- Phare
- Validé par KD/KO
Anticorps Polyclonal de lapin anti-Beta Arrestin 1
Beta Arrestin 1 Polyclonal Antibody for WB, IP, IHC, ELISA
Hôte / Isotype
Lapin / IgG
Réactivité testée
Humain, rat, souris
Applications
WB, IP, IF, IHC, CoIP, ChIP, ELISA
Conjugaison
Non conjugué
N° de cat : 15361-1-AP
Synonymes
Galerie de données de validation
Applications testées
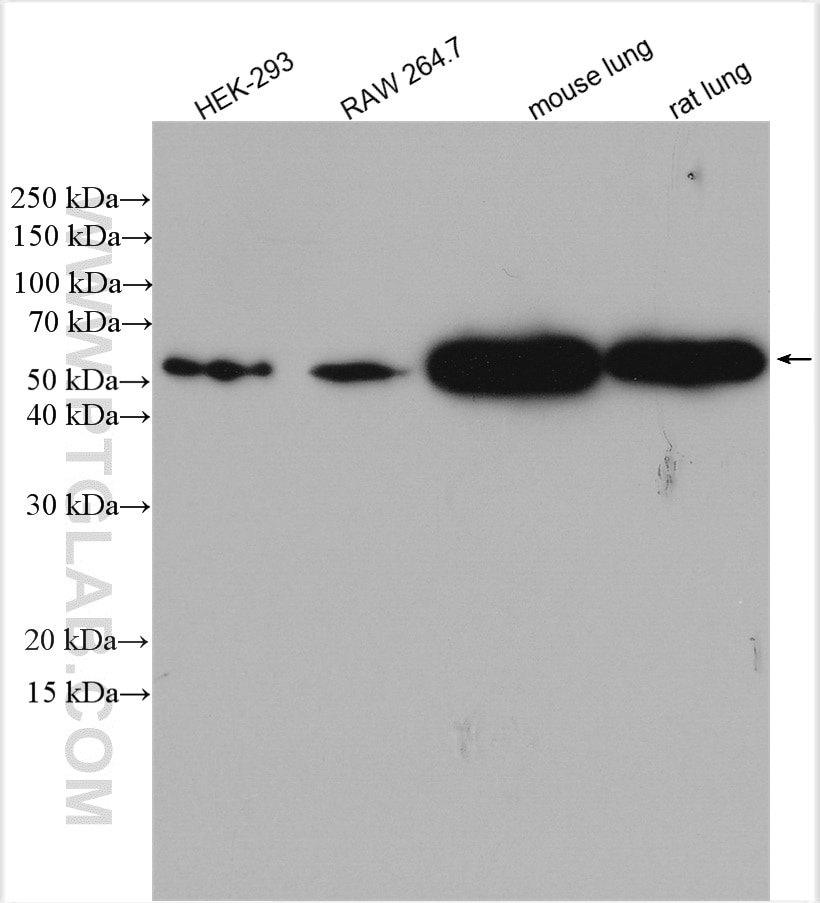
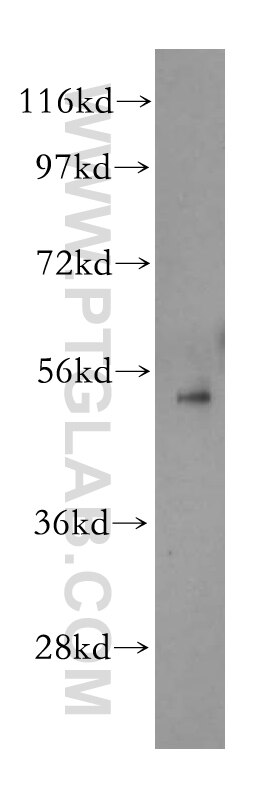
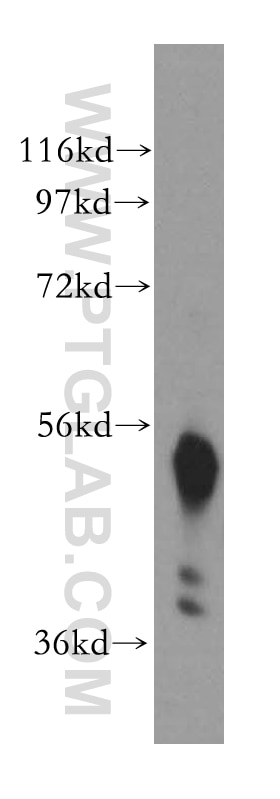
| Résultats positifs en WB | cellules HEK-293, cellules A549, cellules RAW 264.7, cellules U-937, tissu pulmonaire de rat, tissu pulmonaire de souris |
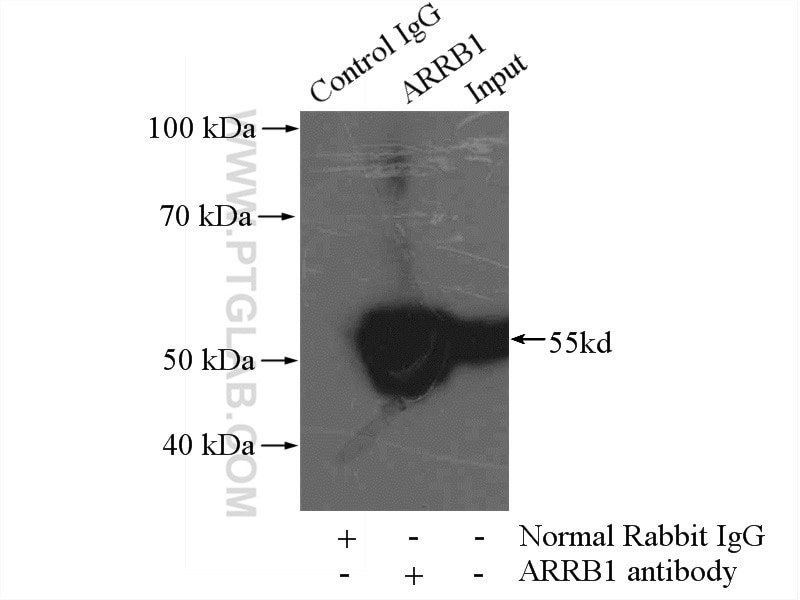
| Résultats positifs en IP | tissu pulmonaire de souris |
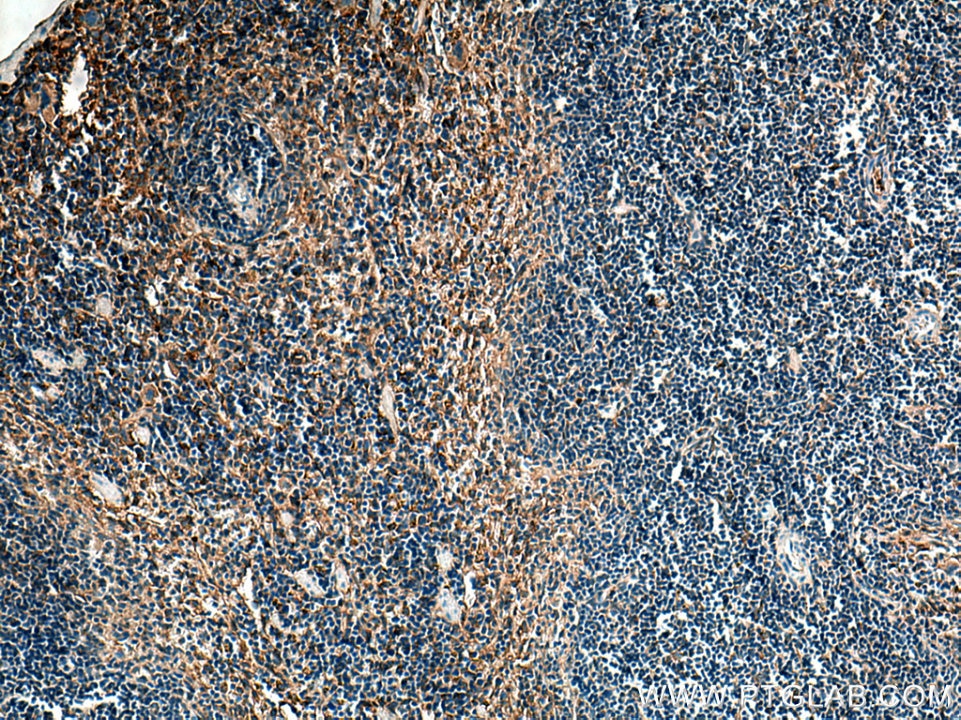
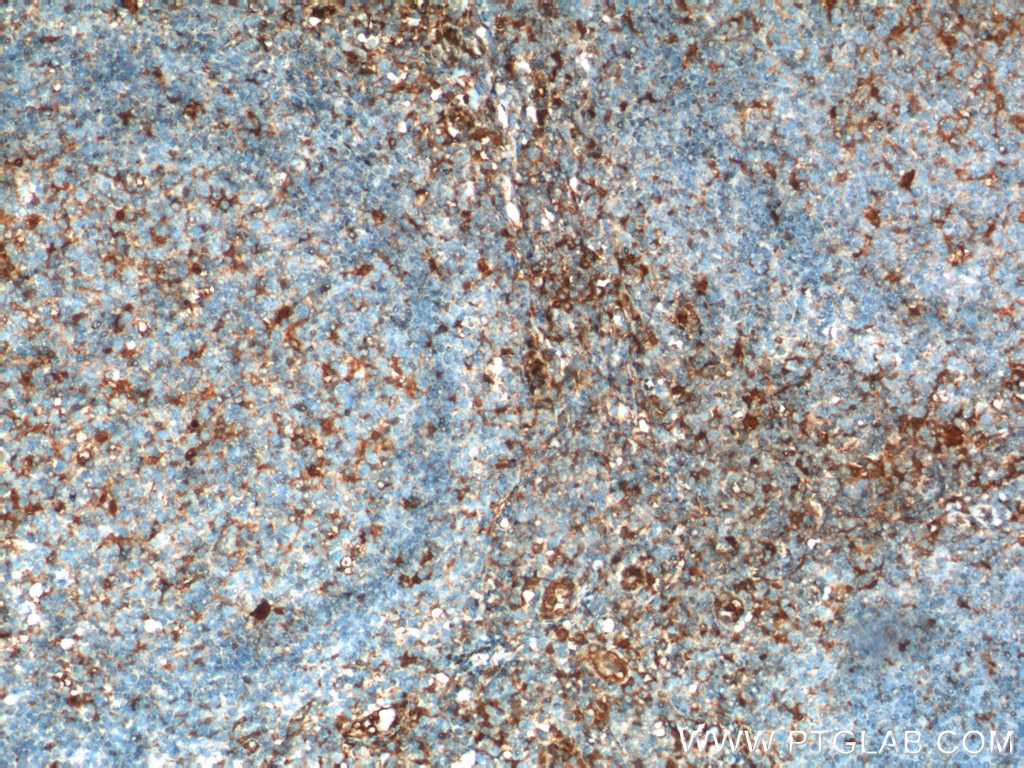
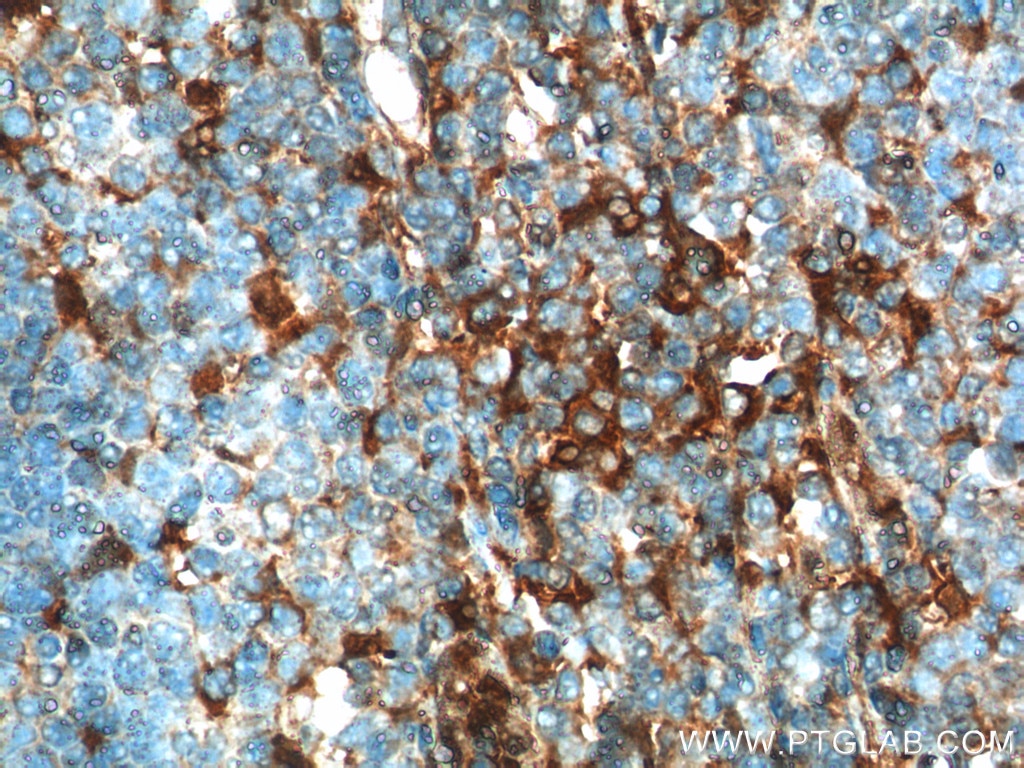
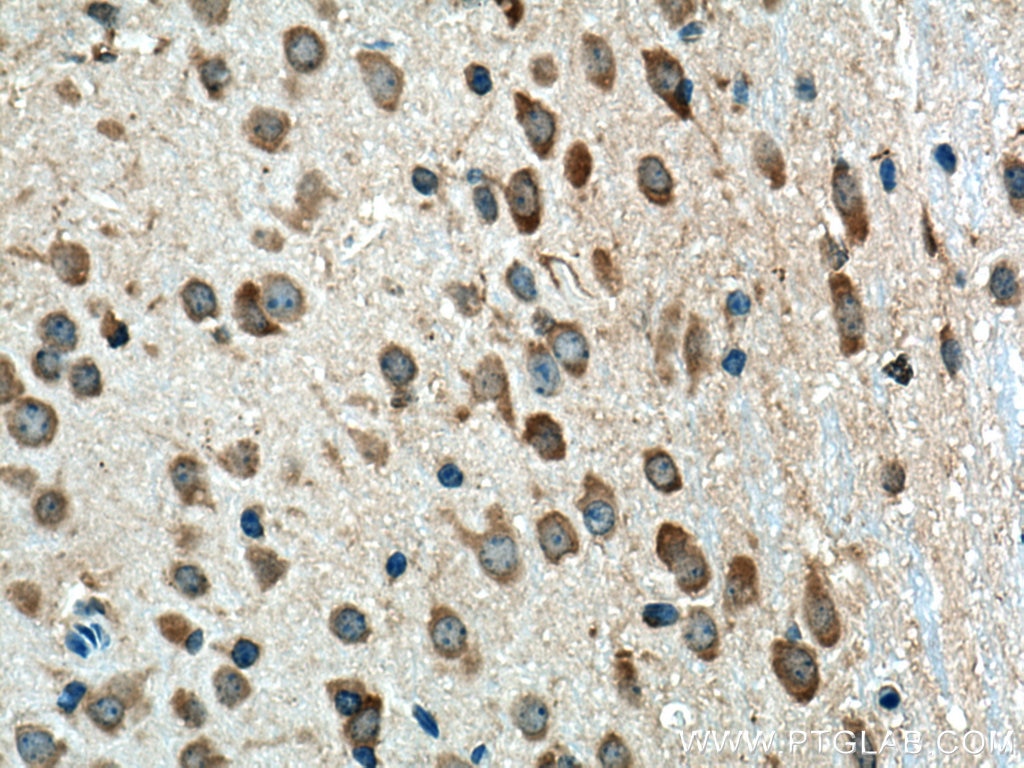
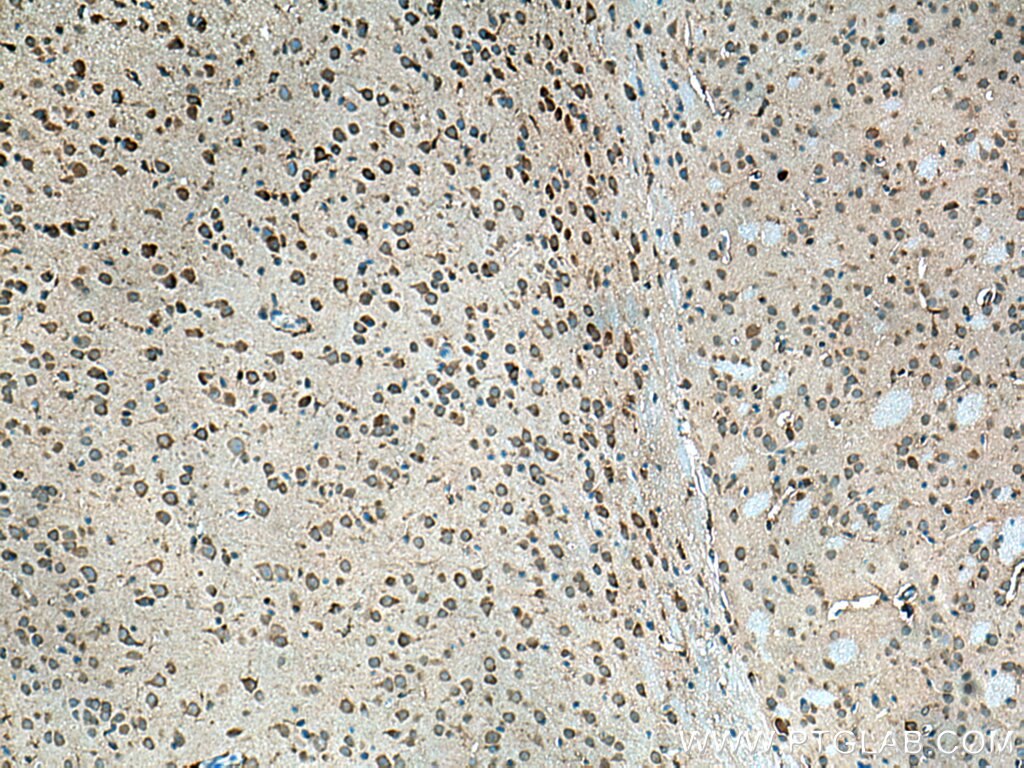
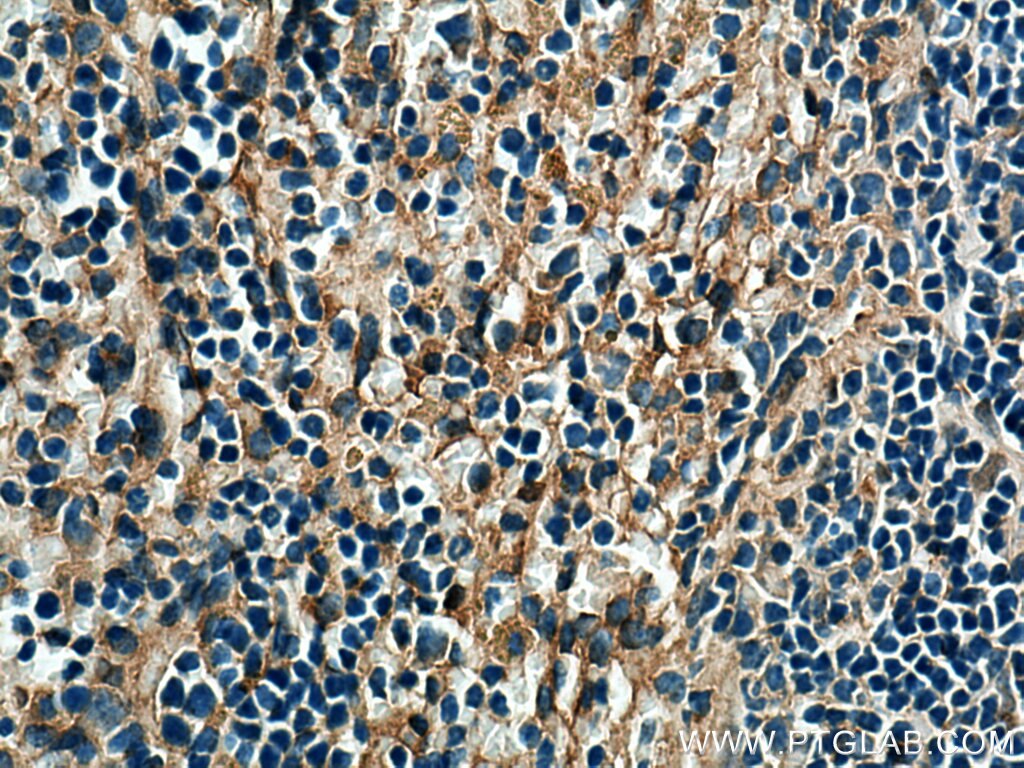
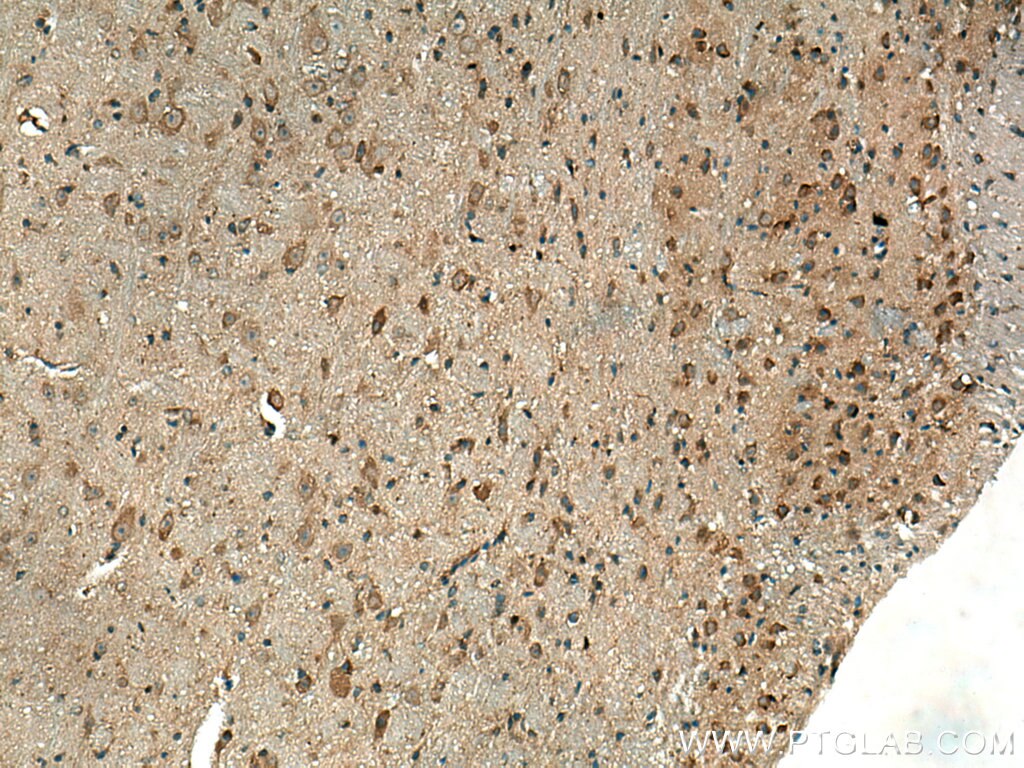
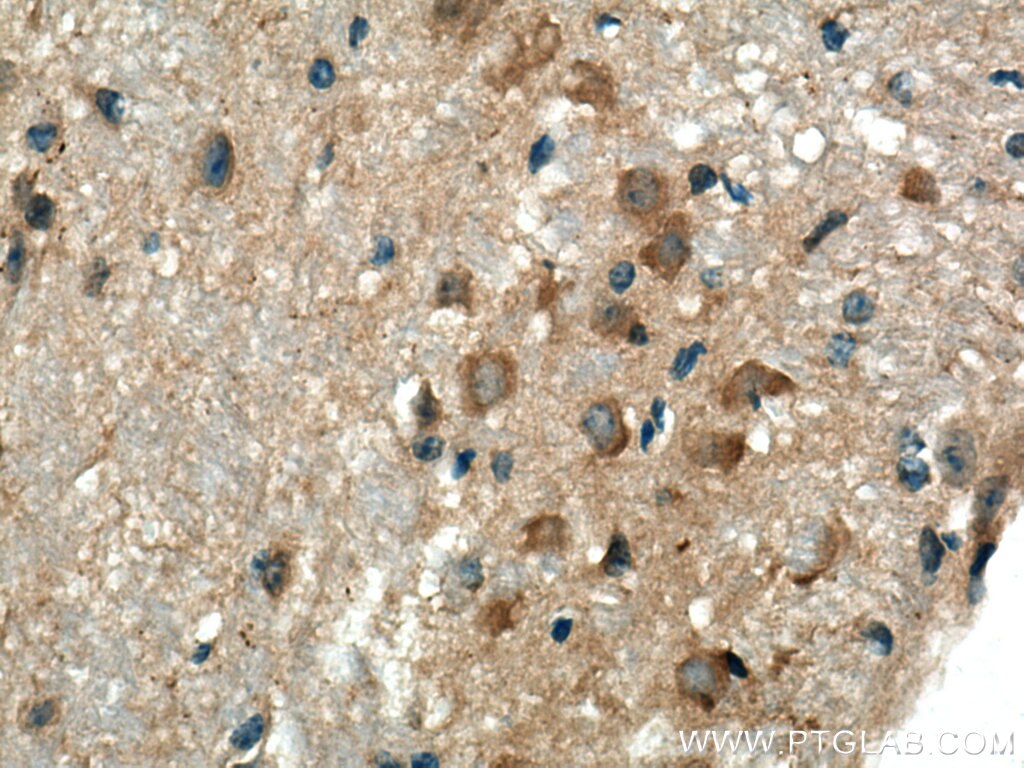
| Résultats positifs en IHC | tissu d'amygdalite humain, tissu cérébral de souris, tissu de cervelet de souris, tissu splénique de souris il est suggéré de démasquer l'antigène avec un tampon de TE buffer pH 9.0; (*) À défaut, 'le démasquage de l'antigène peut être 'effectué avec un tampon citrate pH 6,0. |
Dilution recommandée
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:500-1:2000 |
| Immunoprécipitation (IP) | IP : 0.5-4.0 ug for 1.0-3.0 mg of total protein lysate |
| Immunohistochimie (IHC) | IHC : 1:50-1:500 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, check data in validation data gallery | |
Applications publiées
| KD/KO | See 3 publications below |
| WB | See 9 publications below |
| IF | See 4 publications below |
| IP | See 1 publications below |
| CoIP | See 1 publications below |
| ChIP | See 1 publications below |
Informations sur le produit
15361-1-AP cible Beta Arrestin 1 dans les applications de WB, IP, IF, IHC, CoIP, ChIP, ELISA et montre une réactivité avec des échantillons Humain, rat, souris
| Réactivité | Humain, rat, souris |
| Réactivité citée | rat, Humain, souris |
| Hôte / Isotype | Lapin / IgG |
| Clonalité | Polyclonal |
| Type | Anticorps |
| Immunogène | Beta Arrestin 1 Protéine recombinante Ag7608 |
| Nom complet | arrestin, beta 1 |
| Masse moléculaire calculée | 47 kDa |
| Poids moléculaire observé | 47-55 kDa |
| Numéro d’acquisition GenBank | BC003636 |
| Symbole du gène | Beta Arrestin 1 |
| Identification du gène (NCBI) | 408 |
| Conjugaison | Non conjugué |
| Forme | Liquide |
| Méthode de purification | Purification par affinité contre l'antigène |
| Tampon de stockage | PBS avec azoture de sodium à 0,02 % et glycérol à 50 % pH 7,3 |
| Conditions de stockage | Stocker à -20°C. Stable pendant un an après l'expédition. L'aliquotage n'est pas nécessaire pour le stockage à -20oC Les 20ul contiennent 0,1% de BSA. |
Informations générales
β-Arrestins (ARRBs), the best known regulators of G protein-coupled receptor signaling, are versatile and multifunctional adapter proteins that regulate diverse cellular functions, including cell growth, apoptosis and immune responses. Overexpression of beta Arrestin 1 has been found in various cancers, indicating it as a potential therapeutic target for cancer treatment. Recently expression of ARRB1 in saliva has been identified as a candidate circadian biomarker. ARRB1 migrated as a doublet of two bands of 45 and 55 kDa (PMID:28947386).
Protocole
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for Beta Arrestin 1 antibody 15361-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IHC protocol for Beta Arrestin 1 antibody 15361-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IP protocol for Beta Arrestin 1 antibody 15361-1-AP | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |
Publications
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Cell Metab Autonomous sensing of the insulin peptide by an olfactory G protein-coupled receptor modulates glucose metabolism.
| ||
J Cell Biol BBSome trains remove activated GPCRs from cilia by enabling passage through the transition zone. | ||
Cell Death Dis β-Arrestins promote podocyte injury by inhibition of autophagy in diabetic nephropathy. | ||
J Biol Chem An ionic lock and a hydrophobic zipper mediate the coupling between an insect pheromone receptor BmOR3 and downstream effectors.
| ||
PLoS One Cell Survival Following Radiation Exposure Requires miR-525-3p Mediated Suppression of ARRB1 and TXN1. | ||
Oncol Rep Blue light irradiation inhibits the growth of colon cancer and activation of cancer‑associated fibroblasts. |