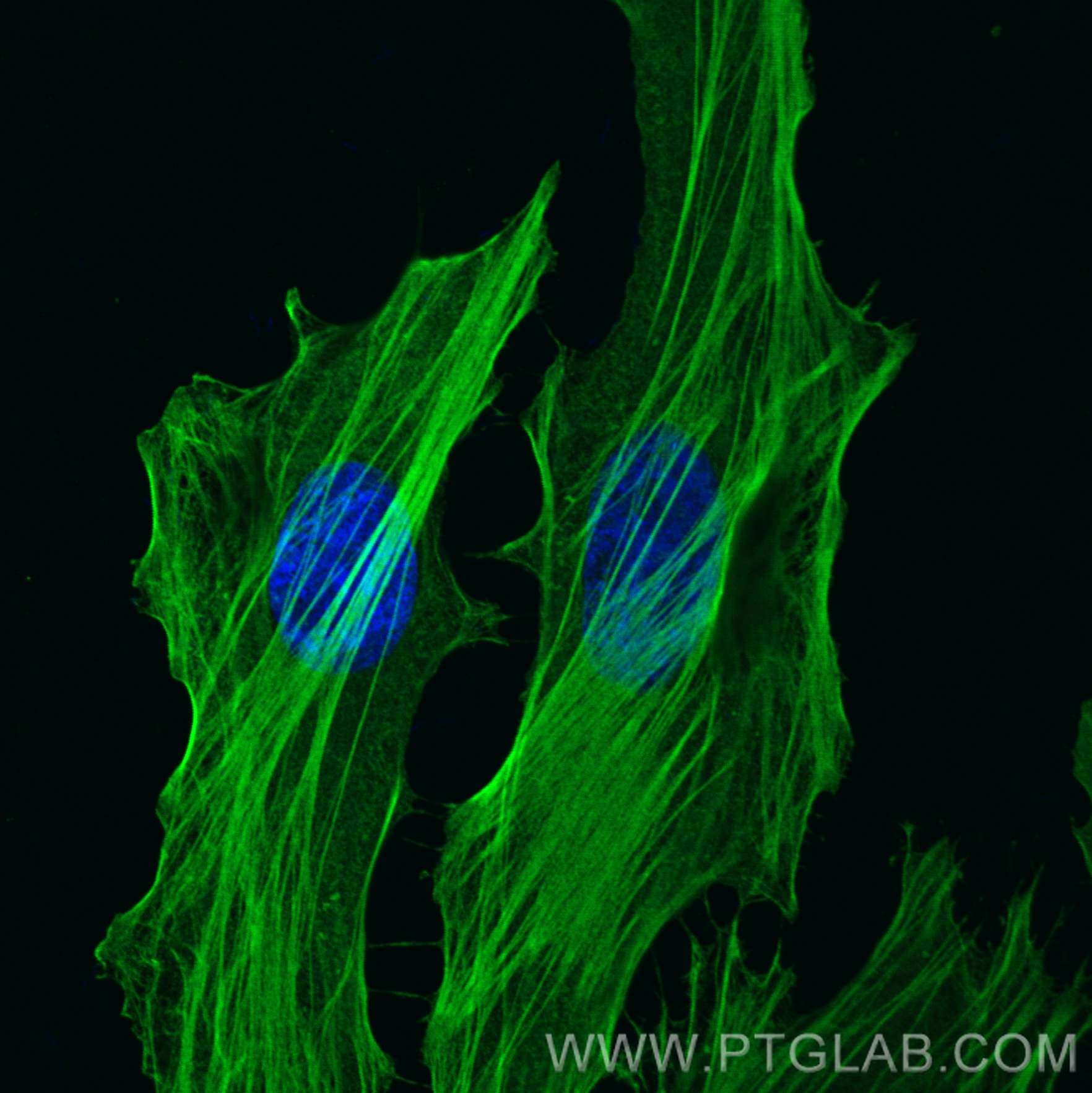
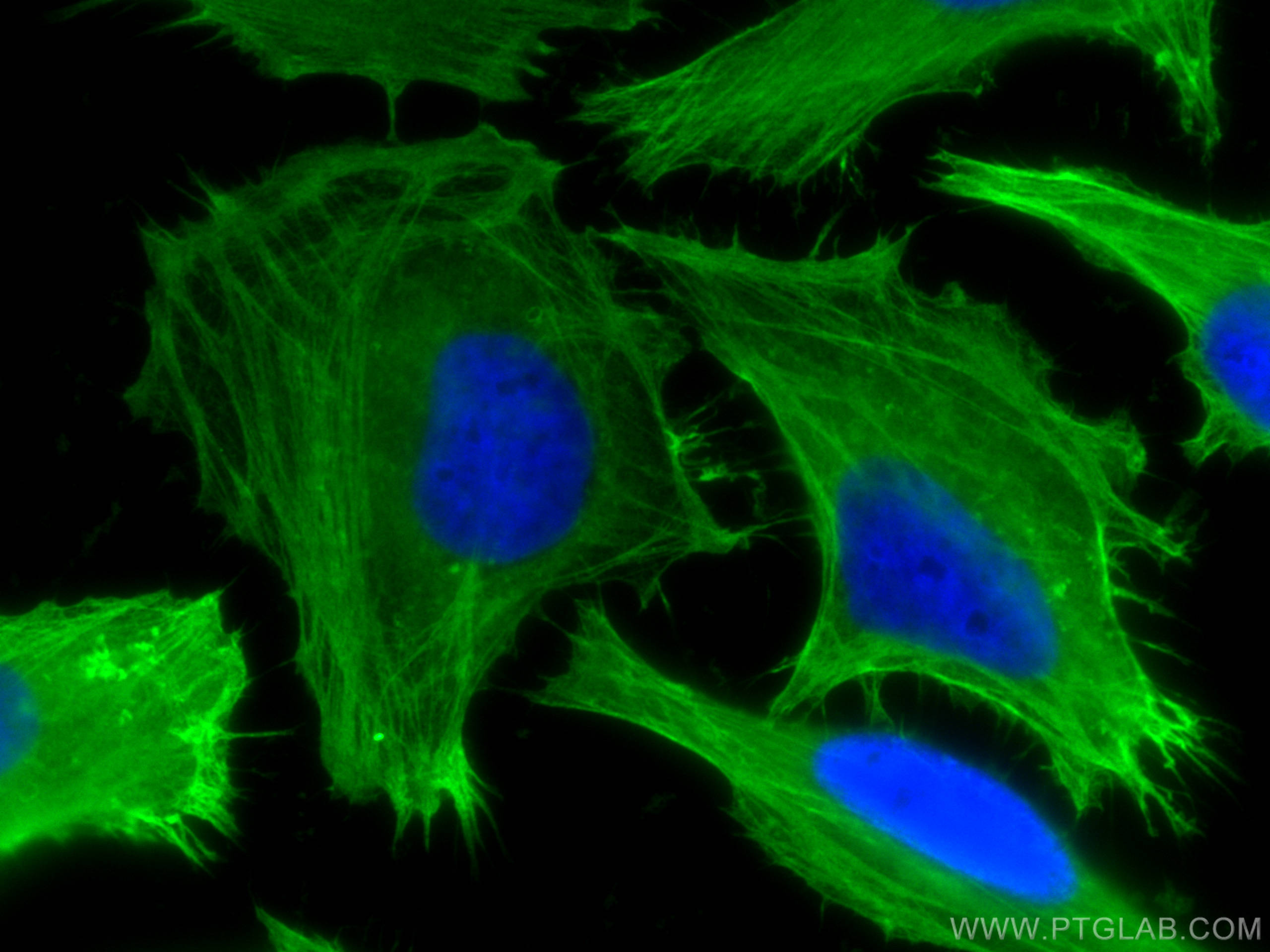
Anticorps Monoclonal anti-Filamin A
Filamin A Monoclonal Antibody for WB, IHC, IF/ICC, ELISA
Hôte / Isotype
Mouse / IgG2a
Réactivité testée
Humain
Applications
WB, IHC, IF/ICC, ELISA
Conjugaison
Non conjugué
CloneNo.
1G4H3
N° de cat : 67133-1-Ig
Synonymes
Galerie de données de validation
Applications testées
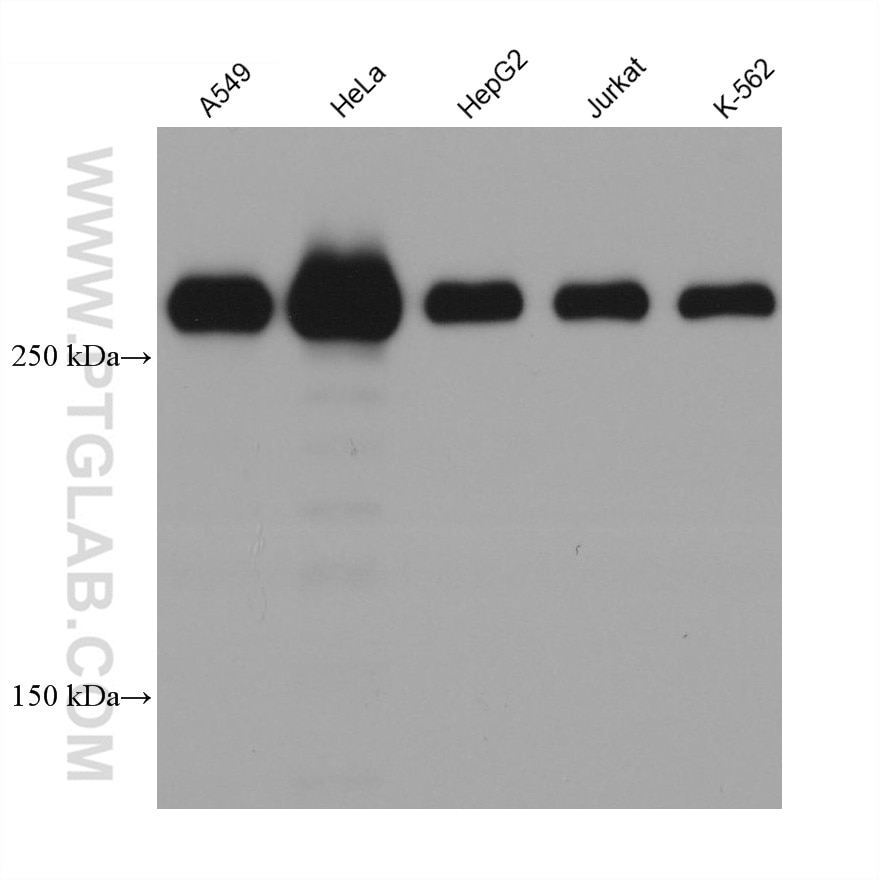
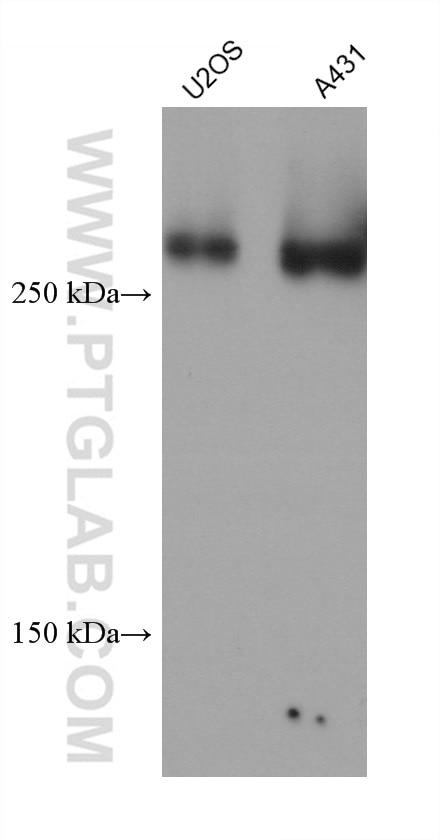
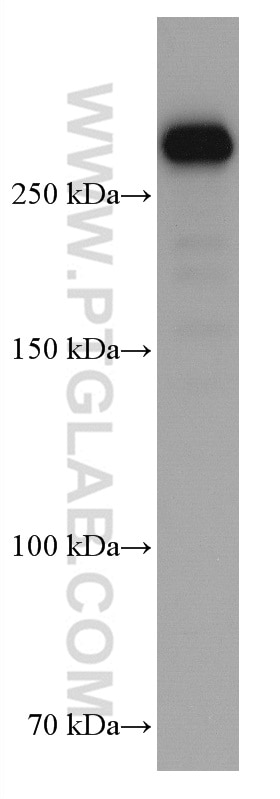
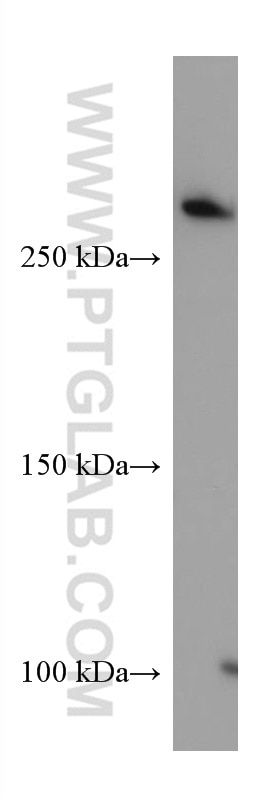
| Résultats positifs en WB | cellules A549, cellules A431, cellules HEK-293, cellules HeLa, cellules HepG2, cellules Jurkat, cellules K-562, cellules MCF-7, cellules U2OS, tissu de muscle squelettique humain |
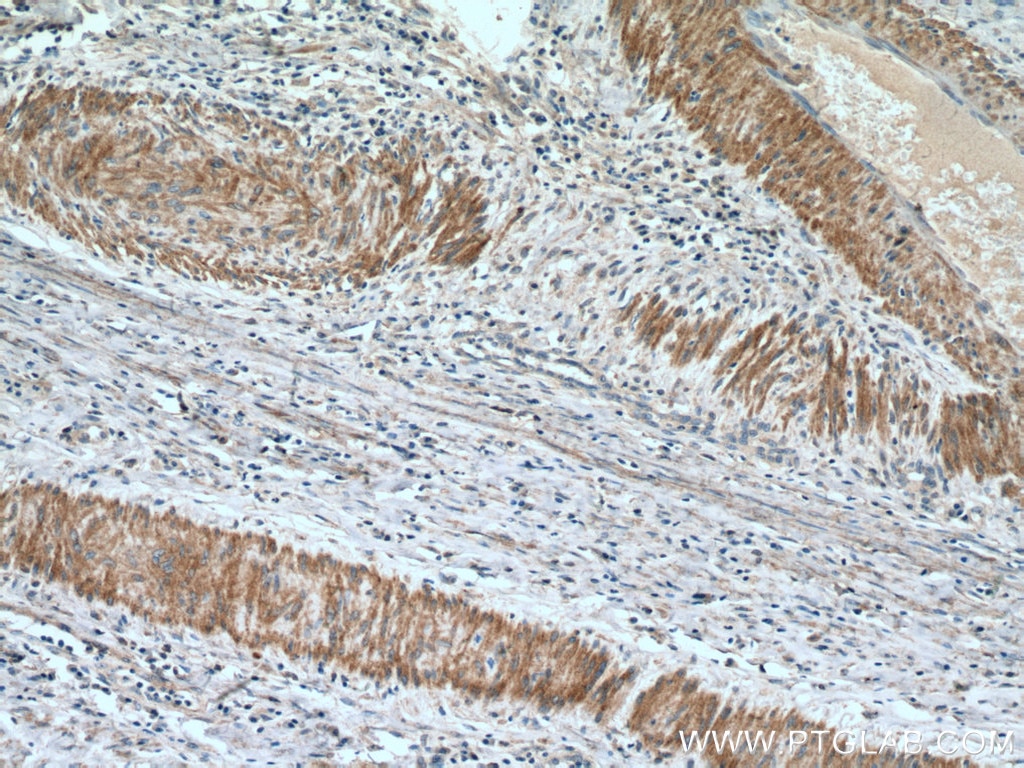
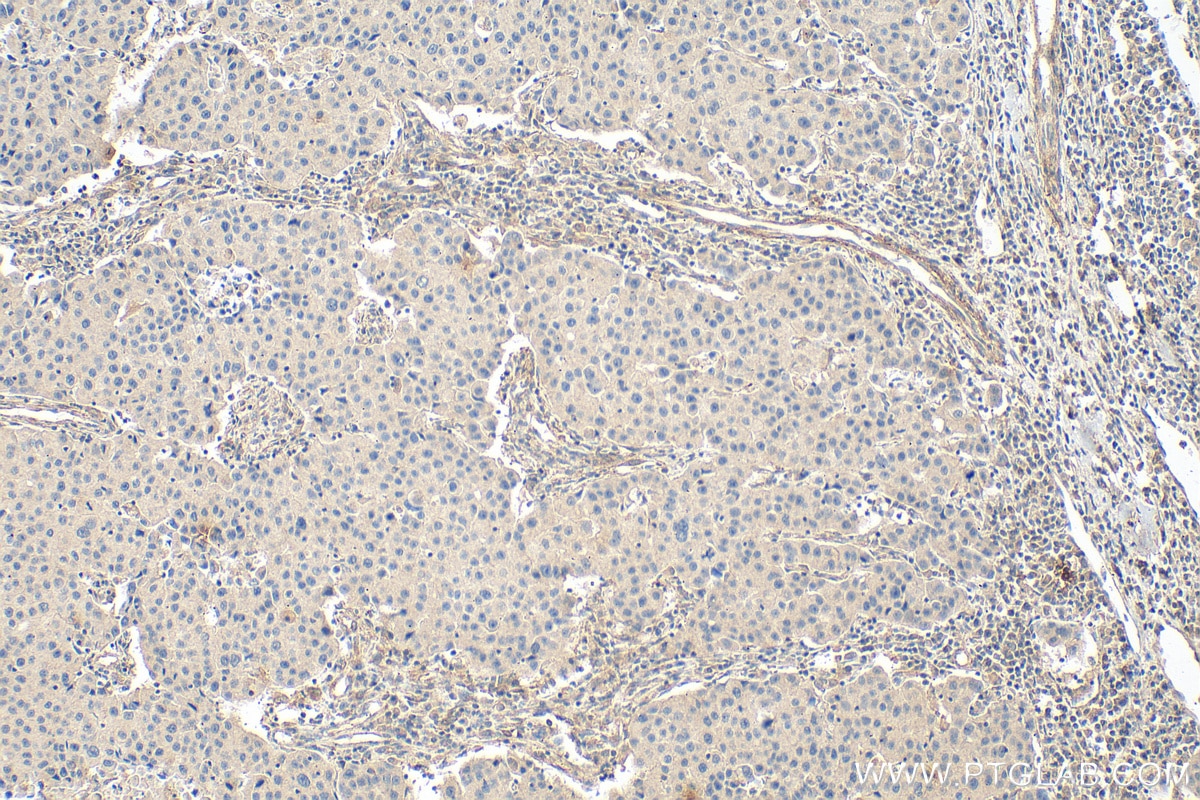
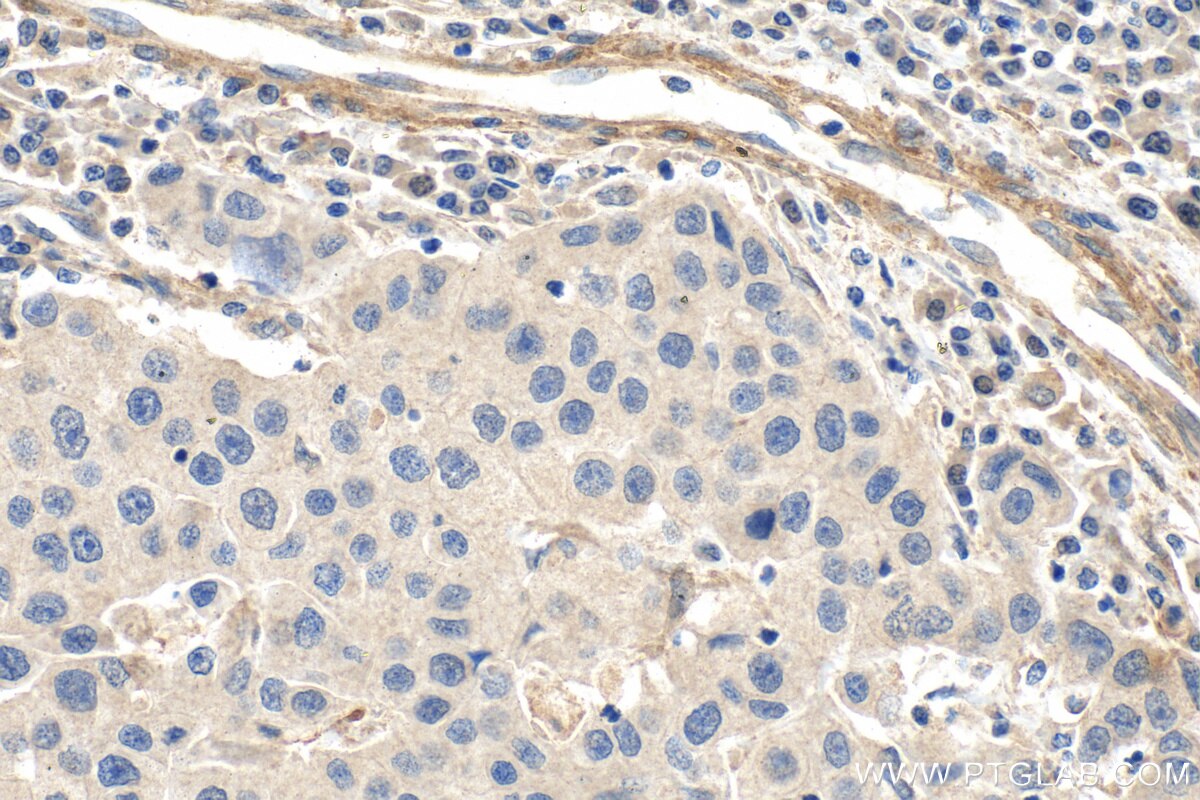
| Résultats positifs en IHC | tissu de cancer du col de l'utérus humain, tissu de cancer du sein humain il est suggéré de démasquer l'antigène avec un tampon de TE buffer pH 9.0; (*) À défaut, 'le démasquage de l'antigène peut être 'effectué avec un tampon citrate pH 6,0. |
| Résultats positifs en IF/ICC | cellules HeLa, |
Dilution recommandée
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:5000-1:50000 |
| Immunohistochimie (IHC) | IHC : 1:500-1:2000 |
| Immunofluorescence (IF)/ICC | IF/ICC : 1:200-1:800 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, check data in validation data gallery | |
Applications publiées
| KD/KO | See 1 publications below |
| WB | See 6 publications below |
| IHC | See 2 publications below |
| IF | See 3 publications below |
Informations sur le produit
67133-1-Ig cible Filamin A dans les applications de WB, IHC, IF/ICC, ELISA et montre une réactivité avec des échantillons Humain
| Réactivité | Humain |
| Réactivité citée | Humain |
| Hôte / Isotype | Mouse / IgG2a |
| Clonalité | Monoclonal |
| Type | Anticorps |
| Immunogène | Filamin A Protéine recombinante Ag23291 |
| Nom complet | filamin A, alpha (actin binding protein 280) |
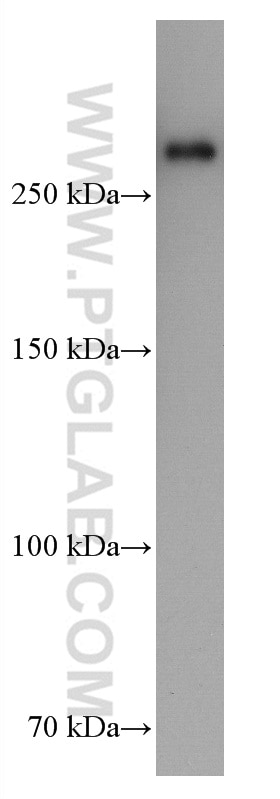
| Masse moléculaire calculée | 2647 aa, 280 kDa |
| Poids moléculaire observé | 280 kDa |
| Numéro d’acquisition GenBank | BC014654 |
| Symbole du gène | FLNA |
| Identification du gène (NCBI) | 2316 |
| Conjugaison | Non conjugué |
| Forme | Liquide |
| Méthode de purification | Purification par protéine A |
| Tampon de stockage | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol |
| Conditions de stockage | Stocker à -20°C. Stable pendant un an après l'expédition. L'aliquotage n'est pas nécessaire pour le stockage à -20oC Les 20ul contiennent 0,1% de BSA. |
Informations générales
FLNA encodes a 280 kDa widely expressed actin binding protein called filamin A which can crosslinks actin filaments and links actin filaments to membrane glycoproteins to form a three-dimensional network (PMID:29931263). And filamin A could interact with many other proteins, involved in receptor activation, cell migration and adhesion, cell proliferation, inflammation and tumorigenesis, studies have been reported that FLNA overexpressed in multiple types of tumors, suggesting FLNA may involved in cancer aggressiveness(PMID:29100390). What's more, FLNA is an causative gene of periventricular nodular heterotopia (PNH) (PMID: 29062687)
Protocole
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for Filamin A antibody 67133-1-Ig | Download protocol |
| IHC protocol for Filamin A antibody 67133-1-Ig | Download protocol |
| IF protocol for Filamin A antibody 67133-1-Ig | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |
Publications
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Front Cell Dev Biol NudC L279P Mutation Destabilizes Filamin A by Inhibiting the Hsp90 Chaperoning Pathway and Suppresses Cell Migration. | ||
Hum Mol Genet Expression and subcellular localization of USH1C/harmonin in human retina provides insights into pathomechanisms and therapy | ||
Mol Med Rep Filamin A regulates EGFR/ERK/Akt signaling and affects colorectal cancer cell growth and migration. | ||
Cell Death Dis NudCL2 regulates cell migration by stabilizing both myosin-9 and LIS1 with Hsp90. | ||
J Exp Clin Cancer Res Focal Adhesion Kinase (FAK)-Hippo/YAP transduction signaling mediates the stimulatory effects exerted by S100A8/A9-RAGE system in triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC). | ||
Cell Death Dis FRMD3 inhibits the growth and metastasis of breast cancer through the ubiquitination-mediated degradation of vimentin and subsequent impairment of focal adhesion |