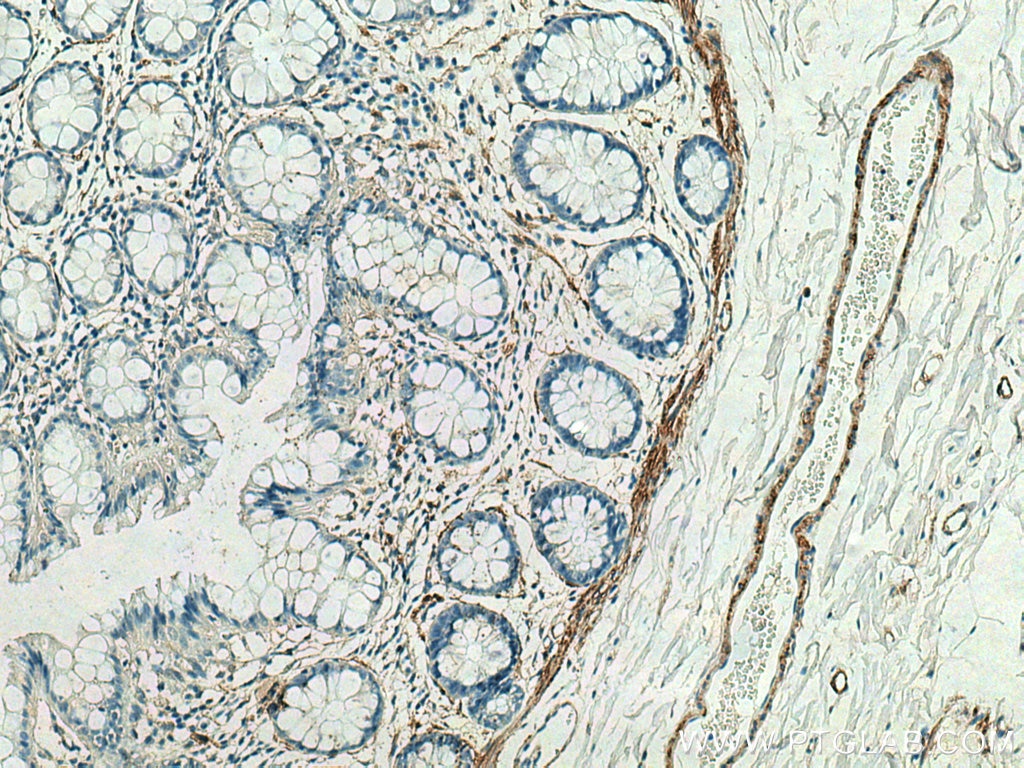
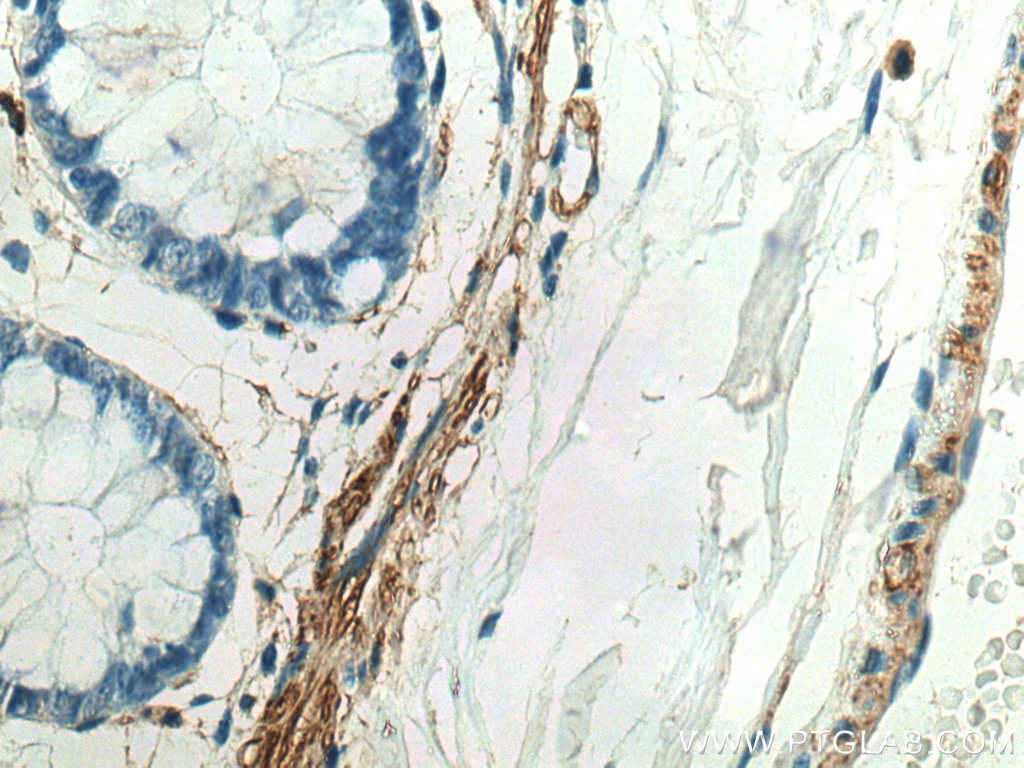
| Résultats positifs en IHC | tissu de côlon humain, il est suggéré de démasquer l'antigène avec un tampon de TE buffer pH 9.0; (*) À défaut, 'le démasquage de l'antigène peut être 'effectué avec un tampon citrate pH 6,0. |
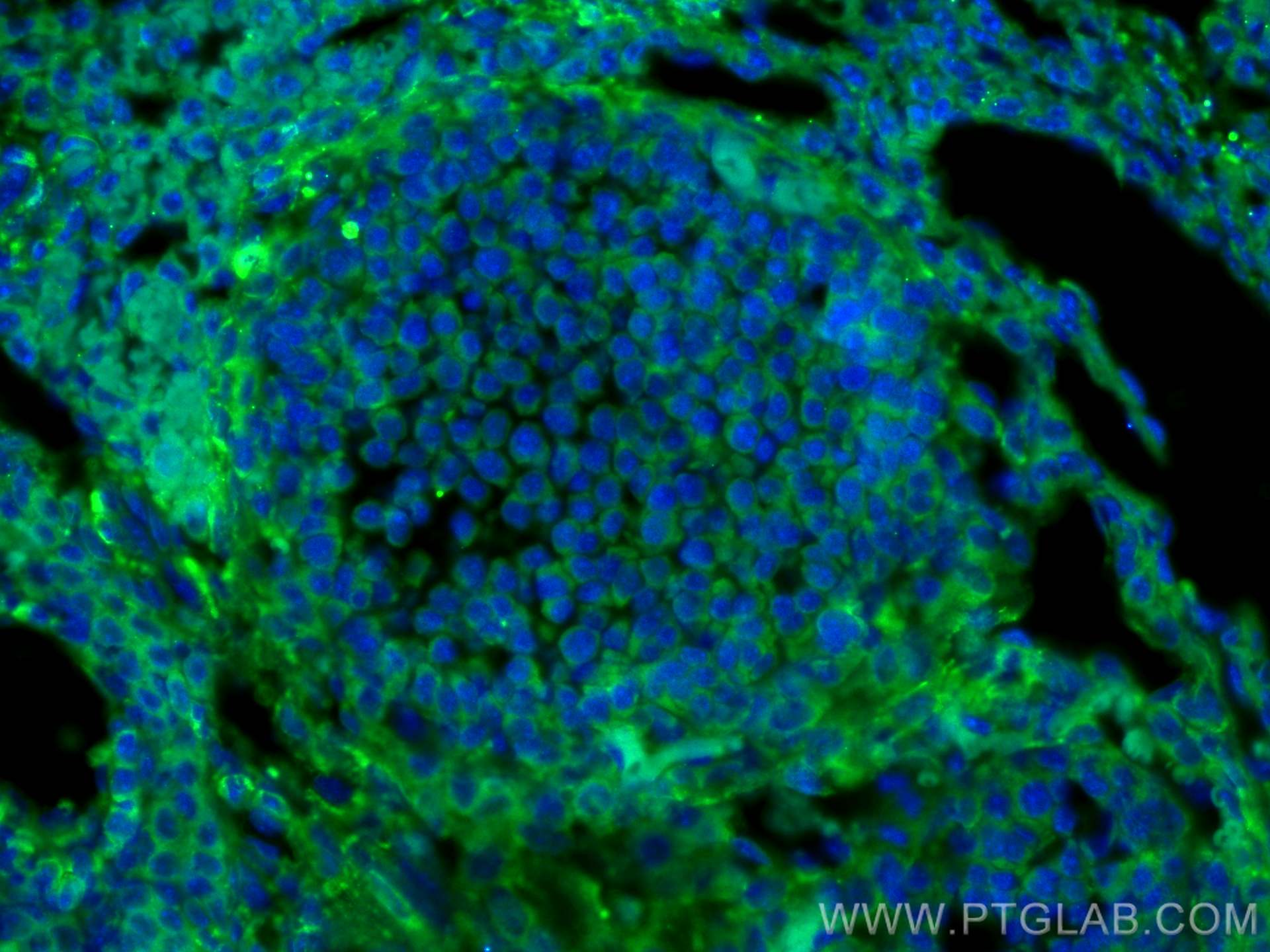
| Résultats positifs en IF-P | tissu ovarien de souris, |
Dilution recommandée
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:500-1:2400 |
| Immunohistochimie (IHC) | IHC : 1:200-1:800 |
| Immunofluorescence (IF)-P | IF-P : 1:50-1:500 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, check data in validation data gallery | |
Applications publiées
| WB | See 18 publications below |
| IHC | See 3 publications below |
| IF | See 4 publications below |
| CoIP | See 1 publications below |
Informations sur le produit
21642-1-AP cible MYLK dans les applications de WB, IHC, IF-P, CoIP, ELISA et montre une réactivité avec des échantillons Humain, rat, souris
| Réactivité | Humain, rat, souris |
| Réactivité citée | rat, Humain, porc, singe, souris |
| Hôte / Isotype | Lapin / IgG |
| Clonalité | Polyclonal |
| Type | Anticorps |
| Immunogène | MYLK Protéine recombinante Ag16306 |
| Nom complet | myosin light chain kinase |
| Masse moléculaire calculée | 1914 aa, 211 kDa |
| Poids moléculaire observé | 135 kDa |
| Numéro d’acquisition GenBank | BC113456 |
| Symbole du gène | MYLK |
| Identification du gène (NCBI) | 4638 |
| Conjugaison | Non conjugué |
| Forme | Liquide |
| Méthode de purification | Purification par affinité contre l'antigène |
| Tampon de stockage | PBS avec azoture de sodium à 0,02 % et glycérol à 50 % pH 7,3 |
| Conditions de stockage | Stocker à -20°C. Stable pendant un an après l'expédition. L'aliquotage n'est pas nécessaire pour le stockage à -20oC Les 20ul contiennent 0,1% de BSA. |
Informations générales
MYLK(Myosin light chain kinase) is also named as MLCK, MLCK1, MYLK1 and belongs to the protein kinase superfamily. It is a key enzyme in muscle contraction. Its activation is sufficient to enhance paracellular permeability and is required for tight junction barrier regulation in response to Na+-nutrient cotransport, inflammatory cytokines, or pathogenic bacteria(PMID:20404178). The expression of smooth muscle MYLK is tissue-specific. Smooth muscle MYLK generates three different proteins, long MYLK, short MYLK, and telokin. The 130-kDa smooth muscle, or short, MYLK (130 kDa) is expressed in smooth muscles. It has 8 isoforms produced by alternative splicing and alternative initiation and our anti-MYLK antibody can recognize these isforms.
Protocole
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for MYLK antibody 21642-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IHC protocol for MYLK antibody 21642-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IF protocol for MYLK antibody 21642-1-AP | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |
Publications
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Research (Wash D C) The Mechanics of Tumor Cells Dictate Malignancy via Cytoskeleton-Mediated APC/Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling | ||
Mucosal Immunol Transmigrated neutrophils in the intestinal lumen engage ICAM-1 to regulate the epithelial barrier and neutrophil recruitment. | ||
Int J Biol Sci Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Activation Modulates Intestinal Epithelial Barrier Function by Maintaining Tight Junction Integrity. | ||
FEBS J Dihydroartemisinin counteracts fibrotic portal hypertension via farnesoid X receptor-dependent inhibition of hepatic stellate cell contraction. | ||
Front Med (Lausanne) Depiction of Aging-Based Molecular Phenotypes With Diverse Clinical Prognosis and Immunological Features in Gastric Cancer. | ||
Metallomics Lanthanum chloride causes blood-brain barrier disruption through intracellular calcium-mediated RhoA/Rho kinase signaling and myosin light chain kinase. |