Phospho-JUN (Ser73) Polyklonaler Antikörper
Phospho-JUN (Ser73) Polyklonal Antikörper für WB, IF/ICC, ELISA
Wirt / Isotyp
Kaninchen / IgG
Getestete Reaktivität
human, Maus, Ratte und mehr (1)
Anwendung
WB, IF/ICC, CoIP, ELISA
Konjugation
Unkonjugiert
Kat-Nr. : 28891-1-AP
Synonyme
Geprüfte Anwendungen
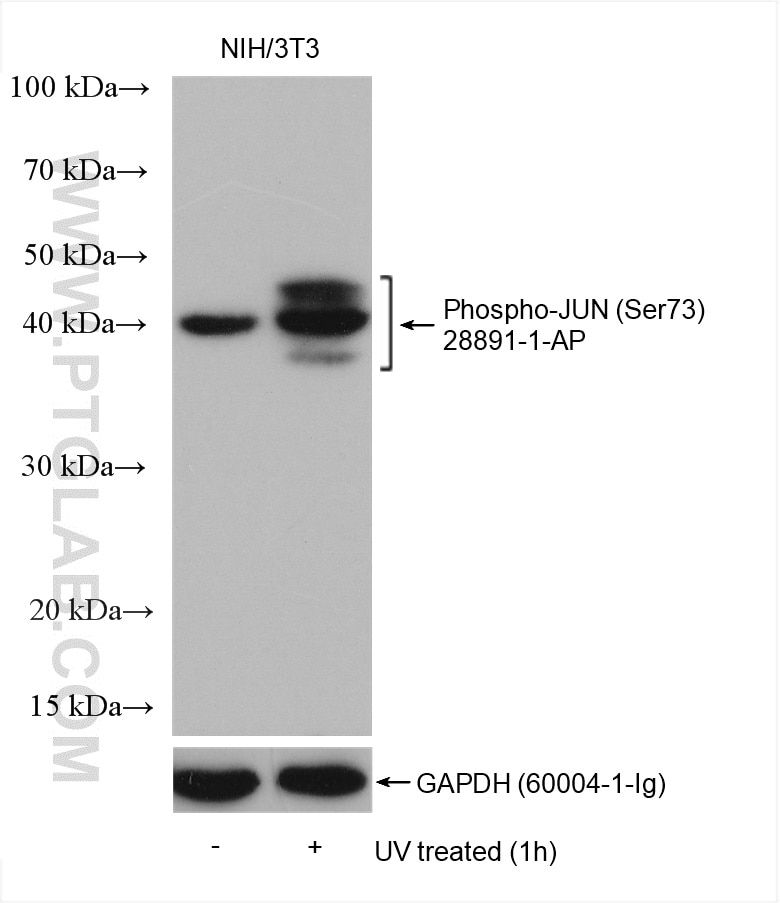
| Erfolgreiche Detektion in WB | Mit UV behandelte NIH/3T3-Zellen |
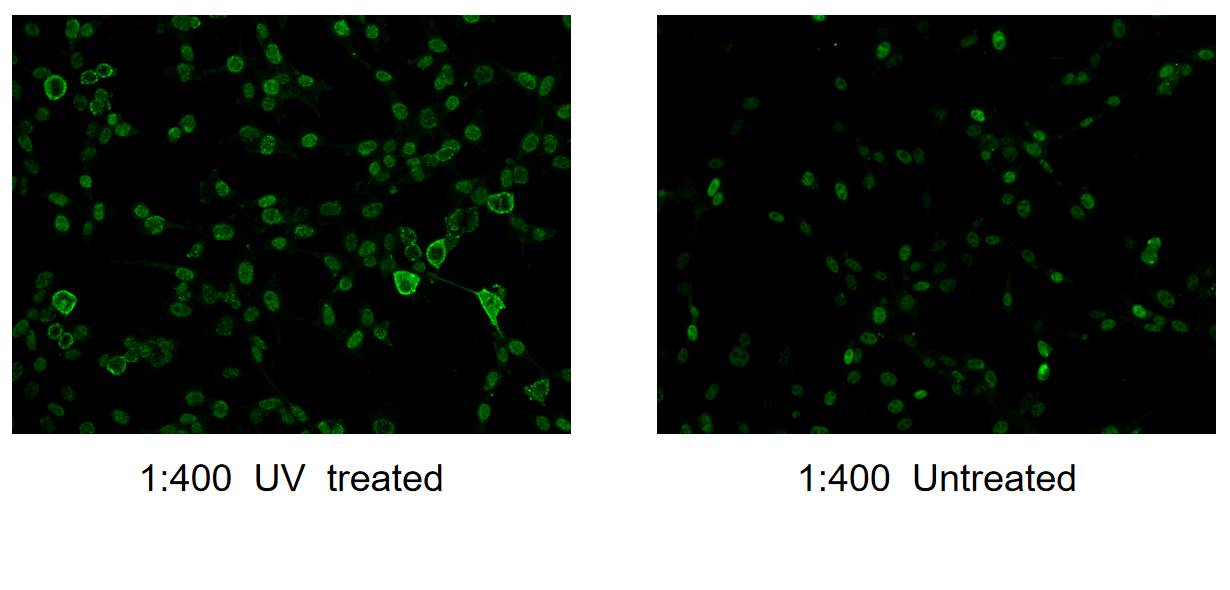
| Erfolgreiche Detektion in IF/ICC | NIH/3T3-Zellen |
Empfohlene Verdünnung
| Anwendung | Verdünnung |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:500-1:2000 |
| Immunfluoreszenz (IF)/ICC | IF/ICC : 1:200-1:800 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, check data in validation data gallery | |
Veröffentlichte Anwendungen
| WB | See 23 publications below |
| IF | See 3 publications below |
| CoIP | See 1 publications below |
Produktinformation
28891-1-AP bindet in WB, IF/ICC, CoIP, ELISA Phospho-JUN (Ser73) und zeigt Reaktivität mit human, Maus, Ratten
| Getestete Reaktivität | human, Maus, Ratte |
| In Publikationen genannte Reaktivität | human, Hausschwein, Maus |
| Wirt / Isotyp | Kaninchen / IgG |
| Klonalität | Polyklonal |
| Typ | Antikörper |
| Immunogen | Peptid |
| Vollständiger Name | jun oncogene |
| Berechnetes Molekulargewicht | 331 aa, 36 kDa |
| Beobachtetes Molekulargewicht | 38-45 kDa |
| GenBank-Zugangsnummer | BC068522 |
| Gene symbol | JUN |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 3725 |
| Konjugation | Unkonjugiert |
| Form | Liquid |
| Reinigungsmethode | Antigen-Affinitätsreinigung |
| Lagerungspuffer | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol |
| Lagerungsbedingungen | Bei -20°C lagern. Nach dem Versand ein Jahr lang stabil Aliquotieren ist bei -20oC Lagerung nicht notwendig. 20ul Größen enthalten 0,1% BSA. |
Hintergrundinformationen
JUN is also named as c-Jun and AP1, belongs to the bZIP family and Jun subfamily. JUN, the most extensively studied protein of the activator protein-1 (AP-1) complex, is involved in numerous cell activities, such as proliferation, apoptosis, survival, tumorigenesis and tissue morphogenesis (PMID: 22180088). JUN is a transcription factor that recognizes and binds to the enhancer heptamer motif 5'-TGA[CG]TCA-3'. It promotes activity of NR5A1 when phosphorylated by HIPK3 leading to increased steroidogenic gene expression upon cAMP signaling pathway stimulation. JUN is a basic leucine zipper (bZIP) transcription factor that acts as homo- or heterodimer, binding to DNA and regulating gene transcription (PMID: 9732876). In additon, extracellular signals can induce post-translational modifications of JUN, resulting in altered transcriptional activity and target gene expression (PMID:8464713). More over, it has uncovered multiple layers of a complex regulatory scheme in which JUN is able to crosstalk, amplify and integrate different signals for tissue development and disease. Jun is predominantly nuclear, ubiquitinated Jun colocalizes with lysosomal proteins (PMID: 15469925). This antibody is raised against synthetic phosphopeptide corresponding to residues surrounding Ser73 of human JUN, which can detect the bands around 42-45 kDa.
Protokolle
| PRODUKTSPEZIFISCHE PROTOKOLLE | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for Phospho-JUN (Ser73) antibody 28891-1-AP | Protokoll herunterladen |
| IF protocol for Phospho-JUN (Ser73) antibody 28891-1-AP | Protokoll herunterladen |
| STANDARD-PROTOKOLLE | |
|---|---|
| Klicken Sie hier, um unsere Standardprotokolle anzuzeigen |
Publikationen
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Small Honeycomb Bionic Graphene Oxide Quantum Dot/Layered Double Hydroxide Composite Nanocoating Promotes Osteoporotic Bone Regeneration via Activating Mitophagy | ||
J Cell Biol JNK regulates ciliogenesis through the interflagellar transport complex and actin networks | ||
J Cell Mol Med SIAH2 suppresses c-JUN pathway by promoting the polyubiquitination and degradation of HBx in hepatocellular carcinoma | ||
Biochem Pharmacol Activation of CXCL13/CXCR5 axis aggravates experimental autoimmune cystitis and interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome. | ||
Int J Biol Sci RHOV promotes lung adenocarcinoma cell growth and metastasis through JNK/c-Jun pathway. | ||
Front Pharmacol Azithromycin Attenuates Bleomycin-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis Partly by Inhibiting the Expression of LOX and LOXL-2. |