- Phare
- Validé par KD/KO
Anticorps Polyclonal de lapin anti-Chk1
Chk1 Polyclonal Antibody for WB, IF, IHC, ELISA
Hôte / Isotype
Lapin / IgG
Réactivité testée
Humain, rat, souris
Applications
WB, IF, IHC, ELISA
Conjugaison
Non conjugué
N° de cat : 10362-1-AP
Synonymes
Galerie de données de validation
Applications testées
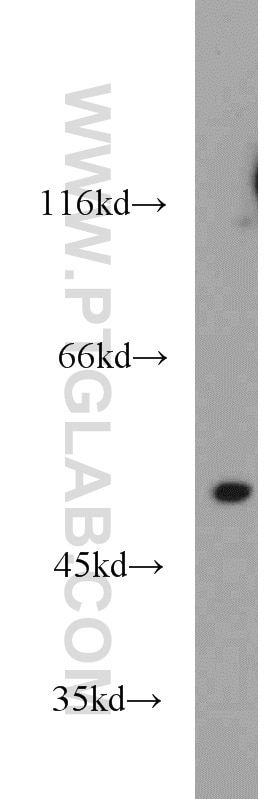
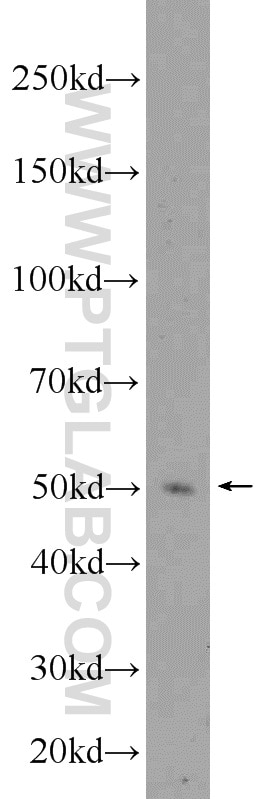
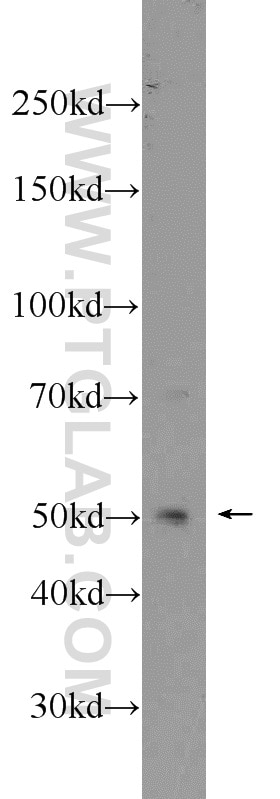
| Résultats positifs en WB | tissu de thymus de souris, cellules HeLa, cellules K-562 |
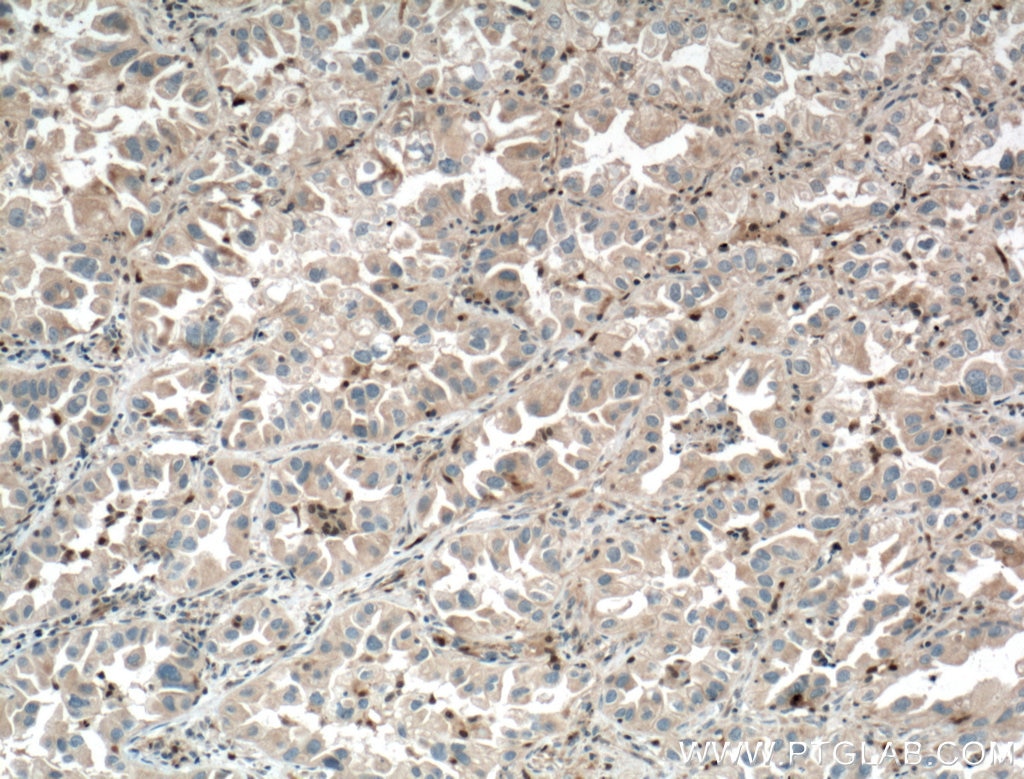
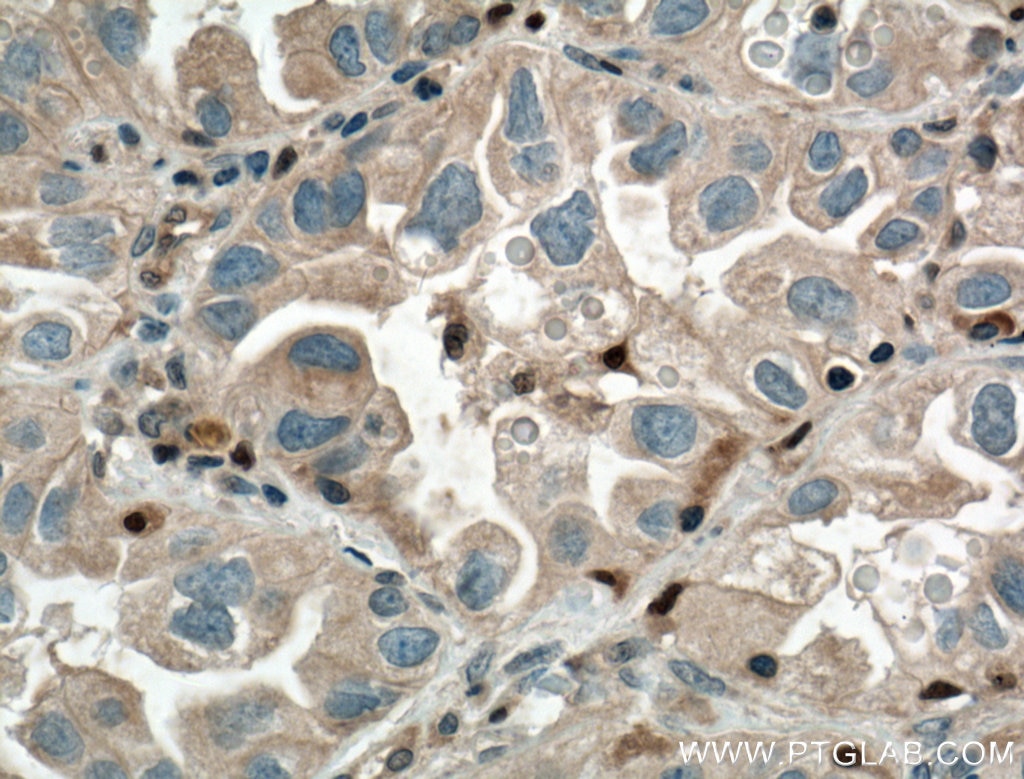
| Résultats positifs en IHC | tissu de cancer du poumon humain il est suggéré de démasquer l'antigène avec un tampon de TE buffer pH 9.0; (*) À défaut, 'le démasquage de l'antigène peut être 'effectué avec un tampon citrate pH 6,0. |
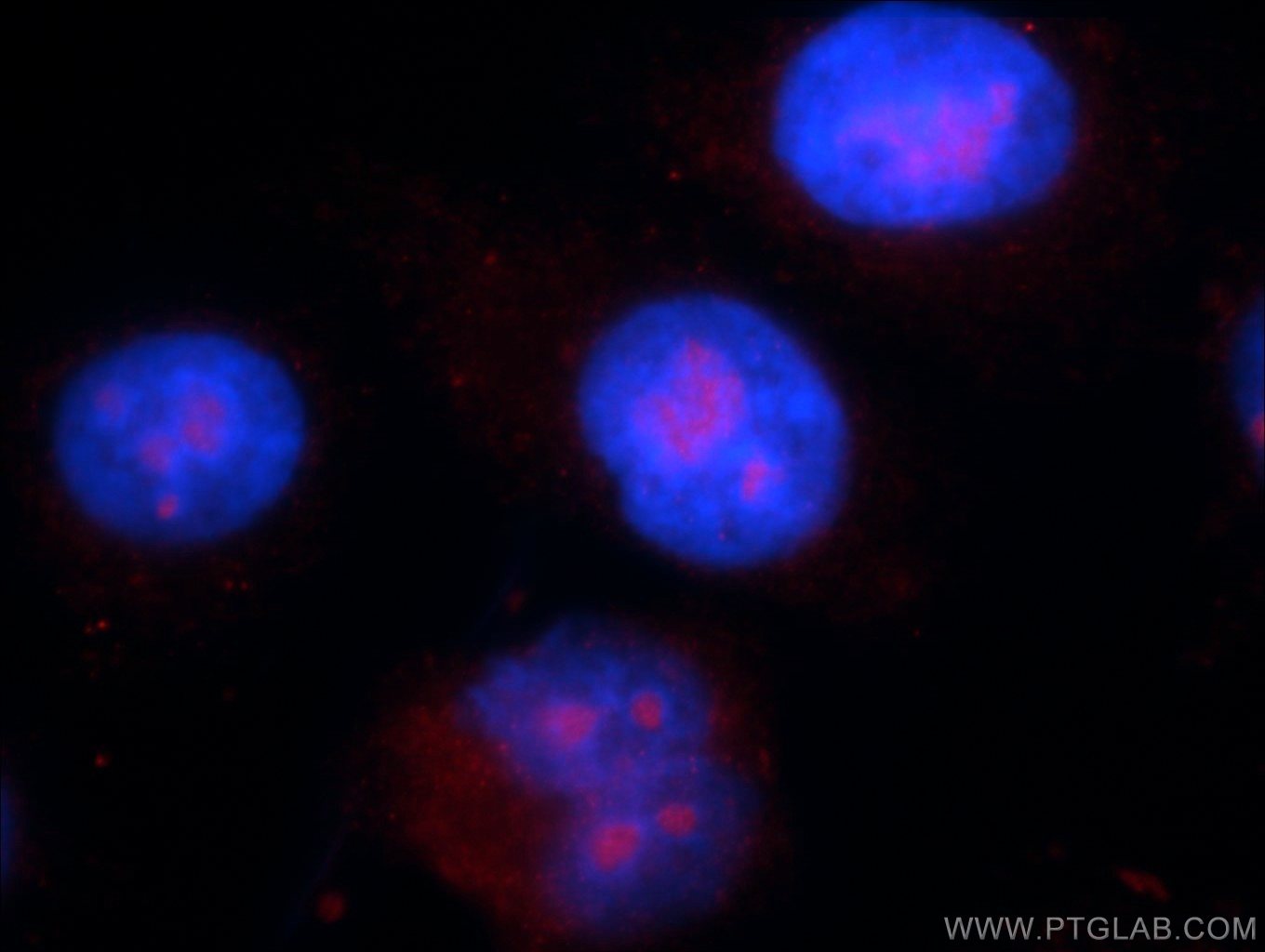
| Résultats positifs en IF/ICC | cellules HepG2 |
Dilution recommandée
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:500-1:1000 |
| Immunohistochimie (IHC) | IHC : 1:50-1:500 |
| Immunofluorescence (IF)/ICC | IF/ICC : 1:10-1:100 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, check data in validation data gallery | |
Applications publiées
| KD/KO | See 1 publications below |
| WB | See 16 publications below |
| IHC | See 1 publications below |
Informations sur le produit
10362-1-AP cible Chk1 dans les applications de WB, IF, IHC, ELISA et montre une réactivité avec des échantillons Humain, rat, souris
| Réactivité | Humain, rat, souris |
| Réactivité citée | rat, Humain, souris |
| Hôte / Isotype | Lapin / IgG |
| Clonalité | Polyclonal |
| Type | Anticorps |
| Immunogène | Chk1 Protéine recombinante Ag0409 |
| Nom complet | CHK1 checkpoint homolog (S. pombe) |
| Masse moléculaire calculée | 54 kDa |
| Poids moléculaire observé | 50-55 kDa |
| Numéro d’acquisition GenBank | BC004202 |
| Symbole du gène | Chk1 |
| Identification du gène (NCBI) | 1111 |
| Conjugaison | Non conjugué |
| Forme | Liquide |
| Méthode de purification | Purification par affinité contre l'antigène |
| Tampon de stockage | PBS avec azoture de sodium à 0,02 % et glycérol à 50 % pH 7,3 |
| Conditions de stockage | Stocker à -20°C. Stable pendant un an après l'expédition. L'aliquotage n'est pas nécessaire pour le stockage à -20oC Les 20ul contiennent 0,1% de BSA. |
Informations générales
In response to DNA damage, mammalian cells prevent cell cycle progression through the control of critical cell cycle regulators. CHK1 (synonym: CHEK1), a homolog of the Schizosaccharomyces pombe Chk1 protein kinase, is required for the DNA damage checkpoint. Human Chk1 protein is modified in response to DNA damage. In vitro Chk1 binds to and phosphorylate the dual-specificity protein phosphatases Cdc25A, Cdc25B, and Cdc25C, which control cell cycle transitions by dephosphorylating cyclin-dependent kinases. CHK1 can be autophosphorylated(PMID:22941630) and ubiquitinated (PMID:19276361). It has 3 isoforms produced by alternative splicing with the molecular weight of 54 kDa, 44 kDa and 50 kDa.
Protocole
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for Chk1 antibody 10362-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IHC protocol for Chk1 antibody 10362-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IF protocol for Chk1 antibody 10362-1-AP | Download protocol |
| FC protocol for Chk1 antibody 10362-1-AP | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |
Publications
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Nat Commun Human Tra2 proteins jointly control a CHEK1 splicing switch among alternative and constitutive target exons.
| ||
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A Checkpoint kinase 1 (Chk1)-short is a splice variant and endogenous inhibitor of Chk1 that regulates cell cycle and DNA damage checkpoints. | ||
Oncotarget UBE2D3 gene overexpression increases radiosensitivity of EC109 esophageal cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. | ||
EBioMedicine High PARP-1 expression predicts poor survival in acute myeloid leukemia and PARP-1 inhibitor and SAHA-bendamustine hybrid inhibitor combination treatment synergistically enhances anti-tumor effects. | ||
Cell Death Dis HBV infection potentiates resistance to S-phase arrest-inducing chemotherapeutics by inhibiting CHK2 pathway in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. | ||
Cell Death Dis PFKFB3 blockade inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma growth by impairing DNA repair through AKT. |