- Featured Product
- KD/KO Validated
RTN4/NOGO Polyklonaler Antikörper
RTN4/NOGO Polyklonal Antikörper für WB, IHC, IF/ICC, FC (Intra), ELISA
Wirt / Isotyp
Kaninchen / IgG
Getestete Reaktivität
human, Maus und mehr (1)
Anwendung
WB, IHC, IF/ICC, FC (Intra), ELISA
Konjugation
Unkonjugiert
Kat-Nr. : 10950-1-AP
Synonyme
Geprüfte Anwendungen
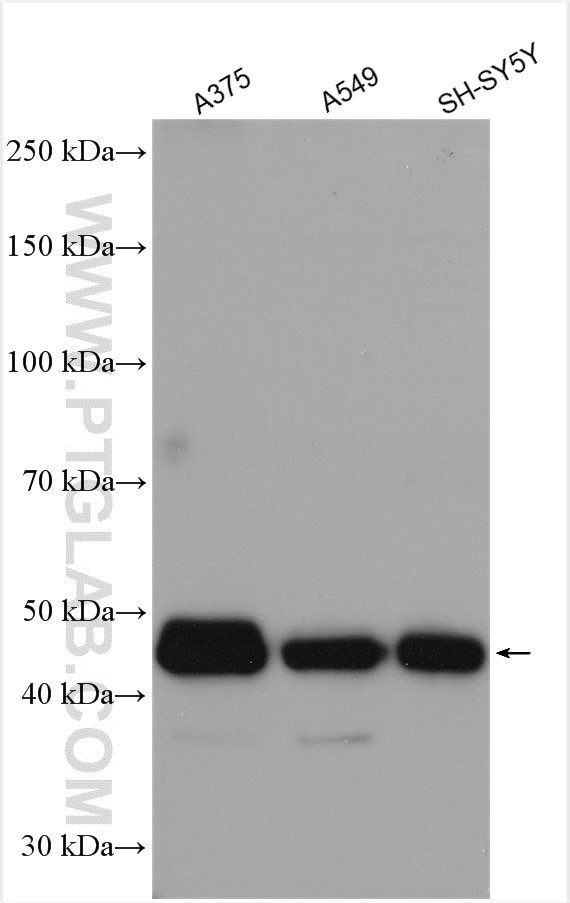
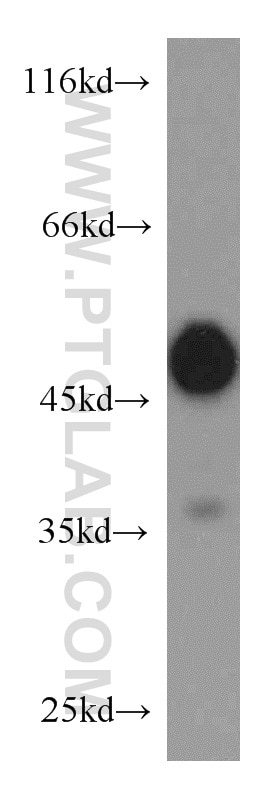
| Erfolgreiche Detektion in WB | A375-Zellen, A549-Zellen, HepG2-Zellen, SH-SY5Y-Zellen |
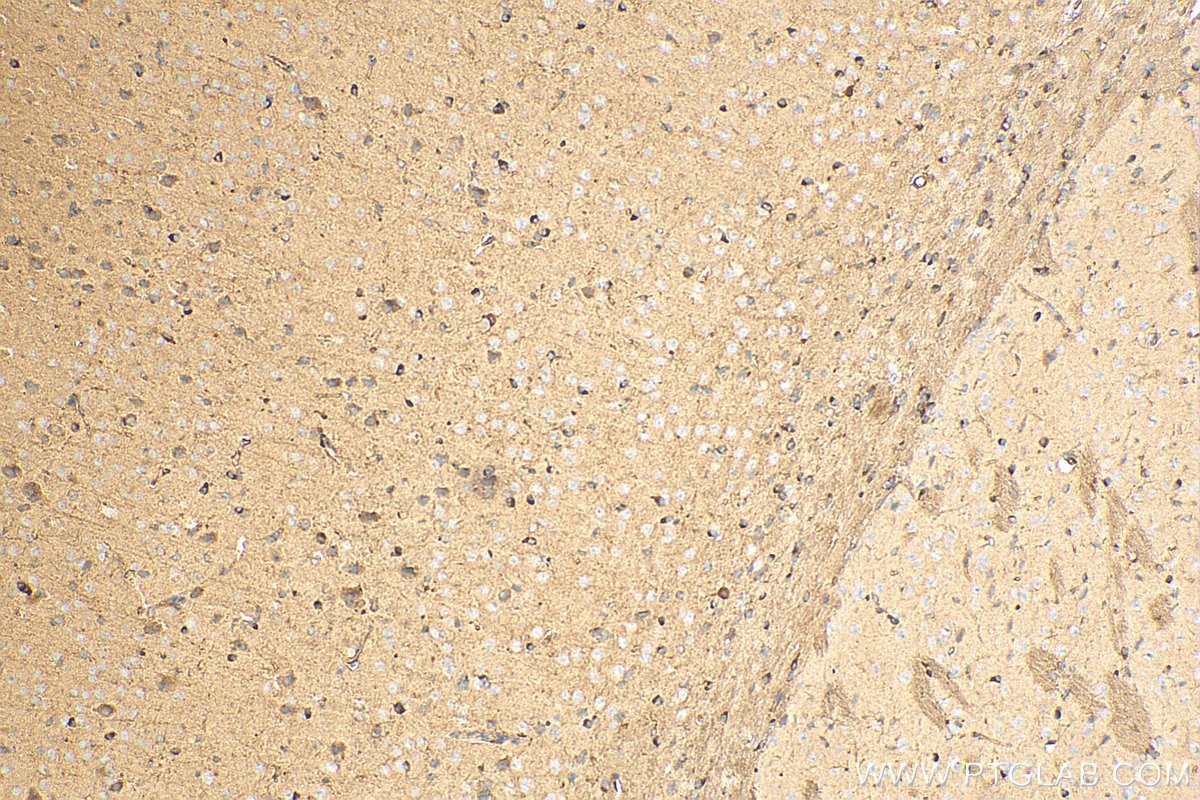
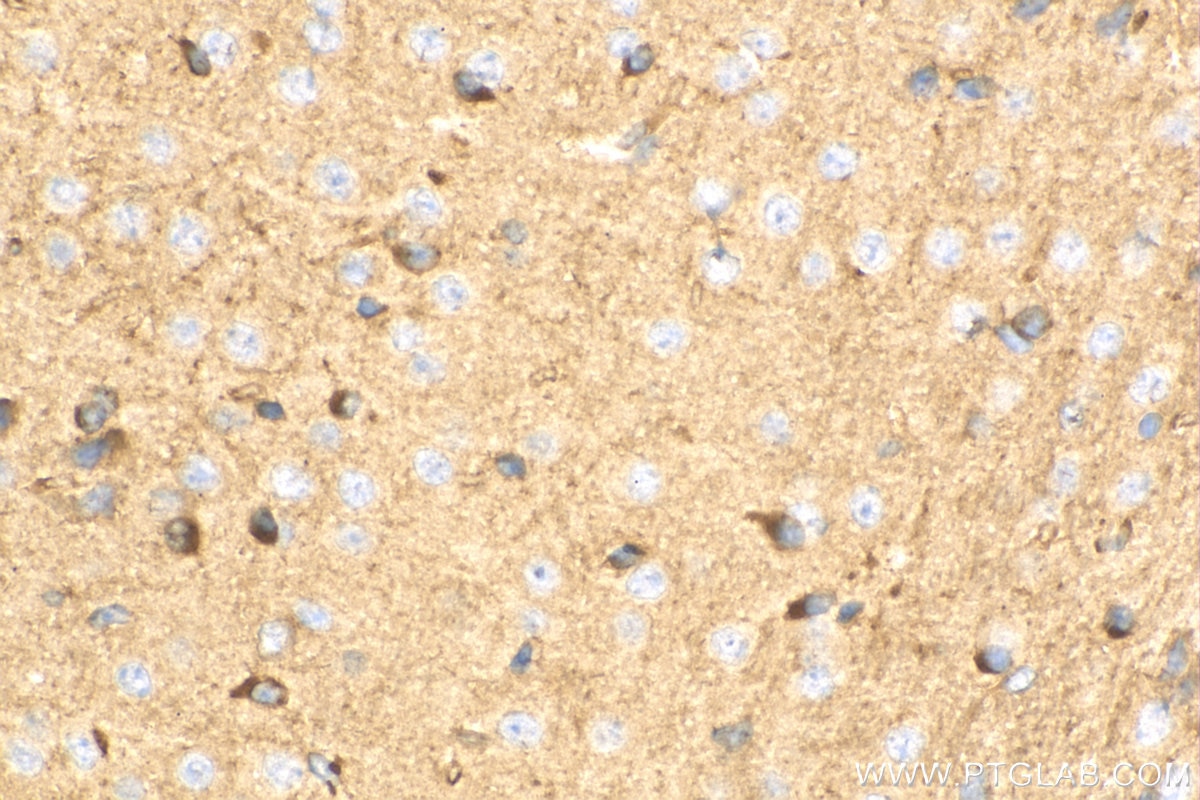
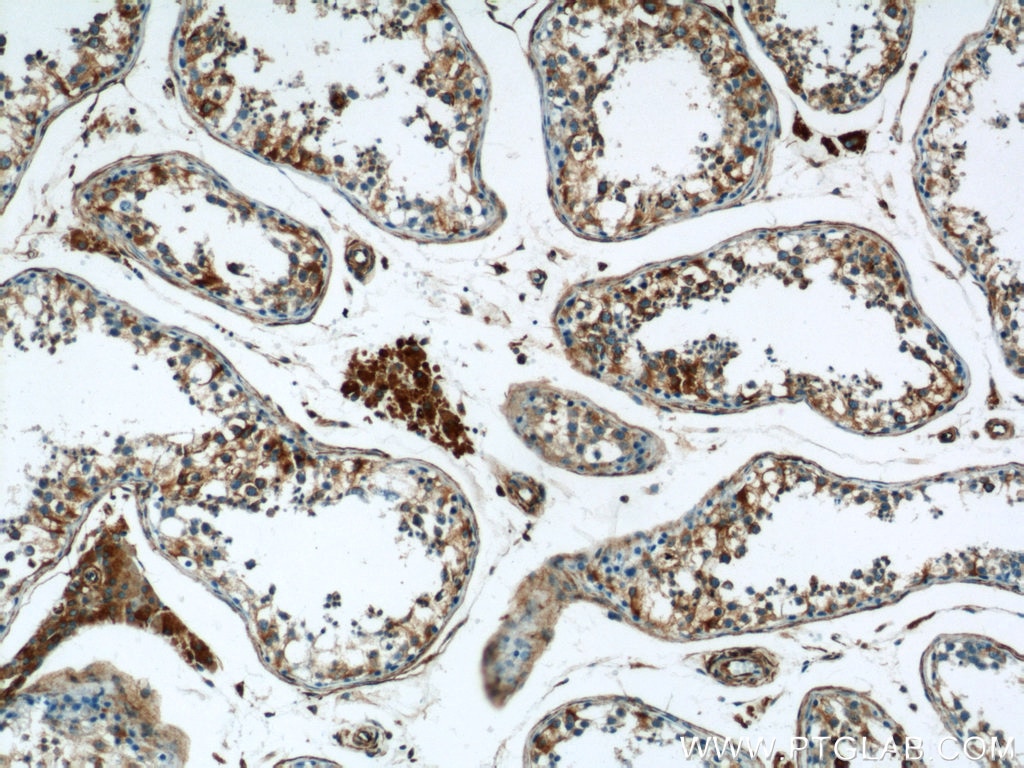
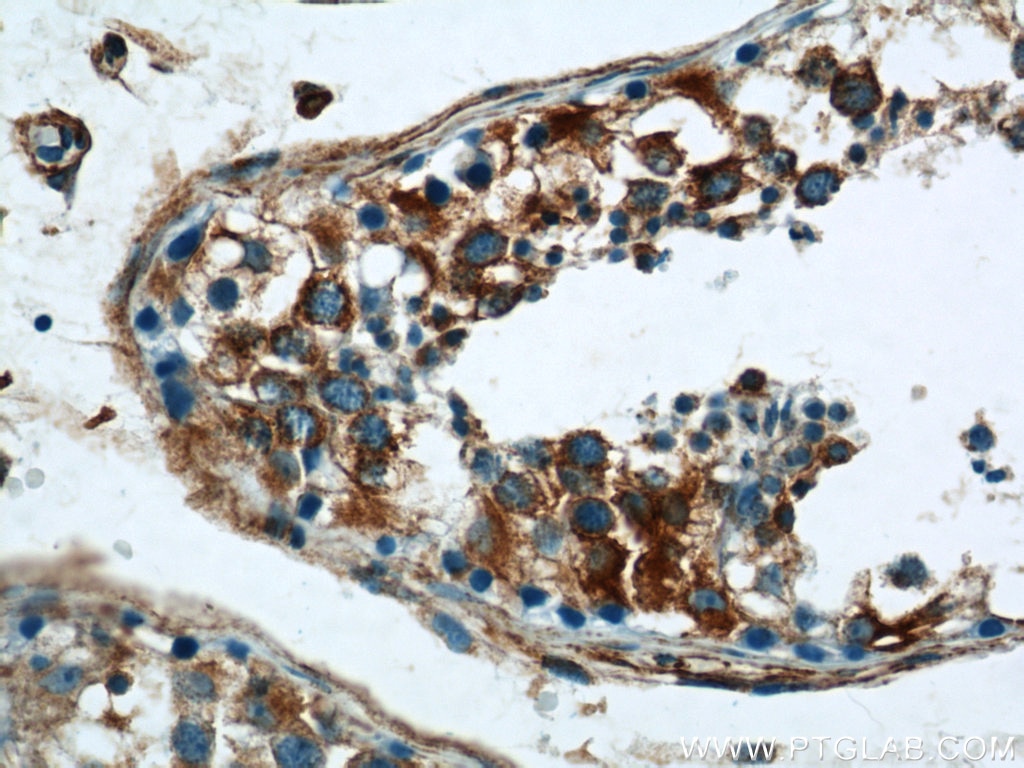
| Erfolgreiche Detektion in IHC | Maushirngewebe, humanes Hodengewebe Hinweis: Antigendemaskierung mit TE-Puffer pH 9,0 empfohlen. (*) Wahlweise kann die Antigendemaskierung auch mit Citratpuffer pH 6,0 erfolgen. |
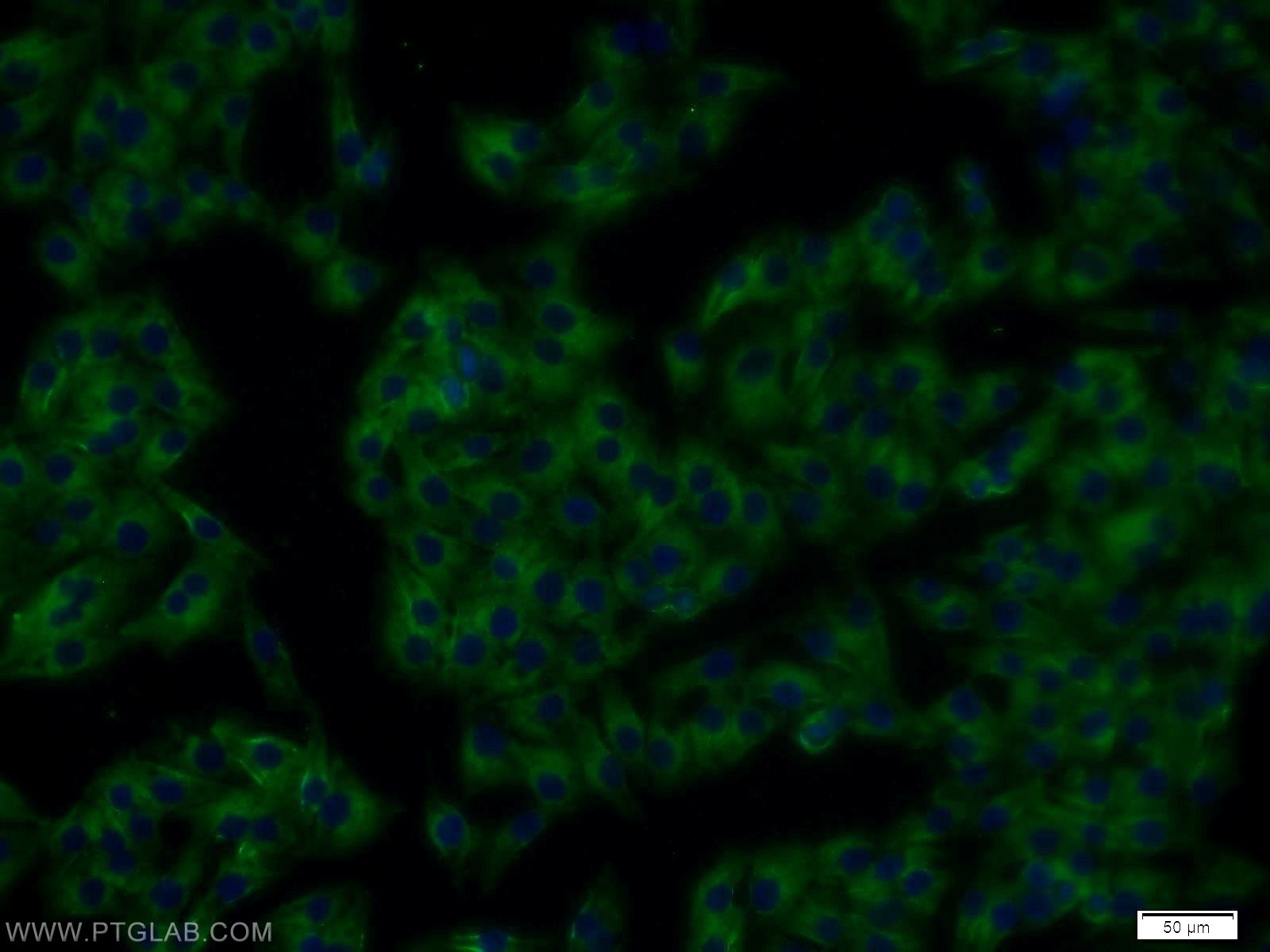
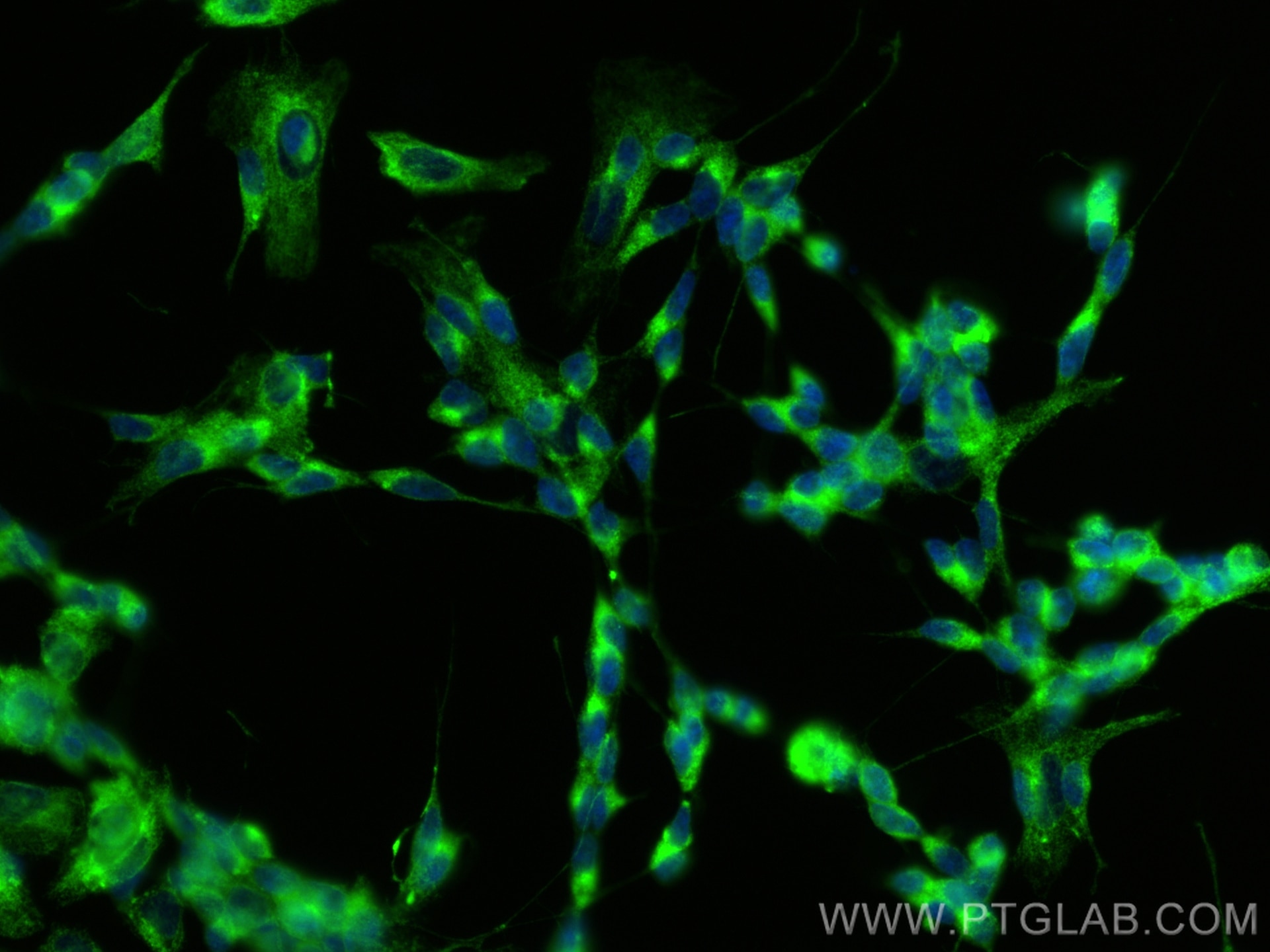
| Erfolgreiche Detektion in IF/ICC | SH-SY5Y-Zellen, A375-Zellen |
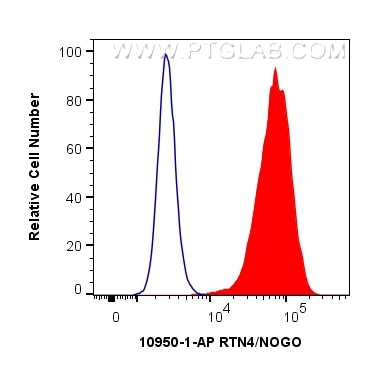
| Erfolgreiche Detektion in FC (Intra) | HeLa-Zellen |
Empfohlene Verdünnung
| Anwendung | Verdünnung |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:5000-1:50000 |
| Immunhistochemie (IHC) | IHC : 1:50-1:500 |
| Immunfluoreszenz (IF)/ICC | IF/ICC : 1:200-1:800 |
| Durchflusszytometrie (FC) (INTRA) | FC (INTRA) : 0.40 ug per 10^6 cells in a 100 µl suspension |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, check data in validation data gallery | |
Veröffentlichte Anwendungen
| KD/KO | See 4 publications below |
| WB | See 10 publications below |
| IHC | See 1 publications below |
| IF | See 3 publications below |
Produktinformation
10950-1-AP bindet in WB, IHC, IF/ICC, FC (Intra), ELISA RTN4/NOGO und zeigt Reaktivität mit human, Maus
| Getestete Reaktivität | human, Maus |
| In Publikationen genannte Reaktivität | human, Maus, Ratte |
| Wirt / Isotyp | Kaninchen / IgG |
| Klonalität | Polyklonal |
| Typ | Antikörper |
| Immunogen | RTN4/NOGO fusion protein Ag1392 |
| Vollständiger Name | reticulon 4 |
| Berechnetes Molekulargewicht | 130 kDa |
| Beobachtetes Molekulargewicht | 45-50 kDa |
| GenBank-Zugangsnummer | BC012619 |
| Gene symbol | NOGO |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 57142 |
| Konjugation | Unkonjugiert |
| Form | Liquid |
| Reinigungsmethode | Antigen-Affinitätsreinigung |
| Lagerungspuffer | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol |
| Lagerungsbedingungen | Bei -20°C lagern. Nach dem Versand ein Jahr lang stabil Aliquotieren ist bei -20oC Lagerung nicht notwendig. 20ul Größen enthalten 0,1% BSA. |
Hintergrundinformationen
Reticulon (RTN) proteins are a group of membrane-bound proteins that largely reside in endoplasmic reticulum (ER) (PMID: 18177508). Reticulon proteins share a common sequence feature, the reticulon homology domain (RHD). They are involved in shaping the tubular endoplasmic reticulum network, membrane trafficking, inhibition of axonal growth, and apoptosis (PMID: 24218324). Four mammalian reticulons (RTN1-4) exist. RTN4 (also known as Neurite outgrowth inhibitor or Nogo) is a myelin-associated neurite growth inhibitory protein. Some isoforms of RTN4 have been described. RTN4A (Nogo-A, runs at ~200 kDa), RTN4B (Nogo-B, 40-55 kDa), and RTN4C (Nogo-C, 22-25 kDa) are three major isoforms (PMID: 31092426; 16469703).
Protokolle
| PRODUKTSPEZIFISCHE PROTOKOLLE | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for RTN4/NOGO antibody 10950-1-AP | Protokoll herunterladen |
| IHC protocol for RTN4/NOGO antibody 10950-1-AP | Protokoll herunterladenl |
| IF protocol for RTN4/NOGO antibody 10950-1-AP | Protokoll herunterladen |
| STANDARD-PROTOKOLLE | |
|---|---|
| Klicken Sie hier, um unsere Standardprotokolle anzuzeigen |
Publikationen
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
PLoS Biol Reticulon and CLIMP-63 regulate nanodomain organization of peripheral ER tubules.
| ||
Autophagy Dengue and Zika viruses subvert reticulophagy by NS2B3-mediated cleavage of FAM134B. | ||
J Cell Sci SEC24A facilitates colocalization and calcium flux between endoplasmic reticulum and mitochondria. | ||
Drug Des Devel Ther Tanshinone IIA Promotes Axonal Regeneration in Rats with Focal Cerebral Ischemia Through the Inhibition of Nogo-A/NgR1/RhoA/ROCKII/MLC Signaling. | ||
Neurol Res Erythropoietin attenuates axonal injury after middle cerebral artery occlusion in mice. | ||
NPJ Parkinsons Dis Deficiency of Perry syndrome-associated p150Glued in midbrain dopaminergic neurons leads to progressive neurodegeneration and endoplasmic reticulum abnormalities |