Protein C inhibitor Polyklonaler Antikörper
Protein C inhibitor Polyklonal Antikörper für WB, IHC, IF/ICC, ELISA
Wirt / Isotyp
Kaninchen / IgG
Getestete Reaktivität
human und mehr (1)
Anwendung
WB, IHC, IF/ICC, CoIP, ELISA
Konjugation
Unkonjugiert
Kat-Nr. : 10673-1-AP
Synonyme
Galerie der Validierungsdaten
Geprüfte Anwendungen
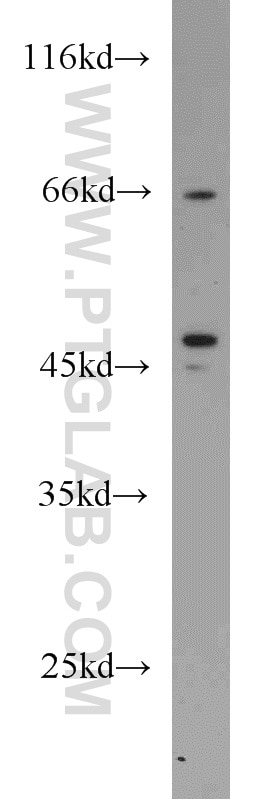
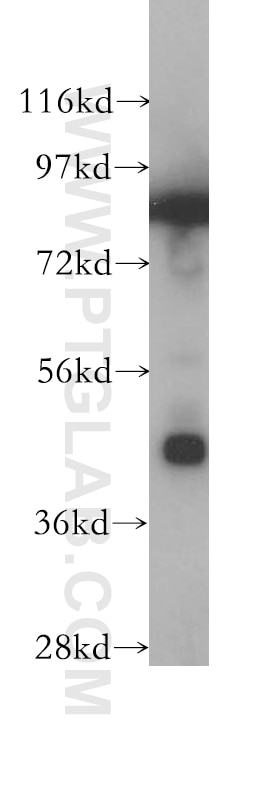
| Erfolgreiche Detektion in WB | HepG2-Zellen, A549-Zellen, HeLa-Zellen, Jurkat-Zellen, L02-Zellen, PC-3-Zellen |
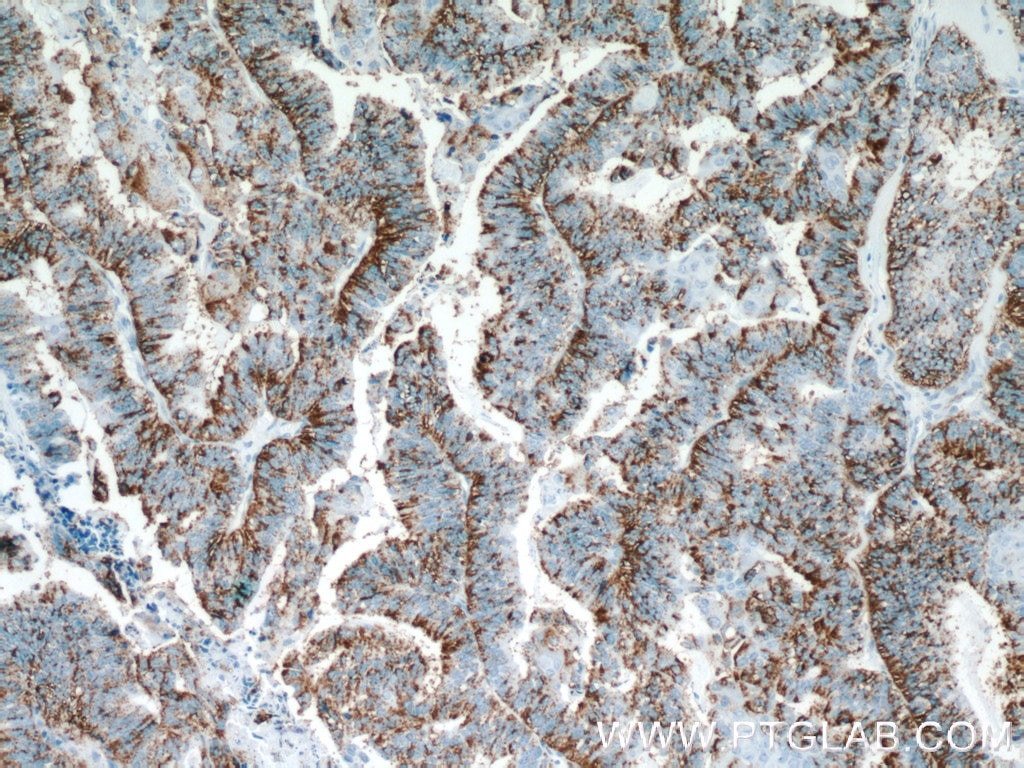
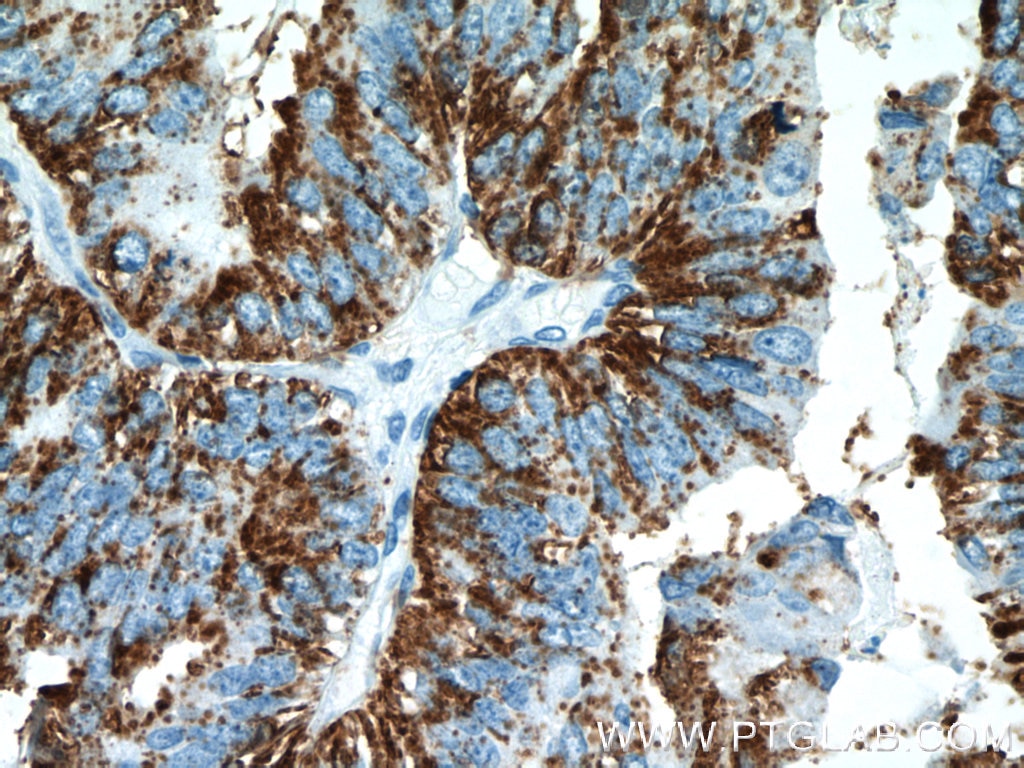
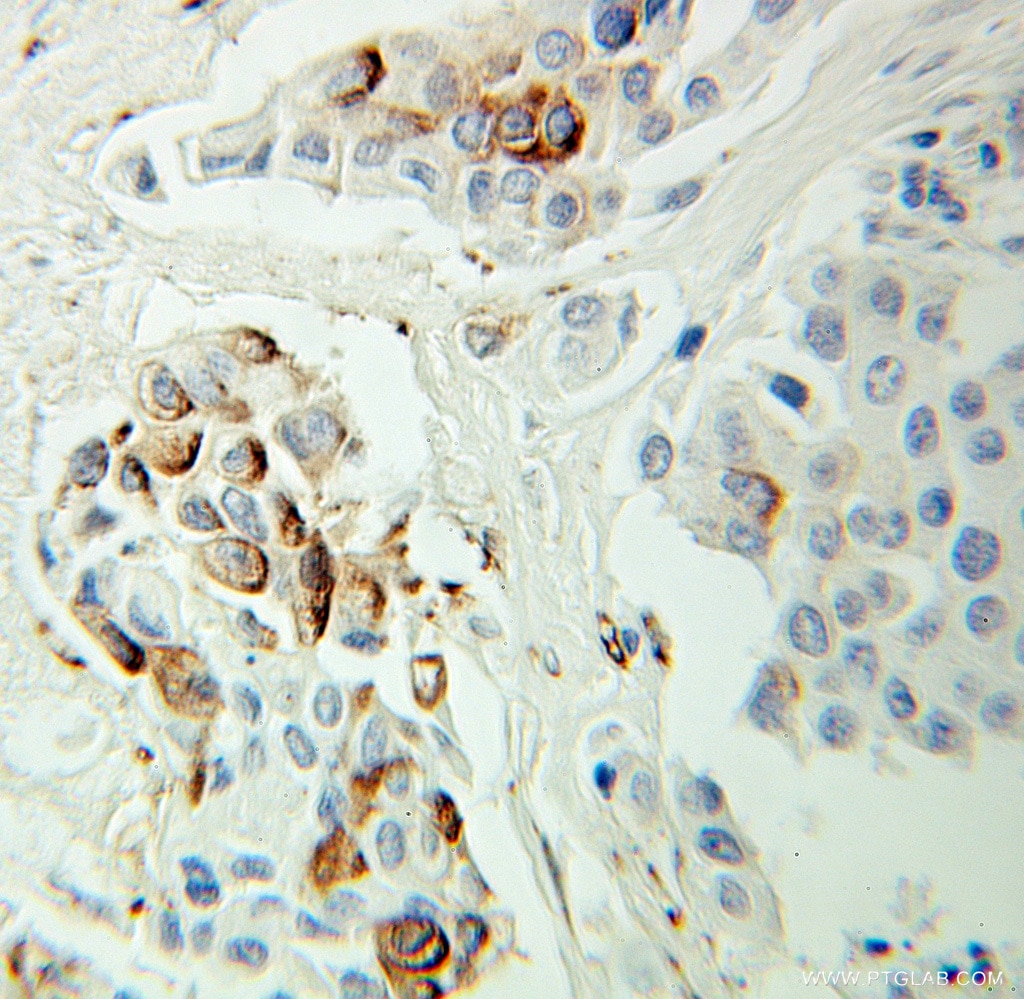
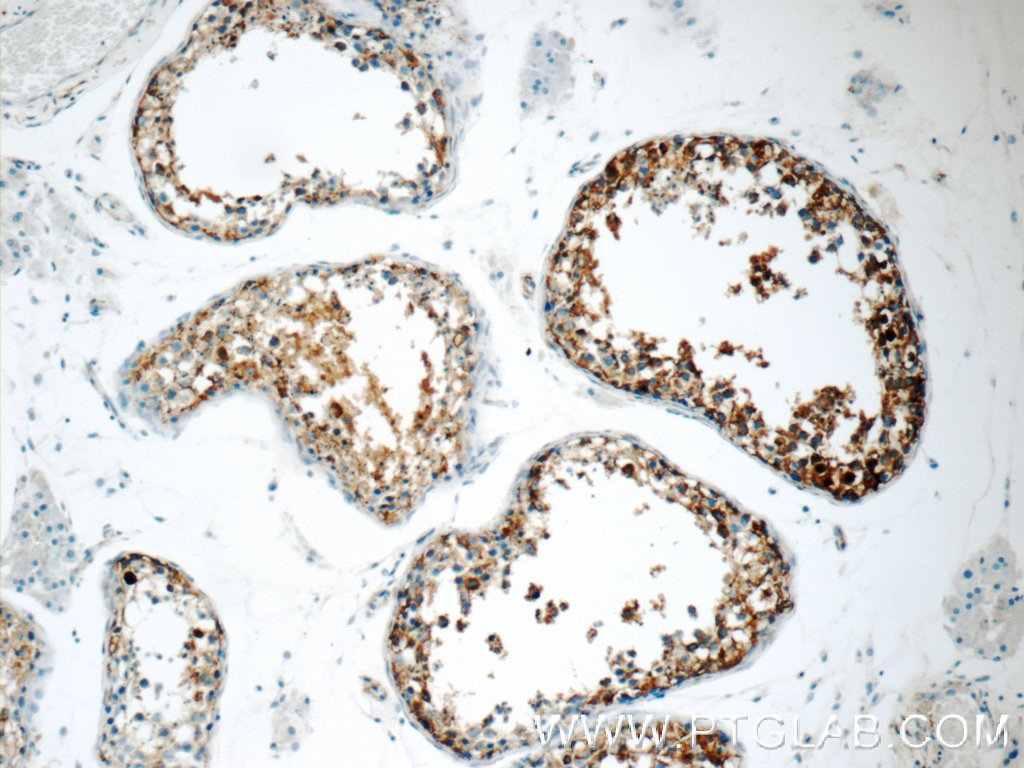
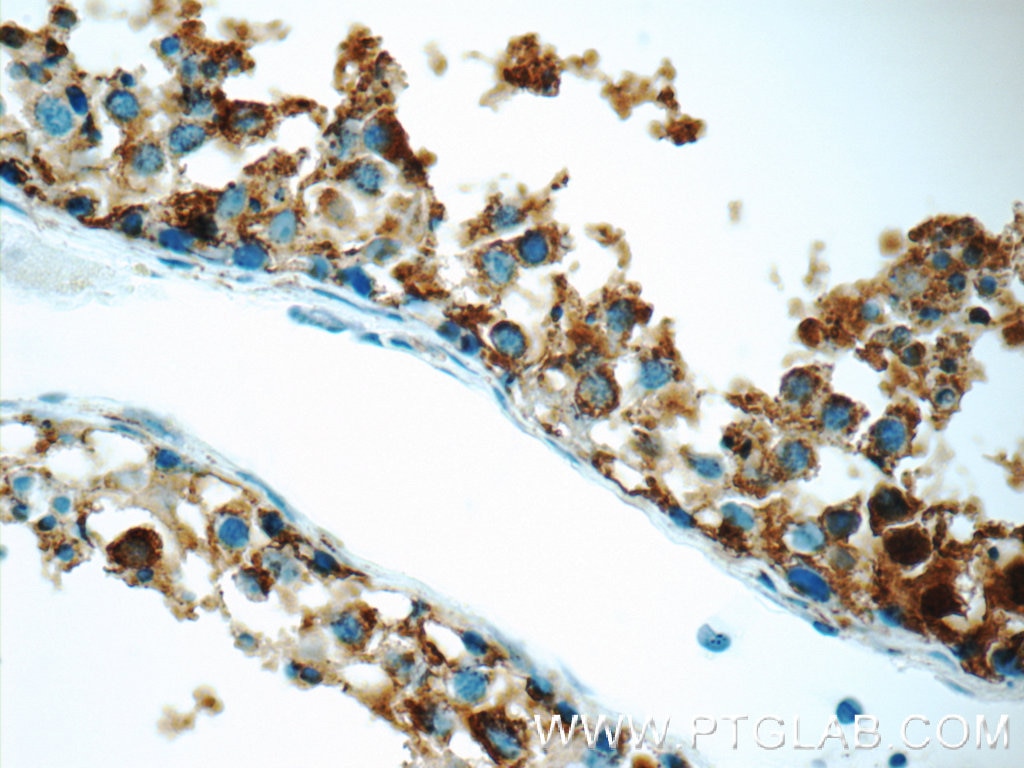
| Erfolgreiche Detektion in IHC | humanes Ovarialkarzinomgewebe, humanes Hodengewebe, humanes Mammakarzinomgewebe Hinweis: Antigendemaskierung mit TE-Puffer pH 9,0 empfohlen. (*) Wahlweise kann die Antigendemaskierung auch mit Citratpuffer pH 6,0 erfolgen. |
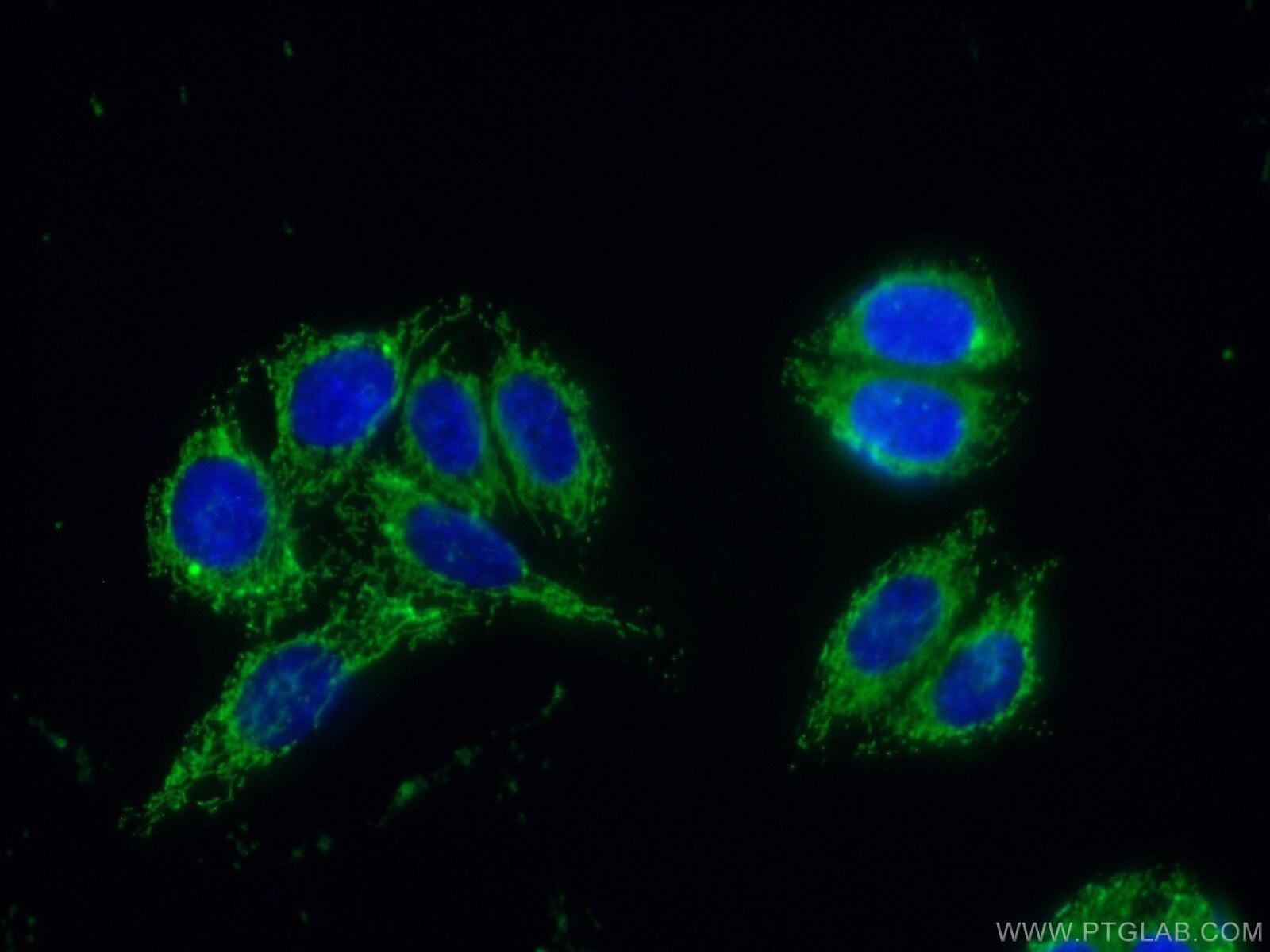
| Erfolgreiche Detektion in IF/ICC | HepG2-Zellen |
Empfohlene Verdünnung
| Anwendung | Verdünnung |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:500-1:600 |
| Immunhistochemie (IHC) | IHC : 1:20-1:200 |
| Immunfluoreszenz (IF)/ICC | IF/ICC : 1:50-1:500 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, check data in validation data gallery | |
Veröffentlichte Anwendungen
| WB | See 1 publications below |
| IHC | See 5 publications below |
| ELISA | See 1 publications below |
| CoIP | See 1 publications below |
Produktinformation
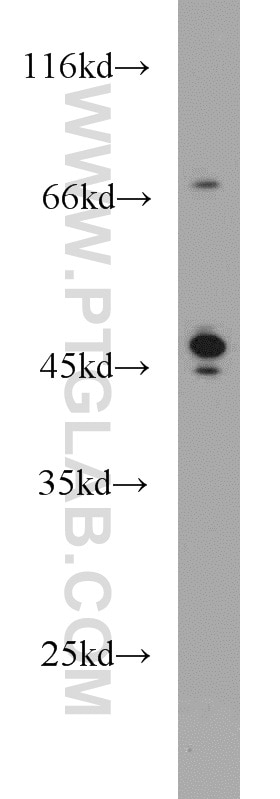
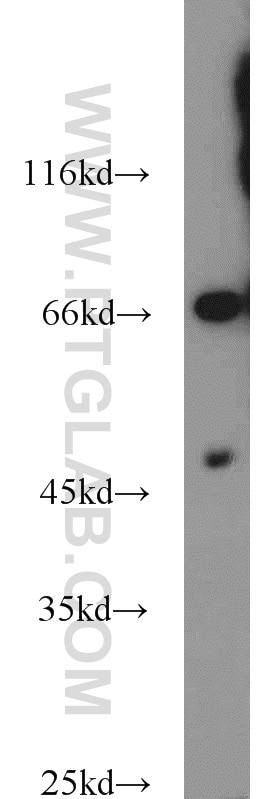
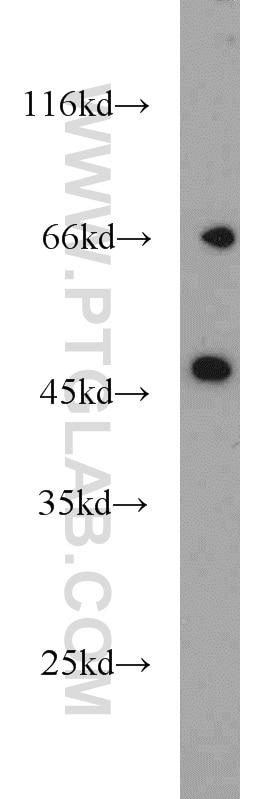
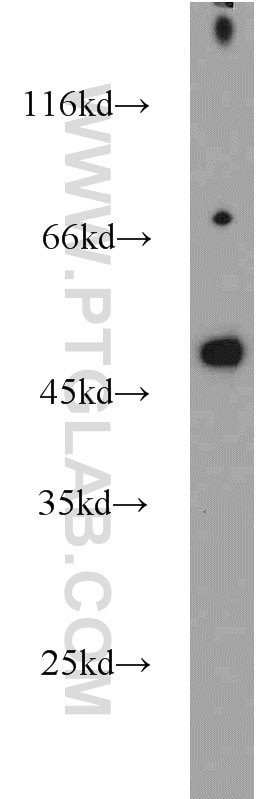
10673-1-AP bindet in WB, IHC, IF/ICC, CoIP, ELISA Protein C inhibitor und zeigt Reaktivität mit human
| Getestete Reaktivität | human |
| In Publikationen genannte Reaktivität | human, Ratte |
| Wirt / Isotyp | Kaninchen / IgG |
| Klonalität | Polyklonal |
| Typ | Antikörper |
| Immunogen | Protein C inhibitor fusion protein Ag1078 |
| Vollständiger Name | serpin peptidase inhibitor, clade A (alpha-1 antiproteinase, antitrypsin), member 5 |
| Berechnetes Molekulargewicht | 46 kDa |
| Beobachtetes Molekulargewicht | 46 kDa |
| GenBank-Zugangsnummer | BC008915 |
| Gene symbol | SERPINA5 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 5104 |
| Konjugation | Unkonjugiert |
| Form | Liquid |
| Reinigungsmethode | Antigen-Affinitätsreinigung |
| Lagerungspuffer | PBS mit 0.02% Natriumazid und 50% Glycerin pH 7.3. |
| Lagerungsbedingungen | Bei -20°C lagern. Nach dem Versand ein Jahr lang stabil Aliquotieren ist bei -20oC Lagerung nicht notwendig. 20ul Größen enthalten 0,1% BSA. |
Hintergrundinformationen
SERPINA5 (also called Protein C Inhibitor, PCI ) is a serpin type of serine protease inhibitor that is found in many tissues and fluids in human, including blood plasma, seminal plasma and urine. PCI found in blood originates from the liver and is capable of inhibiting several serine proteases involved in the regulation of coagulation and fibrinolysis, including activated protein C, thrombin, factor Xa, various kallikreins and plasminogen activators. PCI has been found to have antimicrobial and antitumor properties and thus appears to be a multi-functional protein.
Protokolle
| Produktspezifische Protokolle | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for Protein C inhibitor antibody 10673-1-AP | Protokoll herunterladen |
| IHC protocol for Protein C inhibitor antibody 10673-1-AP | Protokoll herunterladen |
| IF protocol for Protein C inhibitor antibody 10673-1-AP | Protokoll herunterladen |
| Standard-Protokolle | |
|---|---|
| Klicken Sie hier, um unsere Standardprotokolle anzuzeigen |
Publikationen
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Mod Pathol Loss of SerpinA5 protein expression is associated with advanced-stage serous ovarian tumors. | ||
J Neuropathol Exp Neurol Gene expression profiling of NF-1-associated and sporadic pilocytic astrocytoma identifies aldehyde dehydrogenase 1 family member L1 (ALDH1L1) as an underexpressed candidate biomarker in aggressive subtypes. | ||
Proteomics Clin Appl Proteomic analysis of human articular cartilage unravels the dyscoagulation in osteoarthritis and the potential value of serpinA5 as a biomarker for osteoarthritis. | ||
J Cell Mol Med SERPINA5 promotes tumour cell proliferation by modulating the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signalling pathway in gastric cancer | ||
Biomolecules Improvement in Clinical Features of L-NAME-Induced Preeclampsia-like Rats through Reduced SERPINA5 Expression | ||
J Proteome Res Proteomics Analysis of Knee Subchondral Bone Identifies Differentially Expressed Proteins Associated with Osteoarthritis |