- Featured Product
- KD/KO Validated
SQLE Polyklonaler Antikörper
SQLE Polyklonal Antikörper für WB, IHC, IF/ICC, IP, ELISA
Wirt / Isotyp
Kaninchen / IgG
Getestete Reaktivität
human, Maus, Ratte und mehr (1)
Anwendung
WB, IHC, IF/ICC, IP, ChIP, ELISA
Konjugation
Unkonjugiert
Kat-Nr. : 12544-1-AP
Synonyme
Geprüfte Anwendungen
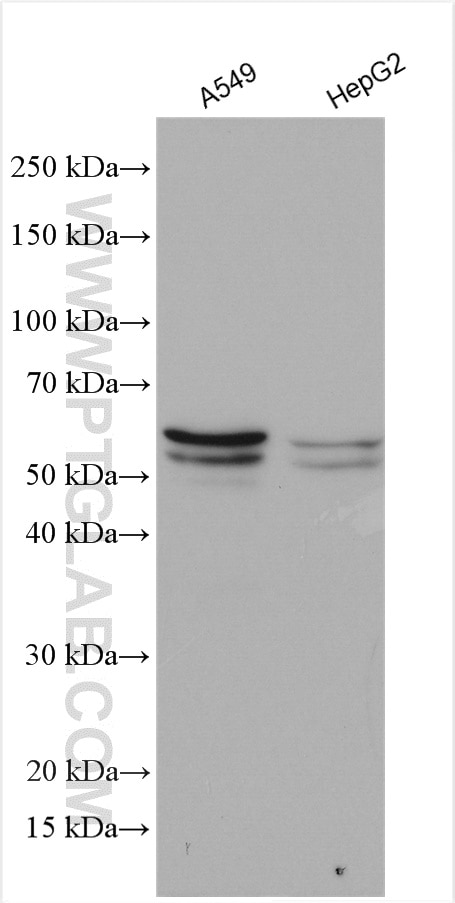
| Erfolgreiche Detektion in WB | A549-Zellen, HepG2-Zellen |
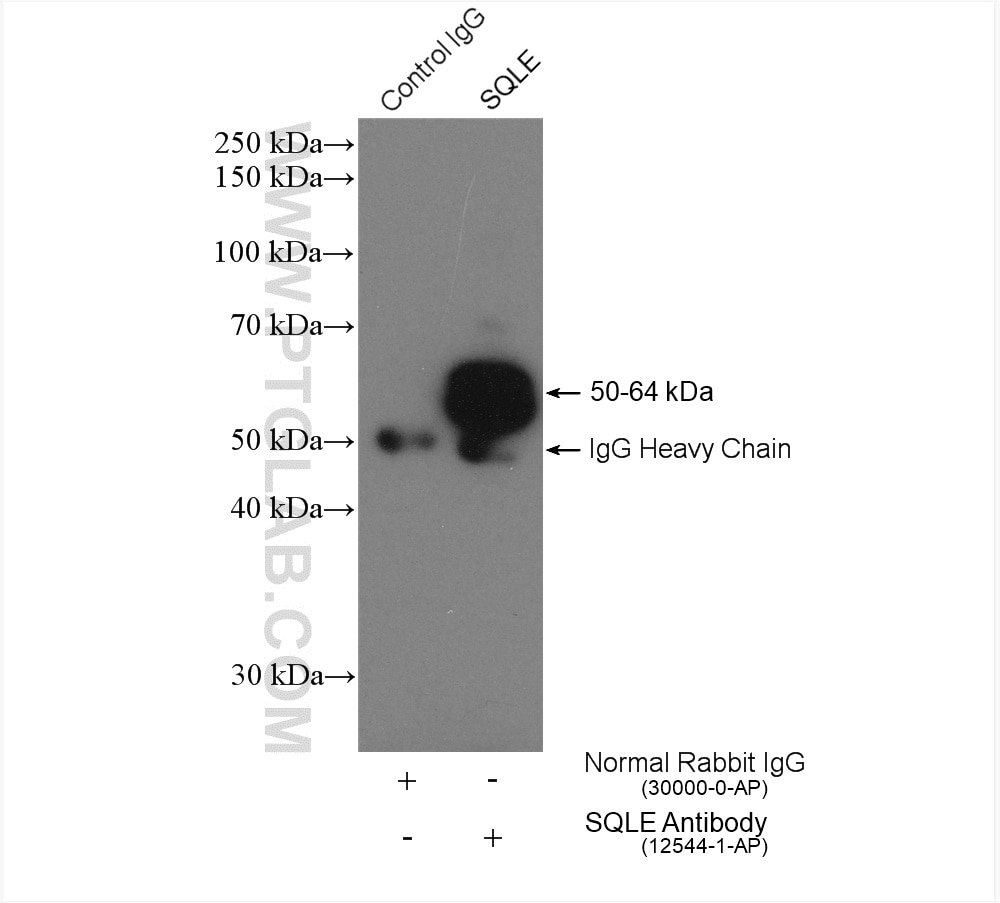
| Erfolgreiche IP | HepG2-Zellen |
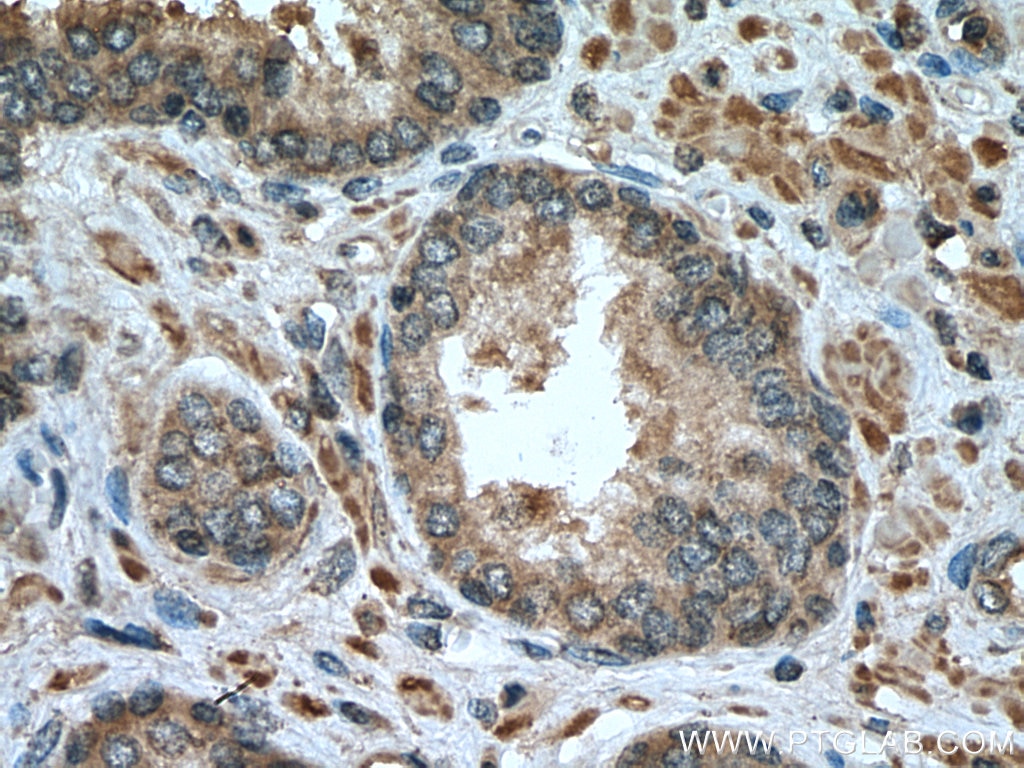
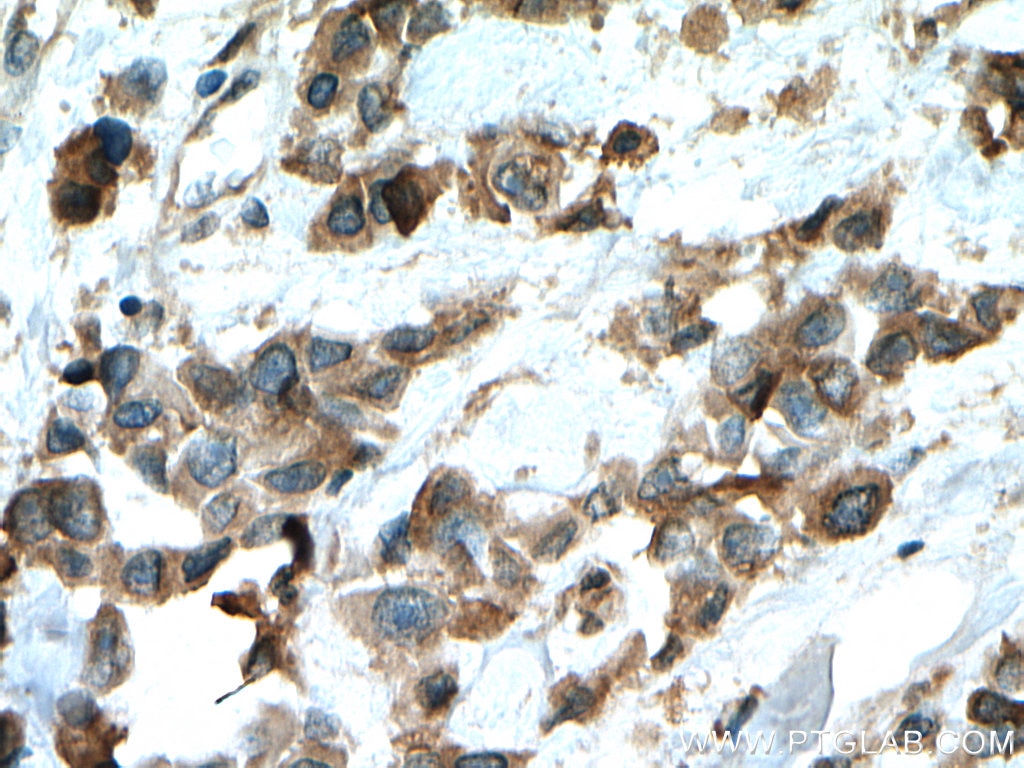
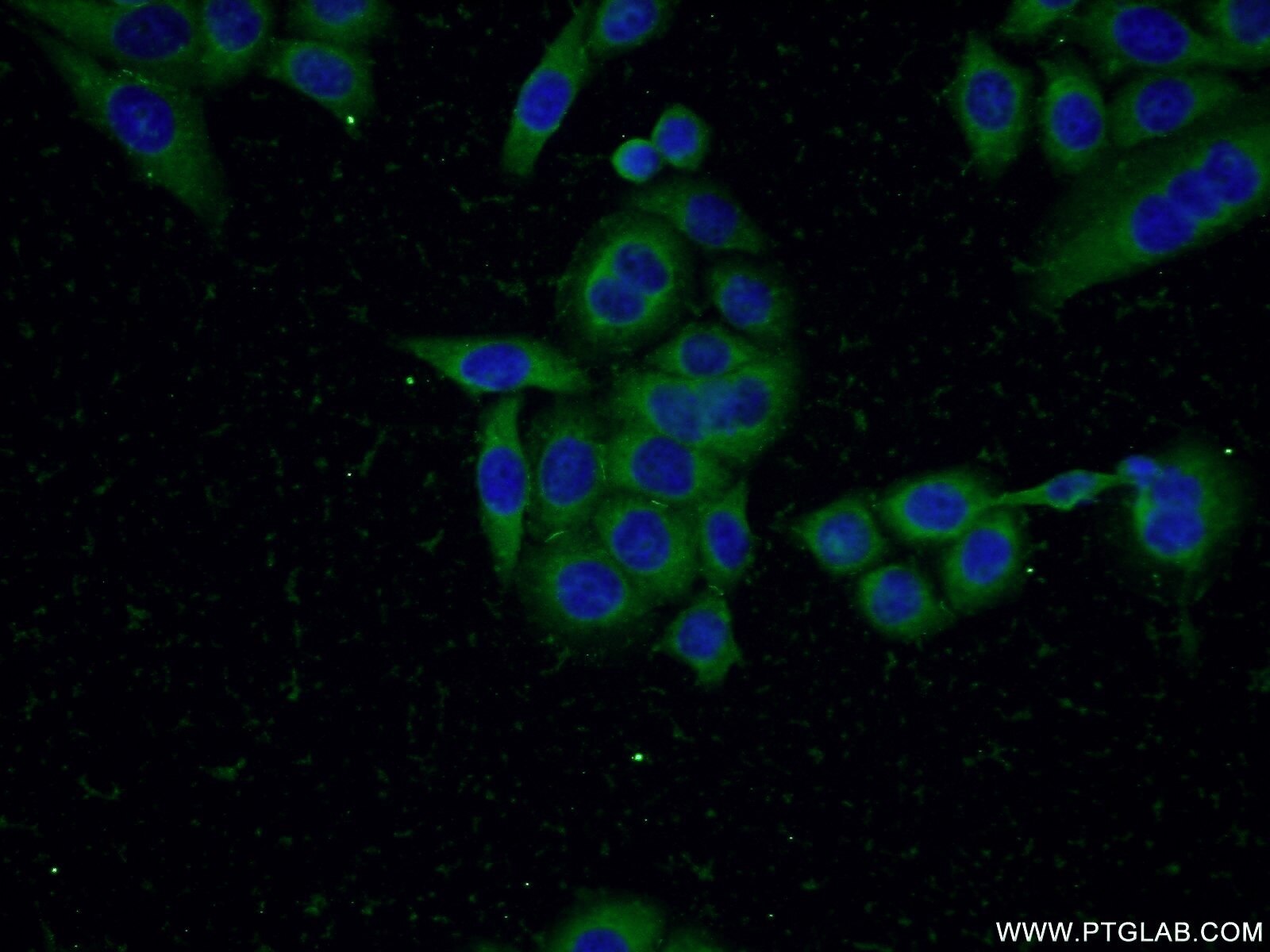
| Erfolgreiche Detektion in IHC | humanes Prostatakarzinomgewebe, humanes Mammakarzinomgewebe Hinweis: Antigendemaskierung mit TE-Puffer pH 9,0 empfohlen. (*) Wahlweise kann die Antigendemaskierung auch mit Citratpuffer pH 6,0 erfolgen. |
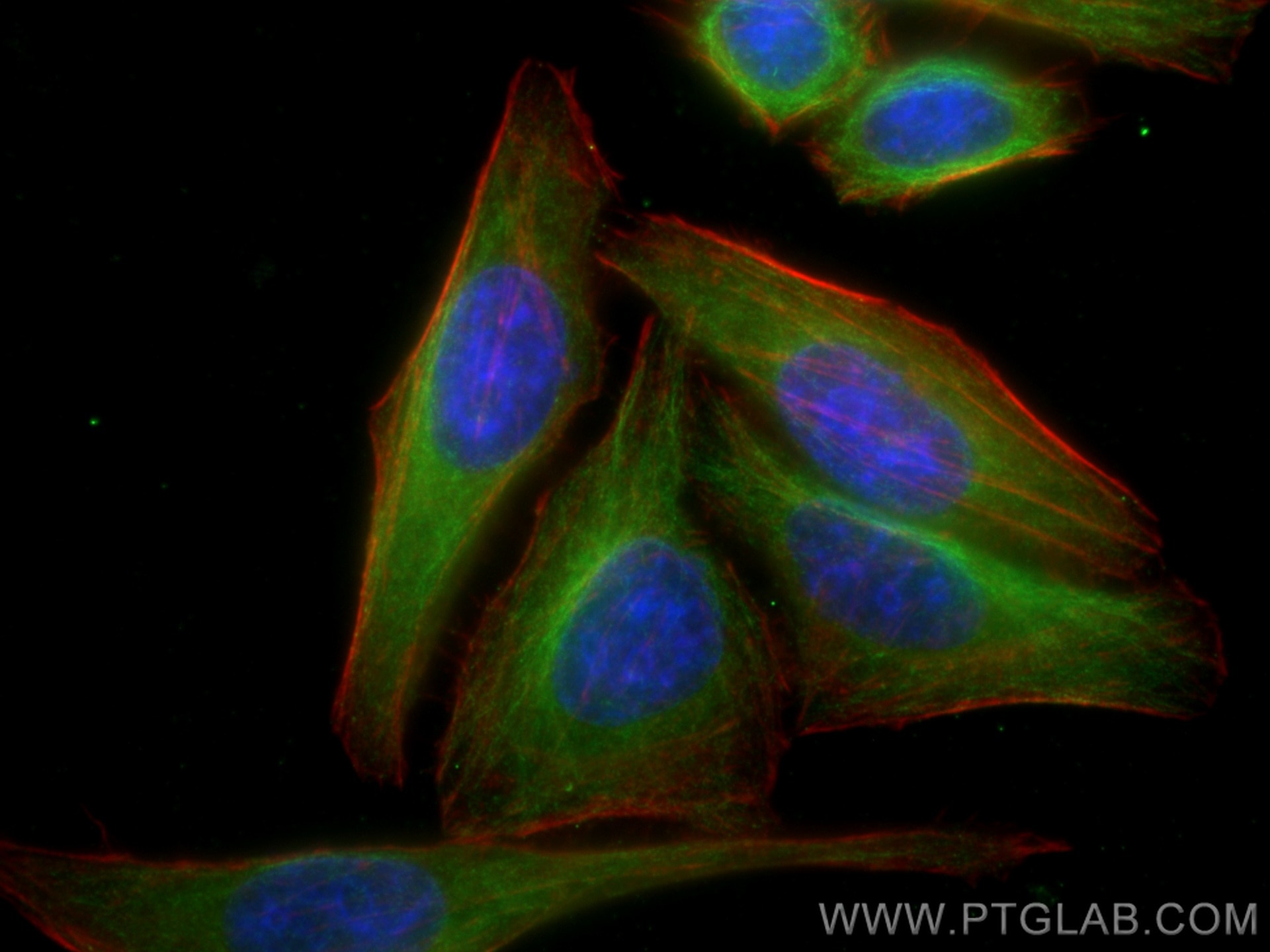
| Erfolgreiche Detektion in IF/ICC | HepG2-Zellen, PC-3-Zellen |
Empfohlene Verdünnung
| Anwendung | Verdünnung |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:500-1:2000 |
| Immunpräzipitation (IP) | IP : 0.5-4.0 ug for 1.0-3.0 mg of total protein lysate |
| Immunhistochemie (IHC) | IHC : 1:50-1:500 |
| Immunfluoreszenz (IF)/ICC | IF/ICC : 1:200-1:800 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, check data in validation data gallery | |
Veröffentlichte Anwendungen
| KD/KO | See 16 publications below |
| WB | See 91 publications below |
| IHC | See 20 publications below |
| IF | See 4 publications below |
| ChIP | See 1 publications below |
Produktinformation
12544-1-AP bindet in WB, IHC, IF/ICC, IP, ChIP, ELISA SQLE und zeigt Reaktivität mit human, Maus, Ratten
| Getestete Reaktivität | human, Maus, Ratte |
| In Publikationen genannte Reaktivität | human, hamster, Maus, Ratte |
| Wirt / Isotyp | Kaninchen / IgG |
| Klonalität | Polyklonal |
| Typ | Antikörper |
| Immunogen | SQLE fusion protein Ag3266 |
| Vollständiger Name | squalene epoxidase |
| Berechnetes Molekulargewicht | 574 aa, 64 kDa |
| Beobachtetes Molekulargewicht | 50-64 kDa |
| GenBank-Zugangsnummer | BC017033 |
| Gene symbol | SQLE |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 6713 |
| Konjugation | Unkonjugiert |
| Form | Liquid |
| Reinigungsmethode | Antigen-Affinitätsreinigung |
| Lagerungspuffer | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol |
| Lagerungsbedingungen | Bei -20°C lagern. Nach dem Versand ein Jahr lang stabil Aliquotieren ist bei -20oC Lagerung nicht notwendig. 20ul Größen enthalten 0,1% BSA. |
Hintergrundinformationen
SQLE, also named as ERG1, SE and SM, belongs to the squalene monooxygenase family. It catalyzes the first oxygenation step in cholesterol synthesis, acting on squalene before cyclization into the basic steroid structure. SQLE may serve as a flux-controlling enzyme beyond 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase (HMGR, considered as rate limiting). It is also posttranslationally regulated by cholesterol-dependent proteasomal degradation. SQLE is subject to feedback regulation via cholesterol-induced degradation, which depends on its lipid-sensing N terminal regulatory domain. Truncation of SQLE occurs during its endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation and requires the proteasome, which partially degrades the SQLE N-terminus and eliminates cholesterol-sensing elements within this region. The MW of SQLE is about 50-64 kDa. (PMID:21356516, PMID: 28972164)
Protokolle
| PRODUKTSPEZIFISCHE PROTOKOLLE | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for SQLE antibody 12544-1-AP | Protokoll herunterladen |
| IHC protocol for SQLE antibody 12544-1-AP | Protokoll herunterladenl |
| IF protocol for SQLE antibody 12544-1-AP | Protokoll herunterladen |
| IP protocol for SQLE antibody 12544-1-AP | Protokoll herunterladen |
| STANDARD-PROTOKOLLE | |
|---|---|
| Klicken Sie hier, um unsere Standardprotokolle anzuzeigen |
Publikationen
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Cell Metab Elevation of JAML Promotes Diabetic Kidney Disease by Modulating Podocyte Lipid Metabolism. | ||
Adv Sci (Weinh) Meisoindigo Acts as a Molecular Glue to Target PKMYT1 for Degradation in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Therapy | ||
Cell Metab Cholesterol-dependent degradation of squalene monooxygenase, a control point in cholesterol synthesis beyond HMG-CoA reductase. | ||
PLoS Biol Reduction of the cholesterol sensor SCAP in the brains of mice causes impaired synaptic transmission and altered cognitive function. | ||
Nat Commun MiR-205-driven downregulation of cholesterol biosynthesis through SQLE-inhibition identifies therapeutic vulnerability in aggressive prostate cancer. |