Anticorps Monoclonal anti-LIG1
LIG1 Monoclonal Antibody for WB, ELISA
Hôte / Isotype
Mouse / IgG2b
Réactivité testée
Humain, rat, souris
Applications
WB, CoIP, ELISA
Conjugaison
Non conjugué
CloneNo.
3D9G8
N° de cat : 67840-1-Ig
Synonymes
Galerie de données de validation
Applications testées
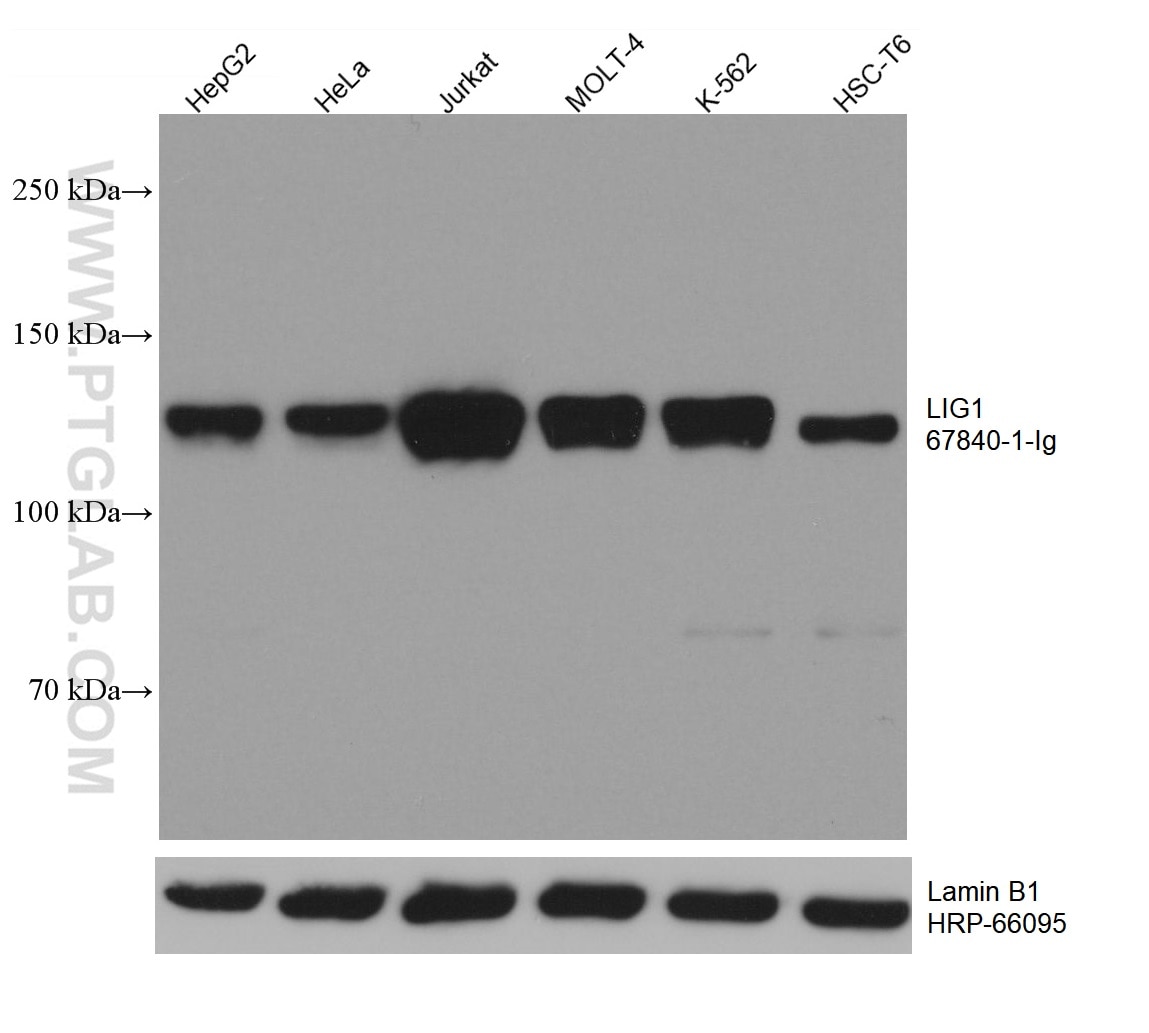
| Résultats positifs en WB | cellules HepG2, cellules HeLa, cellules HSC-T6, cellules Jurkat, cellules K-562, cellules MOLT-4 |
Dilution recommandée
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:5000-1:50000 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, check data in validation data gallery | |
Applications publiées
| WB | See 1 publications below |
| CoIP | See 1 publications below |
Informations sur le produit
67840-1-Ig cible LIG1 dans les applications de WB, CoIP, ELISA et montre une réactivité avec des échantillons Humain, rat, souris
| Réactivité | Humain, rat, souris |
| Réactivité citée | Humain |
| Hôte / Isotype | Mouse / IgG2b |
| Clonalité | Monoclonal |
| Type | Anticorps |
| Immunogène | LIG1 Protéine recombinante Ag12489 |
| Nom complet | ligase I, DNA, ATP-dependent |
| Masse moléculaire calculée | 919 aa, 102 kDa |
| Poids moléculaire observé | 130 kDa |
| Numéro d’acquisition GenBank | BC108318 |
| Symbole du gène | LIG1 |
| Identification du gène (NCBI) | 3978 |
| Conjugaison | Non conjugué |
| Forme | Liquide |
| Méthode de purification | Purification par protéine A |
| Tampon de stockage | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol |
| Conditions de stockage | Stocker à -20°C. Stable pendant un an après l'expédition. L'aliquotage n'est pas nécessaire pour le stockage à -20oC Les 20ul contiennent 0,1% de BSA. |
Informations générales
DNA ligase I (LIG1) joins DNA strand breaks during DNA replication and repair transactions and contributes to genome integrity. 67840-1-Ig is raised agains the C-terminal 670-919 aa residues of the human DNA ligase 1.
Protocole
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for LIG1 antibody 67840-1-Ig | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |