- Featured Product
- KD/KO Validated
PAIP1 Polyklonaler Antikörper
PAIP1 Polyklonal Antikörper für WB, IF/ICC, IP, ELISA
Wirt / Isotyp
Kaninchen / IgG
Getestete Reaktivität
Affe, human
Anwendung
WB, IHC, IF/ICC, IP, ELISA
Konjugation
Unkonjugiert
Kat-Nr. : 10675-1-AP
Synonyme
Galerie der Validierungsdaten
Geprüfte Anwendungen
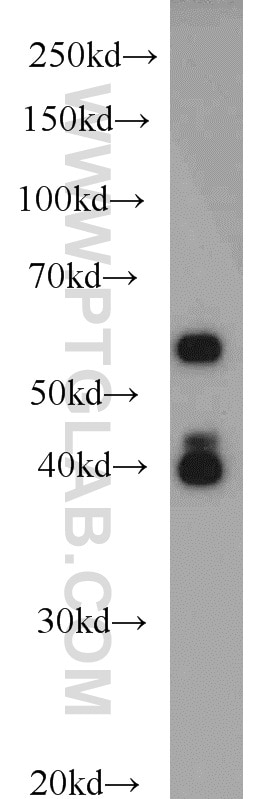
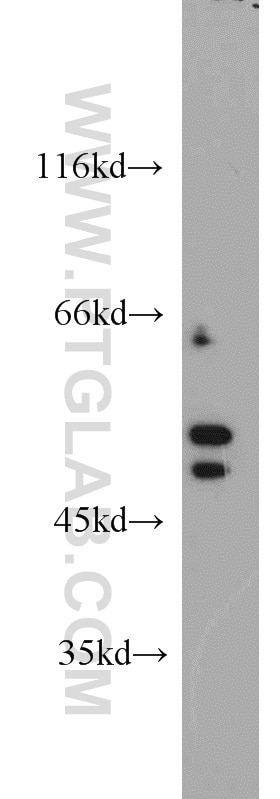
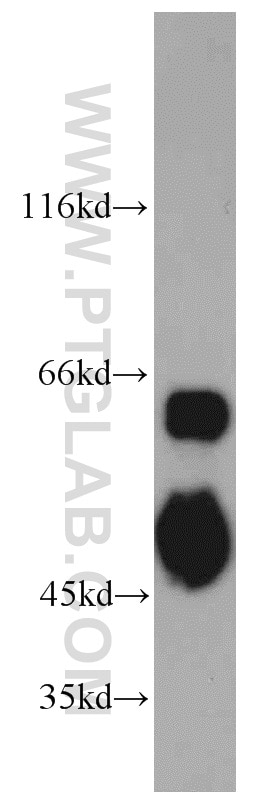
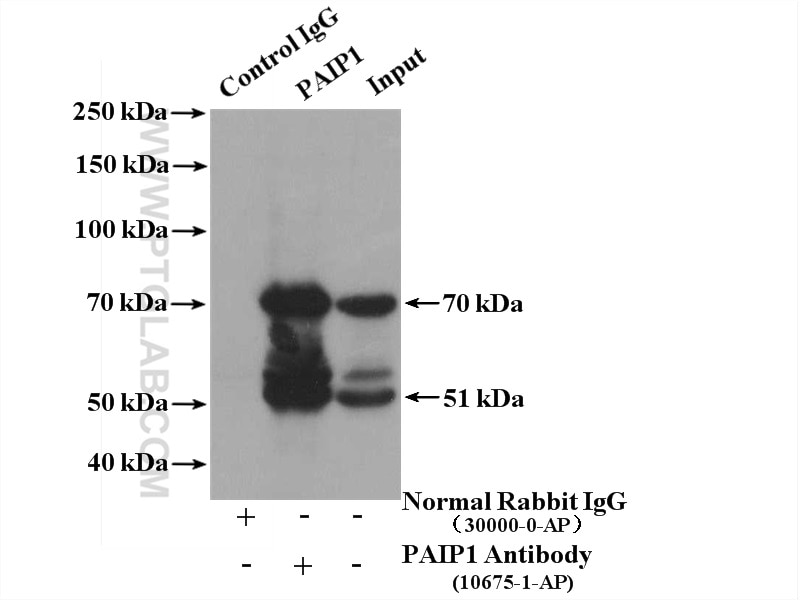
| Erfolgreiche Detektion in WB | HeLa-Zellen, BxPC-3-Zellen, COS-7-Zellen |
| Erfolgreiche IP | HeLa-Zellen |
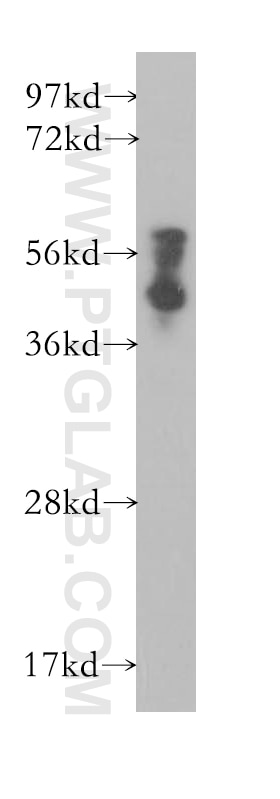
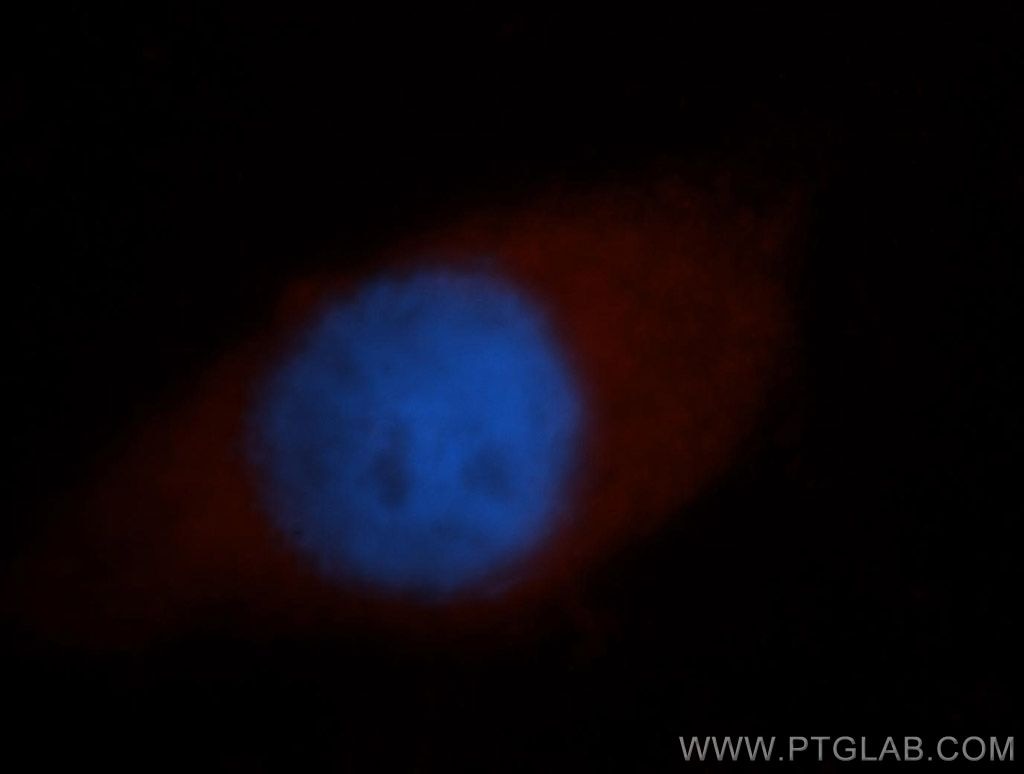
| Erfolgreiche Detektion in IF/ICC | MCF-7-Zellen |
Empfohlene Verdünnung
| Anwendung | Verdünnung |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:500-1:2000 |
| Immunpräzipitation (IP) | IP : 0.5-4.0 ug for 1.0-3.0 mg of total protein lysate |
| Immunfluoreszenz (IF)/ICC | IF/ICC : 1:20-1:200 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, check data in validation data gallery | |
Veröffentlichte Anwendungen
| KD/KO | See 3 publications below |
| WB | See 6 publications below |
| IHC | See 3 publications below |
| IF | See 2 publications below |
Produktinformation
10675-1-AP bindet in WB, IHC, IF/ICC, IP, ELISA PAIP1 und zeigt Reaktivität mit Affe, human
| Getestete Reaktivität | Affe, human |
| In Publikationen genannte Reaktivität | human |
| Wirt / Isotyp | Kaninchen / IgG |
| Klonalität | Polyklonal |
| Typ | Antikörper |
| Immunogen | PAIP1 fusion protein Ag1070 |
| Vollständiger Name | poly(A) binding protein interacting protein 1 |
| Berechnetes Molekulargewicht | 70 kDa |
| Beobachtetes Molekulargewicht | 60 kDa, 51 kDa, 40 kDa |
| GenBank-Zugangsnummer | BC005295 |
| Gene symbol | PAIP1 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 10605 |
| Konjugation | Unkonjugiert |
| Form | Liquid |
| Reinigungsmethode | Antigen-Affinitätsreinigung |
| Lagerungspuffer | PBS mit 0.02% Natriumazid und 50% Glycerin pH 7.3. |
| Lagerungsbedingungen | Bei -20°C lagern. Nach dem Versand ein Jahr lang stabil Aliquotieren ist bei -20oC Lagerung nicht notwendig. 20ul Größen enthalten 0,1% BSA. |
Hintergrundinformationen
In initiation of translation in eukaryotes, binding of the small ribosomal subunit to mRNA requires recognition of the 5-prime cap structure by the cap-binding complex eIF4F. eIF4F consists of eIF4E, eIF4A, and eIF4G. Translation initiation is further regulated by the mRNA 3-prime poly(A) tail and the poly(A)-binding protein (PABC1). PAIP1 interacts with PABC1 and some eIF4 complexes [PMID:9548260]. It is a coactivator in the regulation of translation initiation of poly(A)-containing mRNAs, and associates with EIF4A and PABPC1 may potentiate contacts between mRNA termini [PMID:11051545].
Protokolle
| Produktspezifische Protokolle | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for PAIP1 antibody 10675-1-AP | Protokoll herunterladen |
| IF protocol for PAIP1 antibody 10675-1-AP | Protokoll herunterladen |
| IP protocol for PAIP1 antibody 10675-1-AP | Protokoll herunterladen |
| Standard-Protokolle | |
|---|---|
| Klicken Sie hier, um unsere Standardprotokolle anzuzeigen |
Publikationen
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Biochem J Biological Insights into the Expression of Translation Initiation Factors from Recombinant CHOK1SV Cell Lines and their Relationship to Enhanced Productivity. | ||
Biol Reprod Murine PAIP1 stimulates translation of spermiogenic mRNAs stored by YBX2 via its interaction with YBX2. | ||
Hum Pathol Paip1 predicts poor prognosis and promotes tumor progression through AKT/GSK-3β pathway in lung adenocarcinoma.
| ||
Exp Cell Res Role of Paip1 on angiogenesis and invasion in pancreatic cancer.
| ||
Cancer Res Treat Paip1 Indicated Poor Prognosis in Cervical Cancer and Promoted Cervical Carcinogenesis.
| ||
Arch Biochem Biophys YAP1-activated ZNF131 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation through transcriptional regulation of PAIP1 |