- Featured Product
- KD/KO Validated
RENALASE Polyklonaler Antikörper
RENALASE Polyklonal Antikörper für WB, IHC, IF/ICC, IF-P, IP, ELISA
Wirt / Isotyp
Kaninchen / IgG
Getestete Reaktivität
human, Maus, Ratte
Anwendung
WB, IHC, IF/ICC, IF-P, IP, ELISA
Konjugation
Unkonjugiert
Kat-Nr. : 15003-1-AP
Synonyme
Geprüfte Anwendungen
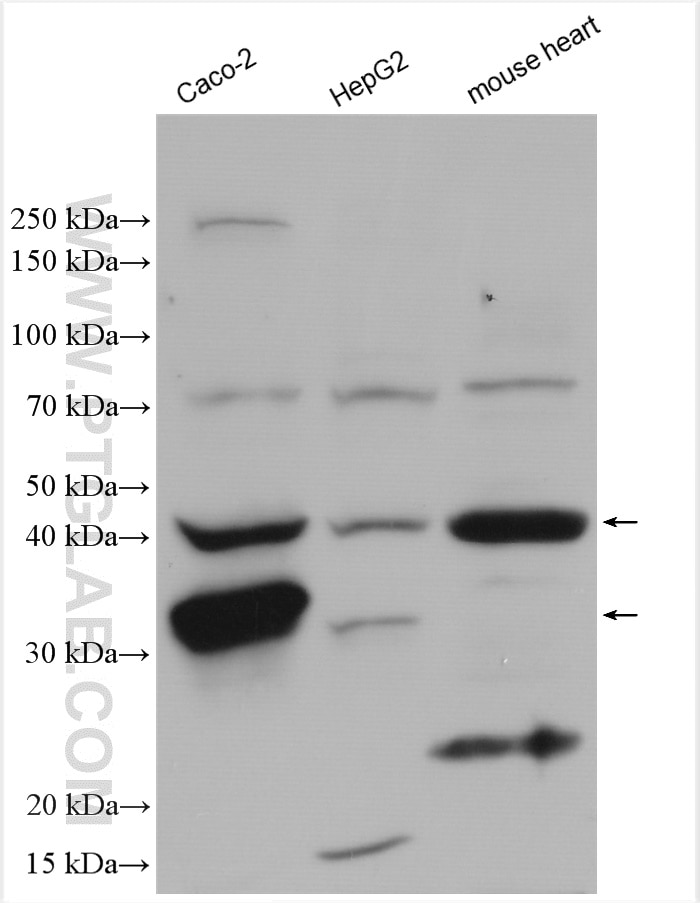
| Erfolgreiche Detektion in WB | Caco-2-Zellen |
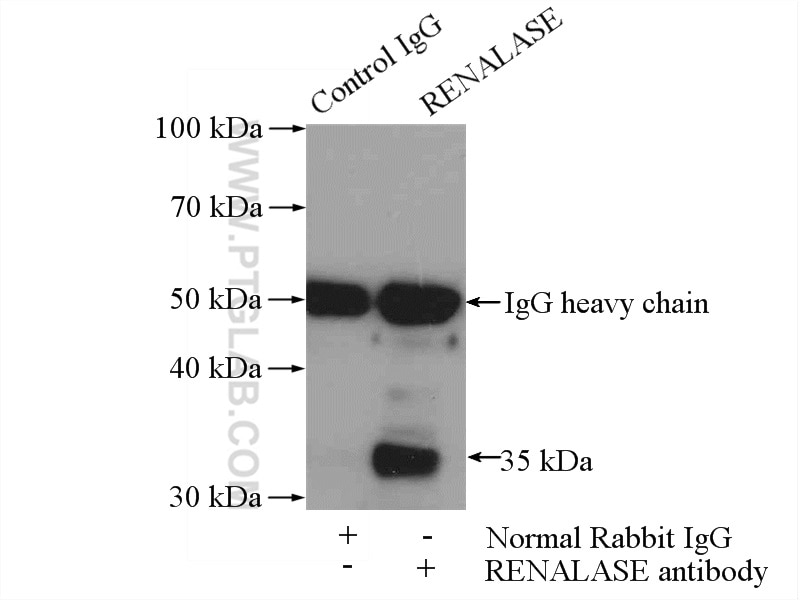
| Erfolgreiche IP | HEK-293-Zellen |
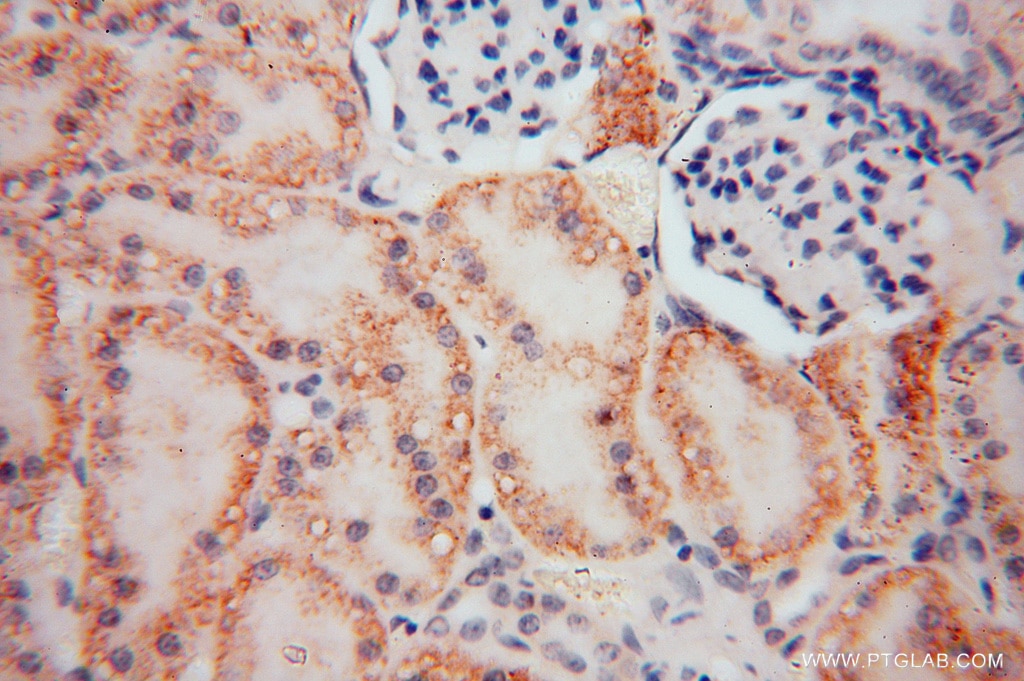
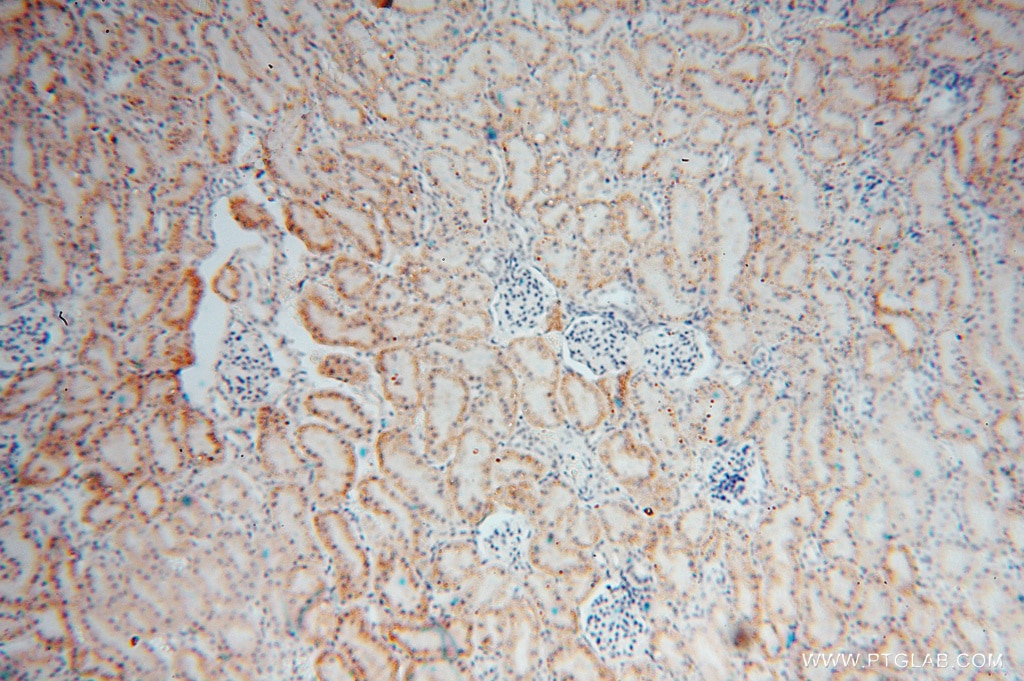
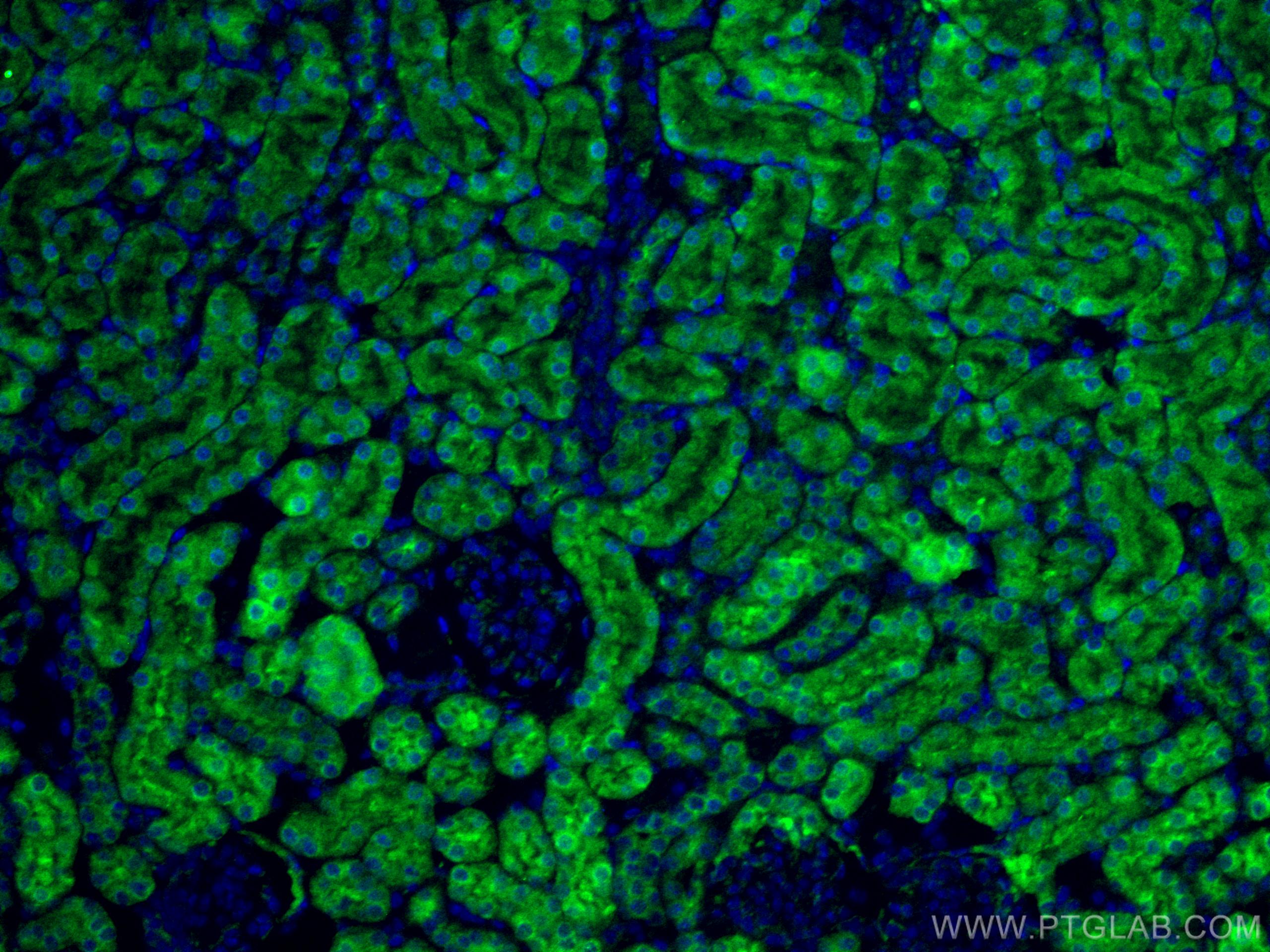
| Erfolgreiche Detektion in IHC | humanes Nierengewebe Hinweis: Antigendemaskierung mit TE-Puffer pH 9,0 empfohlen. (*) Wahlweise kann die Antigendemaskierung auch mit Citratpuffer pH 6,0 erfolgen. |
| Erfolgreiche Detektion in IF-P | Mausnierengewebe |
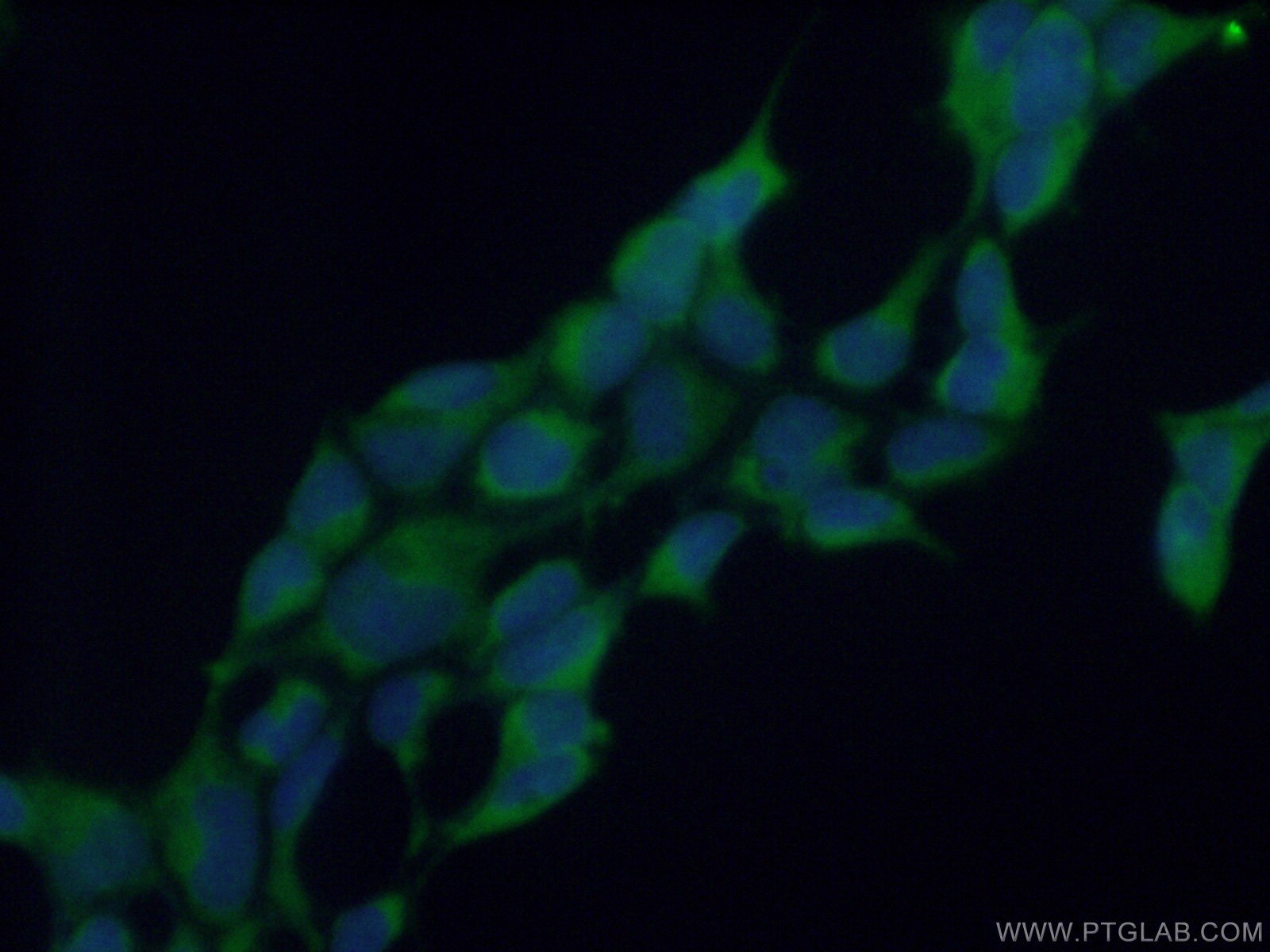
| Erfolgreiche Detektion in IF/ICC | HEK-293-Zellen |
Empfohlene Verdünnung
| Anwendung | Verdünnung |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:500-1:1000 |
| Immunpräzipitation (IP) | IP : 0.5-4.0 ug for 1.0-3.0 mg of total protein lysate |
| Immunhistochemie (IHC) | IHC : 1:20-1:200 |
| Immunfluoreszenz (IF)-P | IF-P : 1:50-1:500 |
| Immunfluoreszenz (IF)/ICC | IF/ICC : 1:50-1:500 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, check data in validation data gallery | |
Veröffentlichte Anwendungen
| KD/KO | See 1 publications below |
| WB | See 7 publications below |
| IHC | See 2 publications below |
| IF | See 3 publications below |
Produktinformation
15003-1-AP bindet in WB, IHC, IF/ICC, IF-P, IP, ELISA RENALASE und zeigt Reaktivität mit human, Maus, Ratten
| Getestete Reaktivität | human, Maus, Ratte |
| In Publikationen genannte Reaktivität | human, Maus, Ratte |
| Wirt / Isotyp | Kaninchen / IgG |
| Klonalität | Polyklonal |
| Typ | Antikörper |
| Immunogen | RENALASE fusion protein Ag13061 |
| Vollständiger Name | chromosome 10 open reading frame 59 |
| Berechnetes Molekulargewicht | 38 kDa |
| Beobachtetes Molekulargewicht | 35 kDa |
| GenBank-Zugangsnummer | BC005364 |
| Gene symbol | RENALASE |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 55328 |
| Konjugation | Unkonjugiert |
| Form | Liquid |
| Reinigungsmethode | Antigen-Affinitätsreinigung |
| Lagerungspuffer | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol |
| Lagerungsbedingungen | Bei -20°C lagern. Nach dem Versand ein Jahr lang stabil Aliquotieren ist bei -20oC Lagerung nicht notwendig. 20ul Größen enthalten 0,1% BSA. |
Hintergrundinformationen
RNLS, also named as Renalase, C10orf59 and MAO-C, belongs to the renalase family. It is probable FAD-dependent amine oxidase secreted by the kidney, which circulates in blood and modulates cardiac function and systemic blood pressure. RNLS degrades catecholamines such as dopamine, norepinephrine and epinephrine in vitro. It lowers blood pressure in vivo by decreasing cardiac contractility and heart rate and preventing a compensatory increase in peripheral vascular tone, suggesting a causal link to the increased plasma catecholamine and heightened cardiovascular risk. High concentrations of catecholamines activate plasma renalase and promotes its secretion and synthesis. RNLS has physiologically relevant catecholamine-oxidizing activity. (PMID:15841207 ) This antibody is specific to RNLS.
Protokolle
| PRODUKTSPEZIFISCHE PROTOKOLLE | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for RENALASE antibody 15003-1-AP | Protokoll herunterladen |
| IHC protocol for RENALASE antibody 15003-1-AP | Protokoll herunterladenl |
| IF protocol for RENALASE antibody 15003-1-AP | Protokoll herunterladen |
| IP protocol for RENALASE antibody 15003-1-AP | Protokoll herunterladen |
| STANDARD-PROTOKOLLE | |
|---|---|
| Klicken Sie hier, um unsere Standardprotokolle anzuzeigen |
Publikationen
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
J Clin Invest Renalase is a novel, soluble monoamine oxidase that regulates cardiac function and blood pressure. | ||
Front Cardiovasc Med Aerobic Exercise Training Improves Renal Injury in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats by Increasing Renalase Expression in Medulla. | ||
Life Sci Renalase is localized to the small intestine crypt and expressed upon the activation of NF-κB p65 in mice model of fasting-induced oxidative stress. | ||
Exp Biol Med (Maywood) Plasma and urine renalase levels and activity during the recovery of renal function in kidney transplant recipients. |