Anticorps Polyclonal de lapin anti-CD40L/CD154
CD40L/CD154 Polyclonal Antibody for WB, IP, IF, IHC, ELISA
Hôte / Isotype
Lapin / IgG
Réactivité testée
Humain, souris et plus (1)
Applications
WB, IHC, IF-P, IP, ELISA
Conjugaison
Non conjugué
N° de cat : 16668-1-AP
Synonymes
Galerie de données de validation
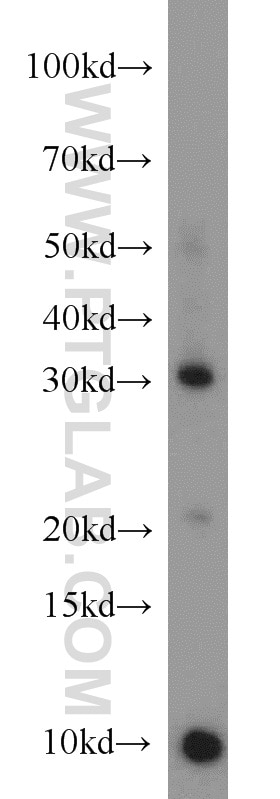
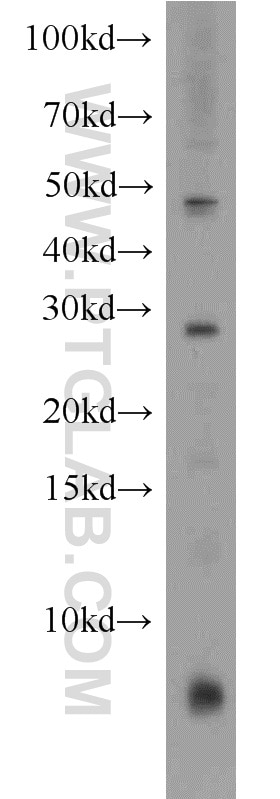
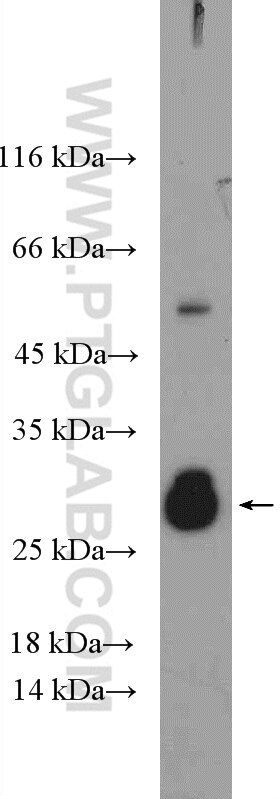
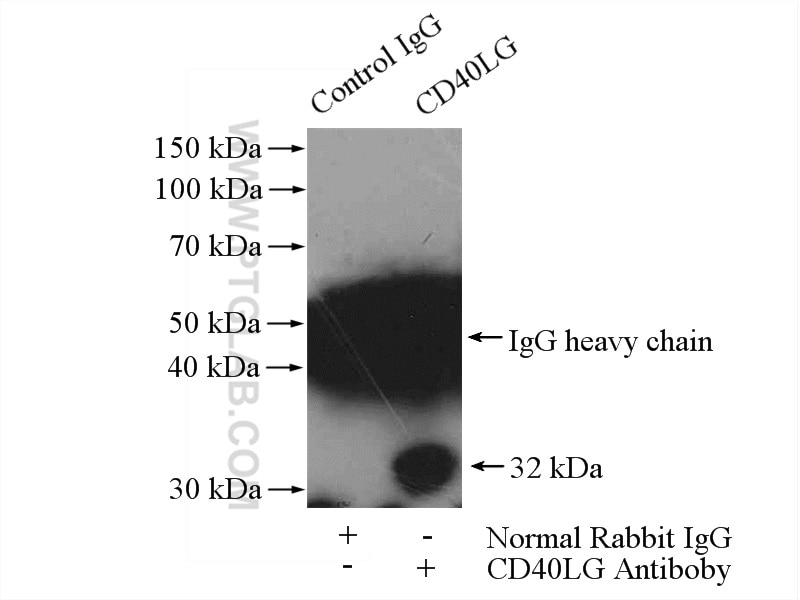
Applications testées
| Résultats positifs en WB | tissu d'intestin grêle de souris, cellules HeLa, cellules Jurkat |
| Résultats positifs en IP | cellules Jurkat |
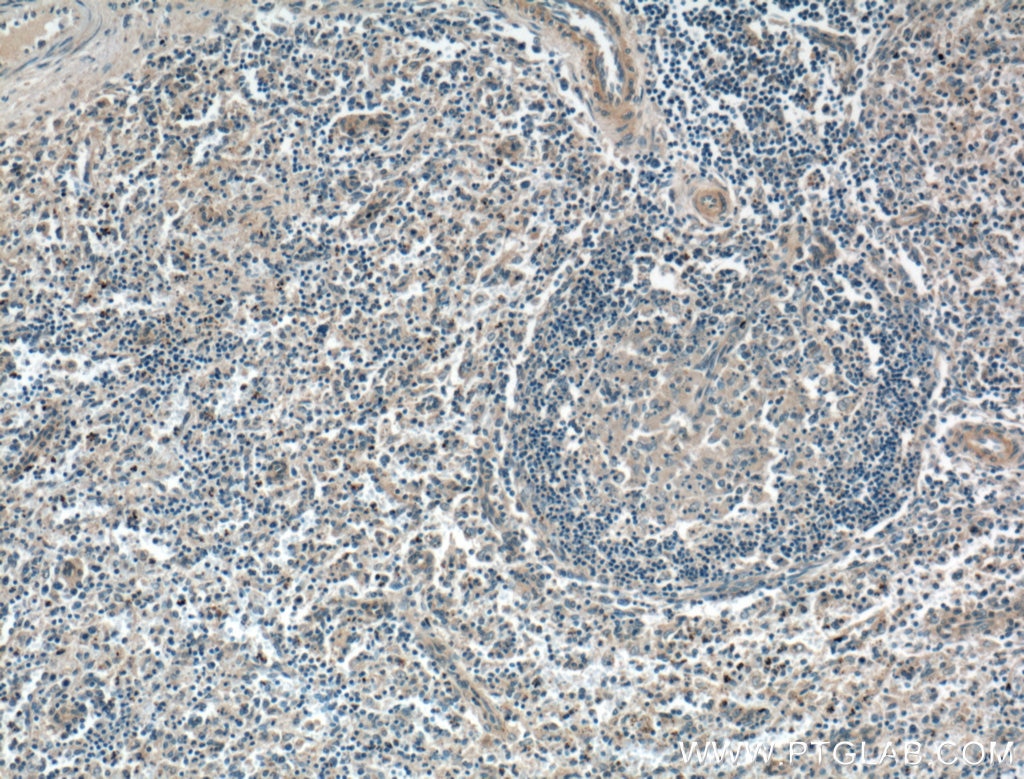
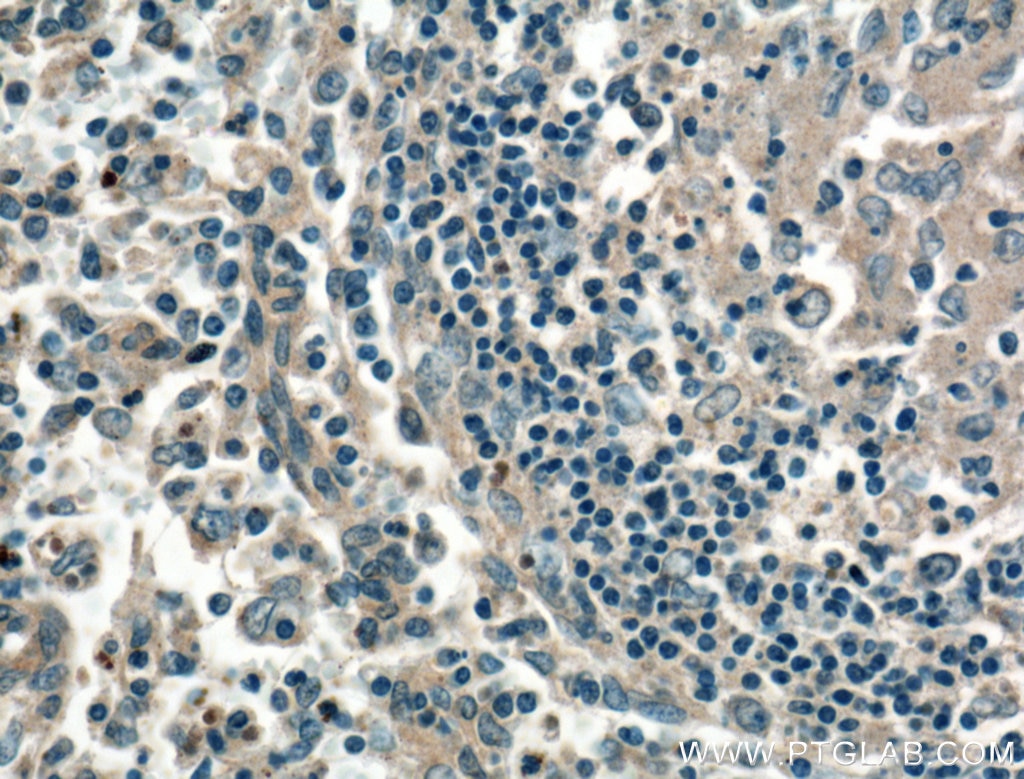
| Résultats positifs en IHC | tissu splénique humain, il est suggéré de démasquer l'antigène avec un tampon de TE buffer pH 9.0; (*) À défaut, 'le démasquage de l'antigène peut être 'effectué avec un tampon citrate pH 6,0. |
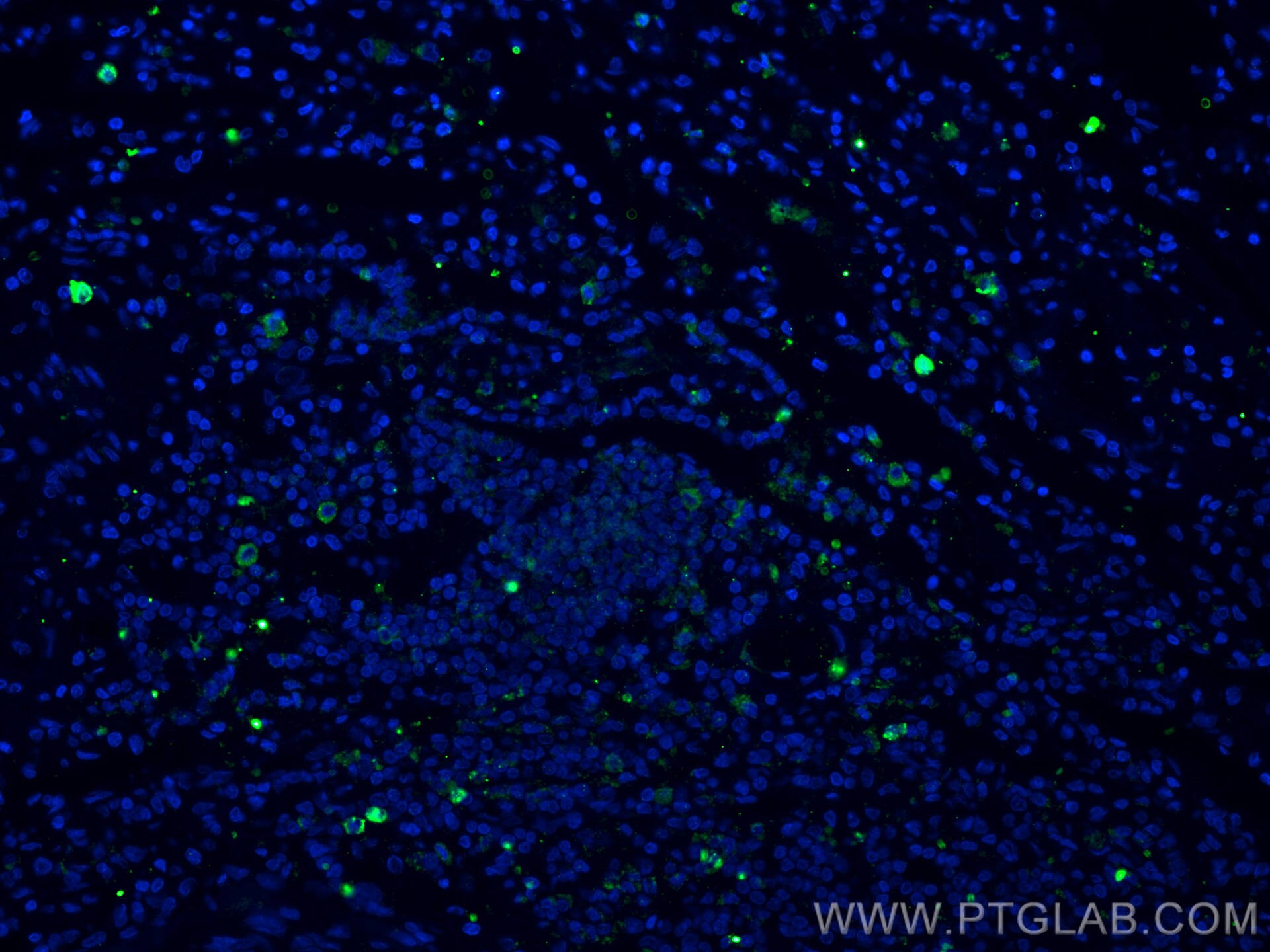
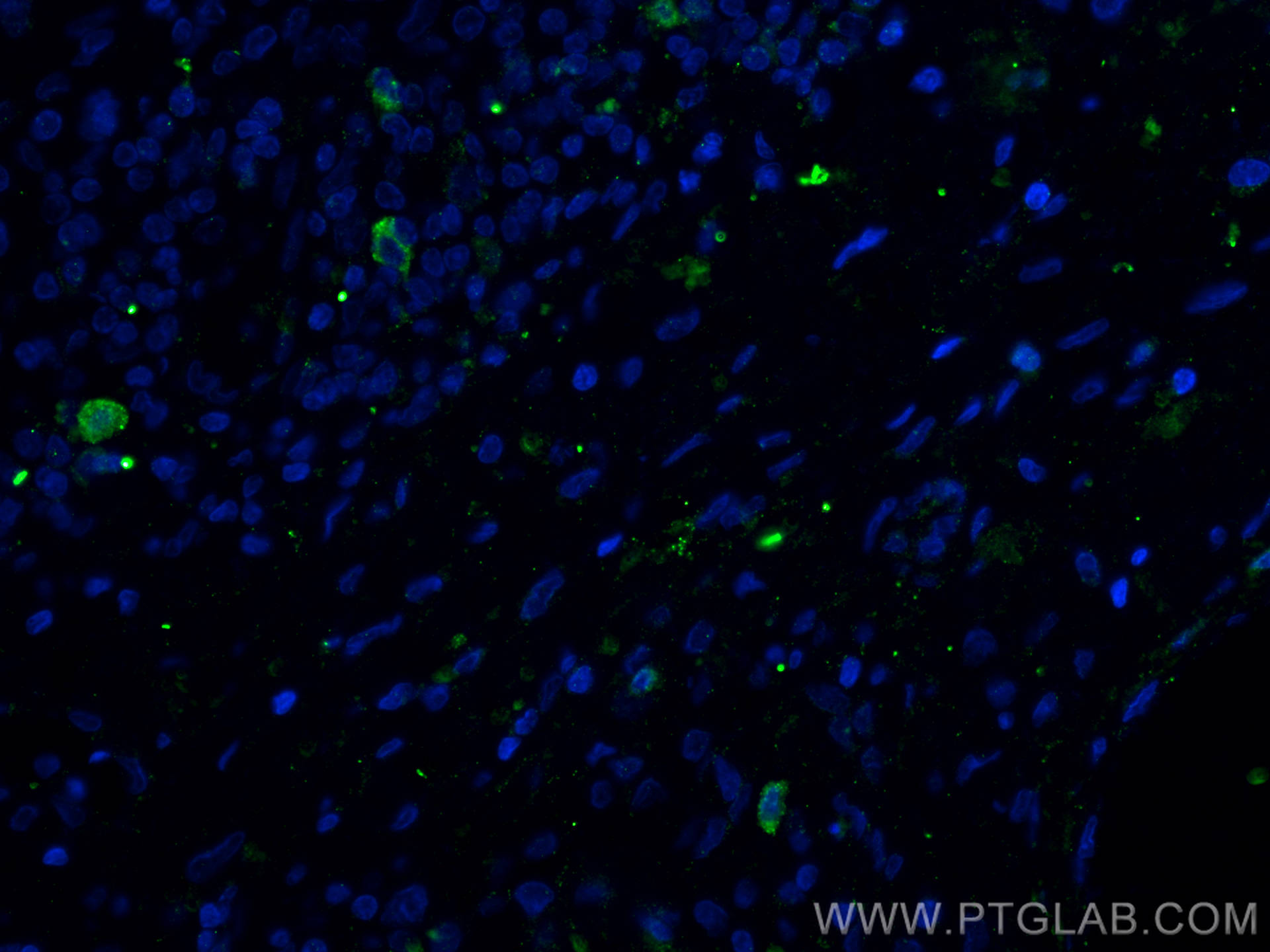
| Résultats positifs en IF-P | tissu de cancer du poumon humain, |
Dilution recommandée
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:500-1:2000 |
| Immunoprécipitation (IP) | IP : 0.5-4.0 ug for 1.0-3.0 mg of total protein lysate |
| Immunohistochimie (IHC) | IHC : 1:50-1:500 |
| Immunofluorescence (IF)-P | IF-P : 1:50-1:500 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, check data in validation data gallery | |
Applications publiées
| WB | See 6 publications below |
| IHC | See 5 publications below |
Informations sur le produit
16668-1-AP cible CD40L/CD154 dans les applications de WB, IHC, IF-P, IP, ELISA et montre une réactivité avec des échantillons Humain, souris
| Réactivité | Humain, souris |
| Réactivité citée | rat, Humain, souris |
| Hôte / Isotype | Lapin / IgG |
| Clonalité | Polyclonal |
| Type | Anticorps |
| Immunogène | CD40L/CD154 Protéine recombinante Ag10147 |
| Nom complet | CD40 ligand |
| Masse moléculaire calculée | 261 aa, 29 kDa |
| Poids moléculaire observé | 29-32 kDa |
| Numéro d’acquisition GenBank | BC071754 |
| Symbole du gène | CD40 Ligand |
| Identification du gène (NCBI) | 959 |
| Conjugaison | Non conjugué |
| Forme | Liquide |
| Méthode de purification | Purification par affinité contre l'antigène |
| Tampon de stockage | PBS avec azoture de sodium à 0,02 % et glycérol à 50 % pH 7,3 |
| Conditions de stockage | Stocker à -20°C. Stable pendant un an après l'expédition. L'aliquotage n'est pas nécessaire pour le stockage à -20oC Les 20ul contiennent 0,1% de BSA. |
Informations générales
The CD40 ligand (CD40L, TRAP, CD154), a member of the TNF superfamily of ligands, is expressed as either a 33 kDa transmembrane homologue or 18 kDa soluble form (sCD154). CD40L is primarily expressed on activated CD4+ T cells and on a small proportion of CD8+ T cells and platelets. It binds to CD40 on antigen-presenting cells (APC), which leads to many effects depending on the target cell type. Recent studies have suggested that CD40/CD40L interactions regulate oxidative stress and affect various signaling pathways in both the immunological and the cardiovascular systems. The CD40/CD40L system is also involved in tumorigenesis.
Protocole
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for CD40L/CD154 antibody 16668-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IHC protocol for CD40L/CD154 antibody 16668-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IF protocol for CD40L/CD154 antibody 16668-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IP protocol for CD40L/CD154 antibody 16668-1-AP | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |
Publications
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Sci Adv Promoting the activation of T cells with glycopolymer-modified dendritic cells by enhancing cell interactions. | ||
J Mol Cell Cardiol TNF-α promotes early atherosclerosis by increasing transcytosis of LDL across endothelial cells: crosstalk between NF-κB and PPAR-γ | ||
Br J Pharmacol CRP promotes atherosclerosis by increasing LDL transcytosis across endothelial cells. | ||
Pharmacol Res PKCβII-mediated cross-talk of TRPV1/CB2 modulates the glucocorticoid-induced osteoclast overactivity. | ||
Sci China Life Sci Compression loading of osteoclasts attenuated microRNA-146a-5p expression, which promotes angiogenesis by targeting adiponectin. | ||