Anticorps Polyclonal de lapin anti-Adrenomedullin
Adrenomedullin Polyclonal Antibody for WB, IF, IHC, ELISA
Hôte / Isotype
Lapin / IgG
Réactivité testée
Humain, souris
Applications
WB, IHC, IF/ICC, ELISA
Conjugaison
Non conjugué
N° de cat : 10778-1-AP
Synonymes
Galerie de données de validation
Applications testées
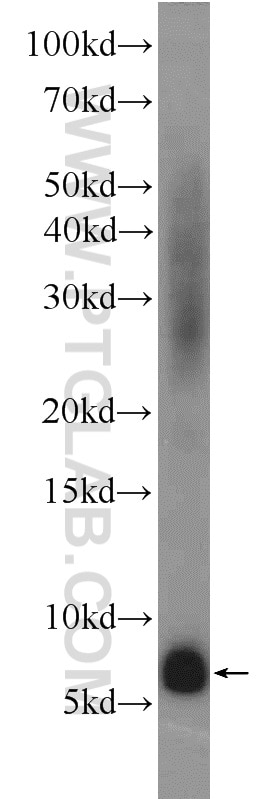
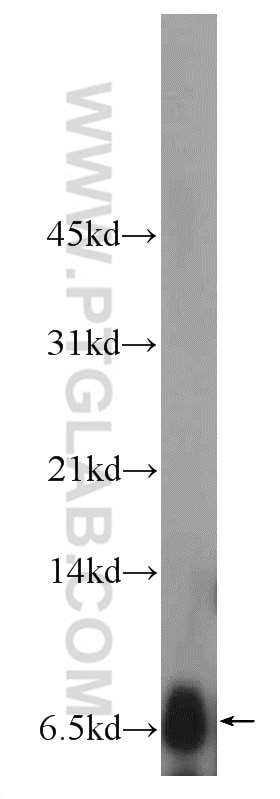
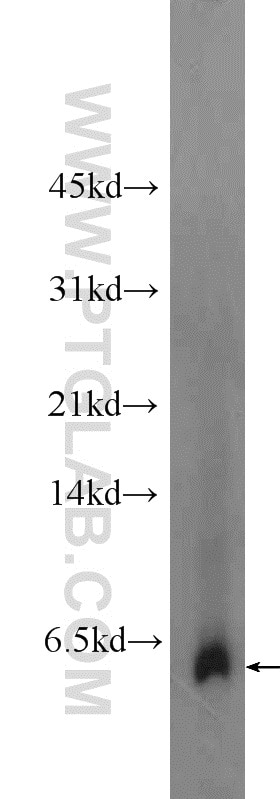
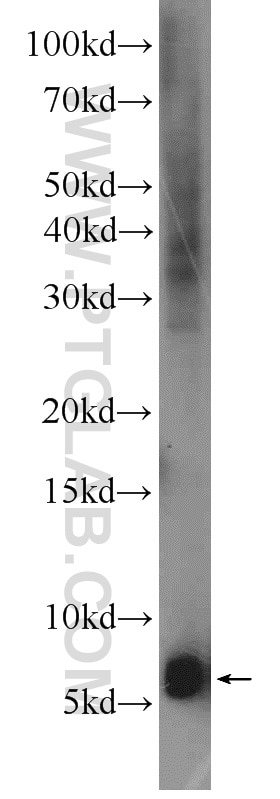
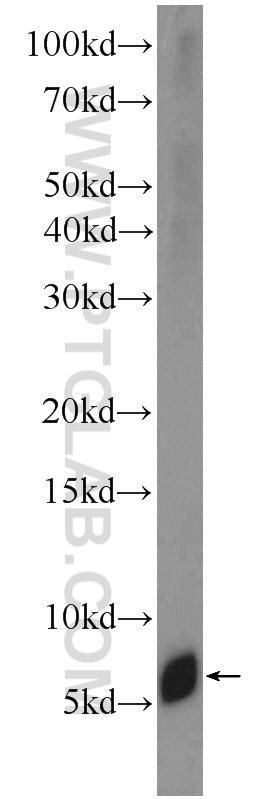
| Résultats positifs en WB | tissu rénal humain, cellules A549, cellules Raji, tissu cérébral humain fœtal, tissu placentaire humain |
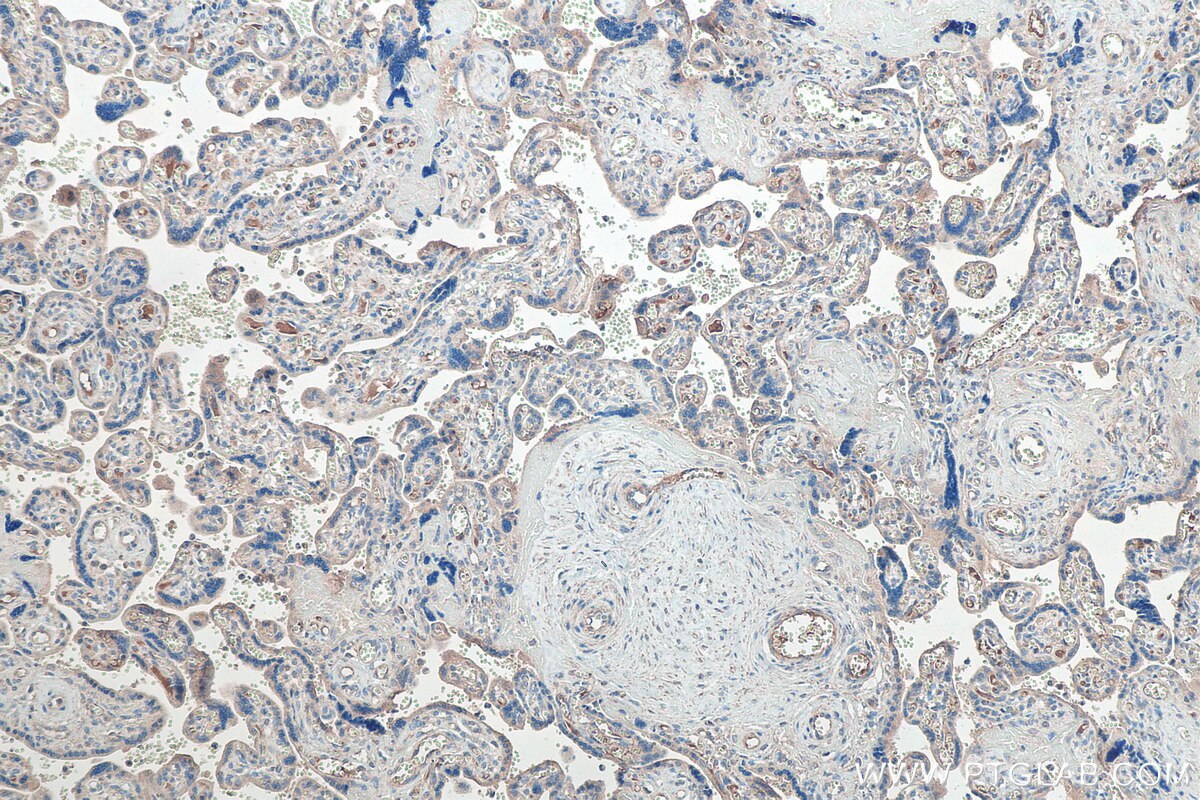
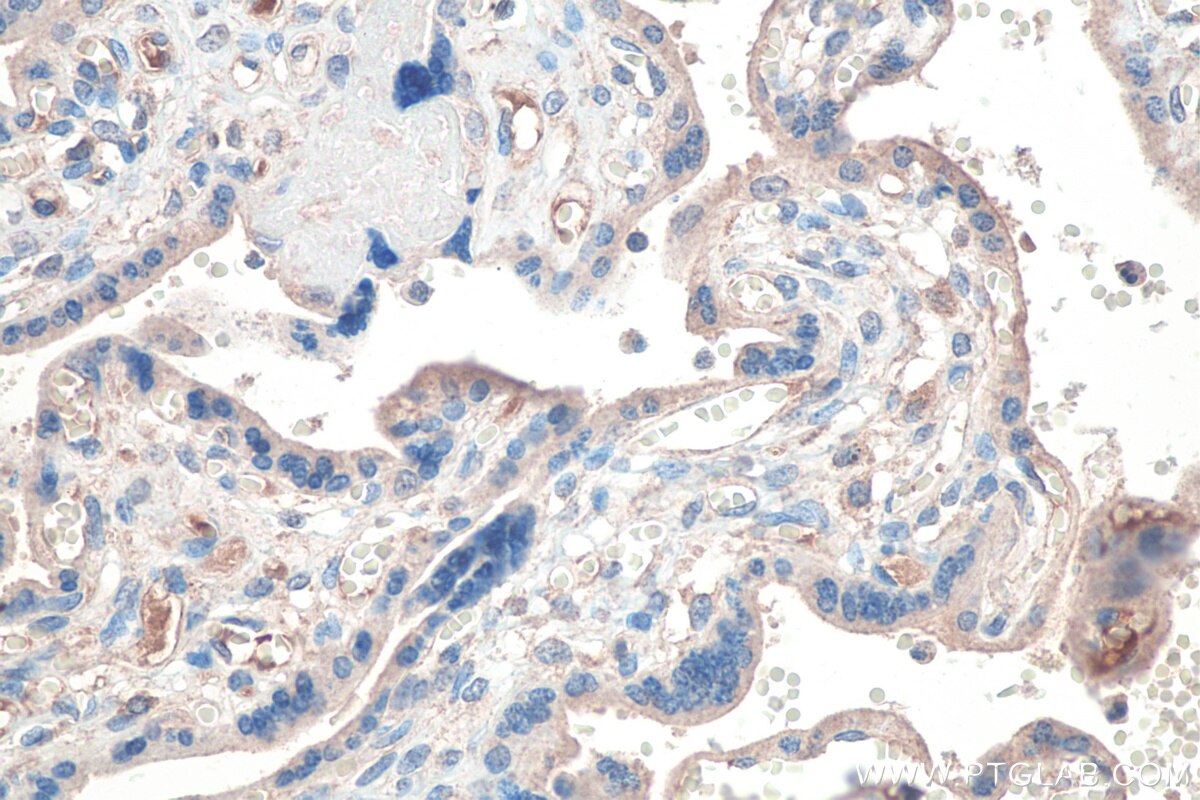
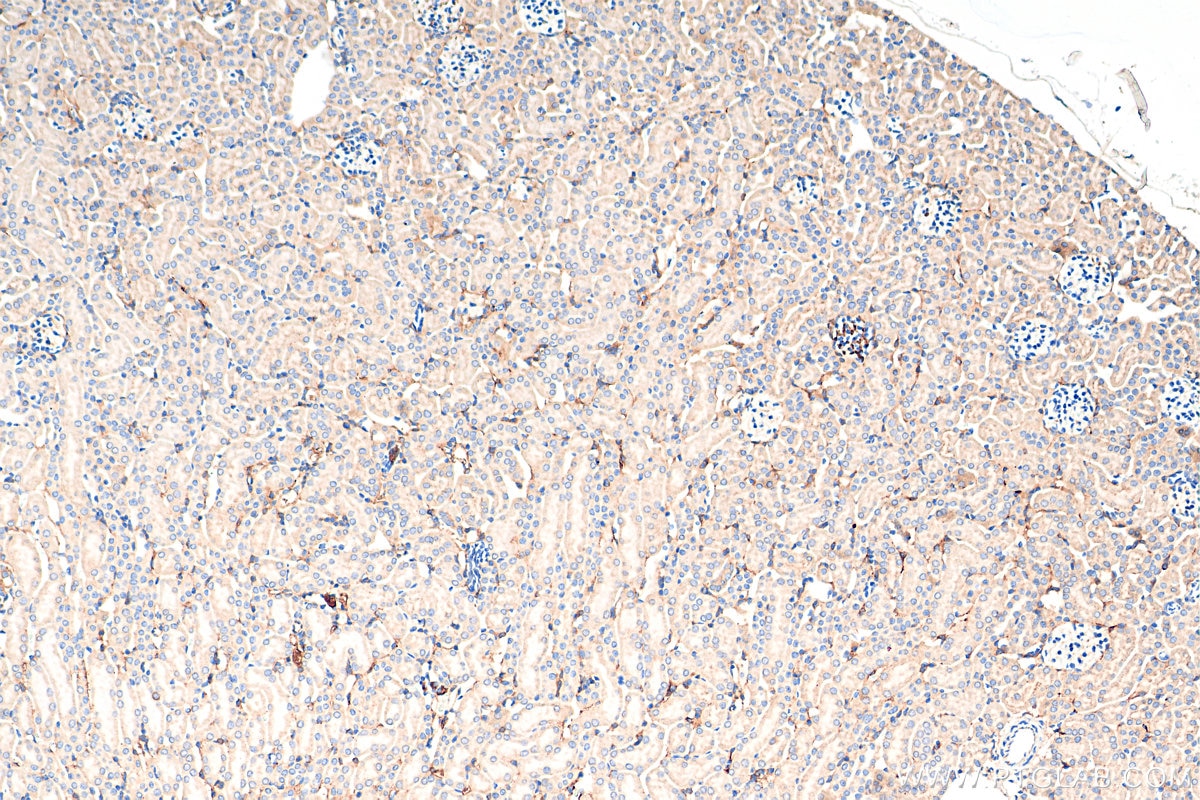
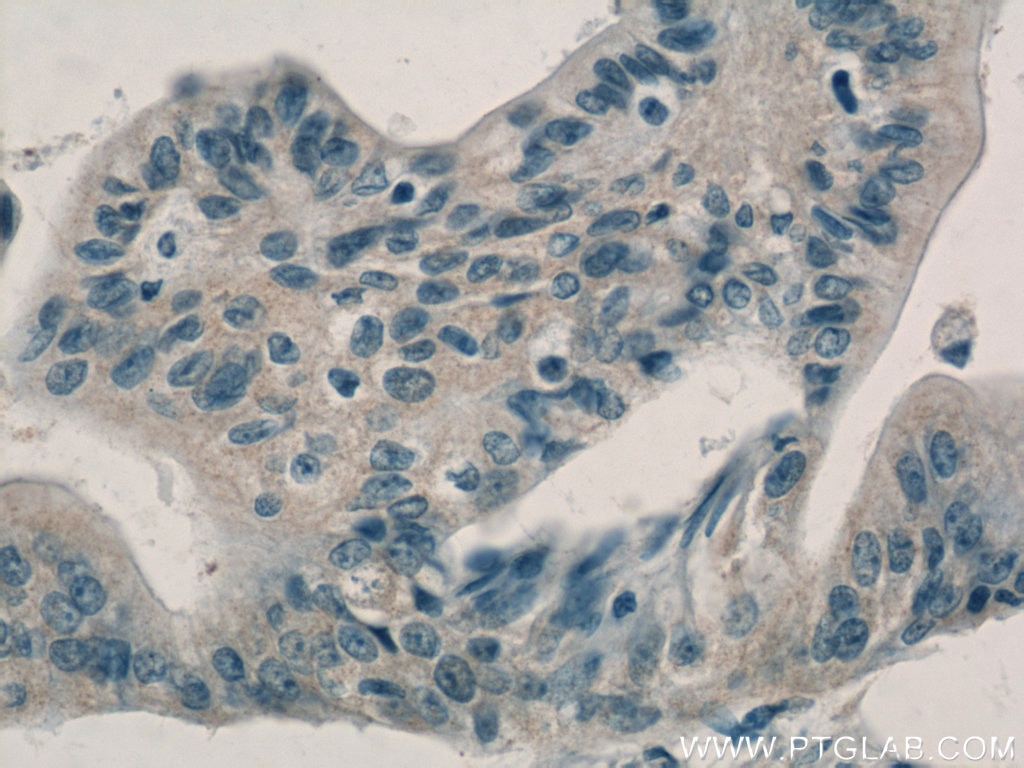
| Résultats positifs en IHC | tissu placentaire humain, tissu de cancer du pancréas humain, tissu rénal de souris, tissu rénal humain il est suggéré de démasquer l'antigène avec un tampon de TE buffer pH 9.0; (*) À défaut, 'le démasquage de l'antigène peut être 'effectué avec un tampon citrate pH 6,0. |
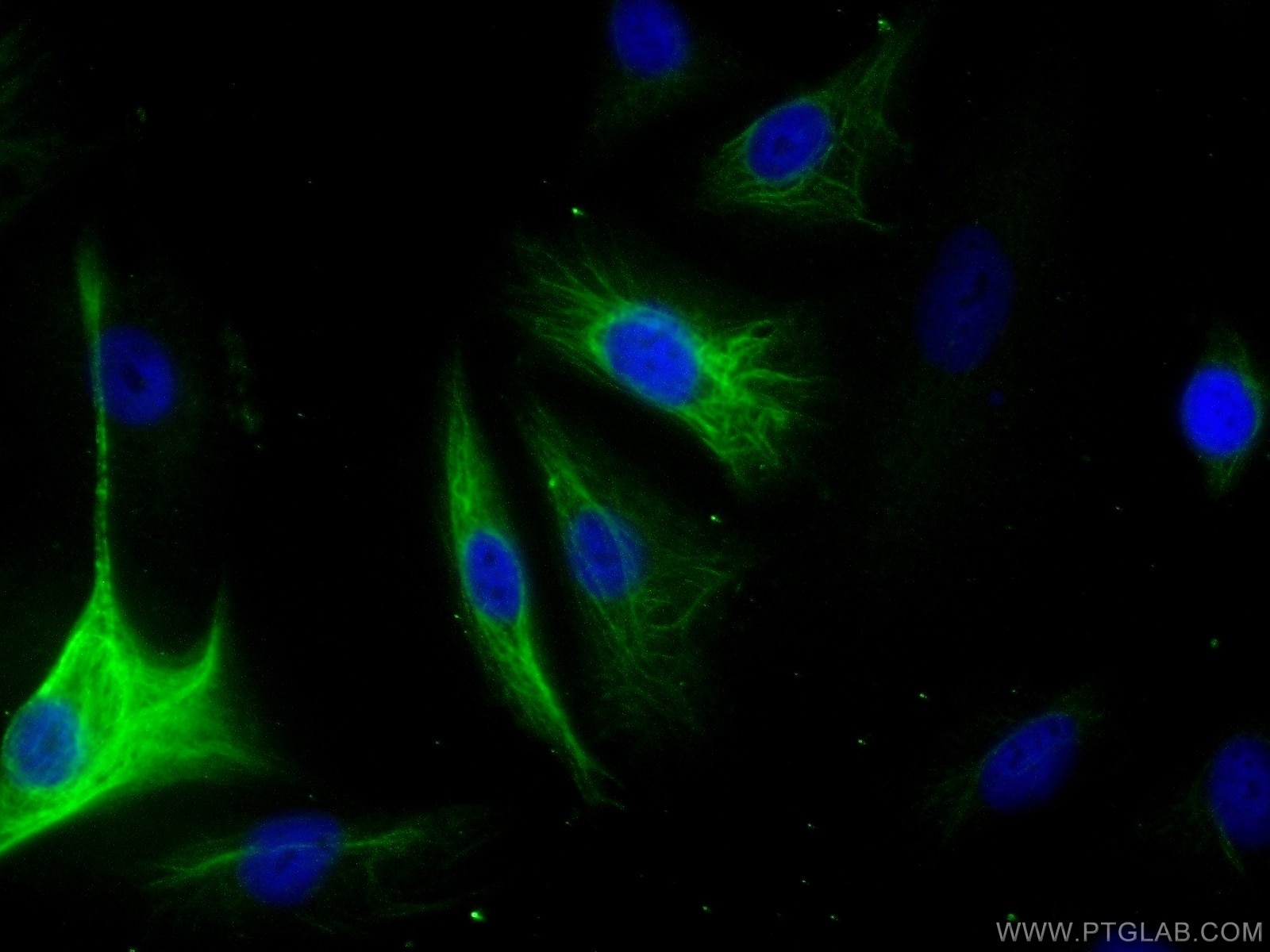
| Résultats positifs en IF/ICC | cellules A549 |
Dilution recommandée
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:500-1:2000 |
| Immunohistochimie (IHC) | IHC : 1:50-1:500 |
| Immunofluorescence (IF)/ICC | IF/ICC : 1:10-1:100 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, check data in validation data gallery | |
Applications publiées
| WB | See 2 publications below |
| IHC | See 1 publications below |
| IF | See 1 publications below |
Informations sur le produit
10778-1-AP cible Adrenomedullin dans les applications de WB, IHC, IF/ICC, ELISA et montre une réactivité avec des échantillons Humain, souris
| Réactivité | Humain, souris |
| Réactivité citée | Humain |
| Hôte / Isotype | Lapin / IgG |
| Clonalité | Polyclonal |
| Type | Anticorps |
| Immunogène | Adrenomedullin Protéine recombinante Ag1197 |
| Nom complet | adrenomedullin |
| Masse moléculaire calculée | 20 kDa |
| Poids moléculaire observé | 6 kDa |
| Numéro d’acquisition GenBank | BC015961 |
| Symbole du gène | Adrenomedullin/ADM |
| Identification du gène (NCBI) | 133 |
| Conjugaison | Non conjugué |
| Forme | Liquide |
| Méthode de purification | Purification par affinité contre l'antigène |
| Tampon de stockage | PBS avec azoture de sodium à 0,02 % et glycérol à 50 % pH 7,3 |
| Conditions de stockage | Stocker à -20°C. Stable pendant un an après l'expédition. L'aliquotage n'est pas nécessaire pour le stockage à -20oC Les 20ul contiennent 0,1% de BSA. |
Informations générales
Adrenomedullin (AM) and proadrenomedullin N-terminal 20 peptide (PAMP) are two small active hormones derived from the expression of a single gene (Adm) that is expressed throughout the GI tract, including the mucosal epithelium, glandular duct cells, neuroendocrine cells, and smooth muscle cells of the GI tract, between the oral cavity and the rectum (PMID:10782362, PMID:27345325). These two peptides coexist in GI cells, where they regulate many physiological functions including vasodilation, angiogenesis, anti-inflammation, organ protection, and tissue repair. AM suppresses inflammatory cytokine production in the intestinal mucosa, improves vascular and lymphatic function, mucosal epithelial repair, and intestinal barrier function in animal models with intestinal inflammation (PMID:27965594, PMID:29311984). Molecular mass species of 18, 14, and 6 kDa were identified in tumor cell lysates and presumably represent AM precursor, processed intermediates, and the authentic peptide, respectively. There is also a 22-kDa immunoreactive species in two cancer cell lines, H720 and MCF-7 (PMID: 8798536).
Protocole
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for Adrenomedullin antibody 10778-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IHC protocol for Adrenomedullin antibody 10778-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IF protocol for Adrenomedullin antibody 10778-1-AP | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |
Publications
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Cells Differentiation Trajectory of Limbal Stem and Progenitor Cells under Normal Homeostasis and upon Corneal Wounding. | ||
Prostate Prostate fibroblasts enhance androgen receptor splice variant 7 expression in prostate cancer cells | ||
CNS Neurosci Ther Identification and validation of a glycolysis-related taxonomy for improving outcomes in glioma |