Anticorps Polyclonal de lapin anti-CKM-Specific
CKM-Specific Polyclonal Antibody for WB, IHC, ELISA
Hôte / Isotype
Lapin / IgG
Réactivité testée
Humain, rat, souris et plus (1)
Applications
WB, IHC, ELISA
Conjugaison
Non conjugué
N° de cat : 18712-1-AP
Synonymes
Galerie de données de validation
Applications testées
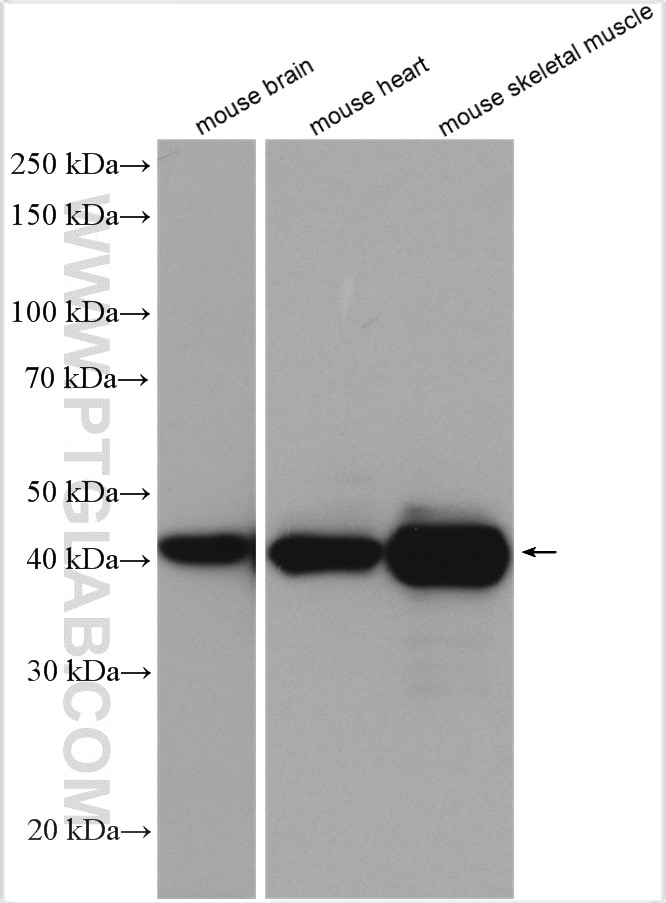
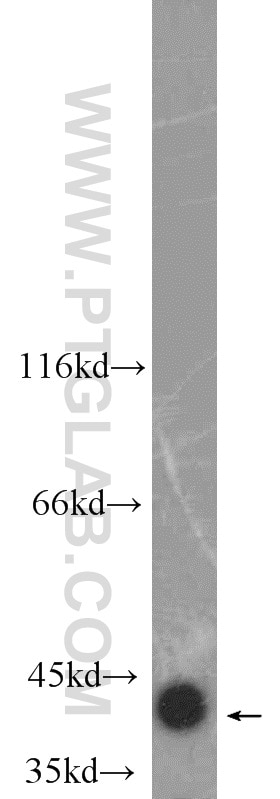
| Résultats positifs en WB | tissu cérébral de souris, tissu cardiaque de souris, tissu de muscle squelettique de souris, tissu d'intestin grêle de souris |
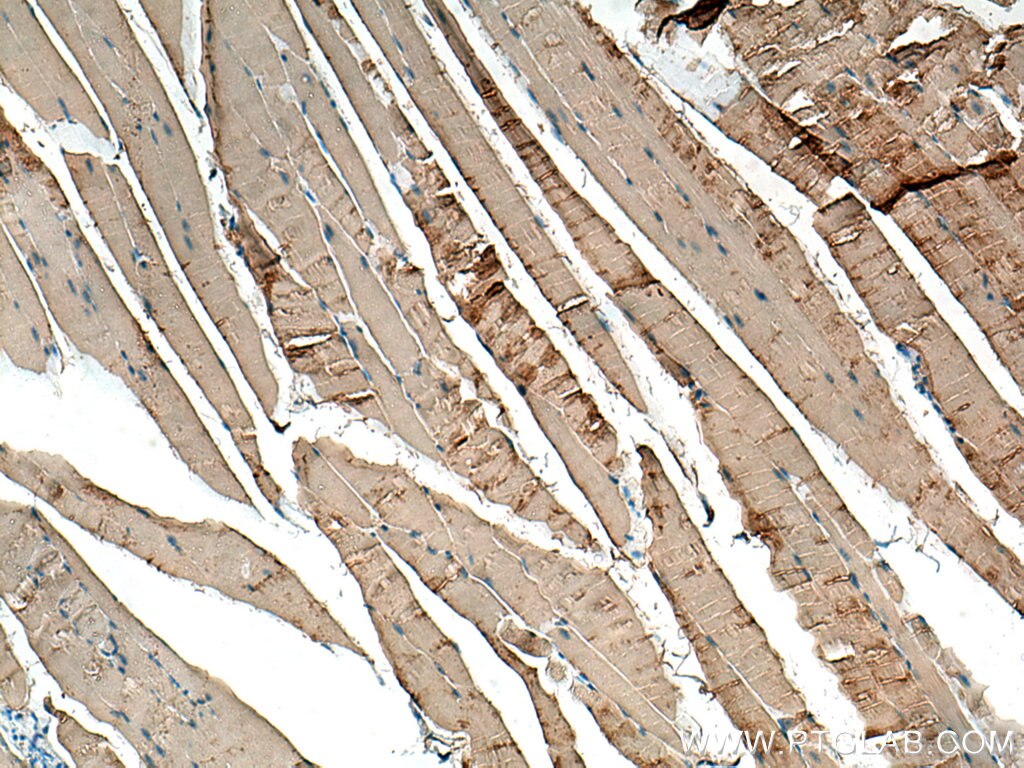
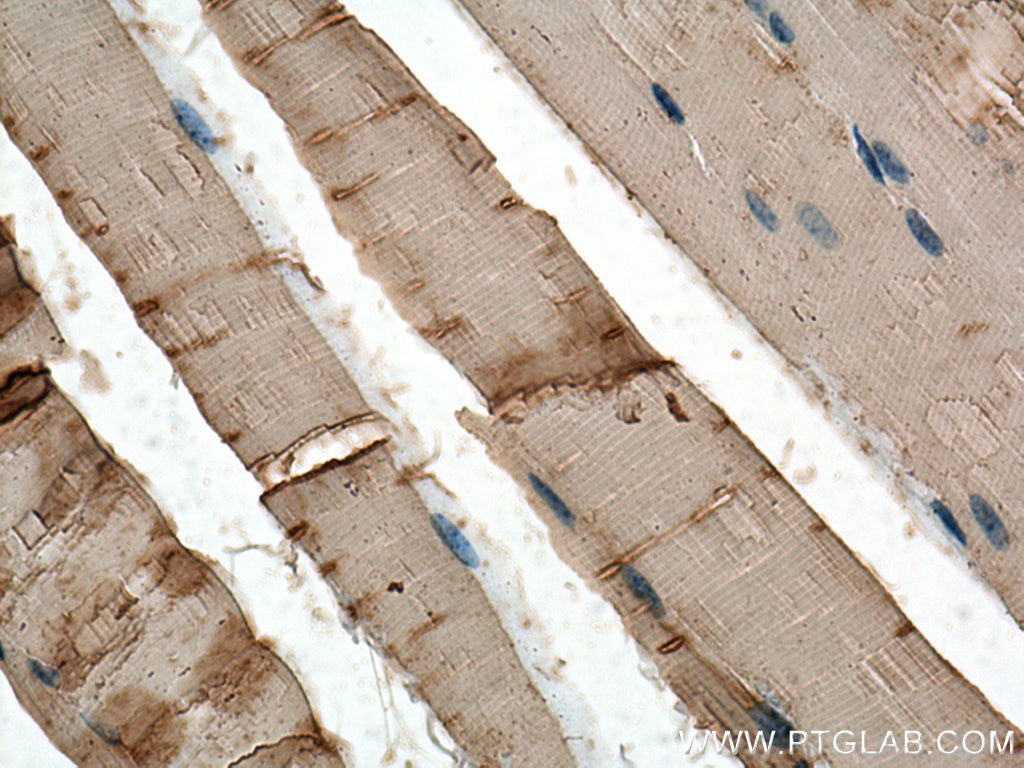
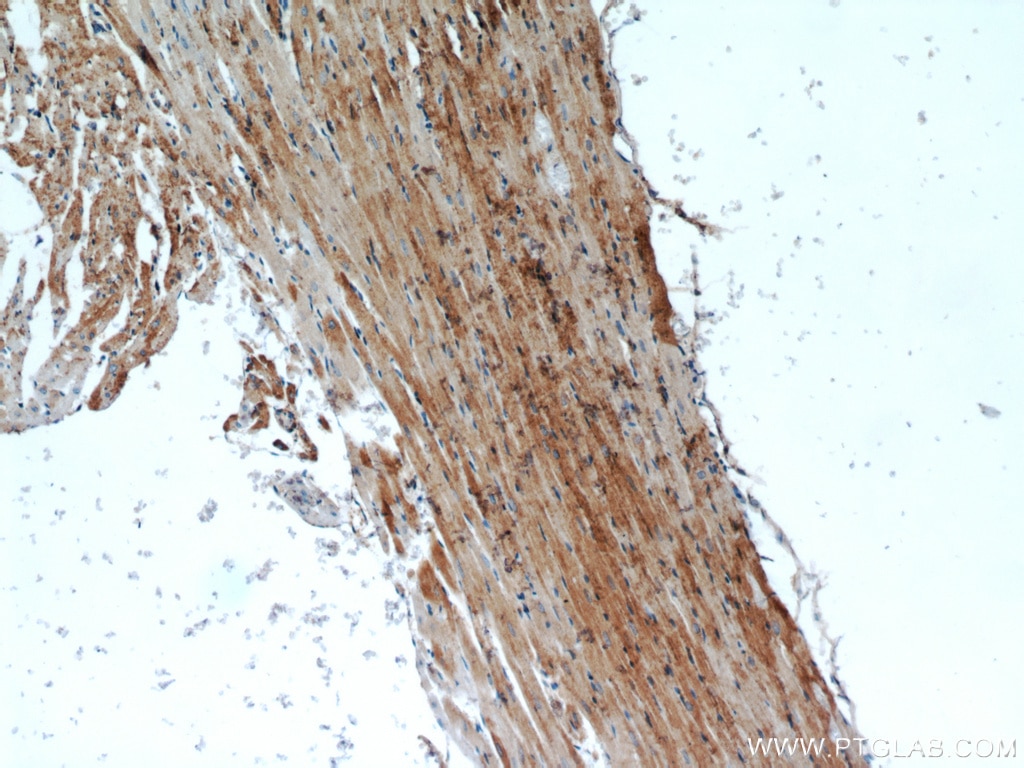
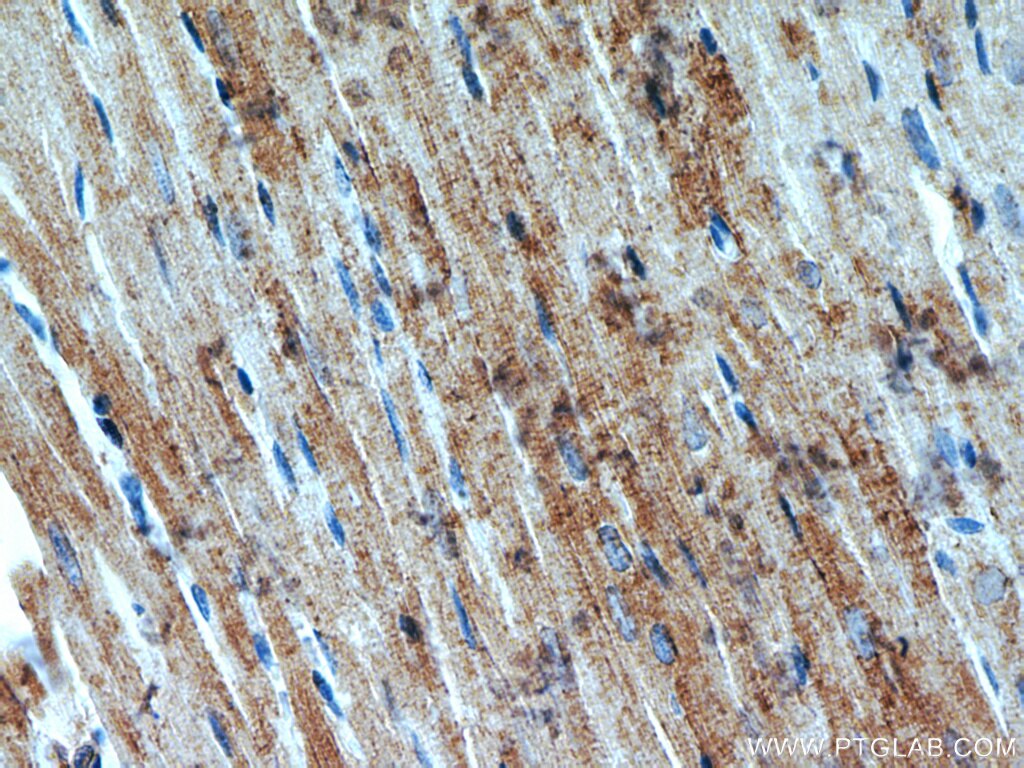
| Résultats positifs en IHC | tissu de muscle squelettique de souris, tissu cardiaque de rat il est suggéré de démasquer l'antigène avec un tampon de TE buffer pH 9.0; (*) À défaut, 'le démasquage de l'antigène peut être 'effectué avec un tampon citrate pH 6,0. |
Dilution recommandée
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:5000-1:50000 |
| Immunohistochimie (IHC) | IHC : 1:50-1:500 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, check data in validation data gallery | |
Applications publiées
| WB | See 5 publications below |
Informations sur le produit
18712-1-AP cible CKM-Specific dans les applications de WB, IHC, ELISA et montre une réactivité avec des échantillons Humain, rat, souris
| Réactivité | Humain, rat, souris |
| Réactivité citée | souris, Bactérie |
| Hôte / Isotype | Lapin / IgG |
| Clonalité | Polyclonal |
| Type | Anticorps |
| Immunogène | Peptide |
| Nom complet | creatine kinase, muscle |
| Masse moléculaire calculée | 43 kDa |
| Poids moléculaire observé | 43 kDa |
| Numéro d’acquisition GenBank | BC007462 |
| Symbole du gène | CKM |
| Identification du gène (NCBI) | 1158 |
| Conjugaison | Non conjugué |
| Forme | Liquide |
| Méthode de purification | Purification par affinité contre l'antigène |
| Tampon de stockage | PBS avec azoture de sodium à 0,02 % et glycérol à 50 % pH 7,3 |
| Conditions de stockage | Stocker à -20°C. Stable pendant un an après l'expédition. L'aliquotage n'est pas nécessaire pour le stockage à -20oC Les 20ul contiennent 0,1% de BSA. |
Informations générales
CKM, also named as CKMM and M-CK, is a member of the ATP:guanido phosphotransferase protein family. It is a cytoplasmic enzyme involved in energy homeostasis and is an important serum marker for myocardial infarction. CKM reversibly catalyzes the transfer of phosphate between ATP and various phosphogens such as creatine phosphate. It acts as a homodimer in striated muscle as well as in other tissues, and as a heterodimer with a similar brain isozyme in heart. CK isoenzymes play a central role in energy transduction in tissues with large, fluctuating energy demands, such as skeletal muscle, heart, brain and spermatozoa. CK MB consists of a dimer of nonidentical chains. With MM being the major form in skeletal muscle and myocardium, MB existing in myocardium, and BB existing in many tissues, especially brain. Inactivation of creatine kinase by gliotoxin was accompanied by the formation of a 37-kDa form of the enzyme.This oxidized form of creatine kinase was rapidly reconverted to the 42 kDa species by the addition of reducing agents concomitant with restoration of activity.(PMID: 10827185). This antibody is specific to CKM.
Protocole
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for CKM-Specific antibody 18712-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IHC protocol for CKM-Specific antibody 18712-1-AP | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |
Publications
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Cell Prolif KLF3 promotes the 8-cell-like transcriptional state in pluripotent stem cells. | ||
Mol Pharmacol Naturally Occurring Mutations to Muscle-Type Creatine Kinase Impact Its Canonical and Pharmacological Activities in a Substrate-Dependent Manner In Vitro. | ||