Anticorps Polyclonal de lapin anti-CTGF
CTGF Polyclonal Antibody for WB, IP, IHC, ELISA
Hôte / Isotype
Lapin / IgG
Réactivité testée
Humain, souris et plus (1)
Applications
WB, IP, IF, IHC, ELISA
Conjugaison
Non conjugué
N° de cat : 23903-1-AP
Synonymes
Galerie de données de validation
Applications testées
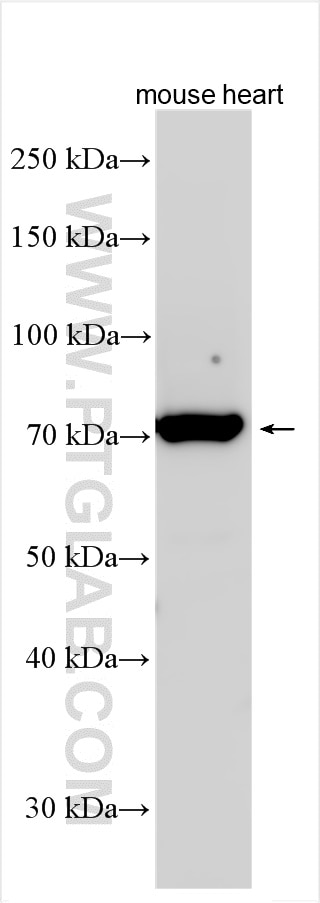
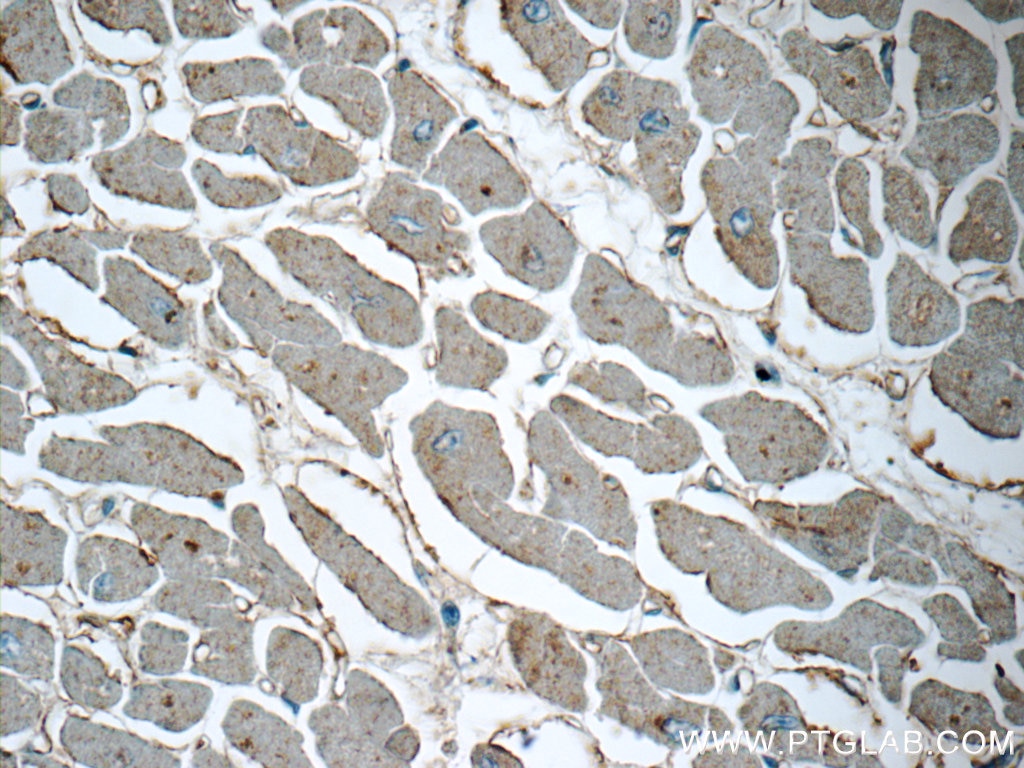
| Résultats positifs en WB | tissu cardiaque de souris, |
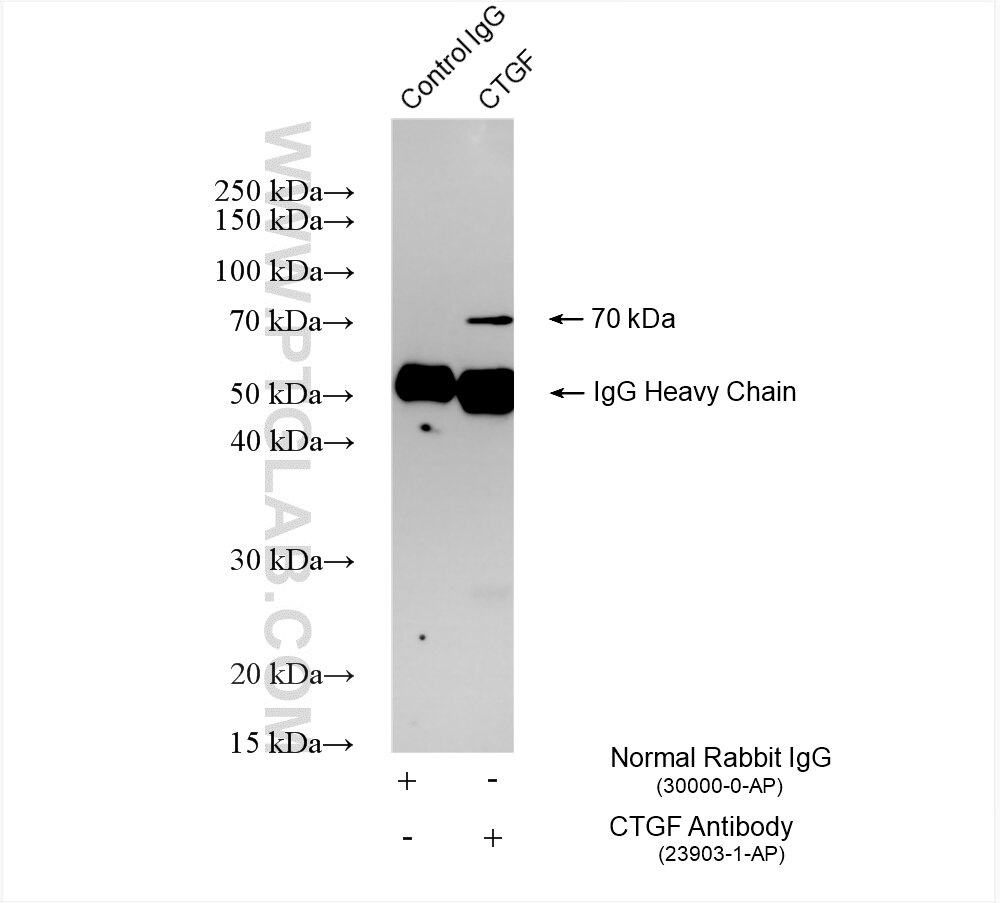
| Résultats positifs en IP | tissu cérébral de souris |
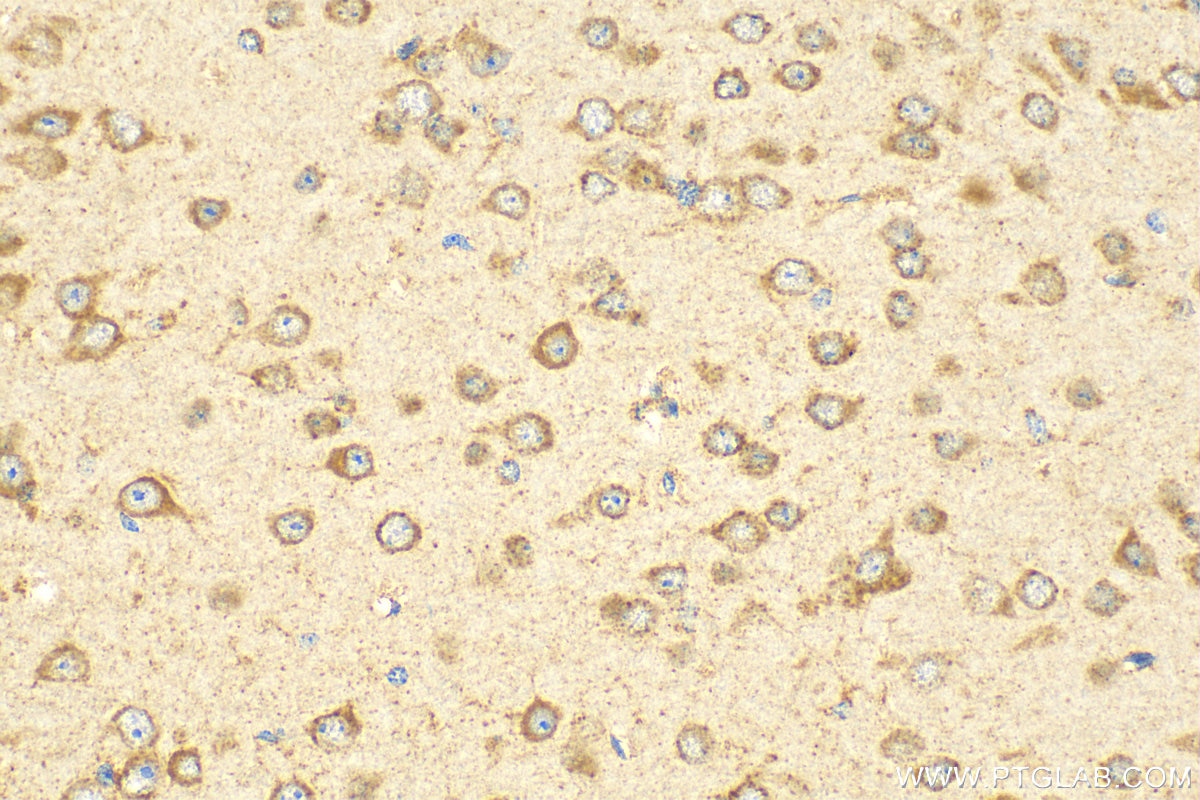
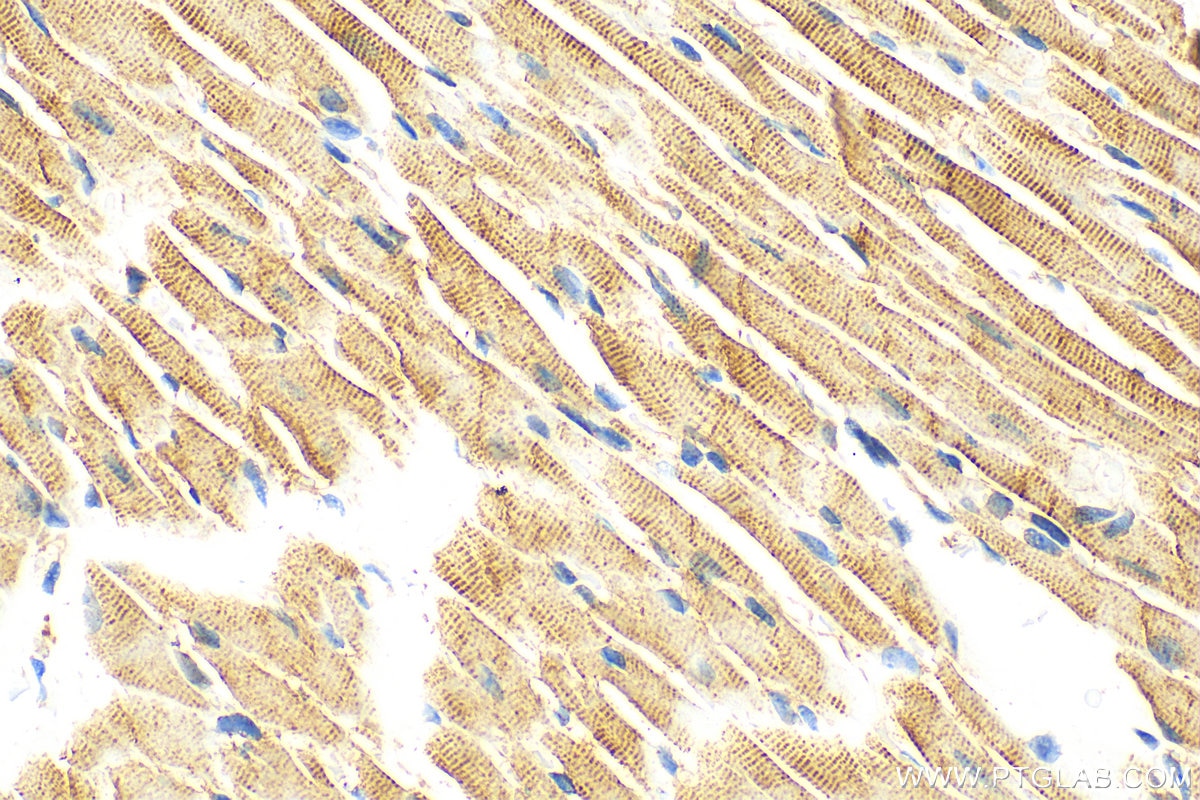
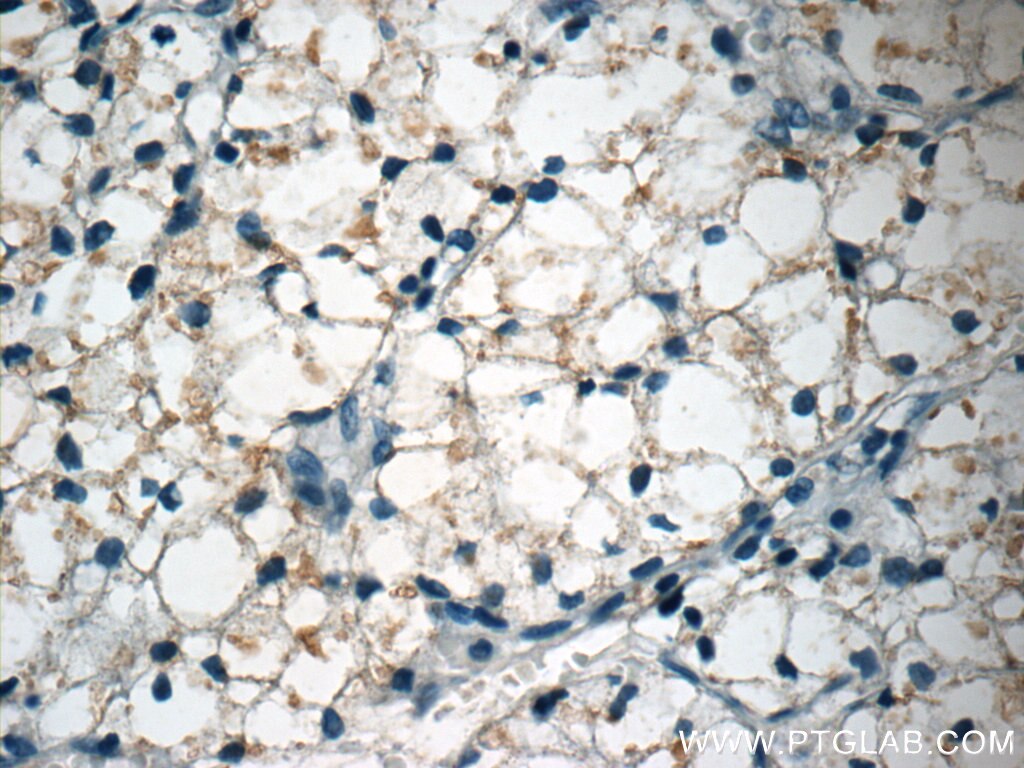
| Résultats positifs en IHC | tissu cardiaque de souris, tissu cardiaque humain, tissu cérébral de souris, tissu de néphroblastome humain il est suggéré de démasquer l'antigène avec un tampon de TE buffer pH 9.0; (*) À défaut, 'le démasquage de l'antigène peut être 'effectué avec un tampon citrate pH 6,0. |
Dilution recommandée
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:500-1:2000 |
| Immunoprécipitation (IP) | IP : 0.5-4.0 ug for 1.0-3.0 mg of total protein lysate |
| Immunohistochimie (IHC) | IHC : 1:50-1:500 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, check data in validation data gallery | |
Applications publiées
| WB | See 11 publications below |
| IHC | See 2 publications below |
| IF | See 2 publications below |
Informations sur le produit
23903-1-AP cible CTGF dans les applications de WB, IP, IF, IHC, ELISA et montre une réactivité avec des échantillons Humain, souris
| Réactivité | Humain, souris |
| Réactivité citée | rat, Humain, souris |
| Hôte / Isotype | Lapin / IgG |
| Clonalité | Polyclonal |
| Type | Anticorps |
| Immunogène | CTGF Protéine recombinante Ag20985 |
| Nom complet | connective tissue growth factor |
| Masse moléculaire calculée | 349 aa, 38 kDa |
| Poids moléculaire observé | 70 kDa |
| Numéro d’acquisition GenBank | BC087839 |
| Symbole du gène | CTGF |
| Identification du gène (NCBI) | 1490 |
| Conjugaison | Non conjugué |
| Forme | Liquide |
| Méthode de purification | Purification par affinité contre l'antigène |
| Tampon de stockage | PBS avec azoture de sodium à 0,02 % et glycérol à 50 % pH 7,3 |
| Conditions de stockage | Stocker à -20°C. Stable pendant un an après l'expédition. L'aliquotage n'est pas nécessaire pour le stockage à -20oC Les 20ul contiennent 0,1% de BSA. |
Informations générales
CTGF, also known as CCN2, is a member of the CCN family of matricellular proteins. CTGF, a cysteine-rich, matrix-associated, heparin-binding protein, is widely expressed in various human tissues and organs. CTGF has important roles in many biological processes, including cell adhesion, migration, proliferation, angiogenesis, skeletal development, and tissue wound repair, and is critically involved in fibrotic disease and several forms of cancers. In western blotting, there are three different forms of CTGF reported: monomeric forms at approximately 36-38 kDa, homodimeric forms at approximately 70 kDa, and lower molecular mass fragment forms (PMID: 14592956).
Protocole
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for CTGF antibody 23903-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IHC protocol for CTGF antibody 23903-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IP protocol for CTGF antibody 23903-1-AP | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |
Publications
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Phytomedicine Aloe-emodin ameliorated MI-induced cardiac remodeling in mice via inhibiting TGF-β/SMAD signaling via up-regulating SMAD7 | ||
Biomater Sci A high-density collagen xerogel thread prevents the progression of peritoneal fibrosis | ||
Ecotoxicol Environ Saf Polystyrene microplastic-induced extracellular vesicles cause kidney-related effects in the crosstalk between tubular cells and fibroblasts | ||
Stem Cells Int hUMSCs Restore Uterine Function by Inhibiting Endometrial Fibrosis via Regulation of the MMP-9/TIMP-1 Ratio in CDDP-Induced Injury Rats | ||
J Cardiovasc Transl Res Exosomes Derived from AT2R-Overexpressing BMSC Prevent Restenosis After Carotid Artery Injury by Attenuating the Injury-Induced Neointimal Hyperplasia. | ||
Tissue Cell Estrogen inhibits the differentiation of fibroblasts induced by high stiffness matrix by enhancing DNMT1 expression |