- Phare
- Validé par KD/KO
Anticorps Polyclonal de lapin anti-AXIN1
AXIN1 Polyclonal Antibody for WB, IHC, ELISA
Hôte / Isotype
Lapin / IgG
Réactivité testée
Humain et plus (1)
Applications
WB, IHC, ELISA
Conjugaison
Non conjugué
N° de cat : 16541-1-AP
Synonymes
Galerie de données de validation
Applications testées
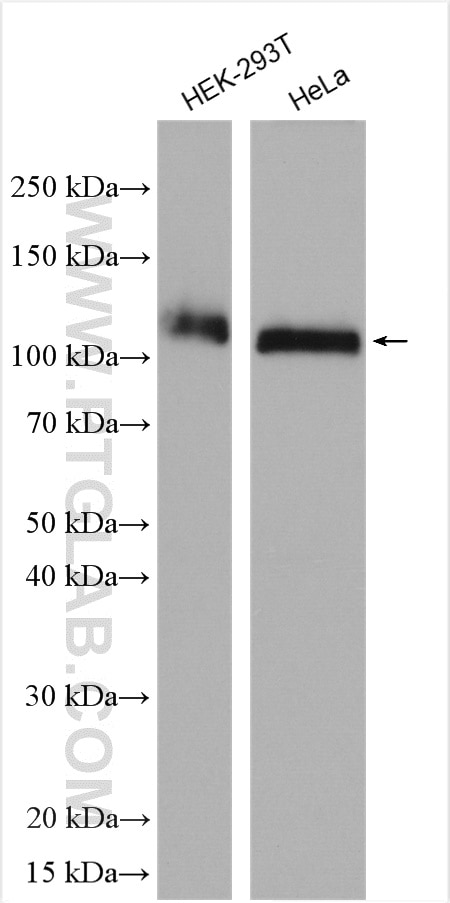
| Résultats positifs en WB | cellules HT-1080, cellules HEK-293T, cellules HeLa |
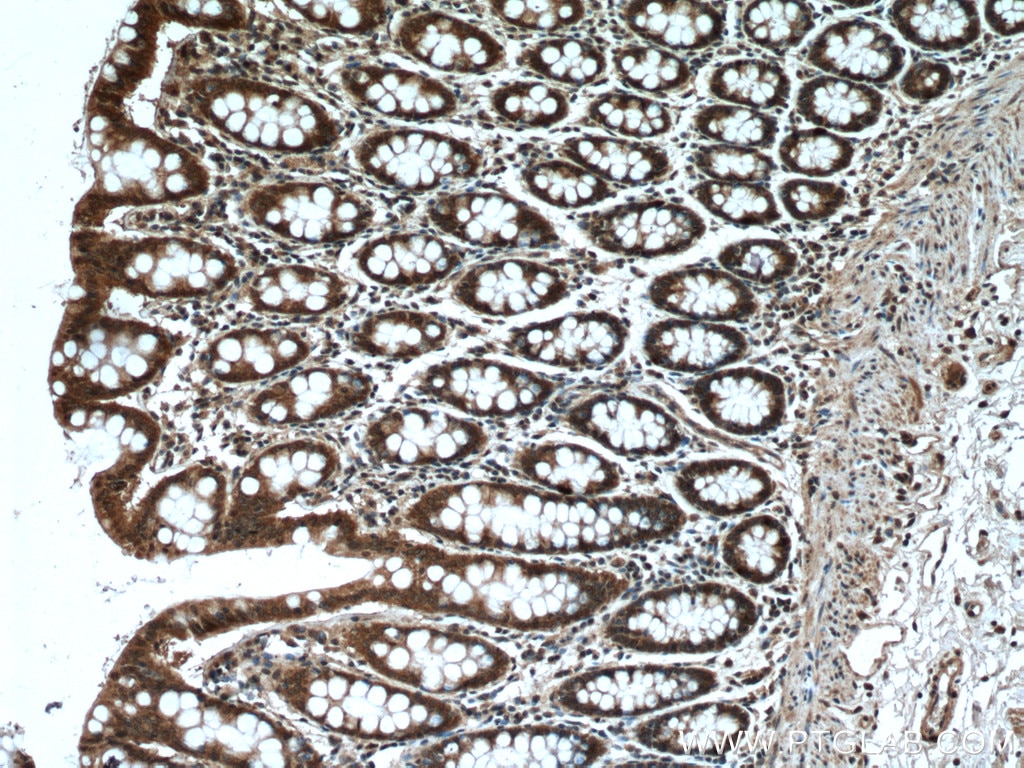
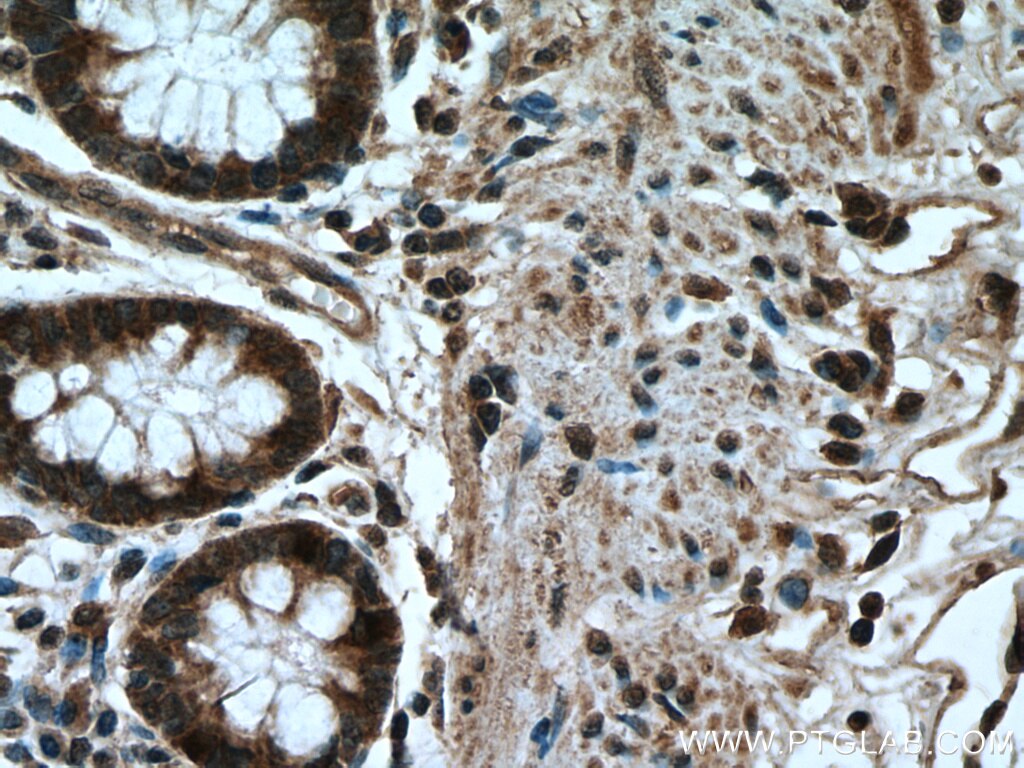
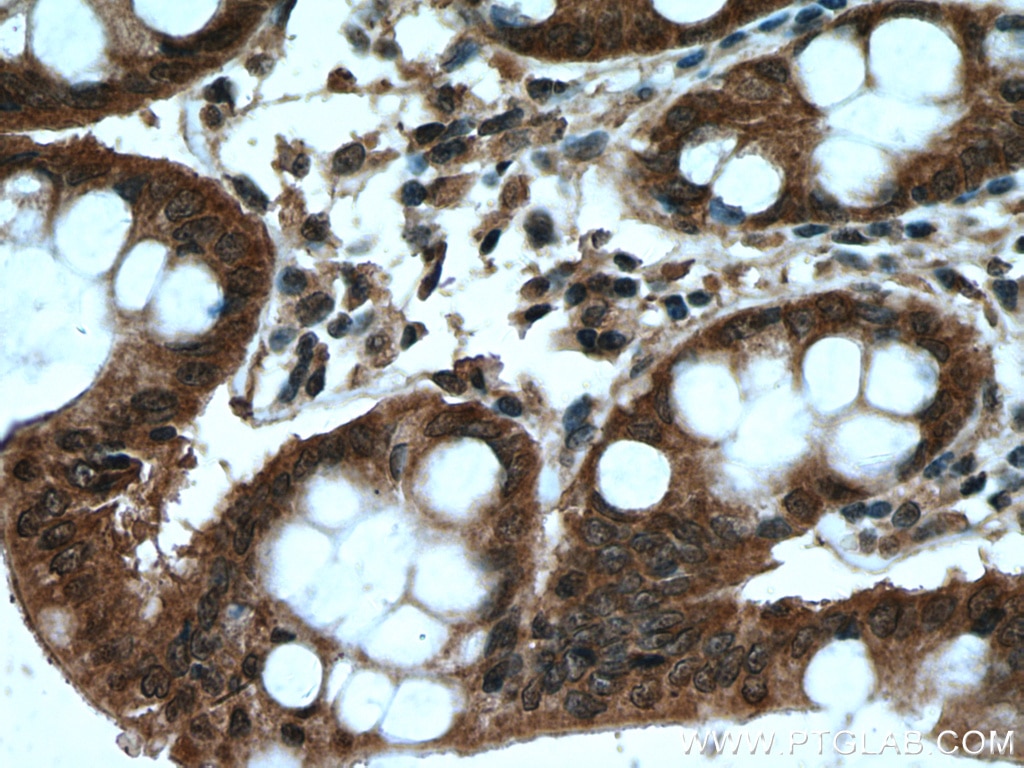
| Résultats positifs en IHC | tissu de côlon humain, il est suggéré de démasquer l'antigène avec un tampon de TE buffer pH 9.0; (*) À défaut, 'le démasquage de l'antigène peut être 'effectué avec un tampon citrate pH 6,0. |
Dilution recommandée
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:500-1:1000 |
| Immunohistochimie (IHC) | IHC : 1:50-1:500 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, check data in validation data gallery | |
Applications publiées
| KD/KO | See 1 publications below |
| WB | See 13 publications below |
Informations sur le produit
16541-1-AP cible AXIN1 dans les applications de WB, IHC, ELISA et montre une réactivité avec des échantillons Humain
| Réactivité | Humain |
| Réactivité citée | Humain, poulet |
| Hôte / Isotype | Lapin / IgG |
| Clonalité | Polyclonal |
| Type | Anticorps |
| Immunogène | AXIN1 Protéine recombinante Ag9858 |
| Nom complet | axin 1 |
| Masse moléculaire calculée | 826aa,92 kDa; 862aa,95 kDa |
| Poids moléculaire observé | 100-110 kDa |
| Numéro d’acquisition GenBank | BC044648 |
| Symbole du gène | AXIN1 |
| Identification du gène (NCBI) | 8312 |
| Conjugaison | Non conjugué |
| Forme | Liquide |
| Méthode de purification | Purification par affinité contre l'antigène |
| Tampon de stockage | PBS avec azoture de sodium à 0,02 % et glycérol à 50 % pH 7,3 |
| Conditions de stockage | Stocker à -20°C. Stable pendant un an après l'expédition. L'aliquotage n'est pas nécessaire pour le stockage à -20oC Les 20ul contiennent 0,1% de BSA. |
Informations générales
Axis inhibition protein1 (AXIN1), also called AXIN, together with AXIN2 are multidomain scaffold proteins that negatively regulate Wnt signaling. AXIN1 is likely to function as a tumor suppressor. Under UV irradiation, AXIN1-HIPK2-TP53 complex forms. The complex also controls cell growth, apoptosis and development. Like AXIN2, AXIN1 undergoes poly(ADP-ribosy)lation by tankyrase TNKS and TNKS2 followed by unbiquitination by RNF146 which leads to its degradation and subsequent activation of Wnt signaling. Its deubiquitination by USP34 is important for nuclear accumulation during Wnt signaling. Recent researches find that CircAXIN1 encodes a novel protein, AXIN1-295aa, which shows at around 40-55 kDa by Western Blot. AXIN1-295aa functions as an oncogenic protein, activating the Wnt signaling pathway to promote GC tumorigenesis and progression, suggesting a potential therapeutic target for GC. Proteintech's AXIN1 antibody 16541-1-AP is a rabbit polyclonal antibdy raised against the N-terminus of human AXIN1.
Protocole
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for AXIN1 antibody 16541-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IHC protocol for AXIN1 antibody 16541-1-AP | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |
Publications
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Int J Mol Sci AXIN2 Reduces the Survival of Porcine Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells (piPSCs). | ||
Front Oncol Targeting TRIM54/Axin1/β-Catenin Axis Prohibits Proliferation and Metastasis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. | ||
Cancer Gene Ther Stabilizing and upregulating Axin with tankyrase inhibitor reverses 5-fluorouracil chemoresistance and proliferation by targeting the WNT/caveolin-1 axis in colorectal cancer cells. | ||
Commun Biol Tankyrase-1-mediated degradation of Golgin45 regulates glycosyltransferase trafficking and protein glycosylation in Rab2-GTP-dependent manner. | ||
Exp Cell Res The transcript ENST00000444125 of lncRNA LINC01503 promotes cancer stem cell properties of glioblastoma cells via reducing FBXW1 mediated GLI2 degradation. | ||
FEBS Lett Exosomes derived from mineralizing osteoblasts promote ST2 cell osteogenic differentiation by alteration of microRNA expression. |