Anticorps Polyclonal de lapin anti-HEPACAM
HEPACAM Polyclonal Antibody for WB, IP, IF, IHC, ELISA
Hôte / Isotype
Lapin / IgG
Réactivité testée
Humain, rat, souris
Applications
WB, IHC, IF/ICC, IP, ELISA
Conjugaison
Non conjugué
N° de cat : 18177-1-AP
Synonymes
Galerie de données de validation
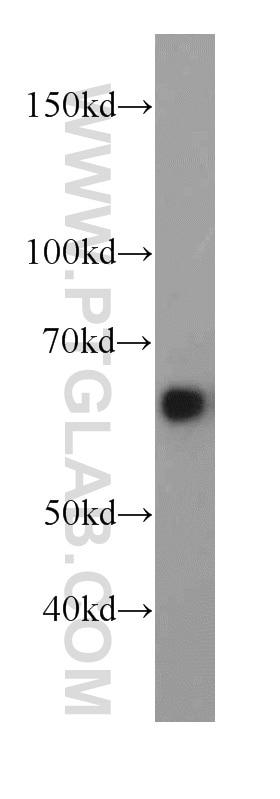
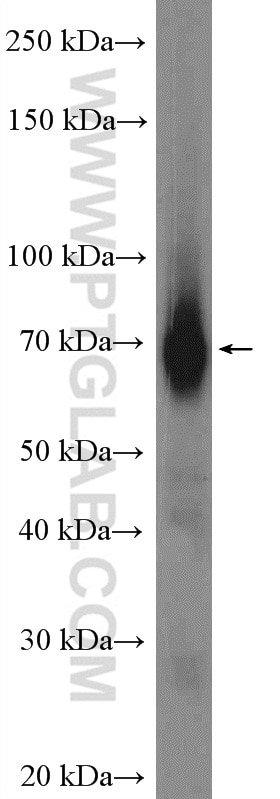
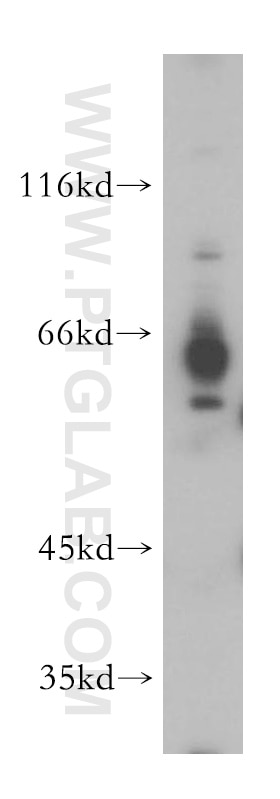
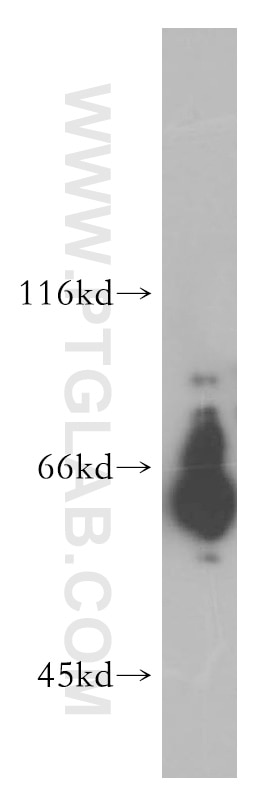
Applications testées
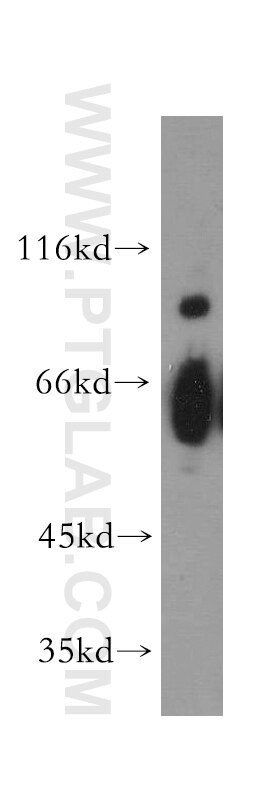
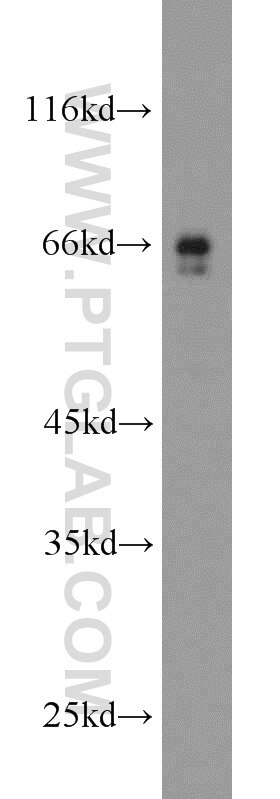
| Résultats positifs en WB | tissu cérébral de souris, cellules HepG2, cellules MCF-7, cellules SH-SY5Y, tissu cérébral de rat, tissu hépatique de souris |
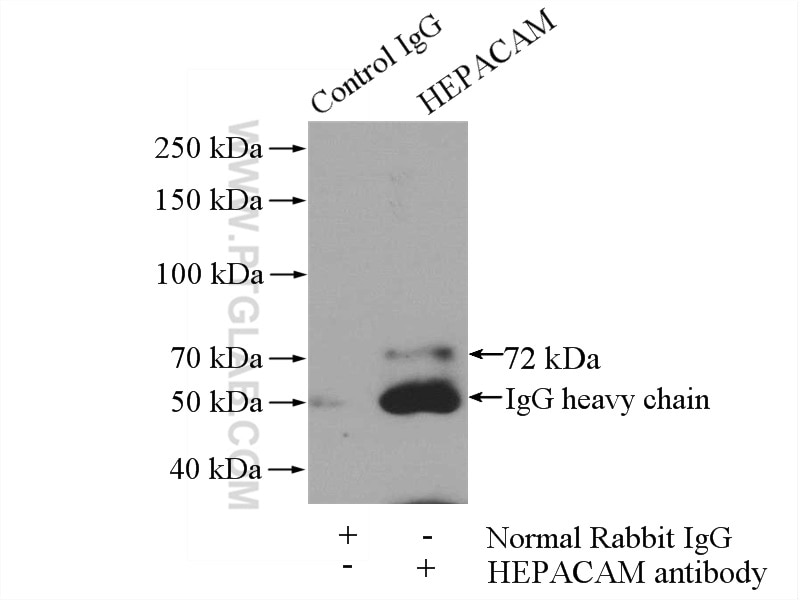
| Résultats positifs en IP | tissu cérébral de rat |
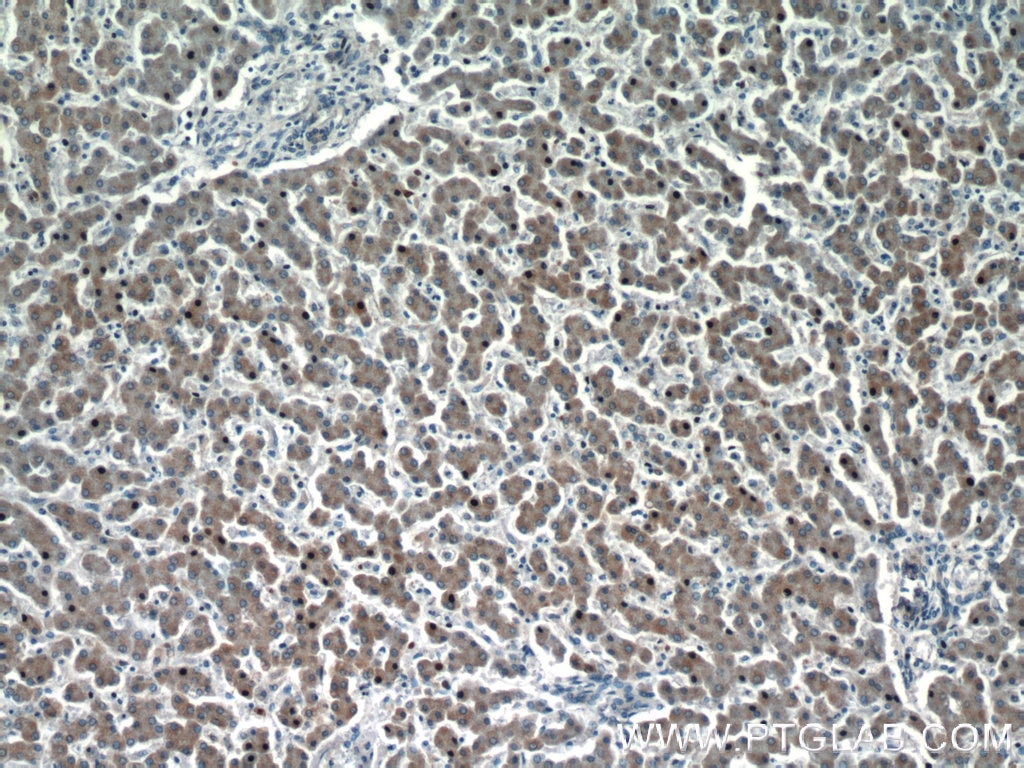
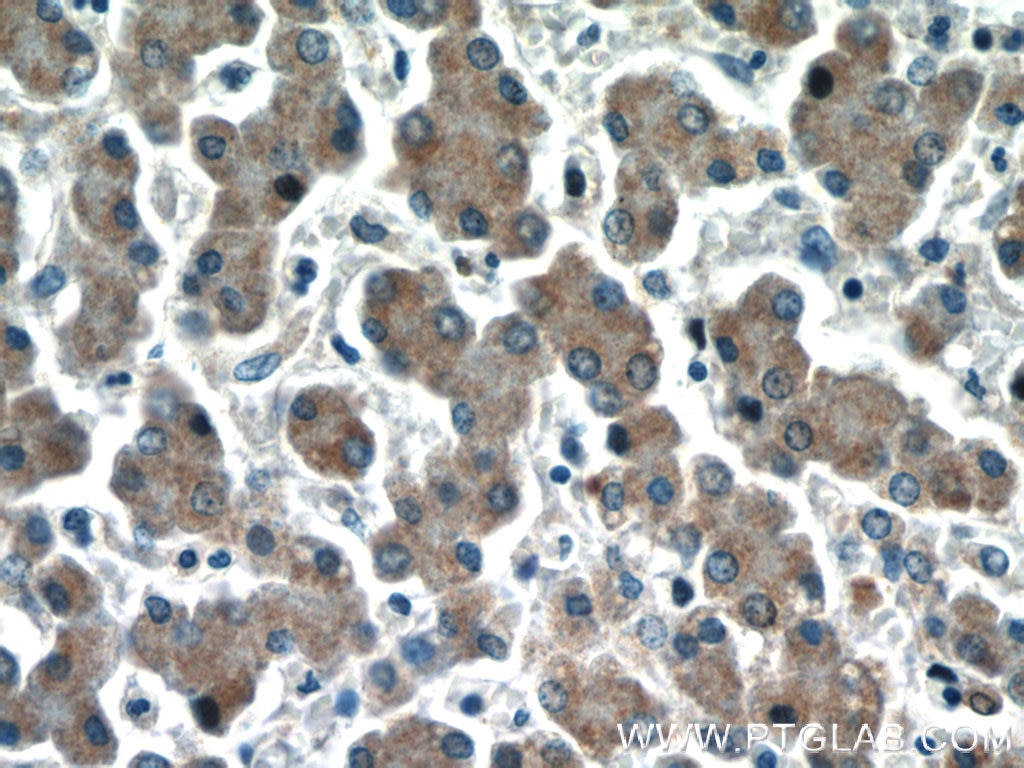
| Résultats positifs en IHC | tissu hépatique humain il est suggéré de démasquer l'antigène avec un tampon de TE buffer pH 9.0; (*) À défaut, 'le démasquage de l'antigène peut être 'effectué avec un tampon citrate pH 6,0. |
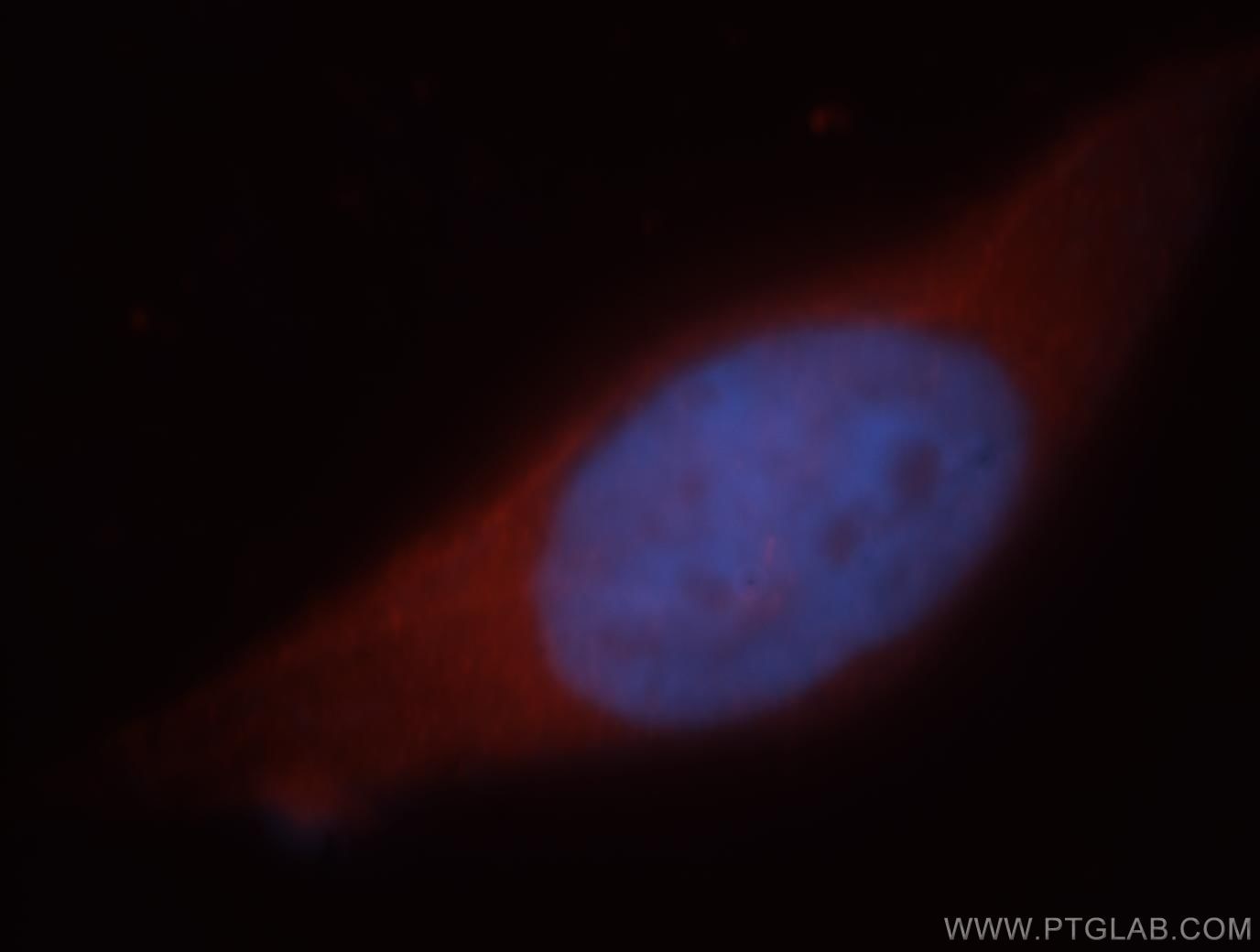
| Résultats positifs en IF/ICC | cellules MCF-7 |
Dilution recommandée
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:500-1:1000 |
| Immunoprécipitation (IP) | IP : 0.5-4.0 ug for 1.0-3.0 mg of total protein lysate |
| Immunohistochimie (IHC) | IHC : 1:20-1:200 |
| Immunofluorescence (IF)/ICC | IF/ICC : 1:10-1:100 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, check data in validation data gallery | |
Applications publiées
| KD/KO | See 2 publications below |
| WB | See 15 publications below |
| IHC | See 13 publications below |
| IF | See 5 publications below |
| IP | See 1 publications below |
Informations sur le produit
18177-1-AP cible HEPACAM dans les applications de WB, IHC, IF/ICC, IP, ELISA et montre une réactivité avec des échantillons Humain, rat, souris
| Réactivité | Humain, rat, souris |
| Réactivité citée | rat, Humain, souris |
| Hôte / Isotype | Lapin / IgG |
| Clonalité | Polyclonal |
| Type | Anticorps |
| Immunogène | HEPACAM Protéine recombinante Ag12870 |
| Nom complet | hepatocyte cell adhesion molecule |
| Masse moléculaire calculée | 416 aa, 46 kDa |
| Poids moléculaire observé | 46-72 kDa |
| Numéro d’acquisition GenBank | BC104831 |
| Symbole du gène | HEPACAM |
| Identification du gène (NCBI) | 220296 |
| Conjugaison | Non conjugué |
| Forme | Liquide |
| Méthode de purification | Purification par affinité contre l'antigène |
| Tampon de stockage | PBS avec azoture de sodium à 0,02 % et glycérol à 50 % pH 7,3 |
| Conditions de stockage | Stocker à -20°C. Stable pendant un an après l'expédition. L'aliquotage n'est pas nécessaire pour le stockage à -20oC Les 20ul contiennent 0,1% de BSA. |
Informations générales
HepaCAM (hepatocyte cell adhesion molecule), also known as GlialCAM, is a single-pass type I membrane glycoprotein of 416 amino acids. It displays a typical structure of immunoglobulin (Ig)-like adhesion molecules including two extracellular Ig-like domains, a transmembrane segment, and a cytoplasmic tail. It has been shown that hepaCAM forms a cis-homodimer on the cell surface, and modulates cell-matrix interaction. It is predominantly expressed in the CNS glial cells. Defects in HEPACAM gene are the cause of megalencephalic leukoencephalopathy with subcortical cysts type 2A (MLC2A). HEPACAM has also been suggested as a tumor suppressor gene.
Protocole
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for HEPACAM antibody 18177-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IHC protocol for HEPACAM antibody 18177-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IF protocol for HEPACAM antibody 18177-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IP protocol for HEPACAM antibody 18177-1-AP | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |
Publications
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Hum Mol Genet Megalencephalic leukoencephalopathy with subcortical cysts protein 1 functionally cooperates with the TRPV4 cation channel to activate the response of astrocytes to osmotic stress: dysregulation by pathological mutations. | ||
Br J Cancer Long noncoding RNA HOTAIR regulates the invasion and metastasis of prostate cancer by targeting hepaCAM. | ||
Development Regionally specified human pluripotent stem cell-derived astrocytes exhibit different molecular signatures and functional properties. | ||
Cell Signal Interleukin 6 induces cell proliferation of clear cell renal cell carcinoma by suppressing hepaCAM via the STAT3-dependent up-regulation of DNMT1 or DNMT3b. | ||
Int J Oncol HepaCAM‑PIK3CA axis regulates the reprogramming of glutamine metabolism to inhibit prostate cancer cell proliferation. |