- Phare
- Validé par KD/KO
Anticorps Monoclonal anti-LPCAT1
LPCAT1 Monoclonal Antibody for WB, IHC, IF/ICC, IF-P, ELISA
Hôte / Isotype
Mouse / IgG2b
Réactivité testée
Humain, rat, souris
Applications
WB, IHC, IF/ICC, IF-P, ELISA
Conjugaison
Non conjugué
CloneNo.
8B6E9
N° de cat : 66044-1-Ig
Synonymes
Galerie de données de validation
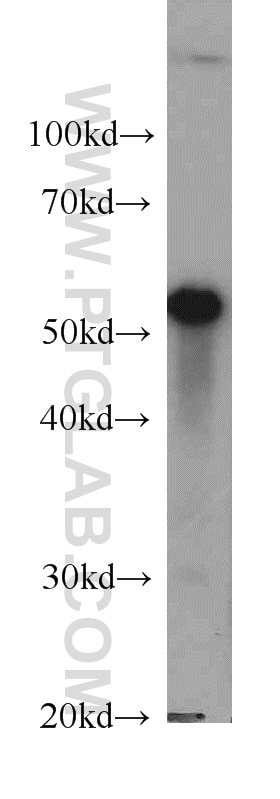
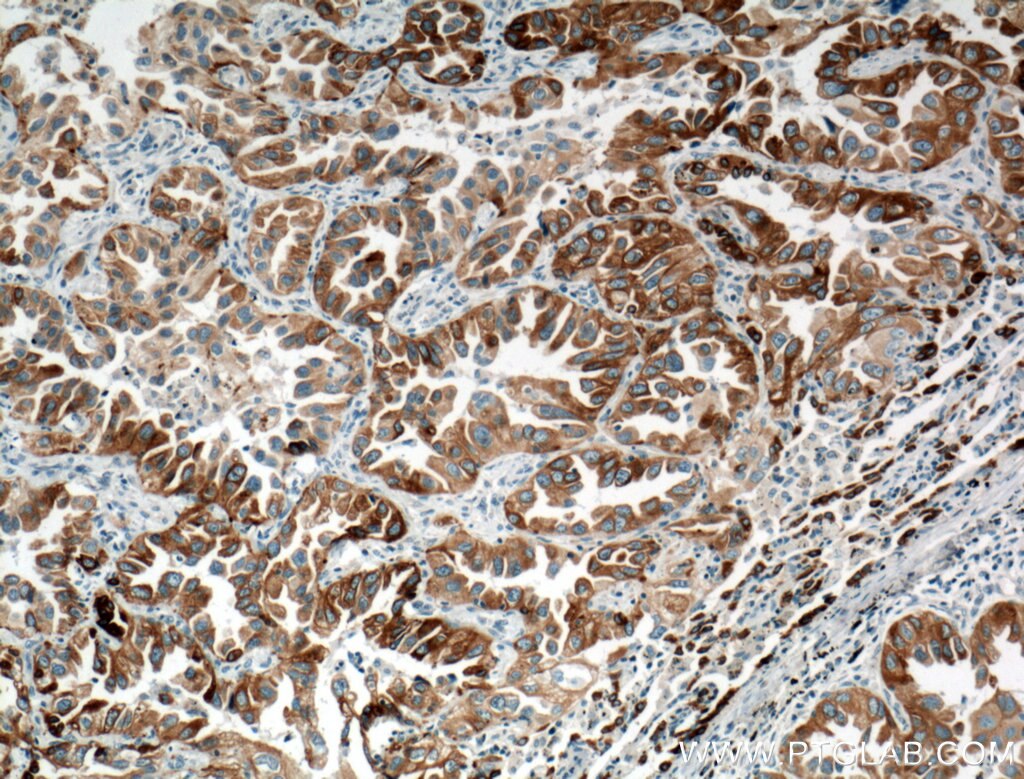
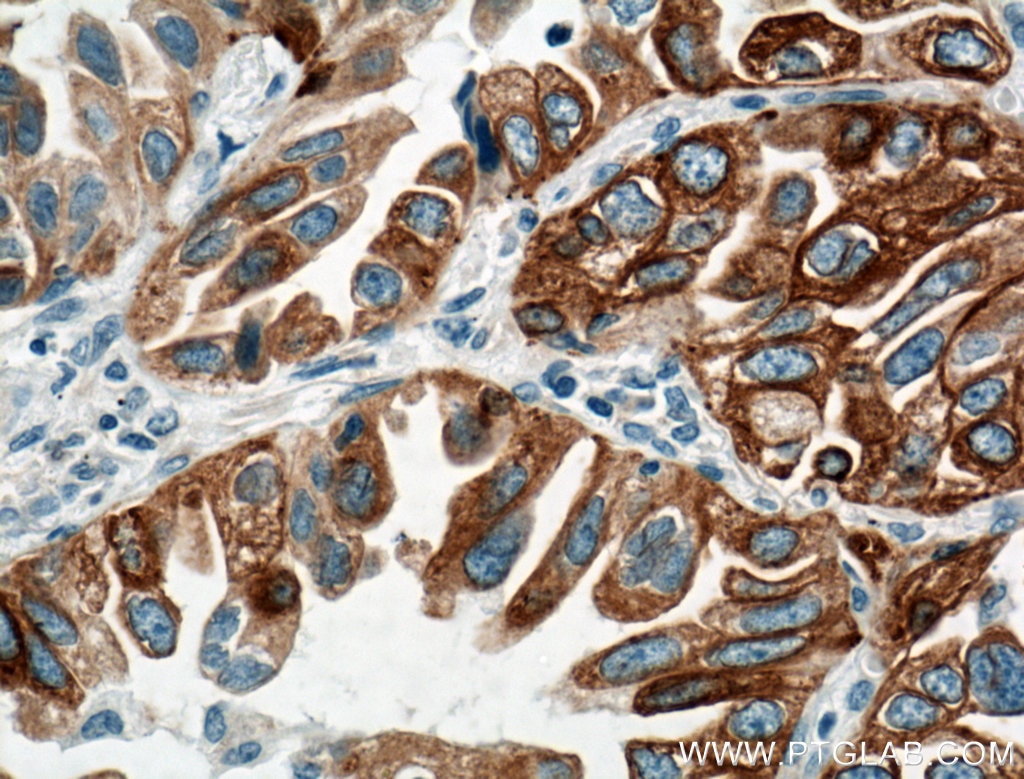
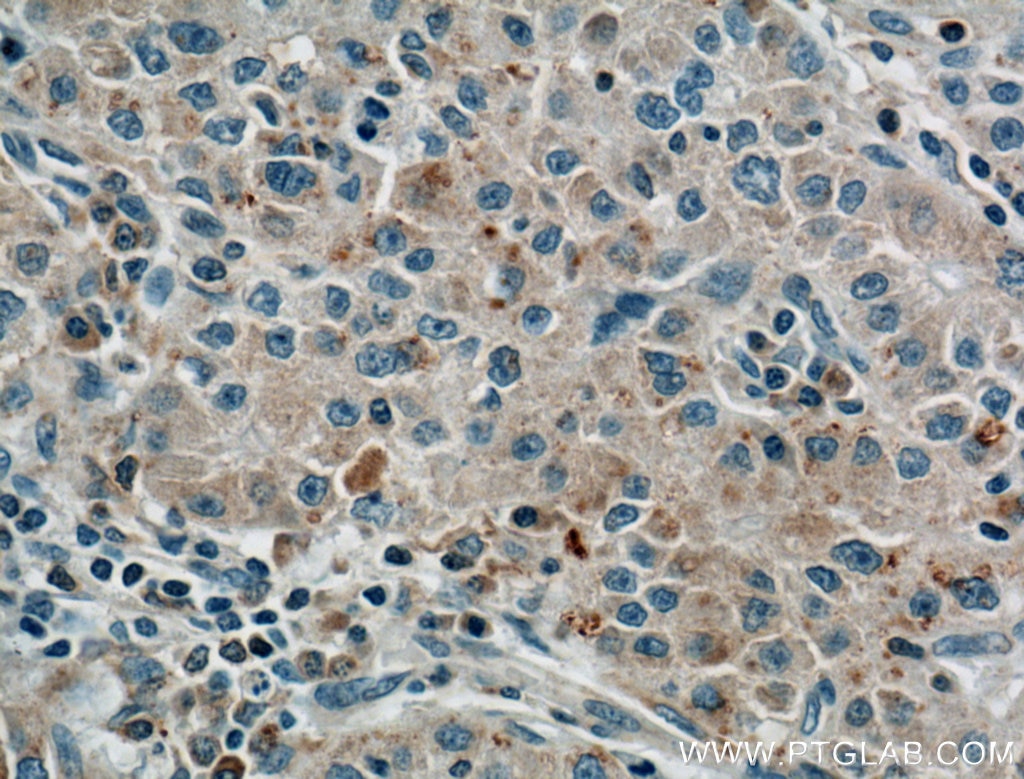
Applications testées
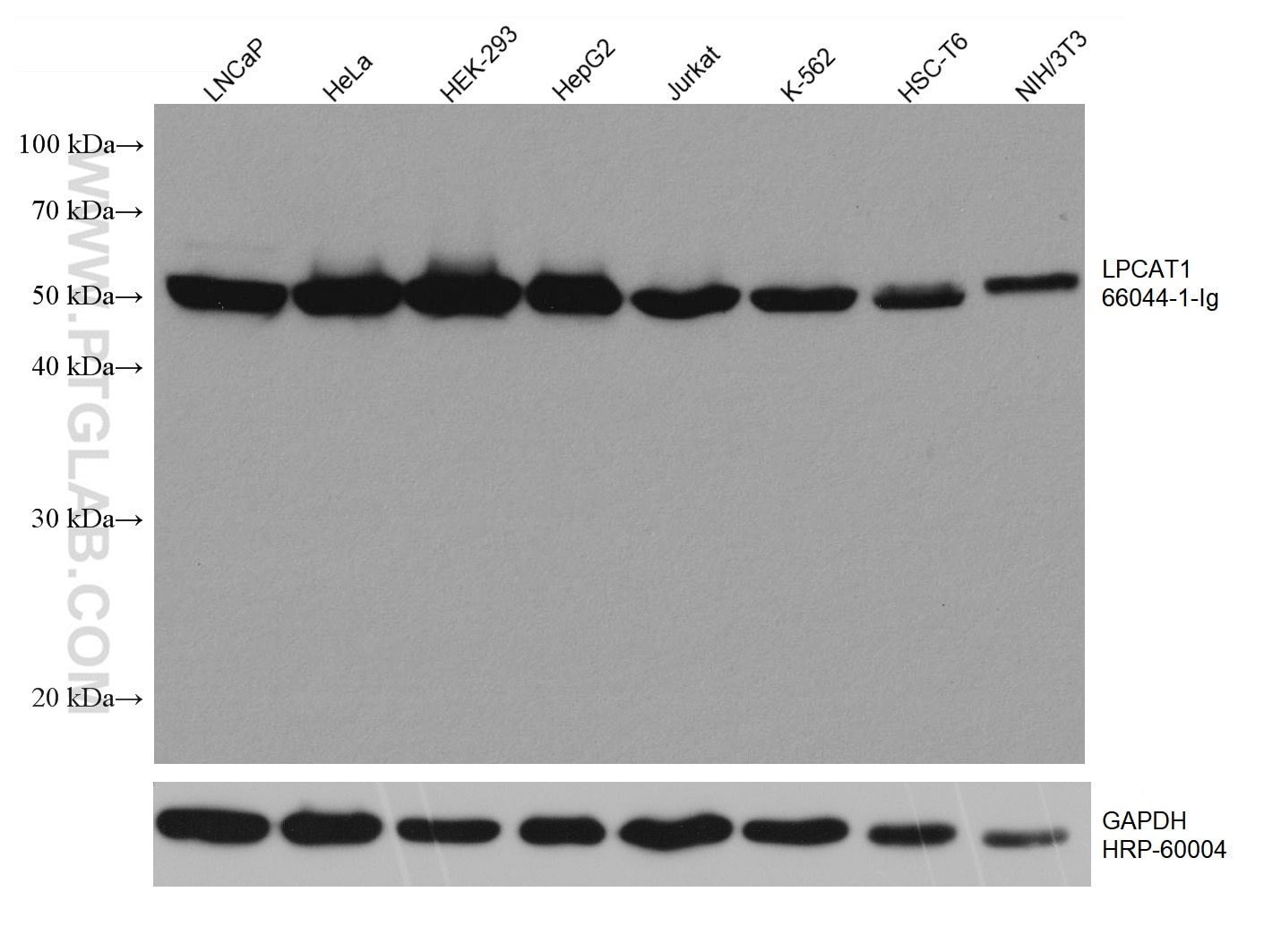
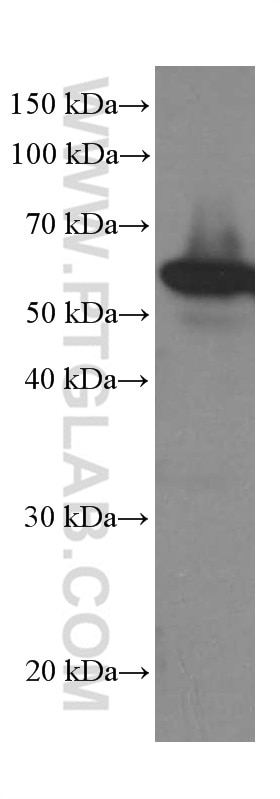
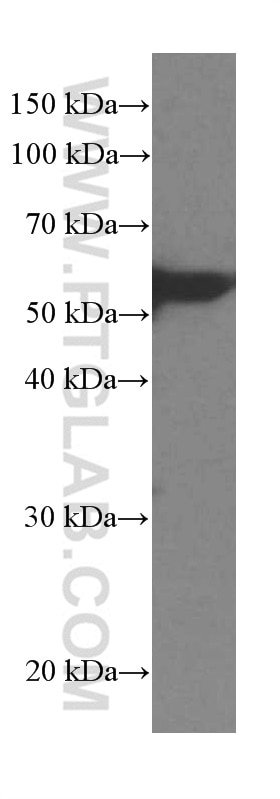
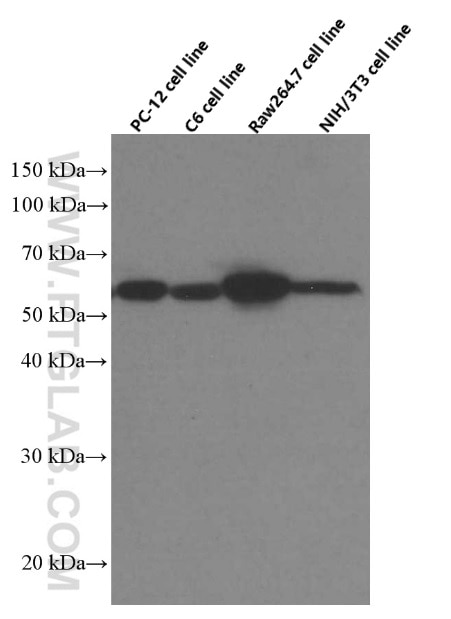
| Résultats positifs en WB | cellules LNCaP, cellules 4T1, cellules HEK-293, cellules HeLa, cellules HepG2, cellules HSC-T6, cellules Jurkat, cellules K-562, cellules MCF-7, cellules NIH/3T3, cellules PC-12, cellules ROS1728 |
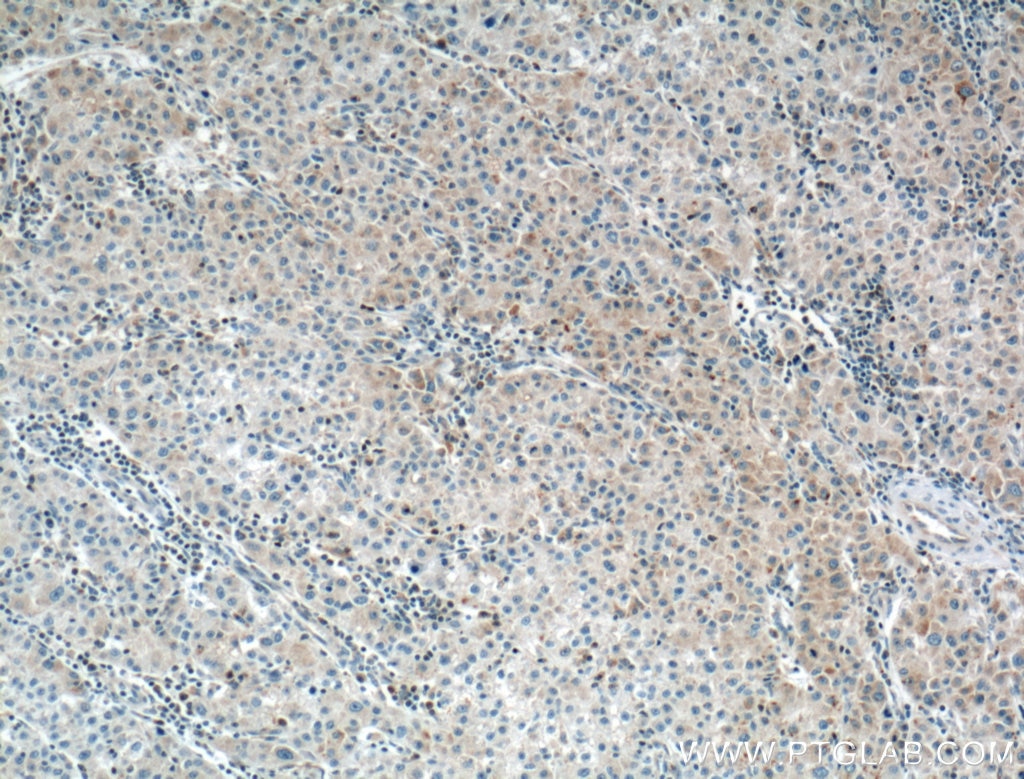
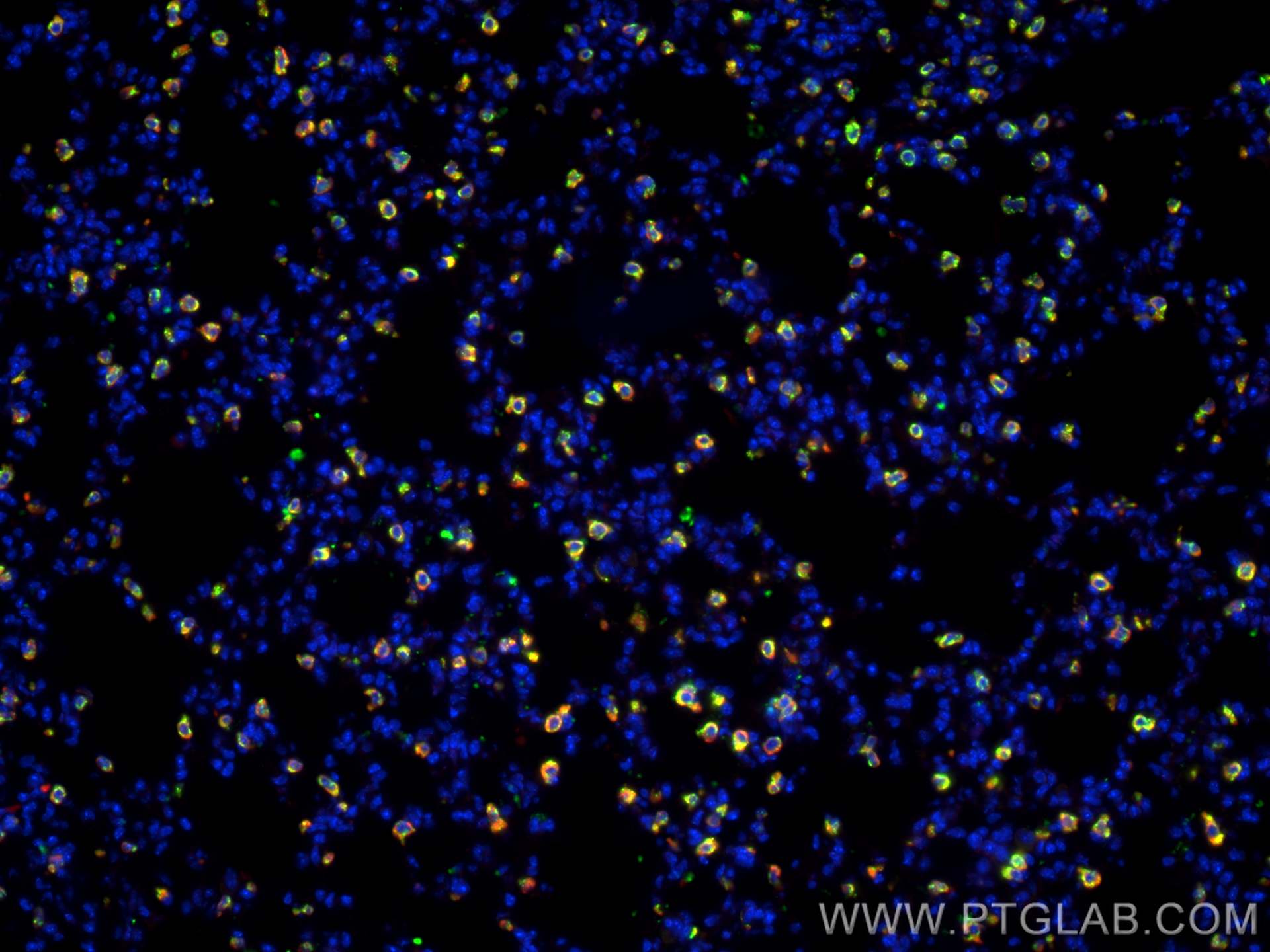
| Résultats positifs en IHC | tissu de cancer du poumon humain, tissu de cancer du foie humain il est suggéré de démasquer l'antigène avec un tampon de TE buffer pH 9.0; (*) À défaut, 'le démasquage de l'antigène peut être 'effectué avec un tampon citrate pH 6,0. |
| Résultats positifs en IF-P | tissu pulmonaire de souris |
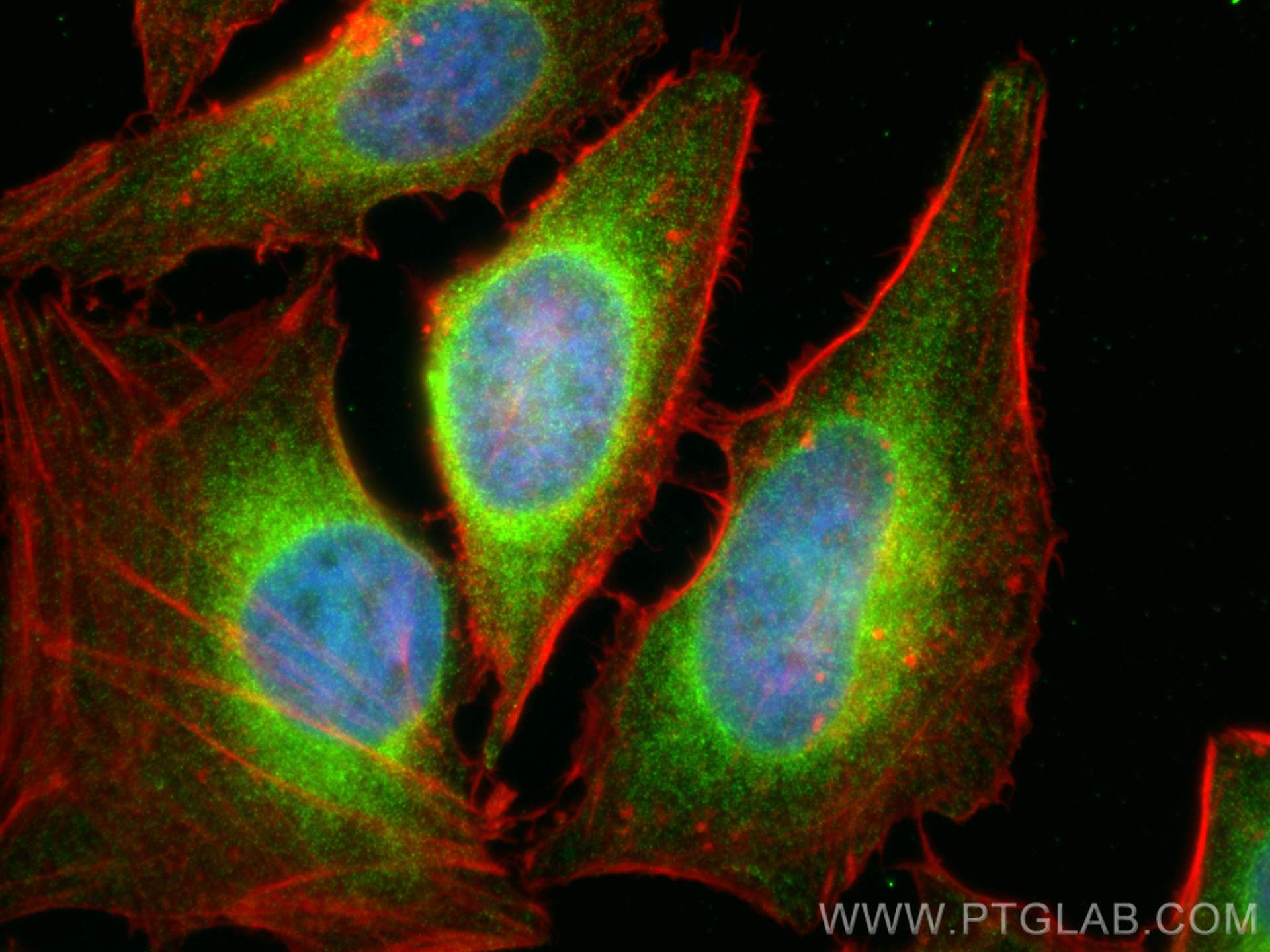
| Résultats positifs en IF/ICC | cellules HeLa, |
Dilution recommandée
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:5000-1:50000 |
| Immunohistochimie (IHC) | IHC : 1:50-1:500 |
| Immunofluorescence (IF)-P | IF-P : 1:200-1:800 |
| Immunofluorescence (IF)/ICC | IF/ICC : 1:400-1:1600 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, check data in validation data gallery | |
Applications publiées
| KD/KO | See 3 publications below |
| WB | See 8 publications below |
| IHC | See 4 publications below |
| IF | See 2 publications below |
Informations sur le produit
66044-1-Ig cible LPCAT1 dans les applications de WB, IHC, IF/ICC, IF-P, ELISA et montre une réactivité avec des échantillons Humain, rat, souris
| Réactivité | Humain, rat, souris |
| Réactivité citée | rat, Humain, souris |
| Hôte / Isotype | Mouse / IgG2b |
| Clonalité | Monoclonal |
| Type | Anticorps |
| Immunogène | LPCAT1 Protéine recombinante Ag9060 |
| Nom complet | lysophosphatidylcholine acyltransferase 1 |
| Masse moléculaire calculée | 534 aa, 59 kDa |
| Poids moléculaire observé | 55 kDa |
| Numéro d’acquisition GenBank | BC020166 |
| Symbole du gène | LPCAT1 |
| Identification du gène (NCBI) | 79888 |
| Conjugaison | Non conjugué |
| Forme | Liquide |
| Méthode de purification | Purification par protéine A |
| Tampon de stockage | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol |
| Conditions de stockage | Stocker à -20°C. Stable pendant un an après l'expédition. L'aliquotage n'est pas nécessaire pour le stockage à -20oC Les 20ul contiennent 0,1% de BSA. |
Informations générales
LPCAT1, also named as AYTL2, PFAAP3 and LysoPAFAT, belongs to the 1-acyl-sn-glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase family. It is a key enzyme for remodeling phospholipids, including phosphatidylcholine. The expression level of LPCAT1 is able to differentiate prostate cancer from noncancerous prostatic changes, and correlates to the tumor grade of prostate cancer. LPCAT1 possesses both acyltransferase and acetyltransferase activities. It mediates the conversion of 1-acyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (LPC) into phosphatidylcholine (PC).
Protocole
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for LPCAT1 antibody 66044-1-Ig | Download protocol |
| IHC protocol for LPCAT1 antibody 66044-1-Ig | Download protocol |
| IF protocol for LPCAT1 antibody 66044-1-Ig | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |
Publications
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Cell Metab Oncogene Amplification in Growth Factor Signaling Pathways Renders Cancers Dependent on Membrane Lipid Remodeling.
| ||
Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis Stearoyl-CoA desaturase 1 deficiency exacerbates palmitate-induced lipotoxicity by the formation of small lipid droplets in pancreatic β-cells | ||
Front Oncol Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis Accelerates Prostate Cancer Progression Through Increased LPCAT1 Expression and Enhanced DNA Repair Pathways. | ||
Sci Rep No evidence for carcinogenicity of titanium dioxide nanoparticles in 26-week inhalation study in rasH2 mouse model | ||
Biochem Biophys Res Commun A miR-205-LPCAT1 axis contributes to proliferation and progression in multiple cancers.
| ||
Cell Death Dis LPCAT1 reprogramming cholesterol metabolism promotes the progression of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.
|